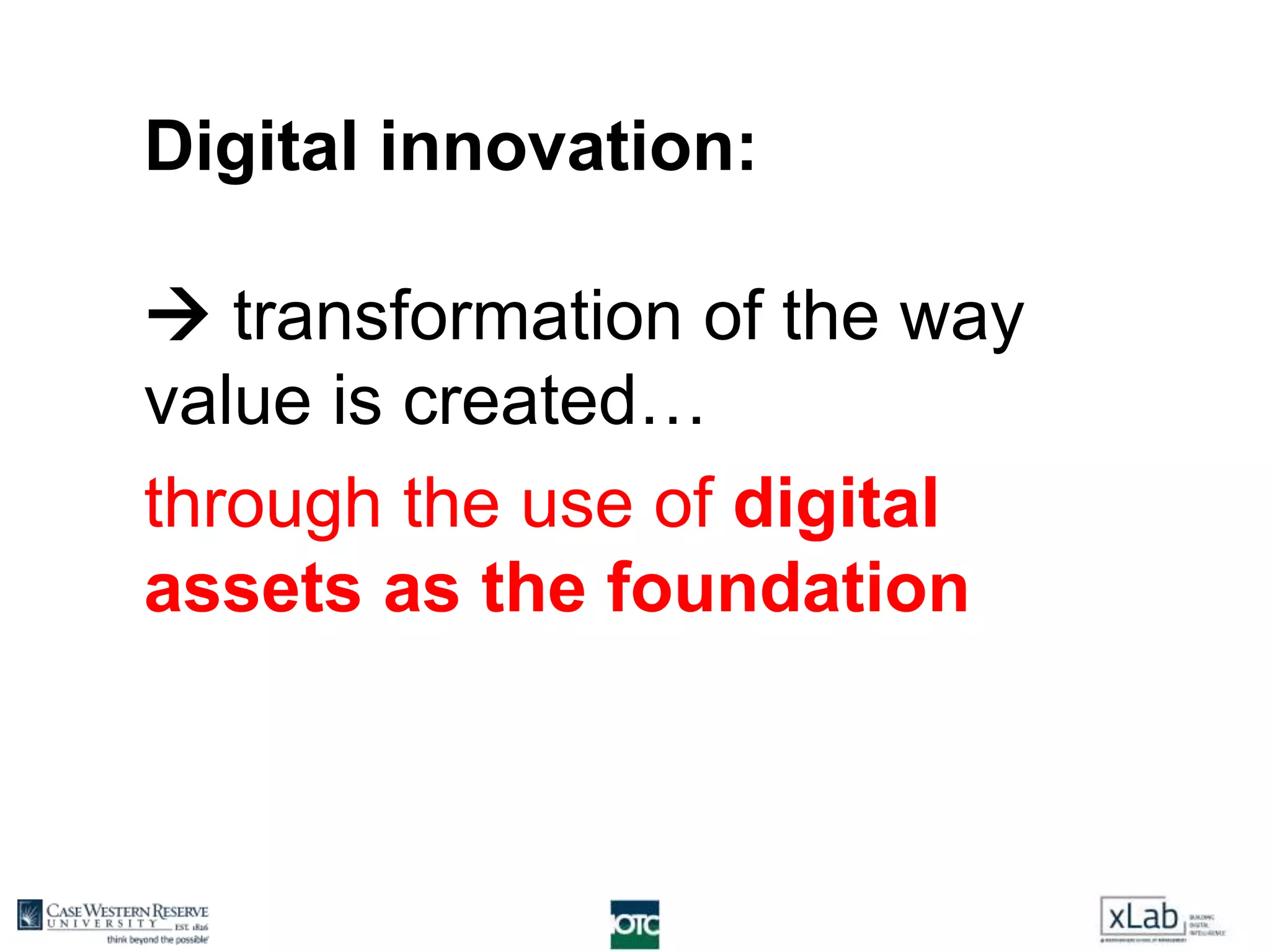
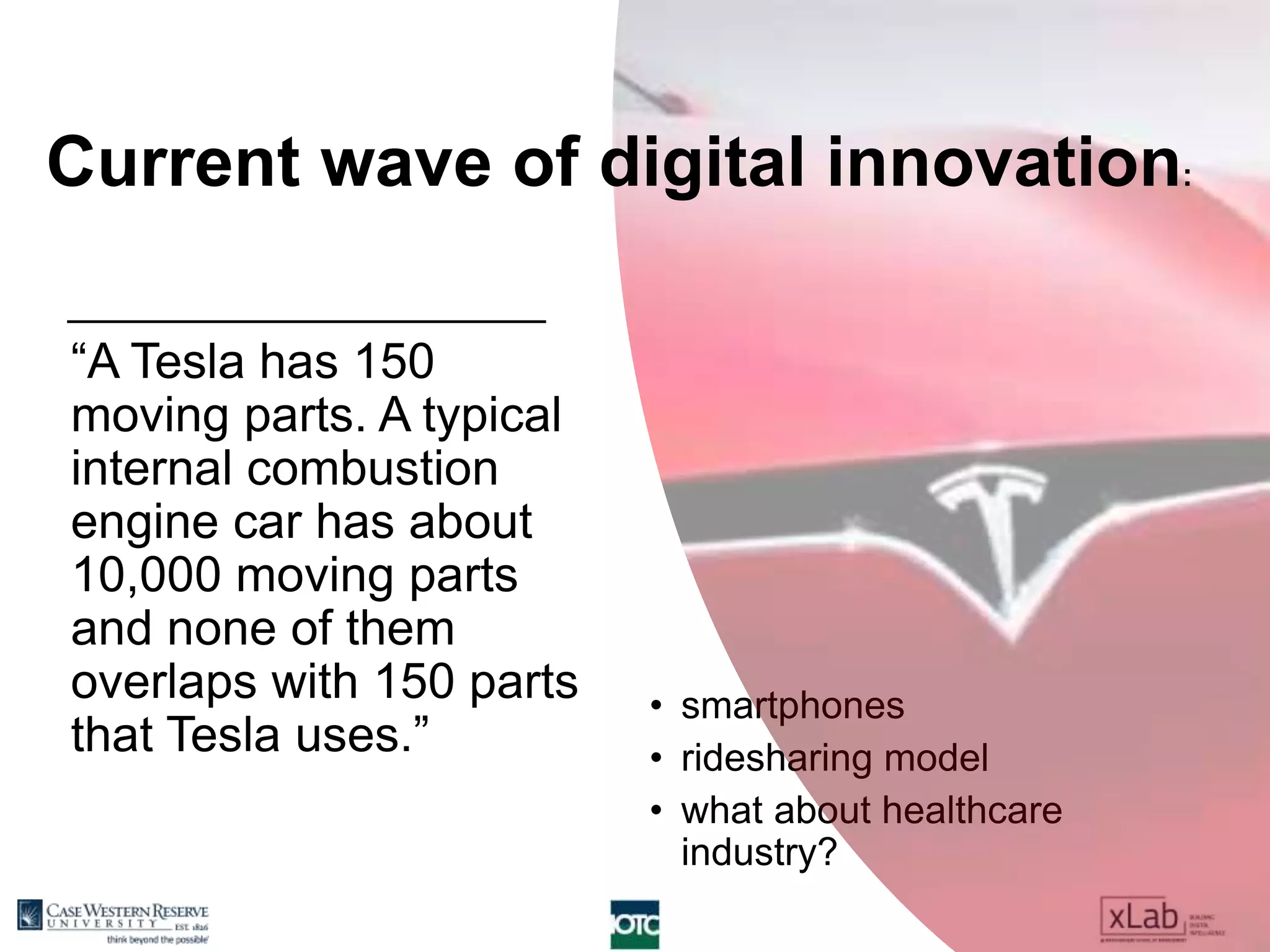
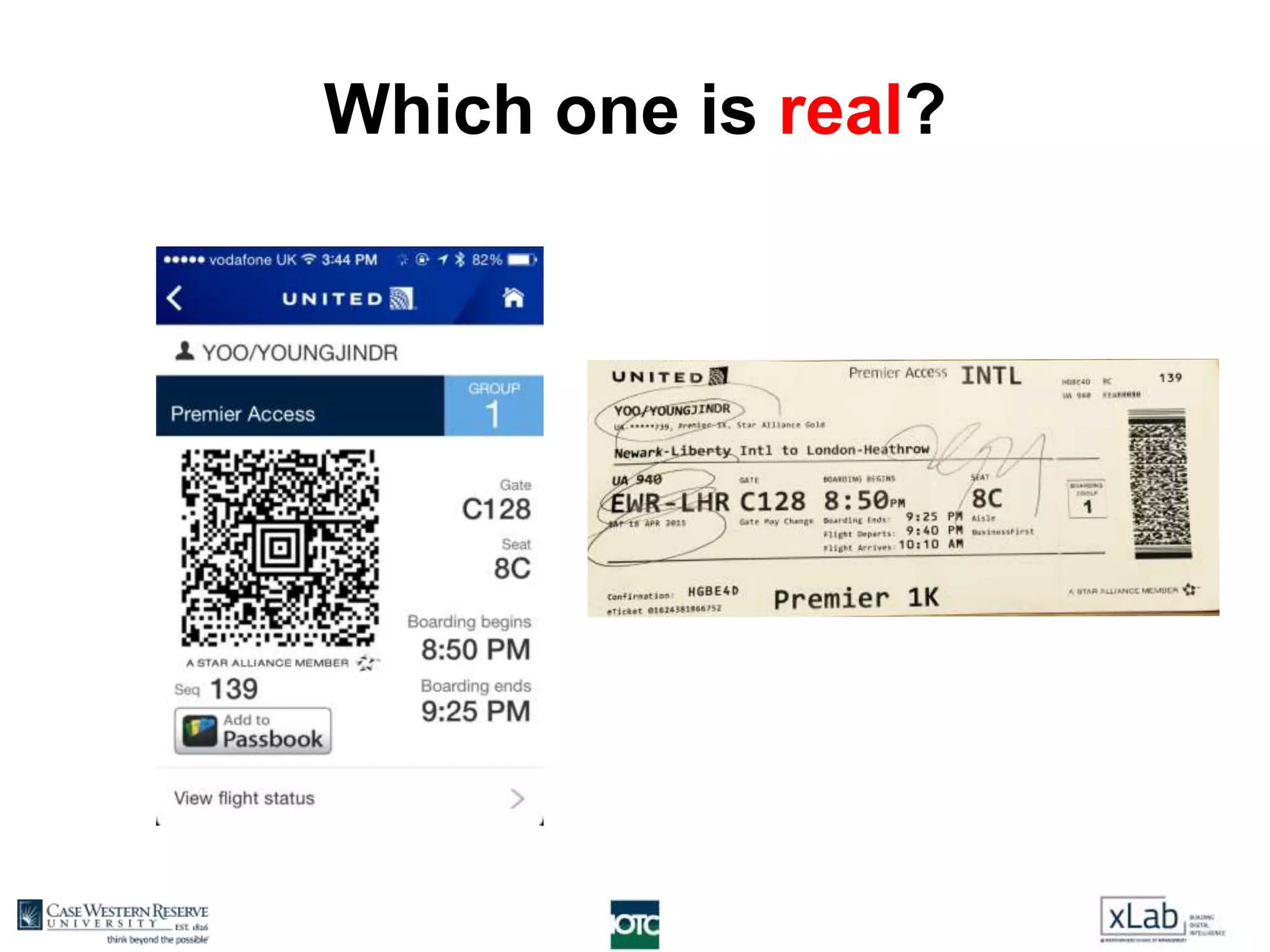
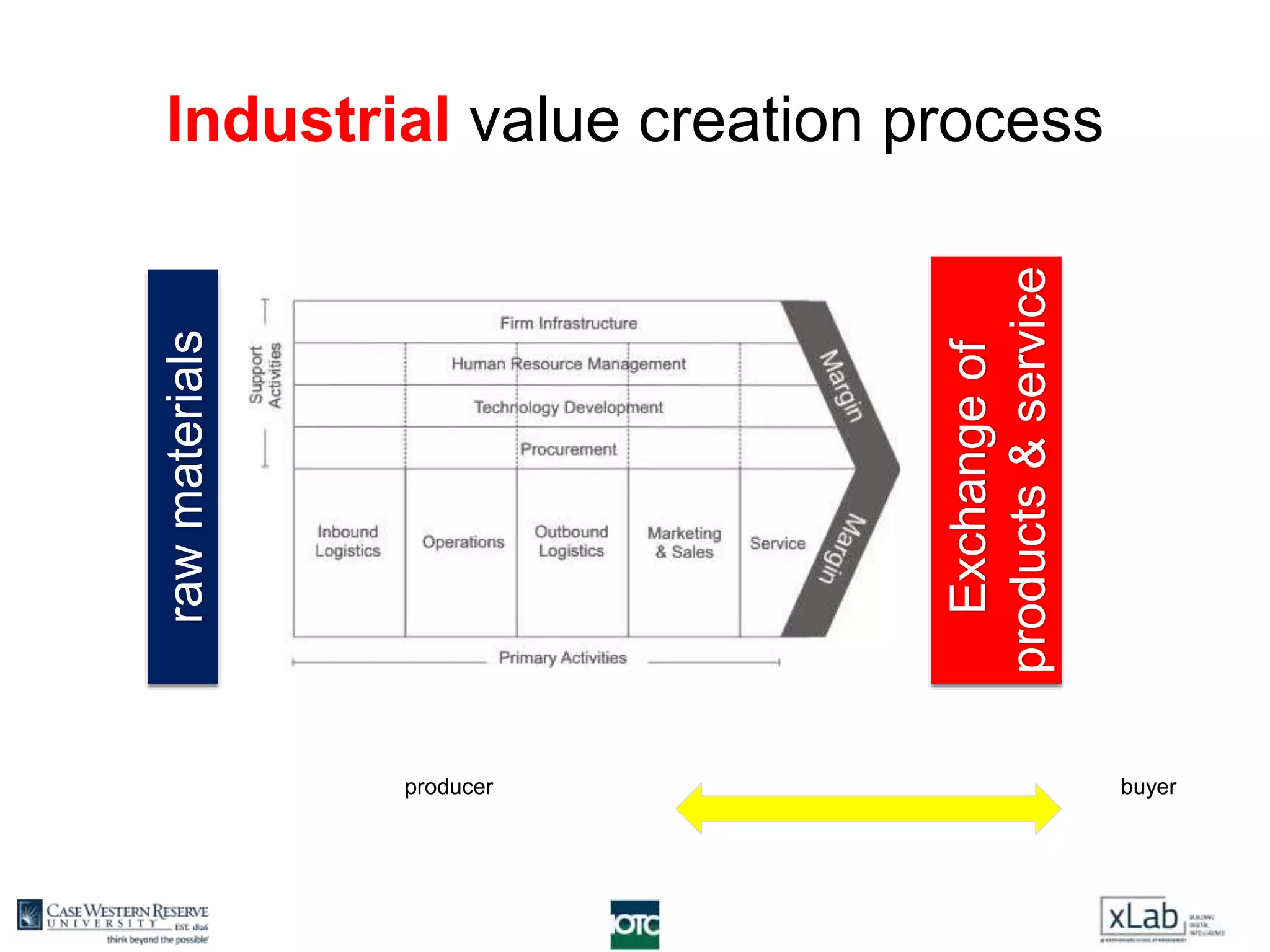
