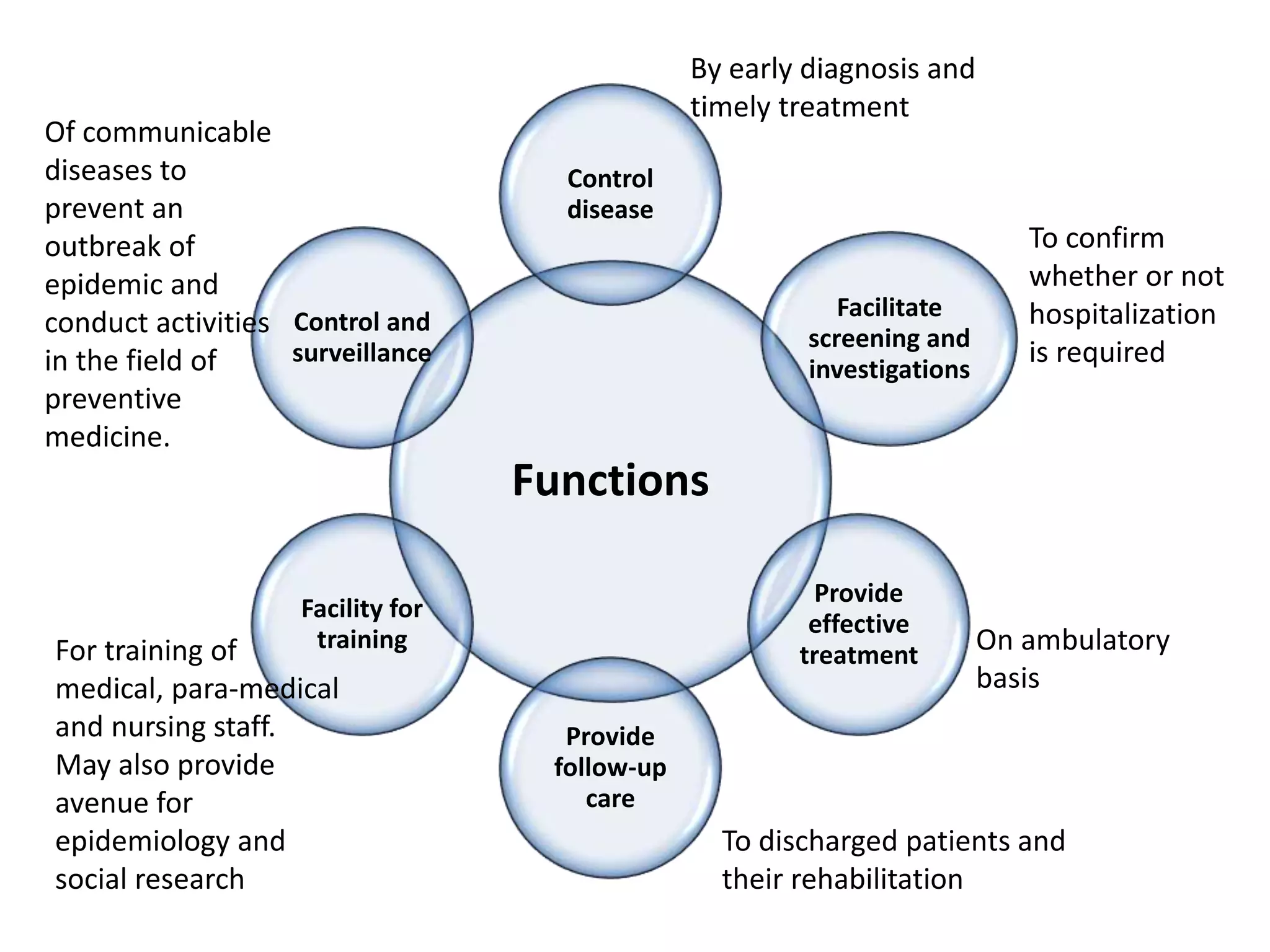
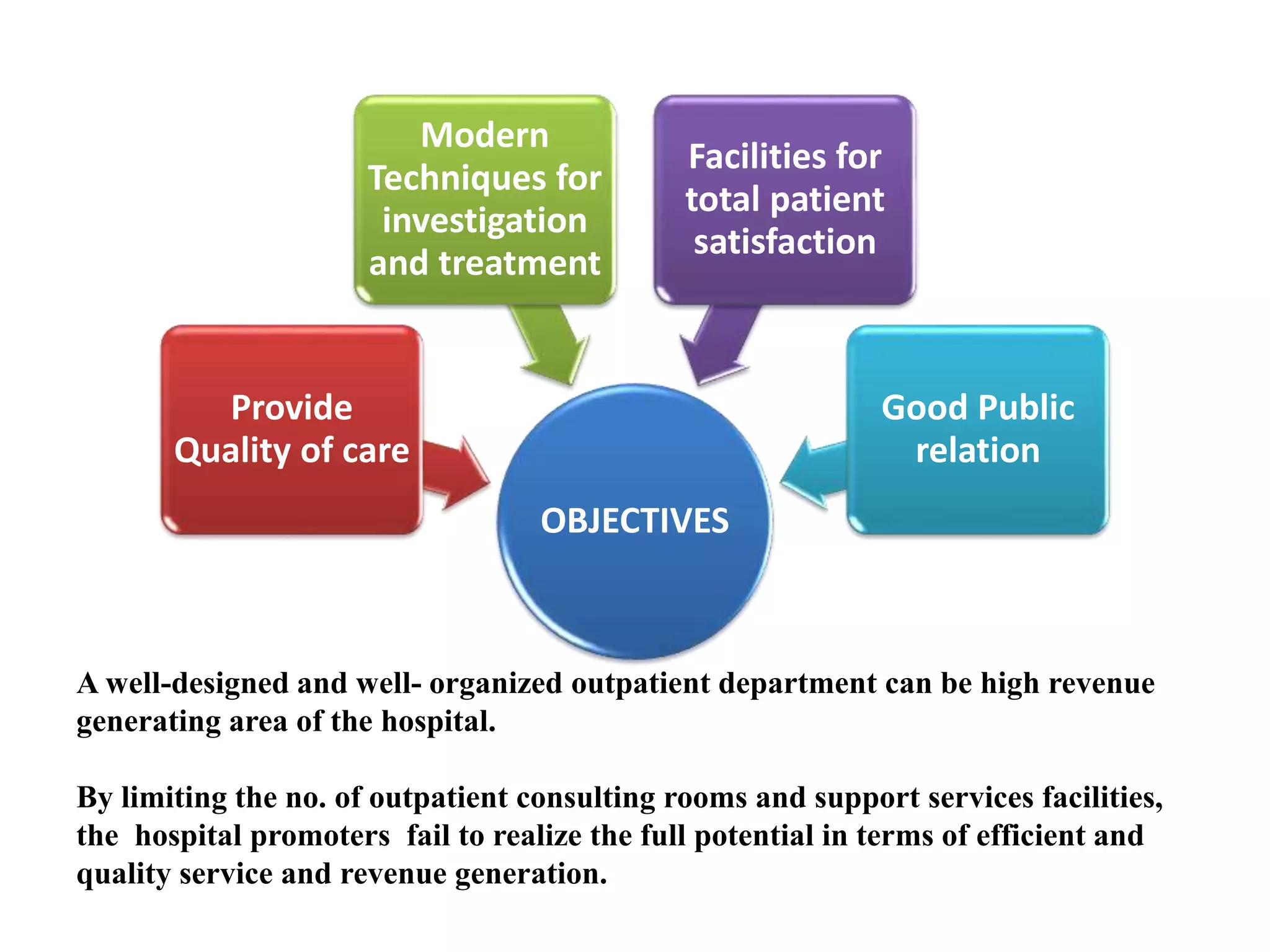
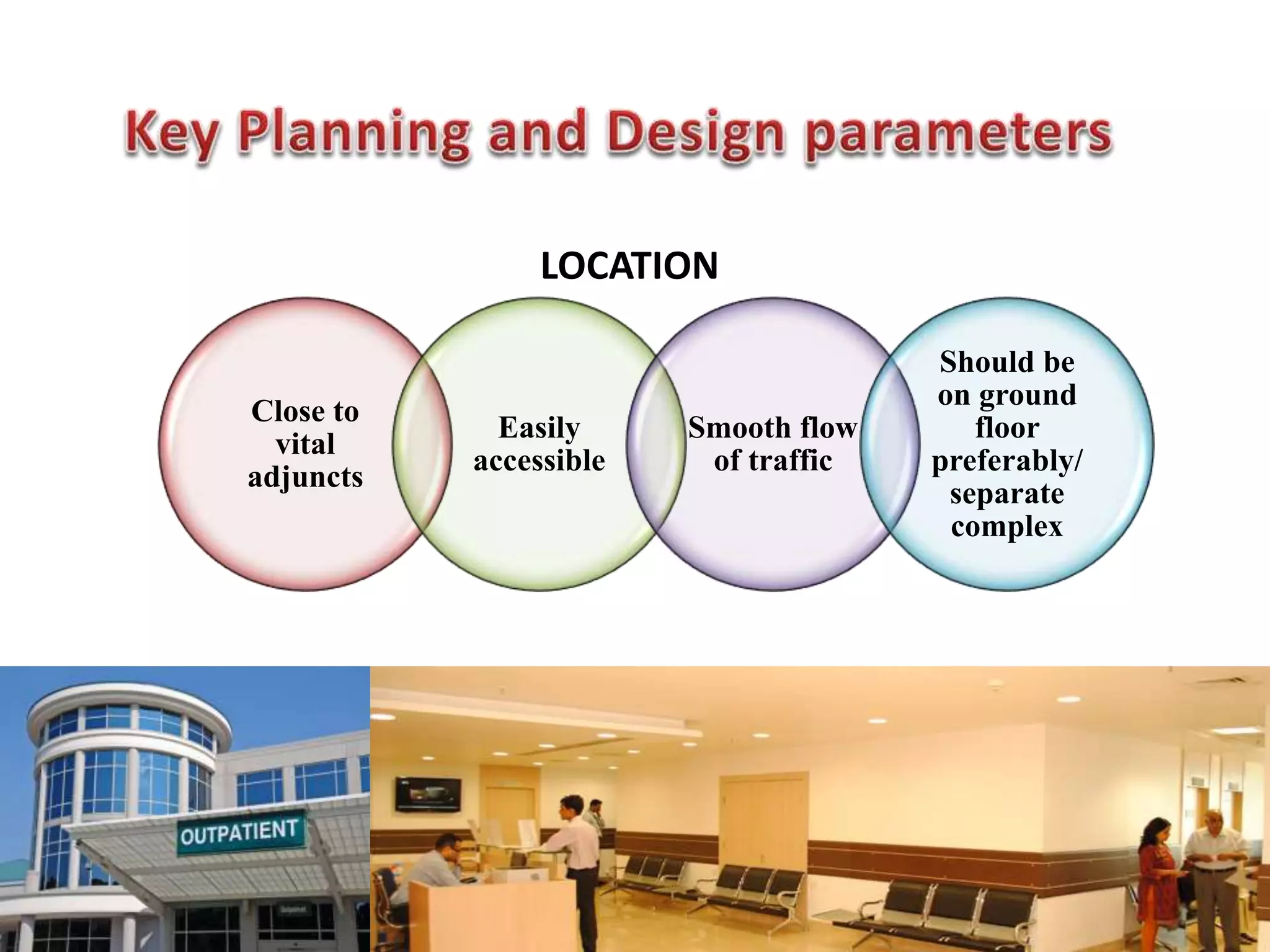
