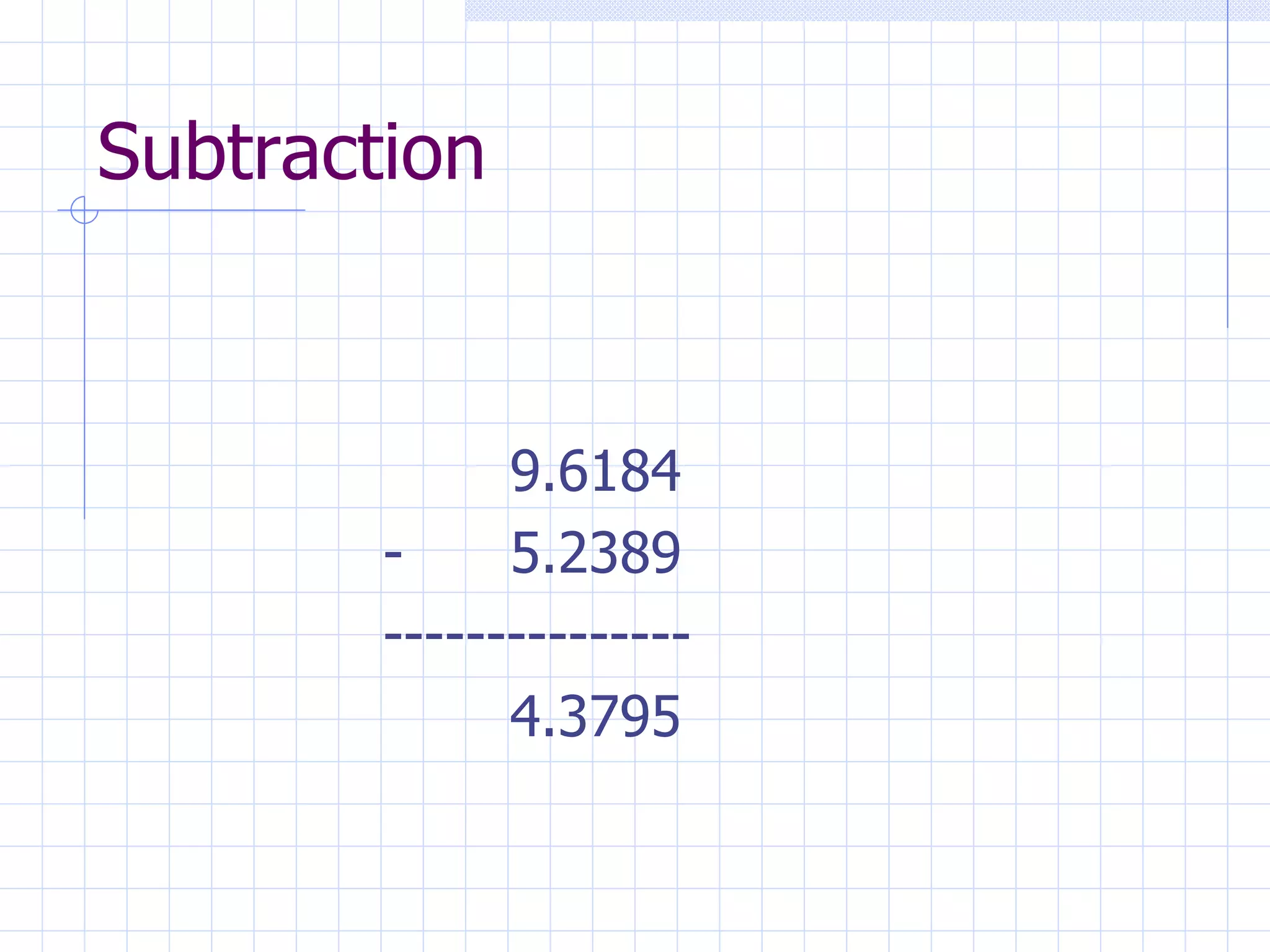
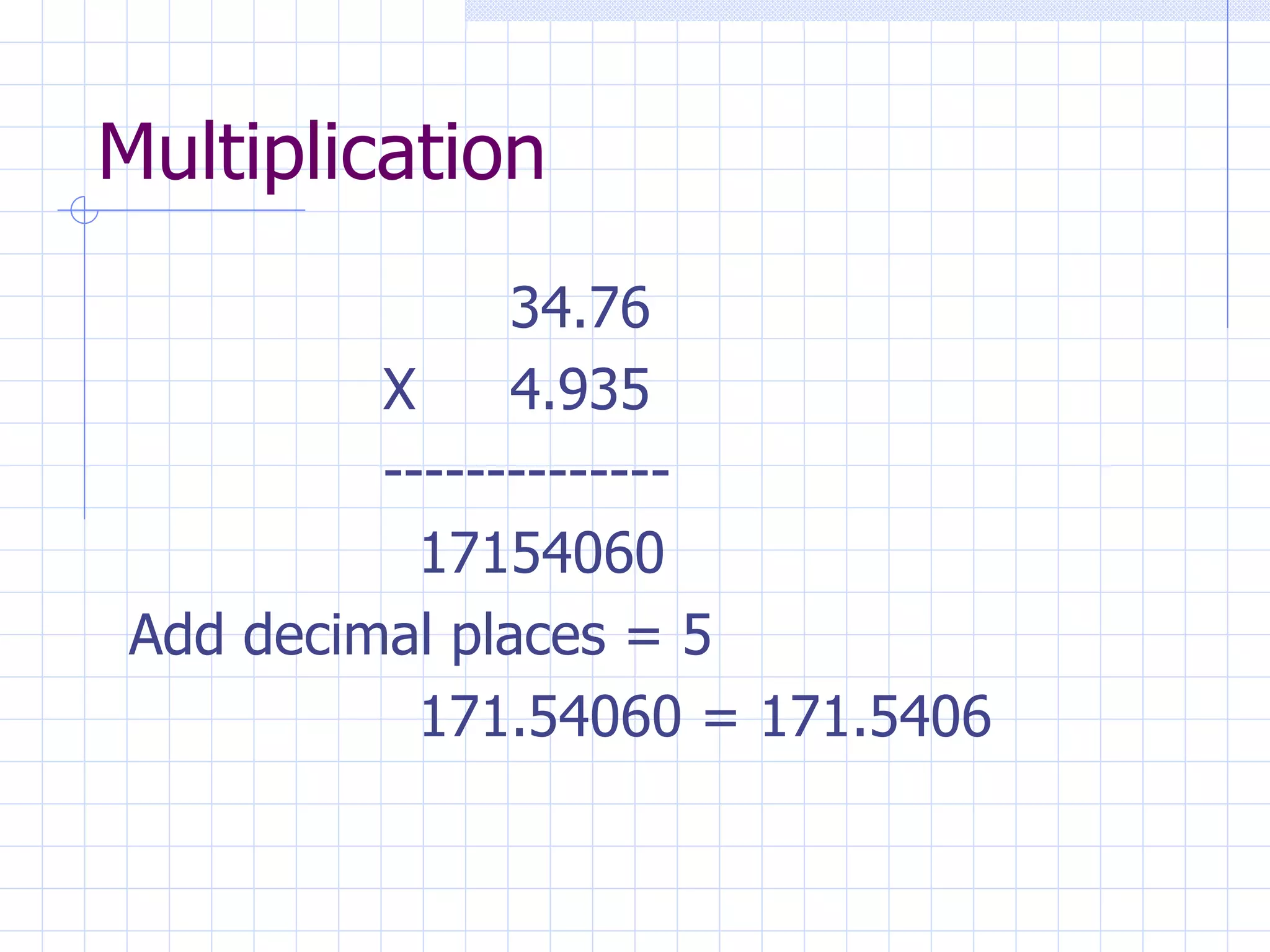
The document provides an overview