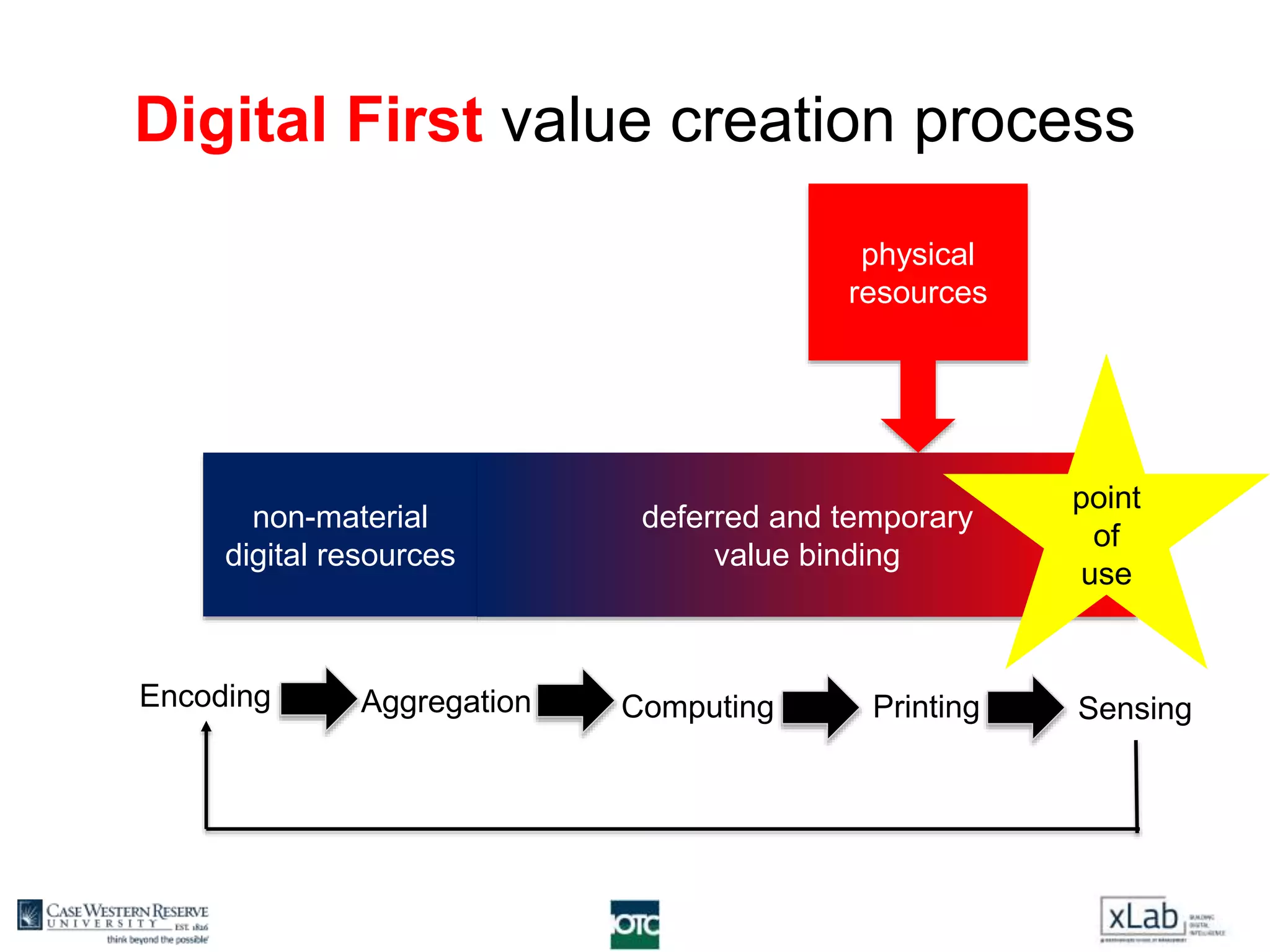
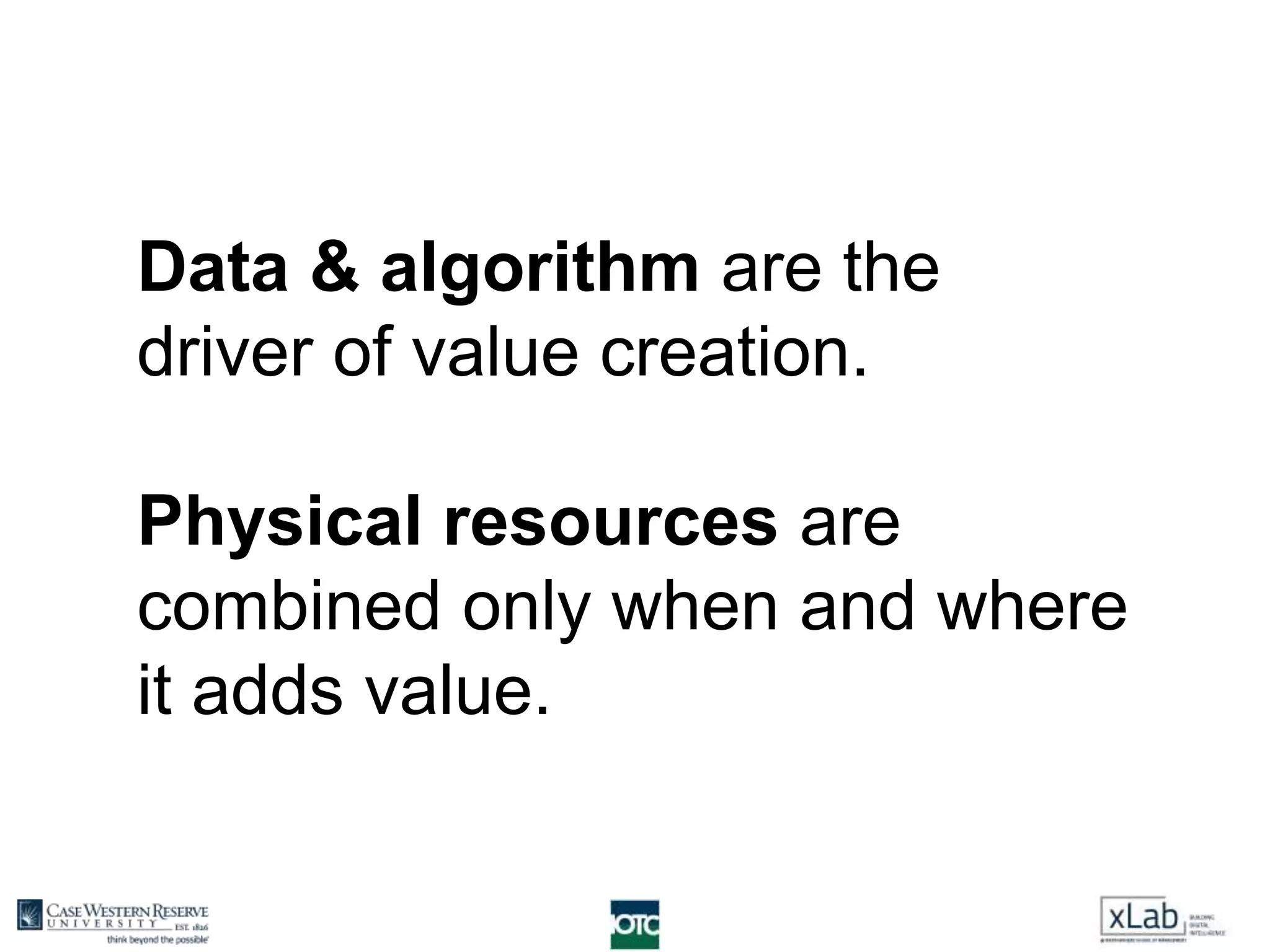
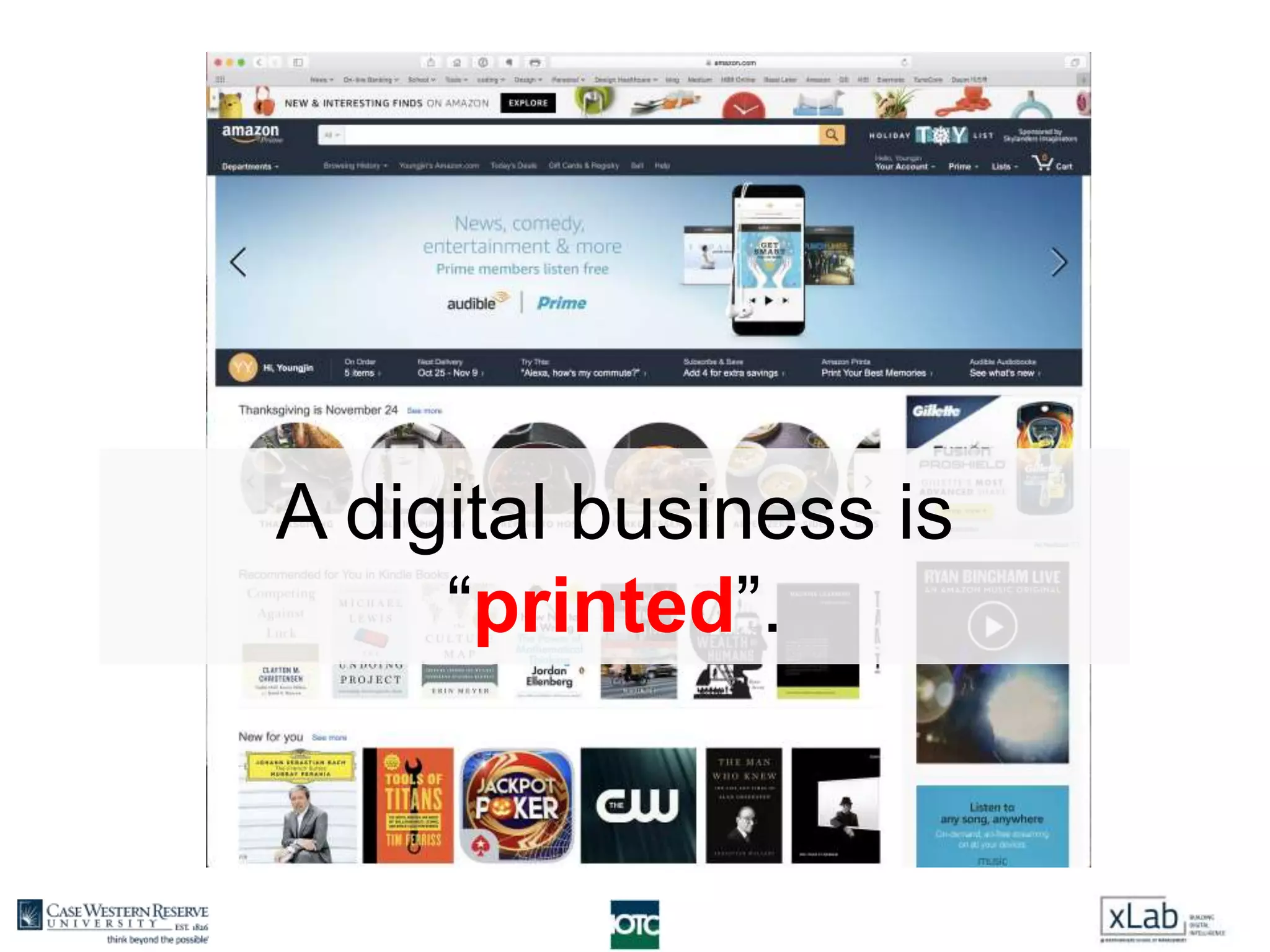
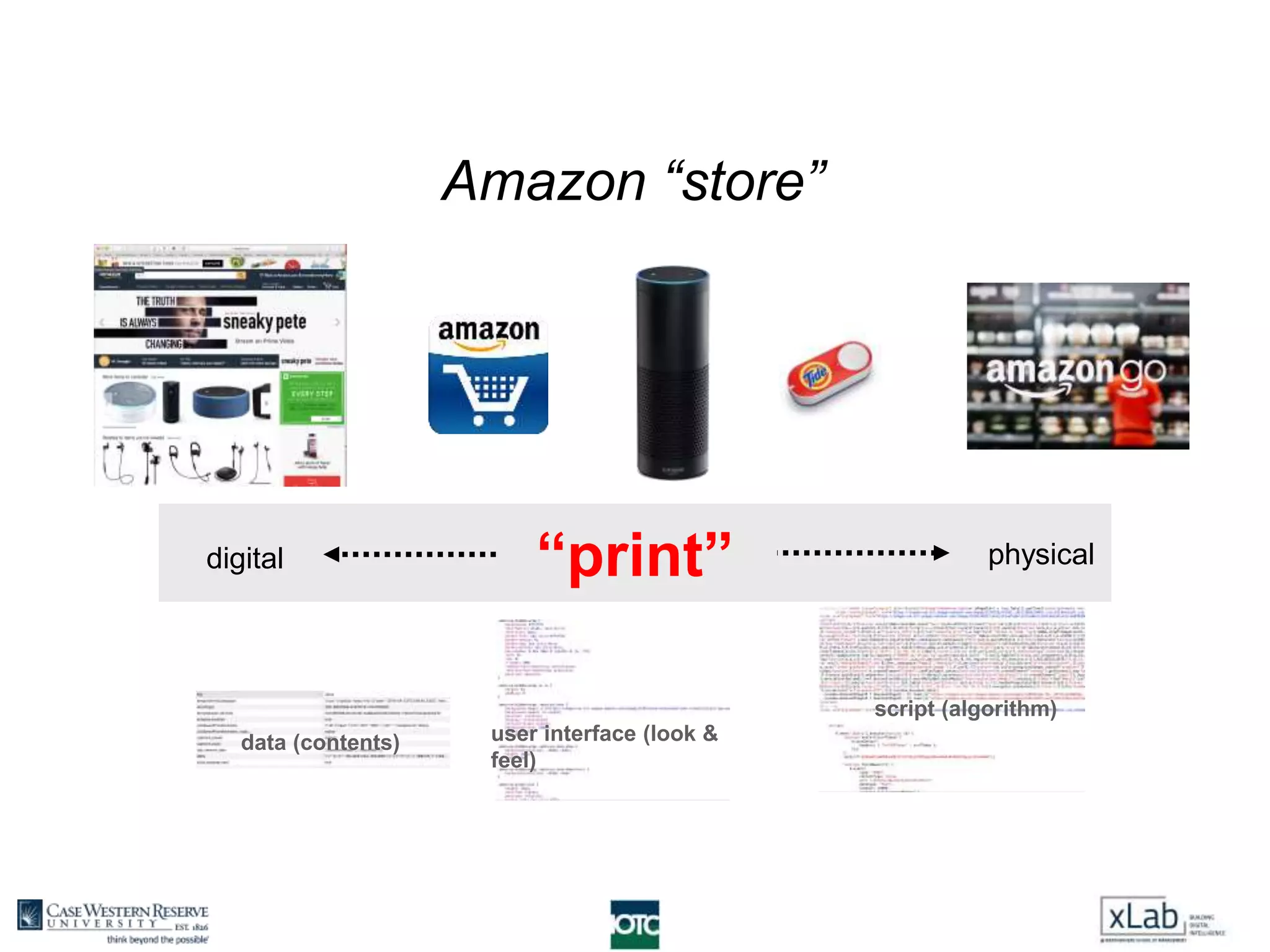
The document discusses the transformation of value creation in the digital economy, highlighting the shift from traditional practices to the use of digital objects and assets. It outlines the concept of a 'digital first' approach, emphasizing the importance of algorithms and software in the value creation process. The text encourages companies to adopt a digital strategy to stay competitive amidst the ongoing digital revolution across various industries.






















![Digital
Technology
Strategic
Framework
Digital Talent
Digital
Business
Model
Connected Healthy Living
Connected Manufacturing
Connected Experience
CWRU Assets Digital First
Solutions Needed
xLab Themes
Technology
Engineering, IOTC,
think[box], Data
Analytics
Management
Design thinking,
Entrepreneurship,
Marketing, Finance
Domain Knowledge
Heatlhcare, Manufacturing,
Data Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-yoo-181115175616/75/Digital-First-Managing-Disruption-in-the-Digital-Economy-31-2048.jpg)