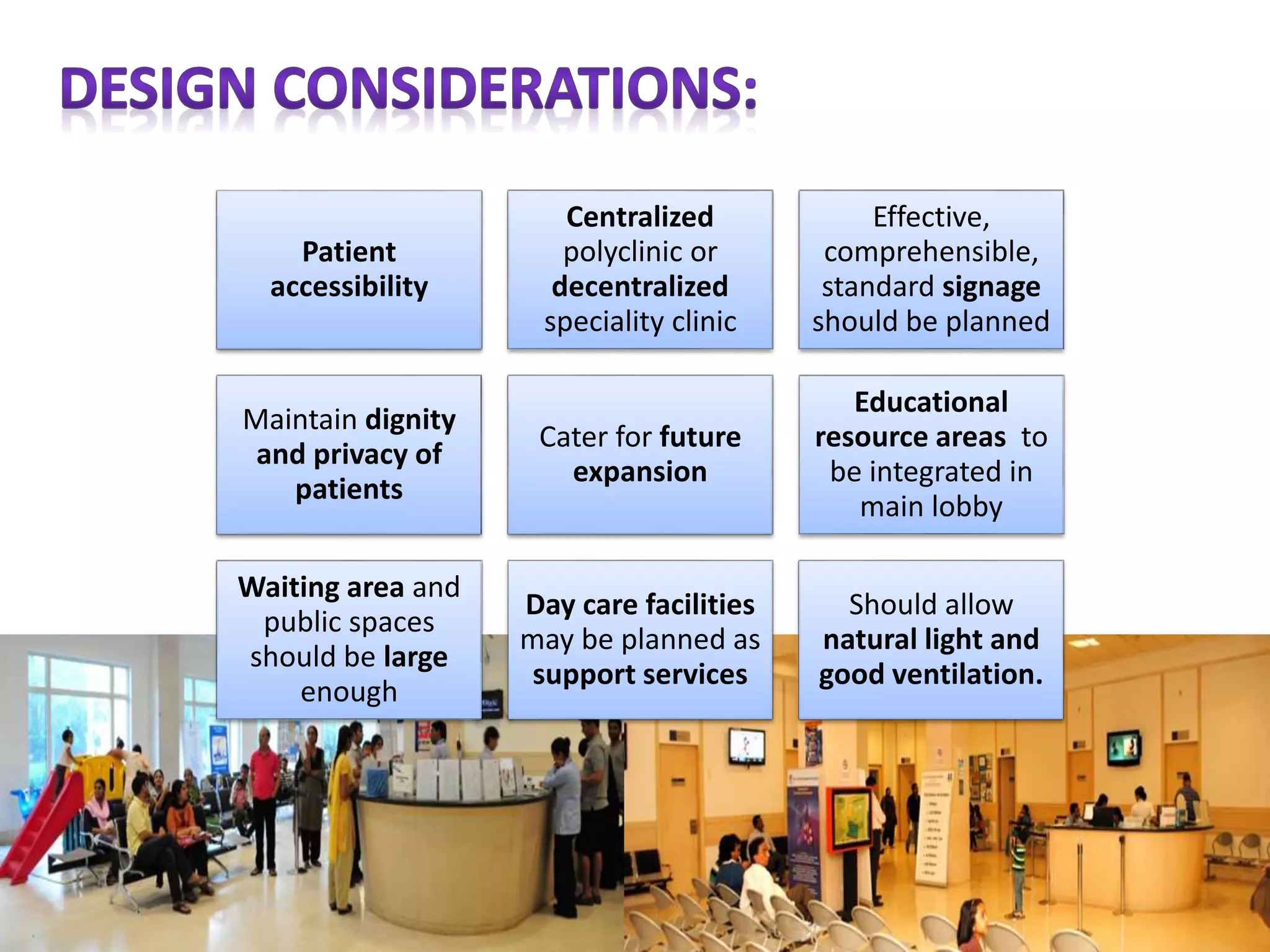
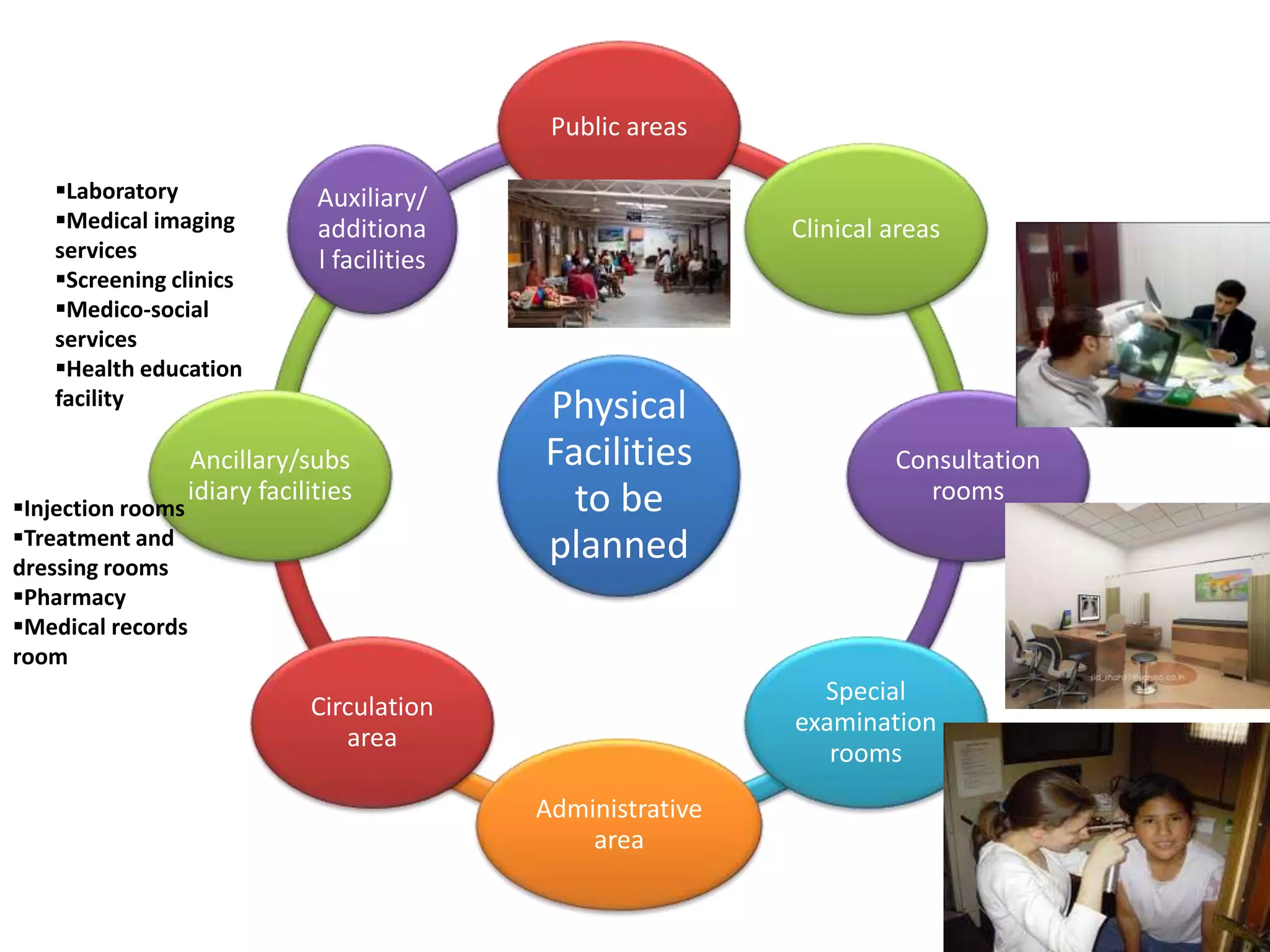
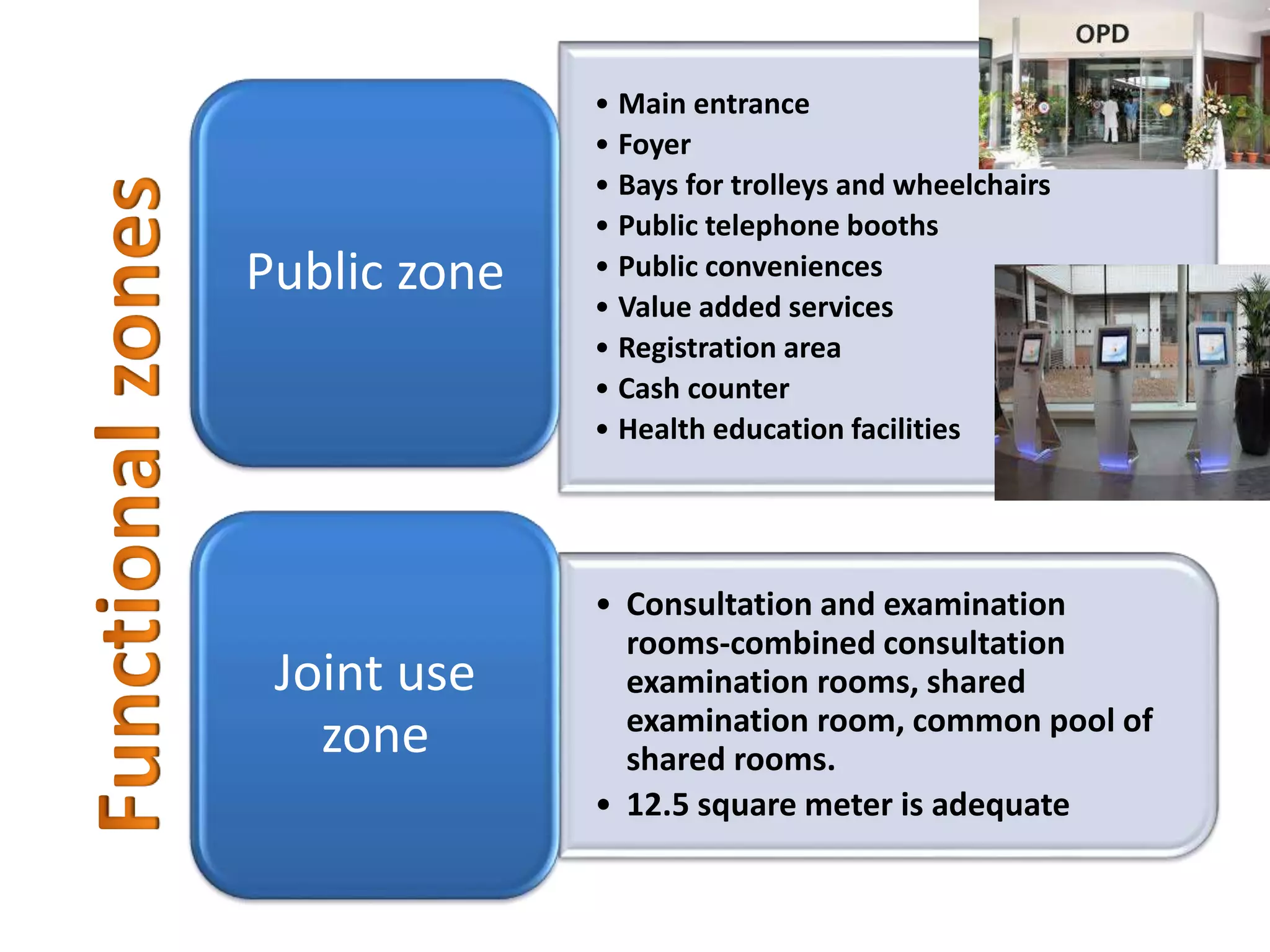