of various medical math concepts and formulas for calculating dosages and drip rates. Key topics covered include:
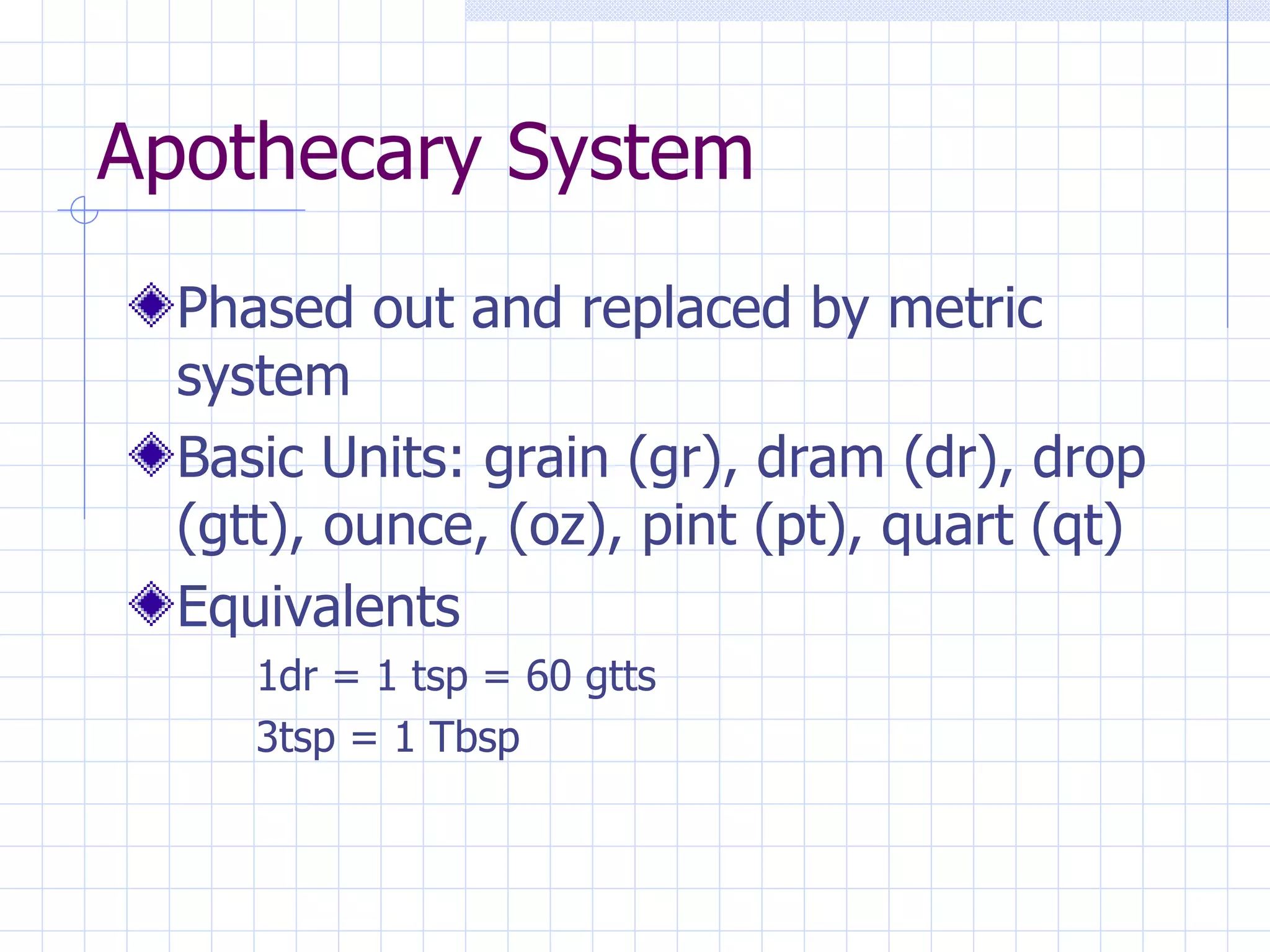
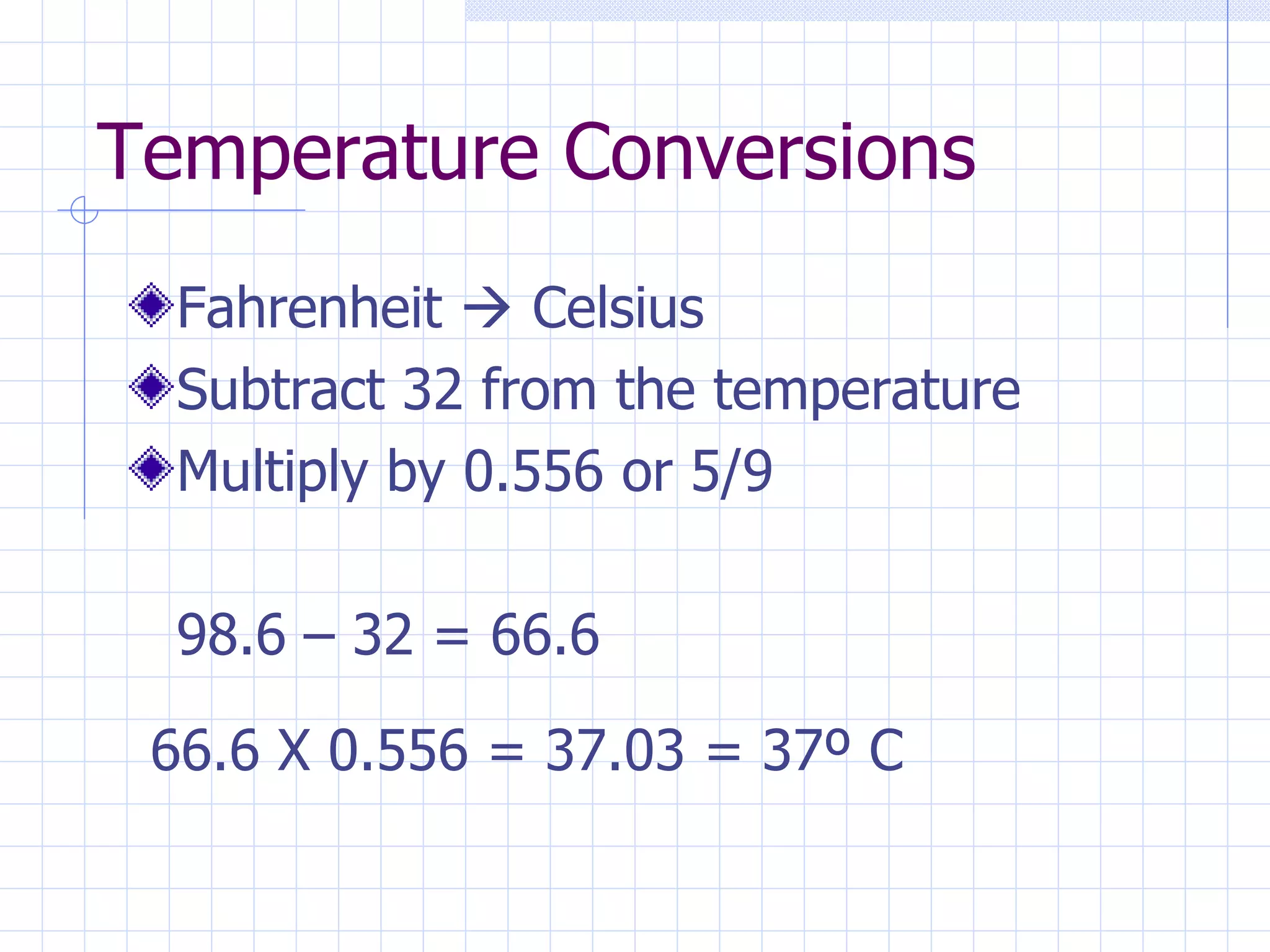
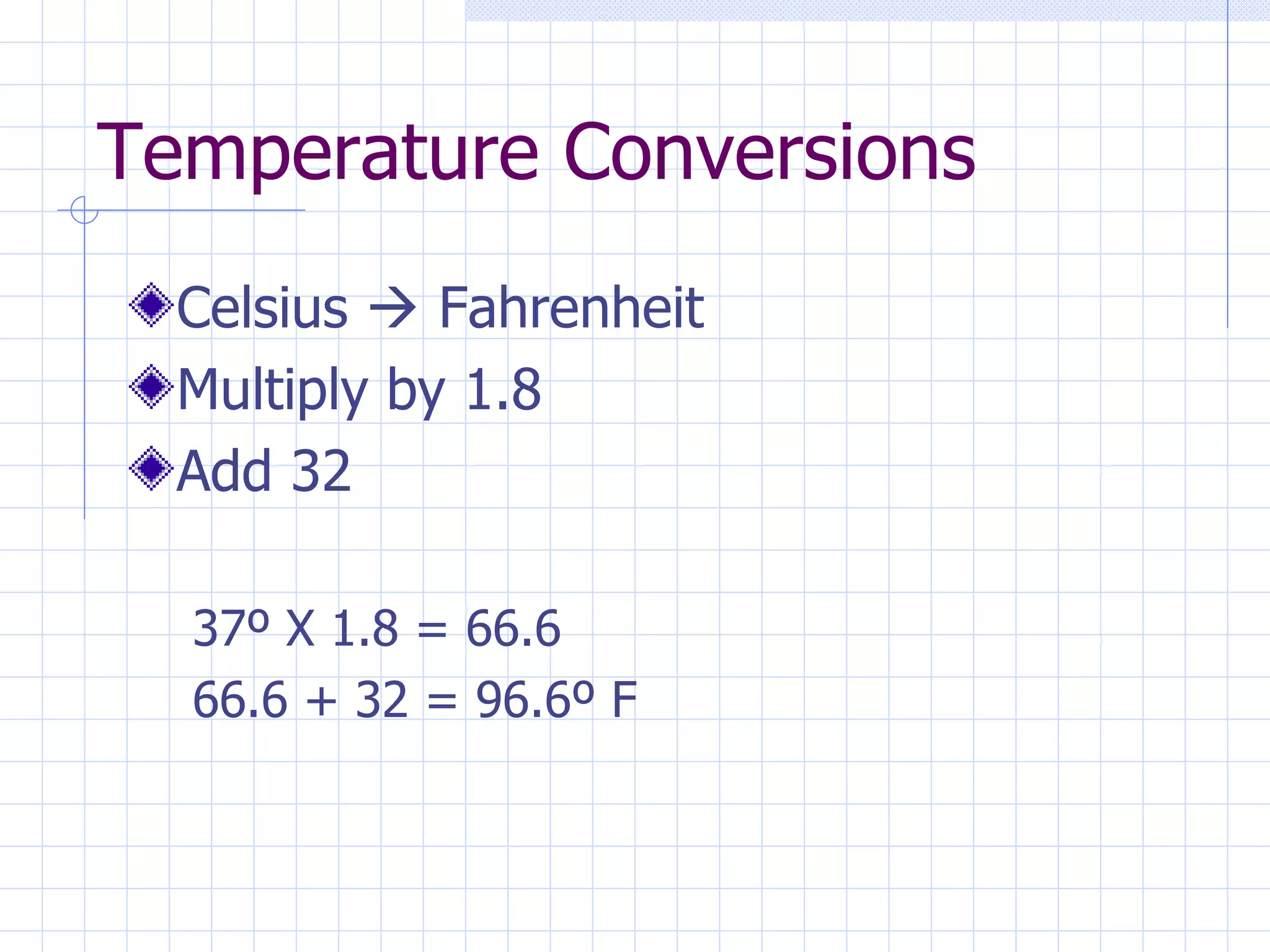
