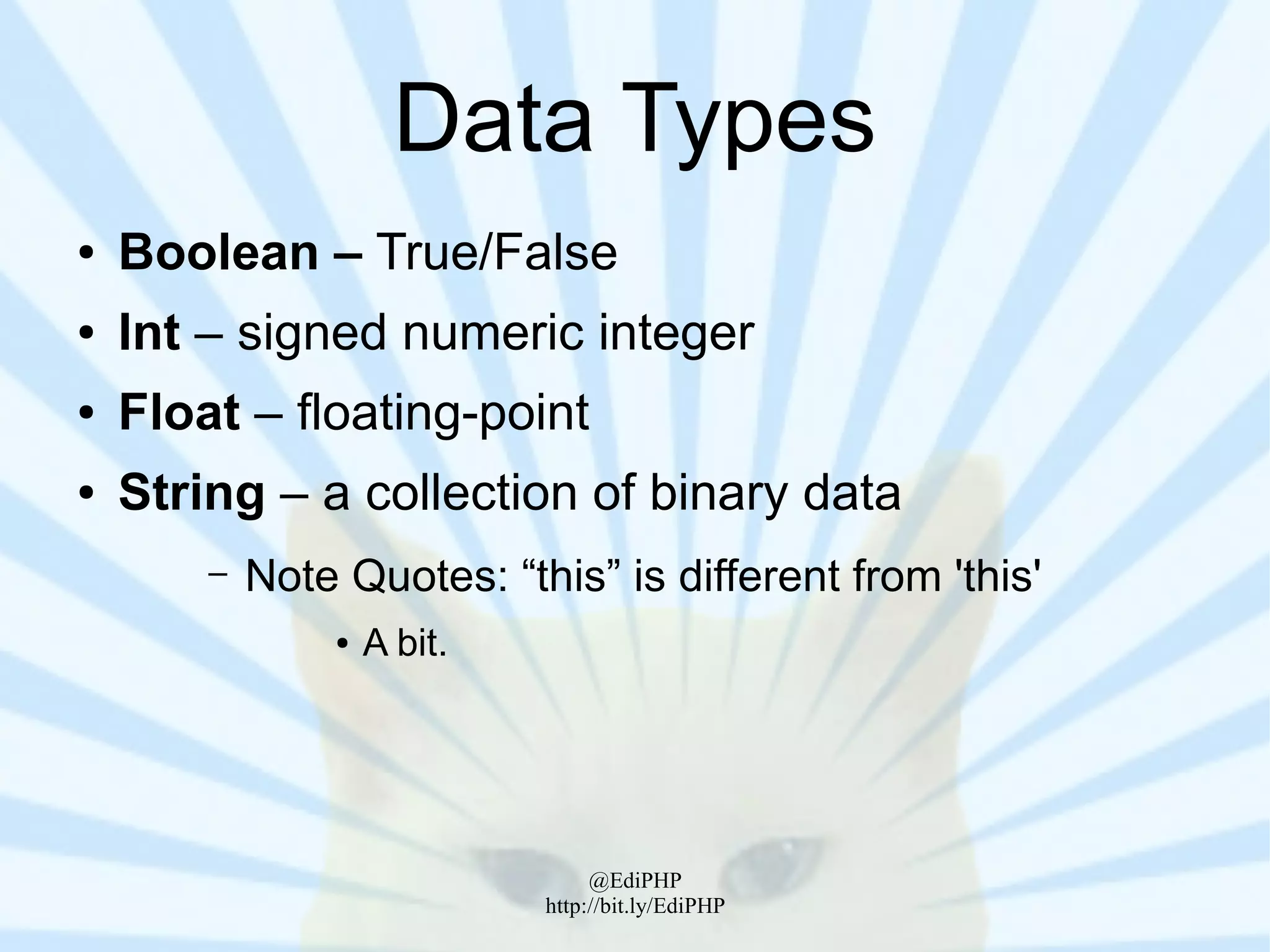
The document discusses PHP concepts like syntax, data types, variables, arrays, operators, loops, functions, object-oriented programming, classes and methods. It provides code examples for filtering bad words in a string, calculating the sum of digits in an array, and creating a Society class with methods to set and get its name. Real-world uses of PHP concepts are demonstrated, including extending the Society class to output its name when cast to a string.



![Arrays
● Can be constructed following ways:
●
$var = Array(1,2,3,4,5,6);
●
$var = Array(‘cat’ => ‘lolcat’, 0 => 4);
● Or:
$var = Array();
$var[] = 'A';
$var[] = 'B';
●
Is equivalent to $var = Array (‘A’, ‘B’, ‘c’);
$var[] = 'c';
@EdiPHP
http://bit.ly/EdiPHP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-091104141356-phpapp01/75/02-Second-meetup-5-2048.jpg)






![Real World examples (2)
● Calculating sum of digits in array
<?php
$arr = array(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,-6);
function sumDigits ($a)
{
$sum = 0;
for ($i=0; $i < count($a); $i++)
{
$sum += $a[$i];
}
return $sum;
@EdiPHP
}
http://bit.ly/EdiPHP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-091104141356-phpapp01/75/02-Second-meetup-12-2048.jpg)






