Temperature dpt
- 1. BODY TEMPERATURE REGULATION Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 2. Definitions: • CORE BODY TEMPERATURE: • The temperature of the deep tissues of the body which remains nearly constant under physiological conditions (within ±1˚F or ±0.6˚C). • Average core body temperature is taken to be around 98.6 ˚F orally and 1˚F higher when measured rectally. • It is measured from tympanic membrane, pulmonary artery, distal esophagus & nasopharynx • The core thermal component is composed of highly perfused tissues whose temperature is kept uniform & high compared with rest of body • It gradually decreases with age Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 3. • SKIN TEMPERATURE: • The skin temperature rises and falls with the temperature of the surroundings or ambient temperature. • It can be measured by placing temperature sensors (thermistors) at skin at various locations • Mean skin temperature can be calculated by measuring skin temperature at several locations and computing the average across these locations (forehead, chest, thigh, calf, abdomen & back) Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 5. • Ambient temperature: • At which there is no active heat loss and heat gain mechanism operated by the body. It is 27+ 2oC • Average Body Temperature: • Used when one wishes to calculate the total amount of heat stored in the body • =(0.33 x surface temp ) + (0.67 x internal temp) Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 6. Thermal gradient • Within the body, there is a difference between core temperature and the shell temperature, called thermal gradient • Ideal difference between core & skin temperature is approximately 4oC • Even within the core, temperature varies from one organ to another • In extreme circumstances, the core temperature can be 20oC higher than the skin Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 7. Thermoregulation: • The ability to maintain nearly constant internal body temperature i.e, the core temperature, is called thermoregulation. • HOMEOTHERMIC(Warm blooded) endotherms: The animals who can maintain nearly constant core body temperature despite wide variation in the surrounding temperature. • POIKILOTHERMIC(Cold blooded) ectotherms: Animals having rudimentary thermoregulation and their core body temperature changes with the change in the ambient temperature. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 8. Recording temperature: Sites for temperature recording are • Mouth • Axilla • Rectum • Skin • Lower one third of esophagus • Tympanic membrane • Rectal temperature is not the same as the temperature in the brain, where temperature is regulated • Tympanic temperature is a good estimate of actual brain temperature Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 9. Devices used to measure temperature • Mercury thermometers • Thermocouples • Thermistors • Ingestible core temperature pills (use low power radio frequency transmissions to communicate with temperature monitor) Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 10. Relationship of body heat to body temperature • The temperature of an object is a measure of the kinetic activity of its molecules • This is proportional to the amount of heat stored in the object • Body temperature is directly proportional to the heat in the body Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 11. Heat capacity or specific heat • A measurement of the changes in body heat stores utilized to characterize temperature regulation quantitatively • Defined as the ratio of heat supplied (or removed) to the corresponding temperature rise(or decrease) • Specific heat of tissues is said to be 0.83 calorie/kg/degree centigrade Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 12. Constancy of internal body temperature Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
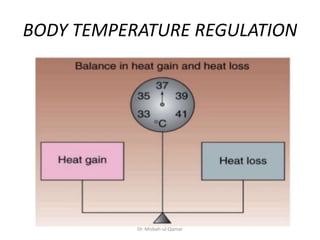
- 13. Heat balance • When the rate of heat production is exactly equal to the rate of heat lost= heat balance Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 14. The insulator system of the body • Skin • Subcutaneous tissues • Fat in subcutaneous tissues Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 15. The radiator system of the body • Flow of blood to the skin • Skin temperature is important in heat transfer to the environment • Delivery of heat to the surface is blood flow dependent Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 16. Heat production • Body produces internal heat due to metabolic processes – At rest or during sleep, metabolic heat production is small – During intense exercise, heat production is large • Heat production can be classified as – Voluntary muscular exercise – Involuntary shivering & non shivering (hormonal action) thermogenesis Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 17. Heat production factors: • Basal metabolism of all the cells of the body • Extra metabolism caused by 1. increased chemical activity of all the cells eg, fever 2. shivering and muscle contraction 3. thyroxine and growth hormones 4. epinephrine, norepinephrine and sympathetic stimulation 5. digestion and absorption of food Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 18. Mechanisms of Heat production: • Basal metabolism BMR: The minimum amount of heat produced when a person is physically and mentally relaxed. • Most of the heat is produced by liver , heart , muscle, skin, brain, endocrine organs and other tissues. • With each degree rise in temperature there is 13 %increase in BMR. • Muscular exercise or shivering produce much more heat. • During exercise around 90% of heat is produced by muscles. • Shivering starts when the surrounding temperature falls to around 23˚C.It is controlled by somatic division of nervous system. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 19. • Diet induced thermogenesis: Food intake increases the basal metabolic rate and heat production. • Diet induced thermogenesis is more marked with protein diet. • Skin exposure causes absorption of heat when the ambient temperature is higher than the body temperature. • Brown fat in some animals and infants only, can be mobilized to produce heat when needed. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 20. Heat loss: • Heat is lost in two steps: • From body core to skin • From skin to atmosphere Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 21. Blood flow to skin from core provides heat transfer • A high rate of skin flow causes heat to be conducted from core to skin with great efficiency • Blood is very effective in this function because of its high capacity to store heat • Therefore skin is an effective controlled “heat radiator’’ system Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 22. • Blood vessels are distributed profusely beneath the skin, specially important is a continuous venous plexus that is supplied by inflow of blood from skin capillaries • In most exposed areas of body (hands, feet, ears) blood is also supplied to the plexus directly from small arteries through highly muscular arterio-venous anastamosis Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 23. Heat radiator –the skin Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 26. Basic physics of how heat is lost from skin surface • Through following mechanisms: • Radiation • Conduction • Convection • Evaporation • the first 3 of these require a temperature gradient to exist between skin & environment Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 27. • Radiation is a mode by which heat can be lost from a hot to a cold object in the form of infrared rays (60% of the total heat loss). • It can take place in vacuum as well. • Example: sun transferring heat to earth • On a hot sunny day, body can also gain heat via radiation Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 28. • Conduction means loss of heat from body to the solid objects due to direct contact(3% of body heat loss). • Conduction from the solid object to air constitute around 15% of heat loss. • Convection causes the heat loss by the movement of air. • Whatever heat is lost by the body ,it is taken away by convection currents. • If the surrounding air is cooler than the body ,heat can be lost very easily. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 29. Conduction and convection in water • a)Specific heat of water is far greater , so per unit volume of water can absorb much more amount of heat • b)Heat conductivity in water is far greater so it is impossible to heat the thin layer of water next to body. • c)If the temperature of water is below body temperature , heat loss from the body is rapid . • Water’s effectiveness in cooling is about 25 times greater than that of air at same temperature Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 30. • Clothing can increase the thickness of private zone of air adjacent to skin. • Heat loss can be reduced by decreasing rate of conduction and convection. • The effectiveness of clothing in maintaining body temperature is almost completely lost if the clothing becomes wet. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 32. Evaporation • Only way to lose heat when the the temperature of the surrounding is greater than the temperature of the body. Evaporation produces cooling. For each gram of water that evaporates,0.58 kcal are lost. Some heat is being continuously lost by the skin in low ambient temperature and it is called INSENSIBLE LOSS. Mild evaporation continues from the respiratory tract during the process of respiration Heat production: At rest= 1.5kcal/min At exercise= 15kcal/min Humidity: High– limits sweat evaporation & heat loss Low– ideal for sweat evaporation & heat loss Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 33. Evaporation of sweat from skin is dependent on following factors • Ambient conditions – Air temperature – Relative humidity • Convection currents around the body • Amount of skin surface exposed to environment Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 34. Relative humidity • It indicates how moist the air is • the amount of water vapor present in air is expressed as a percentage of the amount needed for saturation at the same temperature • High relative humidity reduces the rate of evaporation as in this situation vapor pressure gradient between skin & environment is reduced Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 35. Effectors altering body temperature • Sweat glands • Smooth muscles around arterioles • Skeletal muscles • Endocrine glands releasing thyroxine & epinephrine Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 37. Regulation of sweating: • Autonomic nervous system controls the sweat glands . • Cholinergic nerve fibers supply the sweat glands. • Primary secretions are rich in electrolytes. • Secondary secretions are the secretions in which very little amount of electrolytes is present. • In an acclimatized person ,very little amount of NaCl is lost in sweat due to release of Aldosterone which is responsible for salt and water conservation. • Heat loss by panting is more effective in lower animals. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 38. Mechanism of sweat secretion • Cholinergic sympathetic nerve fibers ending on or near the glandular cells elicit the secretion • Secretory portion of the sweat gland secretes a fluid called primary secretion or precursor secretion • The precursor secretion is an active secretory product of the epithelial cells lining the coiled portion of the sweat gland • Then the concentrations of the constituents in the fluid are modified as the fluid flows through the duct Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 40. Acclimatization of the sweating mechanism Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 41. REGULATION OF BODY TEMPERATURE Temperature regulating centers are located in hypothalamus. Temperature detectors are present throughout the body . Nervous feedback mechanisms help to regulate body temperature . Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 42. Why regulation of body temperature is required? • The enzymes of body work in optimal temperature • Speed of chemical reaction varies with temperature • Temperature spikes above the normal range denature proteins & depress neuronal activity • Very low temperature leads to cardiac fibrillation & failure ( lower lethal core temp is 26C • Very high temperature leads to heat stroke (upper lethal core temp is 43.5C Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 43. Advantage of thermoregulation Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 44. Disadvantage of thermoregulation Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 45. Thermal sensations • The humans can perceive different gradations of cold & heat progressing from freezing cold– to cold– to cool– to indifferent– to warm– to hot– to burning hot Thermal gradations are discriminated by at least 3 types of sensory receptors • Cold receptors • Warmth receptors • Pain receptors Pain receptors are stimulated only by extreme degrees of heat or cold Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 46. Thermal receptors • Cold & warmth receptors are located immediately under the skin at discrete points • Each point have a stimulatory diameter of 1mm • In most areas of body, there are 3-10 times as many cold receptors as warmth receptors • Number in different areas of body varies from 15-25 cold points/cm2 in lips to 3-5 in fingers • Less than 1 cold point/cm2 in some broad surface areas of trunk • There are correspondingly fewer numbers of warmth points Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 47. Working of thermoceptors • Cold & warmth receptors are stimulated by changes in their metabolic rates as temparature alters the rates of intracellular chemical reactions more than twofold for each 10oC change • It is difficult to judge gradations of temperature when small areas of surface are stimulated • When a large area of body is stimulated all at once, thermal signals from the entire area summate Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 48. Skin and deep tissue receptors: • Skin contains 10 times more cold receptors as compared to warmth receptors. • Peripheral temperature detection is primarily responsible for cold detection. • When skin receptors are cooled , reflexes try to increase body temperature and conserve heat immediately by – Causing shivering – Inhibiting sweat formation – Promoting skin vasoconstriction Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 49. Deep receptors for temperature detection: • Present in spinal cord, near deep viscera and around great veins . • These deep tissue receptors are responsible for detecting core body temperature. • Both the skin and deep tissue receptors are responsible for preventing hypothermia. • All types of receptors function by showing transient change in the receptor potential. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 50. • Warmth signals are received by free nerve endings & transmitted by type C nerve fibers@ 0.4- 2 m/sec • Cold signals are transmitted via A delta nerve fibers @ 20m/sec • Some cold sensations are transmitted in type C nerve fibers • Afferents reach hypothalamus through spinothalamic tract Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 51. Pathway for temperature signals • Thermal signals are transmitted in almost parallel but not exactly the same pathways as pain signals • On entering spinal cord, signals travel for few segments upward & downward, then terminate in laminae I, II & III of dorsal horns • After some processing, signals enter ascending thermal fibers that cross to opposite anterolateral sensory tract • Then terminate in both the reticular areas of brain stem & ventrobasal complex of thalamus • Some thermal signals are also relayed to somatosensory cortex from ventrobasal complex Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 53. Temperature decreasing mechanisms : These mechanisms get activated when the temperature of the body is too high and body has to lose heat. • Vasodilation of blood vessels by inhibition of sympathetic centers in the posterior hypothalamus. • Sweating produces cooling by evaporation. • Slight increase in RR • Decreased heat production by decreased shivering and chemical thermogenesis. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 54. Temperature increasing mechanisms: • When the body is too cold the temperature control mechanisms get activated like • Vasoconstriction caused by stimulation of posterior hypothalamic sympathetic center. • Piloerection causes hair to stand upright and trap an insulator layer of air next to the body to conserve heat. • Increase in thermogenesis (heat production) by increasing shivering , sympathetic activation and thyroxine secretion Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 55. Thermogenesis: • MECHANICAL THERMOGENESIS: • Shivering • CHEMICAL THERMOGENESIS: • a) Sympathetic chemical excitation of heat production(short term heat production) • b) Increased thyroxine production (long term heat production) Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 56. Mechanism of shivering: • Primary motor center for shivering is located in the dorsomedial portion of posterior hypothalamus . • This area is inhibited by signals from the heat centers in the anterior hypothalamus . • It is excited by cold signals from skin and spinal cord. • Cold→ primary motor center for shivering→ bilateral tracts down the brainstem→ lateral column of spinal cord→ anterior motor neuron→ increased muscle tone due to over activity of anterior motor neurons • Shivering starts as a result of feedback oscillation of muscle spindle stretch reflex mechanism. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 57. Chemical thermogenesis(high cellular metabolism) • SHORT TERM: • Activation of sympathetic system and release of epinephrine and nor epinephrine is responsible for excessive metabolism. • Epinephrine and nor epinephrine are responsible to uncouple oxidative phosphorylation . • This leads to heat production and no ATP generation. • This phenomenon is more pronounced in animals having brown fat . • In adults 10-15% increase in heat production by chemical thermogenesis. • In children heat production can increase up to 100 %. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 58. • LONG TERM CHEMICAL THERMOGENESIS BY THROXINE: • Anterior hypothalamus is cooled down →TRH release by hypothalamus →TSH release by anterior pituitary→ Thyroxine release by thyroid gland → increased cellular metabolism and heat production. • This mechanism requires months to develop and prolonged exposure to cold. • More pronounced in animals Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 59. Role of anterior hypothalamic pre- optic area: (heat center)• Hypothalamic pre optic area serves as a thermostat for the body. • Anterior hypothalamus has large number of heat sensitive neurons. • It also has around 1/3 cold sensitive neurons. • Heat sensitive neurons increase their firing rate 2-10 fold in response to a 10oC rise in body temperature • When hypothalamic pre optic area is heated ,3 changes take place • a) profuse sweating all over the body • b) intense vasodilation • c) decreased heat production Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 60. Posterior hypothalamus (cold center) • Posterior hypothalamus is important as it integrates the central and peripheral temperature sensory signals. • This special area is located in the posterior hypothalamus bilaterally near the mammillary body. • Signals from the anterior hypothalamic pre optic area and elsewhere in the body are integrated in the posterior hypothalamic area to activate heat producing and heat conserving reactions of the body. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 62. “SET POINT” FOR TEMPERATURE CONTROL • The body core temperature is maintained at 37.1C or 98.8F . • This temperature is called set point of the temperature control system. • If the body temperature rises above this point , all the heat losing mechanisms come into play. • If the body temperature falls below this point , all he heat conserving and heat generating mechanisms are activated. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 63. Behavioral control of body temperature: • Psychic sensations of being over heated or being too cold are sent to the person . • If over heated ,person moves to a cold room , takes cold drinks , light cotton clothing, sprawling, seeking shade etc. • If it is too cold, appropriate adjustments like, moving to a warm room, hot drinks and insulating clothes are made. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 64. Thermal events during exercise • In a cool/ moderate environment, heat production during exercise is directly proportional to exercise intensity • Venous blood draining exercising muscles distributes the excess heat throughout the body core • Method of heat loss during continuous exercise is modified according to ambient conditions Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 66. Heat storage in body during exercise • Any heat produced by working muscles that is not lost, must be stored in body tissues • Body heat gain during exercise= heat produced- heat loss • Exercise using large muscle groups (i.e: legs) can result in large amounts of heat production • Increase in body temperature during exercise depend on – Bodyweight/mass – Specific heat of body tissue Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 67. Heat index • It is the measure of body’s perception of how hot it feels • The index is calculated by combining