This document provides an overview of EMV transaction flows, including:
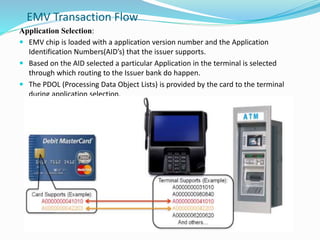
1) EMV transactions involve application selection on the chip card to route transactions to the issuer bank, as well as terminal action analysis and cryptogram generation for online or offline authorization.
2) Offline authentication can involve static data authentication, dynamic data authentication, or combined authentication along with PIN verification on the chip card.
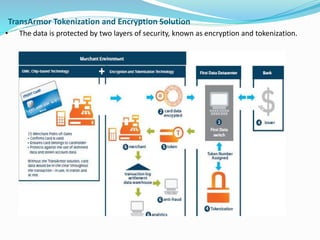
3) Security for e-commerce has evolved with techniques like CVV numbers, address verification, and tokenization to protect stored payment data.