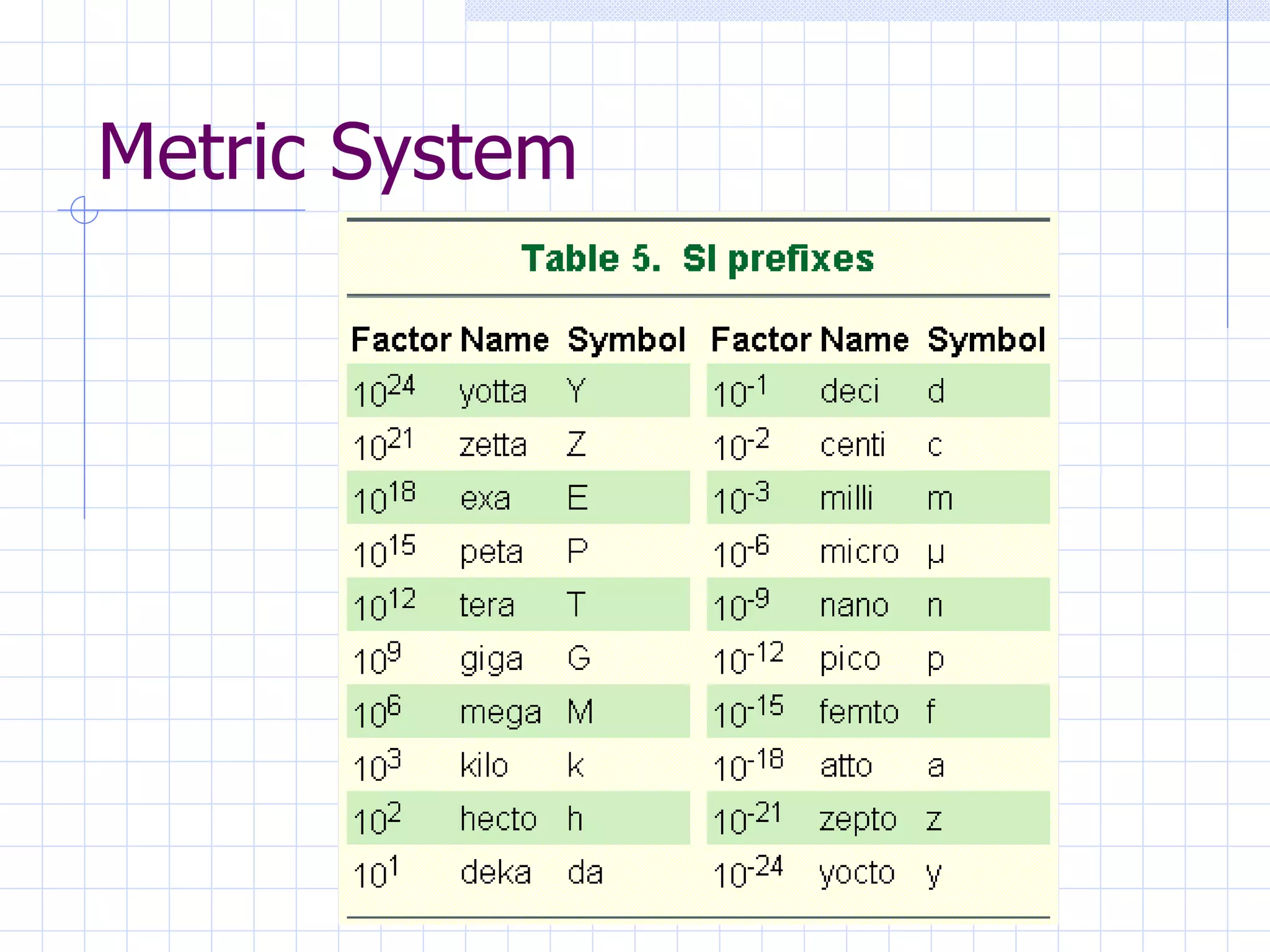
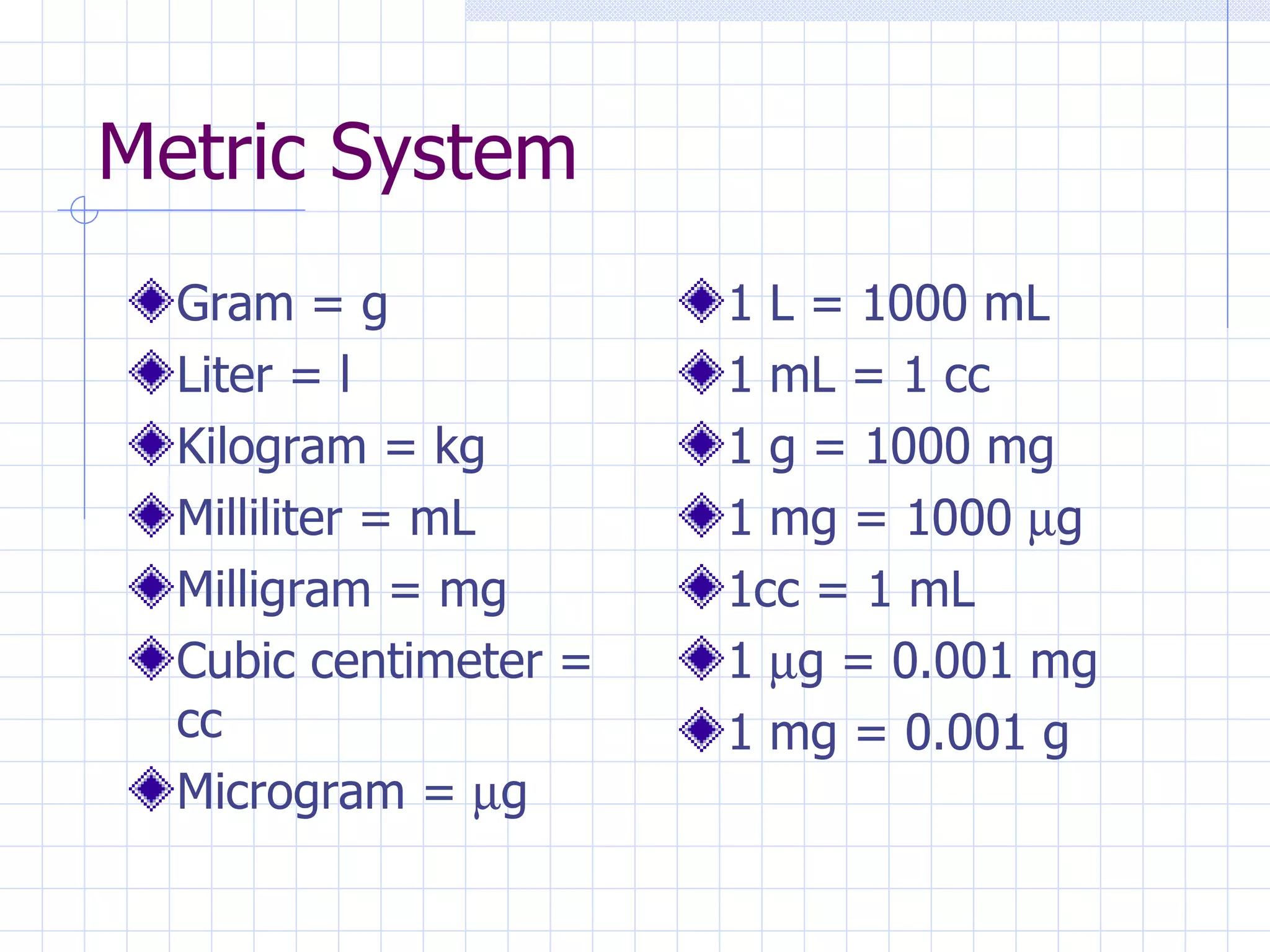
- Converting between