1. The document discusses plate tectonic theory and the key concepts of continental drift and paleomagnetism.
2. Continental drift led to the development of the theory of sea floor spreading and subduction, which are driven by convection currents in the Earth's mantle.
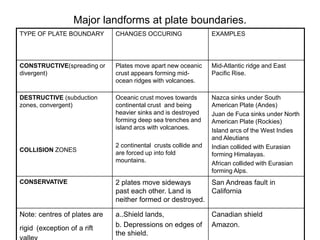
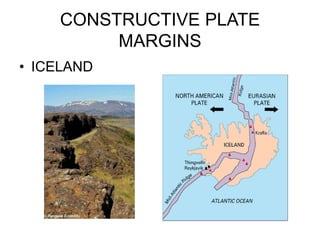
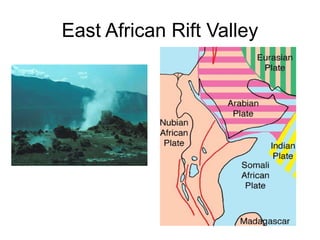
3. There are seven major tectonic plates and many minor plates that are constantly moving against each other along plate boundaries, causing earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building.