Glycolysis to ATP: The Chemiosmosis Process
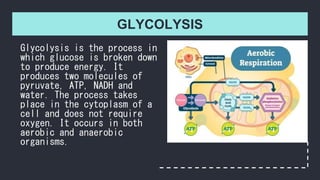
- 1. GLYCOLYSIS Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH and water. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell and does not require oxygen. It occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms.
- 2. KREB’S CYCLE The Krebs cycle or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix, where acetyl-CoA is oxidized to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced, which generate ATP in the electron transport chain.
- 3. ELECTRO TRANSPORT CHAIN The ETC is a collection of proteins bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane and organic molecules, which electrons pass through in a series of redox reactions, and release energy. The energy released forms a proton gradient, which is used in chemiosmosis to make a large amount of ATP by the protein ATP-synthase.
- 5. CHEMIOSMOSIS refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons) to the other side of a biological membrane, and as a result, an electrochemical gradient is generated. This can then be used to drive ATP synthesis. The gradient also incites the ions to return passively with the help of the proteins embedded in the membrane. By “passively”, it means that the ions will move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. INTRODUCTION
- 6. Peter D. Mitchell The theory of Chemiosmosis was proposed by a man named Peter D. Mitchell (1920- 992). He is a British biochemist. In the 1960s, he knew about the phenomenon of membrane potential in which the inner side of the membrane being negative relative to its environment. ATP was also already recognized at that time as the cell’s major energy currency. However, how living organisms produce ATP biologically was not well established.
- 7. 02 04 This process is similar to OSMOSIS where water molecules move passively. In the case of chemiosmosis, though, it involves the ions moving across the membrane; in osmosis, it is the water molecules. Nevertheless, both processes require a gradient. BIOLOGICAL GRADIENTS
- 8. OSMOSIS OSMOSIS (Greek for push) is the net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane. Across this membrane, water will tend to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
- 9. The mitochondria have long been known as the organelles responsible for ATP synthesis. How these organelles generate ATP was initially not clear and was presumed to relate to substrate-level phosphorylation (as what happens in glycolysis).
- 12. In chloroplast, chemiosmosis occurs in the thylakoid. This membrane system has its own transport chain and ATP synthases. One of the major differences between chemiosmosis in mitochondria and in chloroplasts is the source of energy. In mitochondria, the high-energy electrons are extracted from the food molecule (from redox reaction) whereas in chloroplast the source is from the photons captured from the light source. The proton (H+) gradient forms from the H+ ions accumulating in the thylakoid compartment (i.e. the space inside the thylakoid).
- 13. CHEMIOSMOSIS in PROKARYOTIC CELL
- 14. Mercury Mars Neptune Mars is actually a very cold place It’s very far away from the Sun It’s the closest planet to the Sun The hydrogen ions (protons) move across the biological membrane via the ATP synthase (a transport protein) when a proton gradient forms on the other side of the membrane. The proton gradient forms when the hydrogen ions accumulate as they are forcibly moved to the other side during the electron transport and redox reactions. As more hydrogen ions are on the other side they will move back to the cell move by crossing the membrane through the ATP synthase. As they flow through, energy is released and used to convert ADP to ATP through phosphorylation.
- 15. Two Key Components of Chemiosmosis An electron transport chain (ETC) - a series of membrane-bound molecules that passes electrons from an electron donor to a final electron acceptor, creating a proton gradient at the same time. ATP synthase - an enzyme that uses the proton gradient to catalyze the synthesis of ATP.