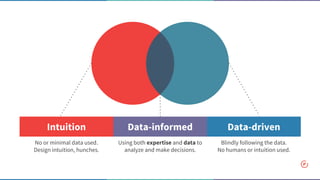
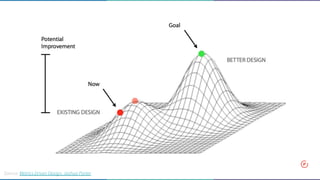
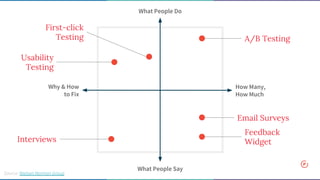
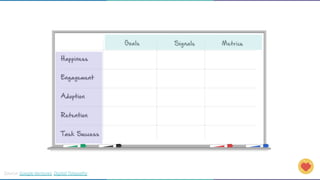
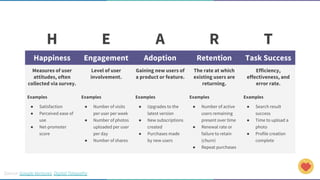
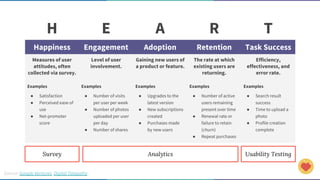
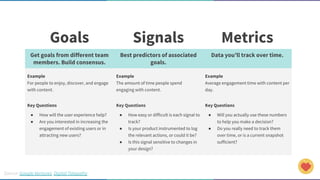
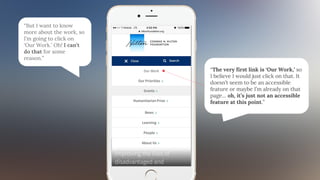
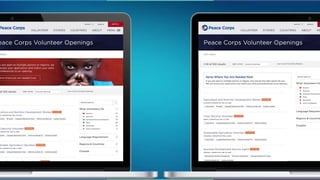
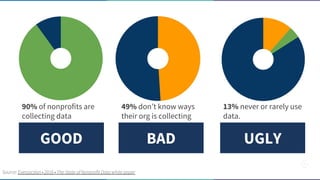
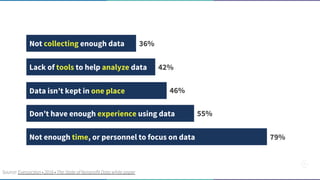
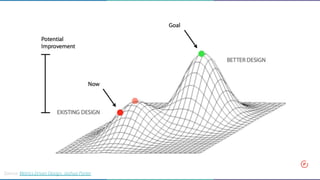
The document discusses the concept of data-informed design, contrasting it with data-driven design, and emphasizes the importance of using both intuition and data for effective decision-making. It highlights various sources of data that can inform design choices, goals for measuring user engagement, and provides a framework (HEART) for evaluating user experiences. Additionally, it outlines challenges faced by organizations in utilizing data effectively and encourages collaboration with analysts to optimize design outcomes.