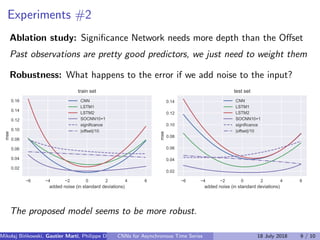
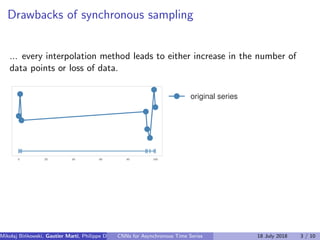
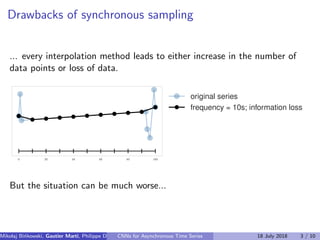
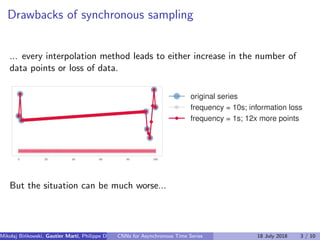
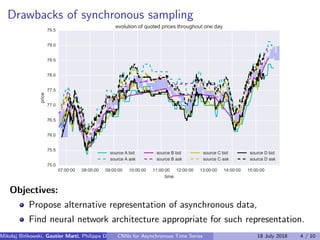
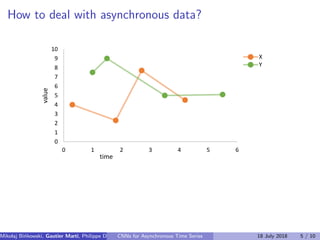
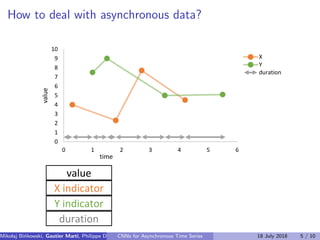
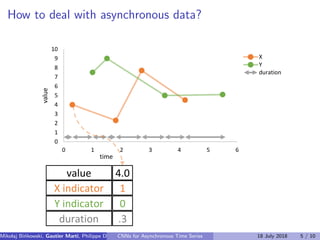
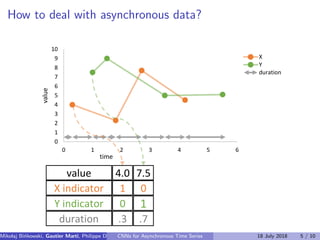
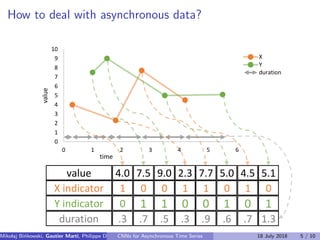
The document discusses the challenges of modeling asynchronous time series data, noting the limitations of traditional interpolation methods which lead to data loss or increase in data points. It presents a proposed architecture that combines autoregressive models with data-dependent weights to improve prediction accuracy for asynchronous data. The authors aim to find a neural network architecture suitable for effectively representing and analyzing such data.






![Proposed Architecture
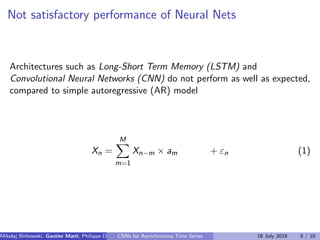
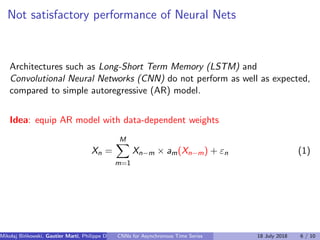
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-18-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-19-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-20-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-21-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
Offset networkSignificance network
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-22-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
Convolution
kx1 kernel
c channels
Convolution
1x1 kernel
c channels
Offset networkSignificance network
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-23-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
× (𝑵 𝑺 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
kx1 kernel
c channels
× (𝑵 𝒐𝒇𝒇 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
1x1 kernel
c channels
Offset networkSignificance network
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-24-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
× (𝑵 𝑺 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
kx1 kernel
c channels
Convolution
1x1 kernel
dI channels
Convolution
kx1 kernel
dI channels
× (𝑵 𝒐𝒇𝒇 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
1x1 kernel
c channels
Offset networkSignificance network
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-25-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
× (𝑵 𝑺 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
kx1 kernel
c channels
Convolution
1x1 kernel
dI channels
Convolution
kx1 kernel
dI channels
× (𝑵 𝒐𝒇𝒇 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
1x1 kernel
c channels
Offset network
𝒙𝑰
Significance network
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
𝐨𝐟𝐟
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-26-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
Weighting
𝑯 𝒏−𝟏 = 𝝈 𝑺 ⨂ (𝐨𝐟𝐟 + 𝒙 𝑰
)
× (𝑵 𝑺 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
kx1 kernel
c channels
𝑺
𝛔
Convolution
1x1 kernel
dI channels
Convolution
kx1 kernel
dI channels
× (𝑵 𝒐𝒇𝒇 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
1x1 kernel
c channels
Offset network
𝒙𝑰
Significance network
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
𝐨𝐟𝐟
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-27-320.jpg)
![Proposed Architecture
The model predicts
yn = E[xI
n|x−M
n ],
where
x−M
n = (xn−1, . . . , xn−M)
- regressors
I = (i1, i2, . . . , idI
)
- target dimensions
with
ˆyn =
M
m=1
W·,m ⊗ σ(S(x−M
n ))·,m
data dependent weights
⊗ off(xn−m) + xI
n−m
adjusted regressors
Weighting
𝑯 𝒏−𝟏 = 𝝈 𝑺 ⨂ (𝐨𝐟𝐟 + 𝒙 𝑰
)
× (𝑵 𝑺 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
kx1 kernel
c channels
𝑺
𝛔
Convolution
1x1 kernel
dI channels
Convolution
kx1 kernel
dI channels
× (𝑵 𝒐𝒇𝒇 − 𝟏) layers
Convolution
1x1 kernel
c channels
Offset network
𝒙𝑰
Significance network
Input series 𝒙 𝒕−𝟔 𝒙 𝒕−𝟓 𝒙 𝒕−𝟒 𝒙 𝒕−𝟑 𝒙 𝒕−𝟐 𝒙 𝒕−𝟏
d - dimensional
timesteps
Locally connected layer
fully connected for each of 𝒅𝑰 dimensions
𝑯 𝒏 = 𝑾𝑯 𝒏−𝟏 + 𝒃
𝐨𝐟𝐟
ෝ𝒙 𝒕
𝑰
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-28-320.jpg)
![Experiments
Datasets:
artificially generated,
synchronous asynchronous
Electricity consumption [UCI
repository]
Quotes [16 tasks]
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 8 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-29-320.jpg)
![Experiments
Datasets:
artificially generated,
synchronous asynchronous
Electricity consumption [UCI
repository]
Quotes [16 tasks]
Benchmarks:
(linear) VAR model
vanilla LSTM, 1d-CNN
25-layer conv. ResNet
Phased LSTM [Neil et al. 2016]
Sync 16 Sync 64 Async 16 Async 64 Electricity Quotes0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
MSE
VAR
CNN
ResNet
LSTM
Phased LSTM
SOCNN (ours)
Mikolaj Bi´nkowski, Gautier Marti, Philippe Donnat (Imperial College)CNNs for Asynchronous Time Series 18 July 2018 8 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnns-asynchronous-time-series-hkml-s1e1-180719114639/85/Autoregressive-Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Asynchronous-Time-Series-30-320.jpg)