measurement systems like metric, apothecary, and Fahrenheit/Celsius
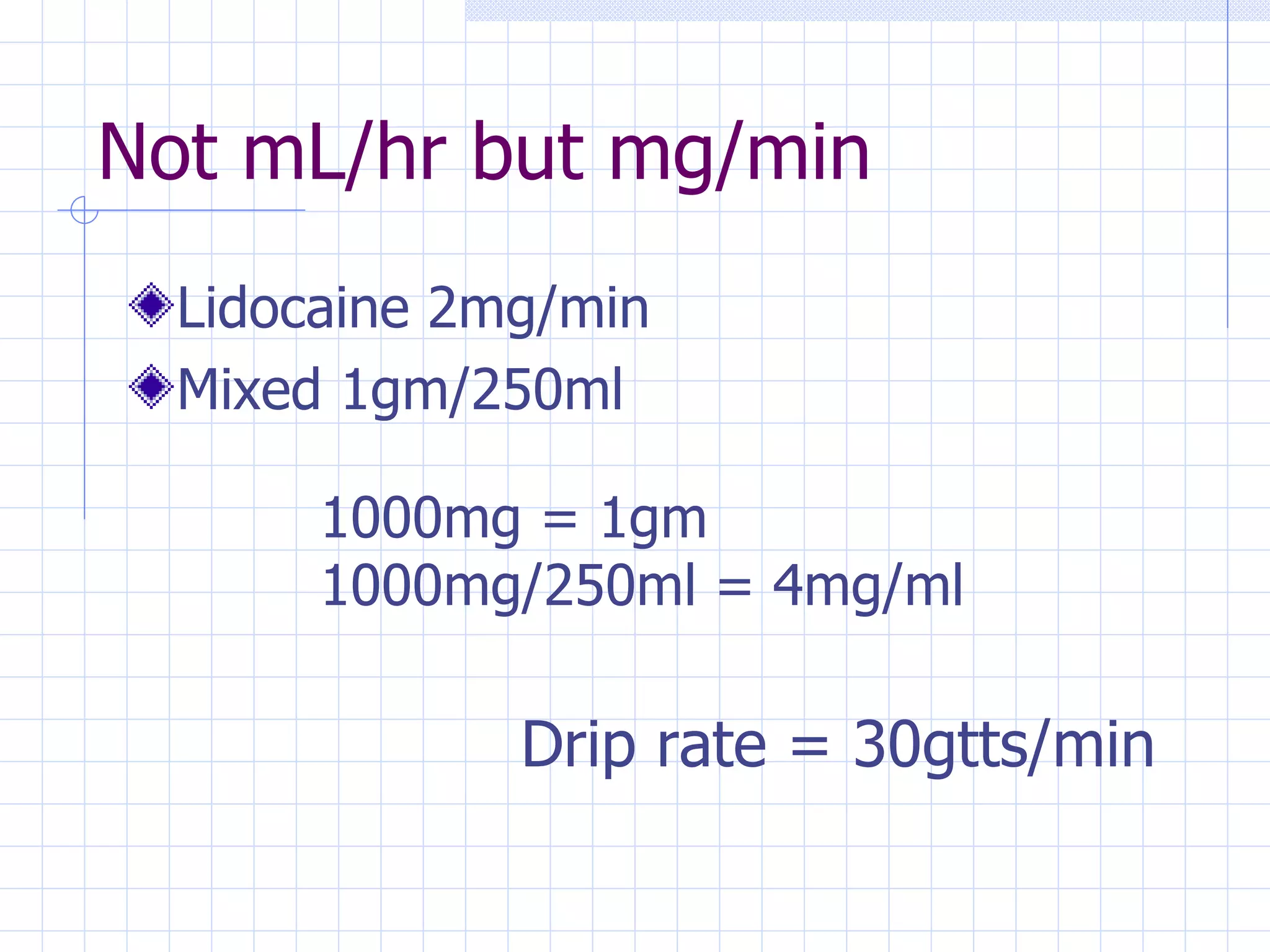
- Calculating dosages using concentration and volume formulas
- Determining drip rates using concentration, dosage, and number of drops per minute
- Weight-based dosage calculations using patient weight in kg and mg/kg formulas
Practice problems are provided for many of these concepts to help users learn and apply the various medical math formulas.