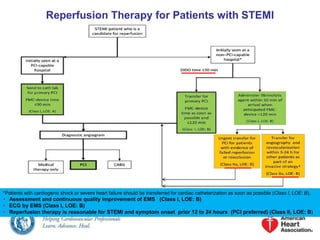
The 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of STEMI provides recommendations for reperfusion therapy. It recommends that patients with cardiogenic shock or severe heart failure be transferred for immediate cardiac catheterization. It also recommends ECG assessment by emergency medical services. Primary PCI is the preferred reperfusion strategy for STEMI when it can be performed within 12-24 hours of symptom onset. The guidelines recommend the use of drug-eluting stents in primary PCI and antiplatelet therapy to support PCI. It also provides recommendations for fibrinolytic therapy, PCI after fibrinolysis, and adjunctive antithrombotic therapies.
![Primary PCI in STEMI
APEX-AMI Trial
? PRAMI Trial
• Manual aspiration thrombectomy is reasonable for patients
undergoing primary PCI. [+TAPAS / -TASTE TRIAL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acc2013stemiguideline-141031153139-conversion-gate01/85/ACC-AHA-2013-STEMI-GUIDELINES-SUMMARY-NEW-ADDITIONS-3-320.jpg)
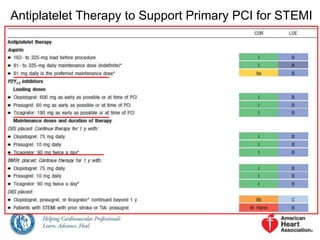
![Use of Stents in Patients With STEMI
Placement of a stent (BMS or DES) is useful in primary PCI for
patients with STEMI. [EES DES best]
I IIa IIb III
BMS* should be used in patients with high bleeding risk, inability
to comply with 1 year of DAPT, or anticipated invasive or surgical
procedures in the next year.
I IIa IIb III
DES should not be used in primary PCI for patients with STEMI
who are unable to tolerate or comply with a prolonged course of
DAPT because of the increased risk of stent thrombosis with
premature discontinuation of one or both agents.
I IIa IIb III
*Balloon angioplasty without stent placement may be used in selected patients.
Harm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acc2013stemiguideline-141031153139-conversion-gate01/85/ACC-AHA-2013-STEMI-GUIDELINES-SUMMARY-NEW-ADDITIONS-4-320.jpg)

![Indications for PCI of an Infarct Artery in Patients Who
Were Managed With Fibrinolytic Therapy or Who Did
Not Receive Reperfusion Therapy
[PHARMACOINVASIVE]
[CAG (CLASS IIA)]
[OAT TRIAL]
*Although individual circumstances will vary, clinical stability is defined by the absence of low output,
hypotension, persistent tachycardia, apparent shock, high-grade ventricular or symptomatic
supraventricular tachyarrhythmias, and spontaneous recurrent ischemia.
PCI is indicated in a noninfarct artery at a time separate from primary PCI
• In patients who have spontaneous symptoms of myocardial ischemia (CLASS I)
• In patients with intermediate/high-risk findings on noninvasive testing (CLASS IIA)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acc2013stemiguideline-141031153139-conversion-gate01/85/ACC-AHA-2013-STEMI-GUIDELINES-SUMMARY-NEW-ADDITIONS-7-320.jpg)