the air temperature & relative humidity to compute an apparent temperature • If air temperature is 82oF & humidity is 80%, HI is 89oF. • High humidity increases an individual’s perception of how hot the environment feels Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 69. Physiologic responses to exercise in hot weather • Competition b/w active muscles & skin for limited blood supply – Muscles– blood & oxygen for sustained activity – Skin– blood to facilitate heat loss to keep the body cool • Cardiovascular response: adjustment—dec. blood volume returning to heart dec. end diastolic volume dec. SV • Compensation: cardiovascular drift gradual upward drift in HR • Energy production: exercise in hot environment inc. O2 uptake use of more glycogen produce more lactate earlier fatigue & exhaustion Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 70. • Body fluid balance: sweat– filtration of plasma. Reabsorption of Na & Cl in passing through the duct • Increased sweat rates– quick movement, less time for reabsorption, loss of sodium & chloride • With training aldosterone stimulated for more reabsorption of Na & Cl • Sweat production in hot weather: 1L/hr/m2– 2-4% of body weight dec. blood volume dehydration triggering aldosterone, ADH dec. Na excretion & inc. water reabsorption in kidneys fluid retention Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 72. Exercise performance in hot environment It is impaired due to following factors • Accelerated muscle fatigue – Increased free radical production – Decreased muscle pH – Muscle glycogen depletion • Cardiovascular dysfunction – Reduced stroke volume – Decreased cardiac output – Decreased muscle blood flow • CNS dysfunction – Decreased motivation – Reduced voluntary activation of motor units – Muscle fatigue Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 73. Exercise in the cold • What is cold stress? • It is an environmental condition which causes loss of body heat & threaten homeostasis • Major cold stressors are: – Air – Water Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 74. Following mechanisms are observed in case of exercise in cold • Shivering which increases 4-5 fold increase in resting heat production • Nonshivering thermogenesis which increases metabolism by activating sympathetic nervous system increased internal heat production • Peripheral vasoconstriction due to sympathetic stimulation of smooth muscles in arterioles 2 advantages: decreased heat loss from surface & decreased metabolism of skin cells (less O2 requirement) Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 75. Physiological response to exercise in cold • When muscle is cooled, it is weakened fatigue occurs more rapidly • With prolonged exposure to cold – Vasoconstriction decreased circulation to subcutaneous fat decreased FFA for fuel – Energy supplies diminish – Susceptibility to hypothermia increases Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 76. Heat Acclimatization • These are several mechanisms by which a person’s ability to tolerate heat is improved who have been living in hot climate for long time. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 77. Mechanisms of acclimatization to heat • The mechanisms are: • More effective sweating: when exposed to high teperature, acclimatized person sweats more heavily upto 4L/hr as against 1.6L/hr in unacclimatized person • Conservation of NaCl: excessive sweating in unacclimatized person hyponatremia (due to loss of NaCl in sweat)greater secretion of aldosterone NaCl content of sweat & urine decreases remarkably in acclimatized person • More vasopressin (ADH) is secreted renal blood flow is decreased urinary volume is decreased to conserve water • Dilation of cutaneous blood vessels • Total blood volume may also decrease Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 78. Acclimatization to cold • Not as efficient as heat acclimatization • Only seen in primitive (fishermen, washermen) people who live at 0oC • There is decreased shivering at low temperatures also • Less cold induced pain perception is also observed in cold acclimatized person Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 79. ABNORMALITIES OF TEMPERATURE REGULATION Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 80. FEVER/PYREXIA • Fever refers to increased body temperature above normal , caused by toxic substances that can affect temperature regulating centers. • Resetting of the set point to a higher level • Causes of fever: • Bacterial and viral infection • Brain tumors • Environmental conditions Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 81. RESETTING THE HYPOTHALAMIC TEMPERATURE REGULATION CENTER • PYROGENS: • Substances that can raise the hypothalamic set point above normal • They include: • Proteins • Breakdown products of proteins • Lipopolysaccharide toxins released from bacterial cell wall When the hypothalamic set point is raised all the mechanisms to raise body temperature become active as well. