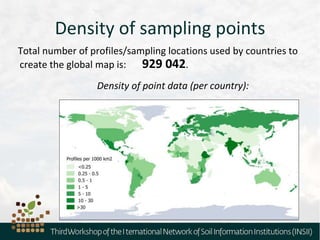
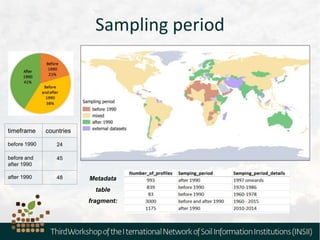
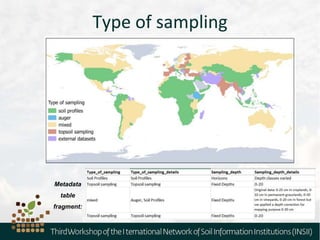
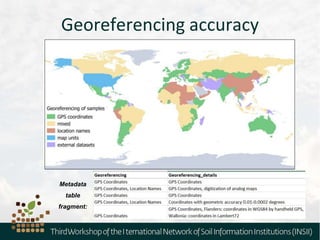
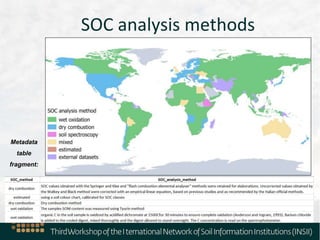
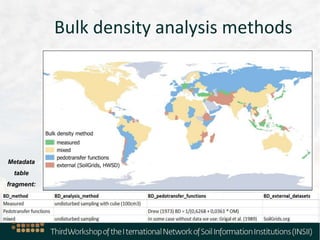
The document outlines the metadata requirements for soil profiling and sampling as part of a global mapping initiative, including details on methods, analysis, upscaling, and data collection challenges. It specifies the total number of sampling locations (929,042) and the density of data across various countries, as well as sampling periods and methods. Additionally, it highlights the biggest challenges faced by countries in data collection and future mapping updates.