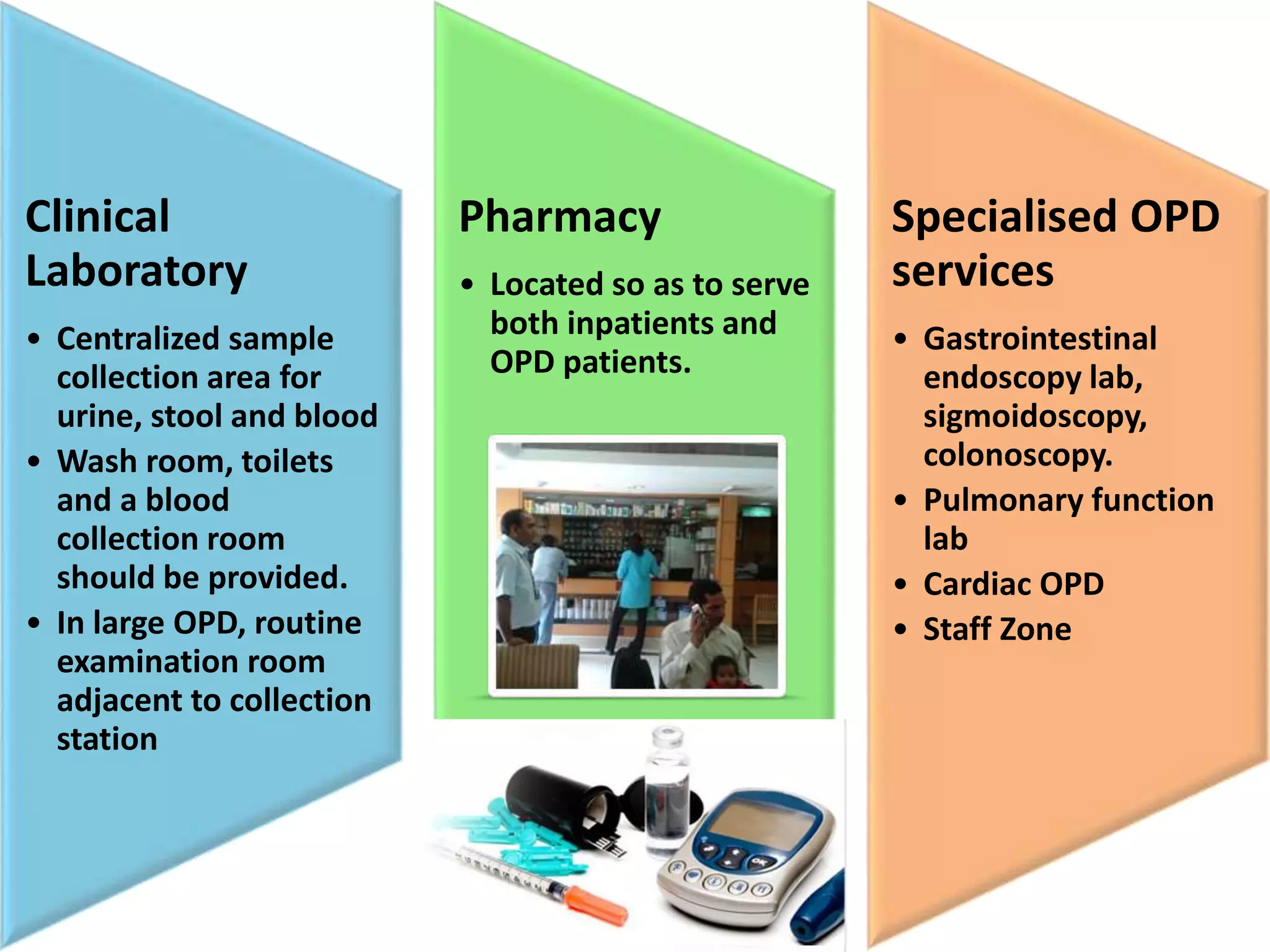
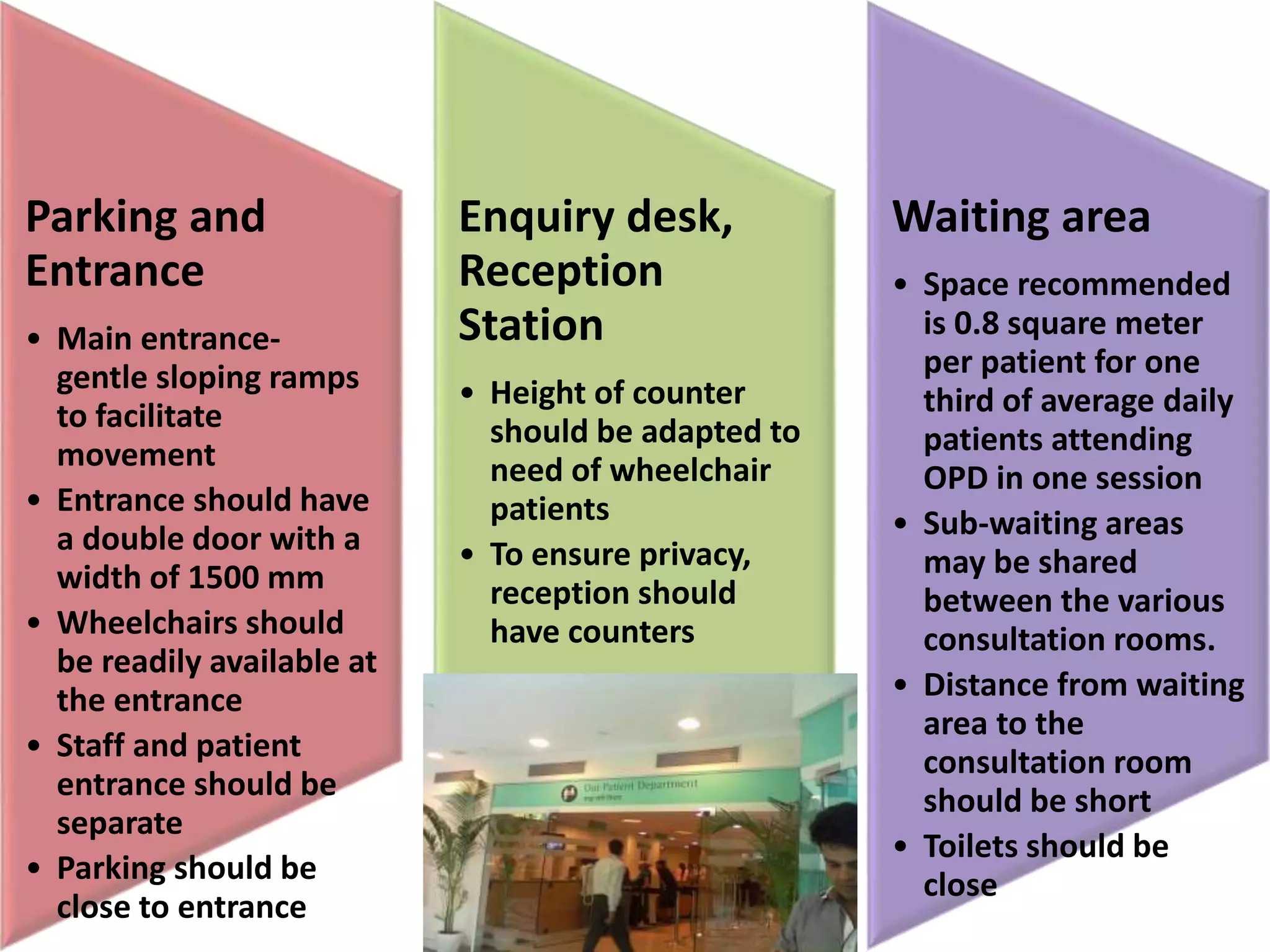