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 82. Mechanism of action of pyrogens: • Pyrogens either act directly on the hypothalamic center • Or they act indirectly via the cytokines especially IL-1 • Bacterial breakdown products → phagocytosed by leukocytes and macrophages → cytokines especially IL1 is released by the phagocytic cells → IL1 induces the formation of PGE 2 → PGE 2 acts on hypothalamus to cause fever reaction. • Antipyretics are the drugs that decrease the formation of PGE2 and reduce fever e.g, aspirin Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 83. Features of febrile conditions • CHILLS: Shivering and vasoconstriction result into chills in an attempt to raise the body temperature up to the new hypothalamic set point. • CRISES OR FLUSH : When the pyrogen is removed and set point is back to normal , all the body mechanisms to lose heat like sweating and vasodilation become active . • This takes the body temperature back to normal Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 85. Hyperpyrexia: • Fever of above 41.5˚C or 106.7˚F is called hyperpyrexia • Seen in • Severe infections • CNS hemorrhage Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 86. Hyperthermia: • Differs from hyperpyrexia in that • The set point remains unchanged • Doesn’t respond to antipyretics Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 87. Types of hyperthermia: • Heat stroke • Drug induced – Amphetamines – Cocaine • Malignant Hyperthermia • Inherited genetic abnormality in Ca release in skeletal muscle. Increased release of calcium turns on muscle contraction • Triggered by some anaesthetic agents Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 88. Disorders due to increased heat: • In order of increasing severity • Heat syncope • Heat cramps • Heat exhaustion • Heat stroke Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 89. Heat syncope: • Due to history of vigorous physical activity for about 2 hours • Results from cutaneous vasodilation • Cerebral and systemic hypotension • Leading to syncope • TREATMENT: • Rest in a cool place • Fluids by mouth Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 90. Heat cramps: • Due to excessive Na loss in sweat , painful heat cramps occur. • Relieved by NaCl replacement and cold environment. Heat exhaustion: • Excessive loss of salt and water in sweat leads to hemoconcentration, hypovolemia ,hypotension, headache, vertigo, nausea and collapse of patient(due to less blood supply to brain) • The skin is cold and clammy with normal or subnormal temperature • Treatment :recumbent position of the patient • Removal of patient to a cold place • Salt and water replacement Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 91. Heat stroke: ( failed compensation) • Life threatening emergency which damages the hypothalamus • Core temperature rises to point that hypothalamus ceases to function • Hyperthermia • Set point remains unchanged • Doesn’t respond to antipyretics • Sign: absence of sweating Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 92. HEAT STROKE: • Body temperature rises up to 105-108 ˚F • Failure of all the heat dissipating mechanisms. • Occurs during heat wave when temperature and humidity is very high • Symptoms: • Hot and dry skin. • Dizziness ,abdominal distress and vomiting ,delirium ,loss of reflexes, loss of consciousness ,circulatory shock ,hyperpyrexia ,death may occur due to neuronal damage , renal failure and MI Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 93. Loss of temperature regulation at low temperature • The hypothalamic temperature regulation is impaired when the body temperature falls to around 94˚F • Lost when the body temperature falls to 85˚F • There is two folds decrease in the cellular metabolic rate for each 10 degree fall in temperature. • CNS depression ensues sleepiness and loss of shivering. • At 77˚ F there is cardiac standstill Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 94. Hypothermia: Decrease in body temperature below 35C (95F) is called hypothermia. • it is a clinical state of subnormal body temperature when the body fails to produce enough heat to maintain the normal activities • Elderly are more susceptible to hypothermia Setback of hypothermia: Impairment of metabolic activities Becomes fatal when temperature drops below 31C Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 95. Presentation of hypothermia • Person exposed to cold for a long period of time • Also seen in patients of • Myxedema , Addisons disease , hypoglycemia • FEATURES: • Shallow breathing , bradycardia ,hypotension ,loss of consciousness, arrythmias Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 96. Frostbite: • Surface area of the body can freeze upon exposure to cold. This is called frostbite. • Ice crystals develop in the blood stream and cells causing permanent circulatory and tissue damage. • Upon thawing , gangrene develops and the area has to be removed surgically. • The vascular smooth muscles become paralyzed due to extreme cold leading to improved blood supply to the tissues .This protective mechanism is very well developed in arctic animals. Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 97. Pathophysiological changes in frostbite Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
- 98. Artificial hypothermia: The temperature of a person is decreased by • Sedatives….which reduce the over activity of hypothalamic center • Use of ice or cooling blankets USES: Heart surgery can be done after hypothermia so that heart can be stopped artificially for several minutes at a time. Hypothermia decreases whole body metabolic rate by approx. 8%, oxygen demand diminishes & oxygen consumption in tissues is reduced Low metabolic rate allow aerobic metabolism to continue during periods of compromised oxygen supply Dr. Misbah-ul-Qamar
