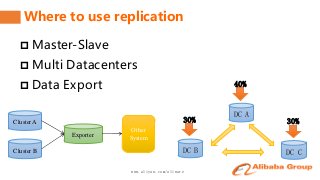
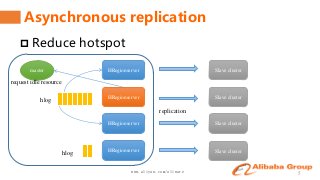
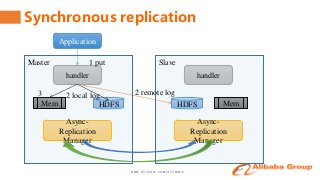
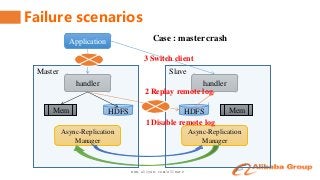
Shen Chunhui and Meng Qingyi
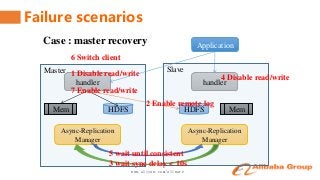
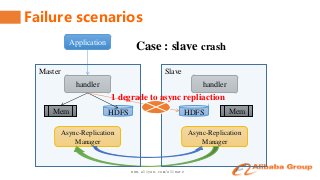
This talk will share the detailed implementation and actual practice about synchronous replication between clusters on alibaba's internal HBase branch.
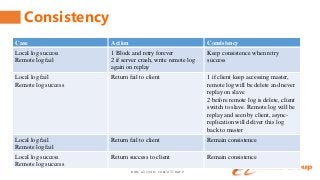
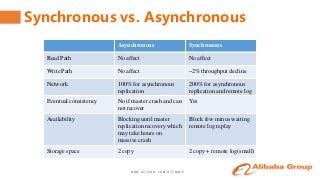
It contains the content of how to keep the data consistency, how to switch the client access between clusters automatically, the related perfomance and monitor.
hbaseconasia2017 hbasecon hbase https://www.eventbrite.com/e/hbasecon-asia-2017-tickets-34935546159#