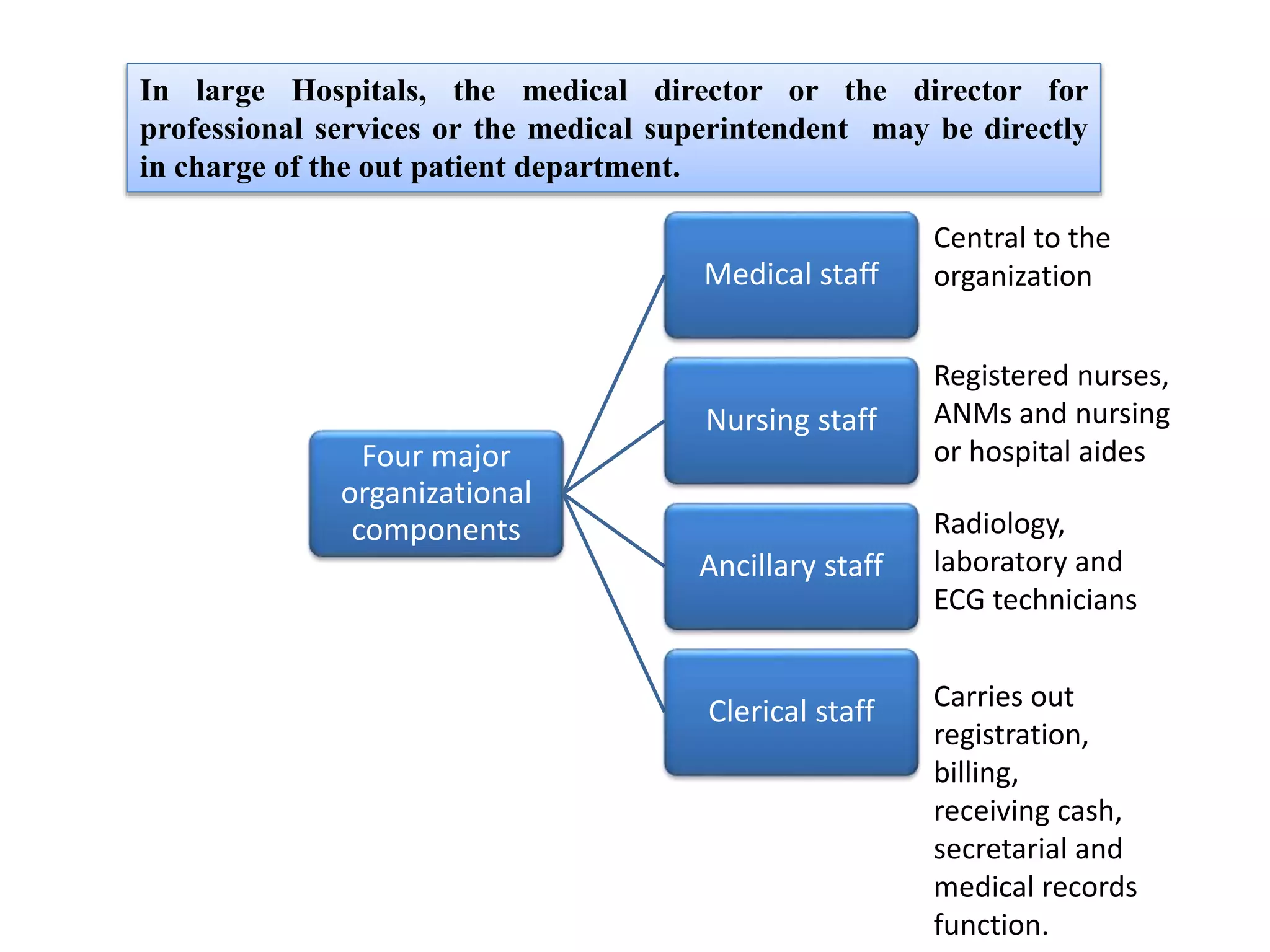
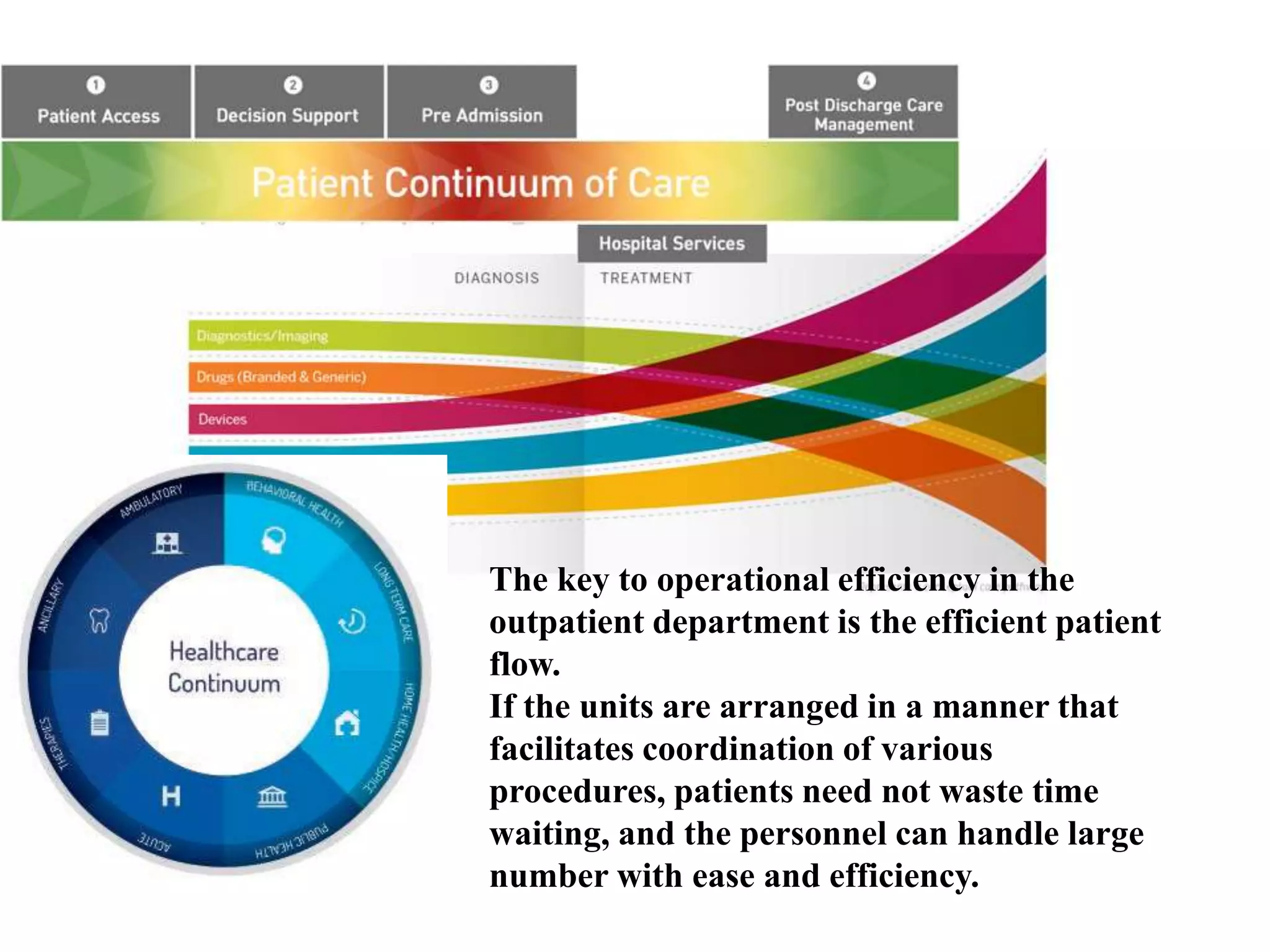
Outpatient care has evolved significantly over time. It was originally designed to offer only basic minor services, but now encompasses a wide range of treatments, diagnostic tests, and minor surgeries. The outpatient department is the first point of contact between patients and the hospital, and aims to provide quality care through diagnosis, treatment and follow-up in an ambulatory setting. Efficient organization and flow of patients is key to ensuring operational efficiency in the outpatient department.