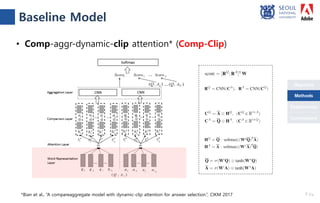
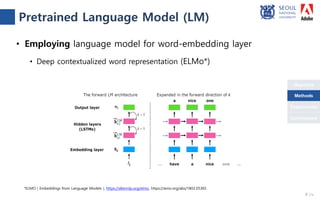
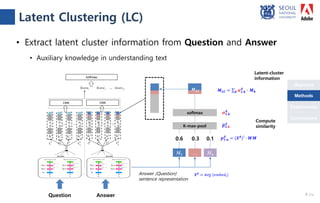
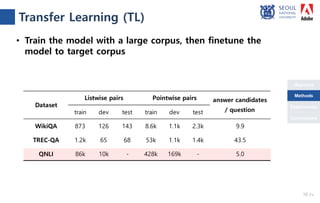
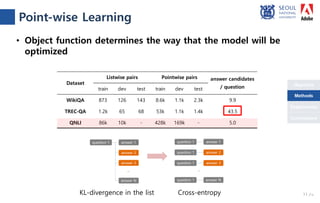
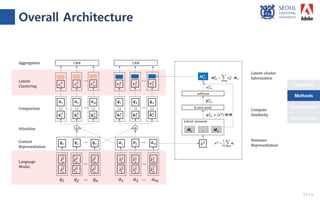
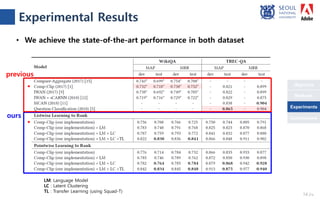
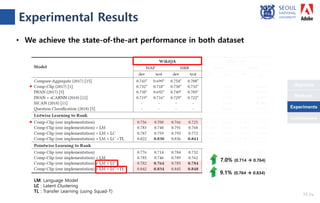
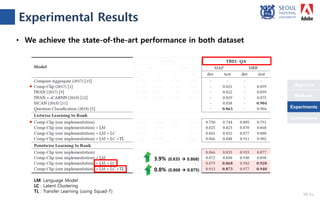
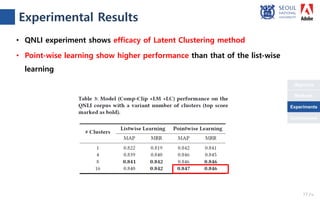
The document presents a novel compare-aggregate model enhanced with latent clustering for improved answer selection in question answering systems. The study demonstrates state-of-the-art performance through extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, utilizing pretrained language models and transfer learning techniques. Key findings indicate that leveraging large data sets and adopting a pointwise objective function significantly enhances model efficacy.