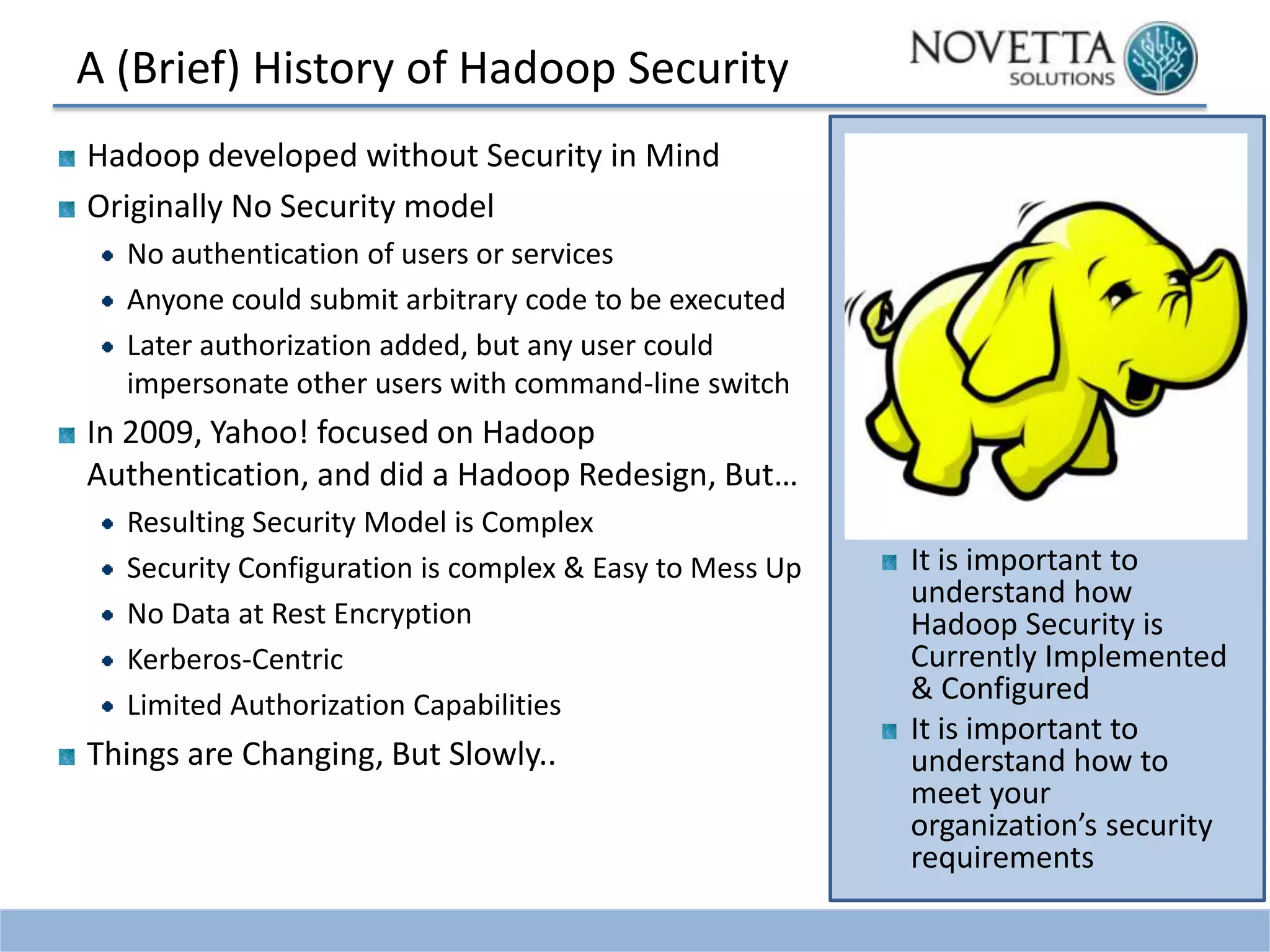
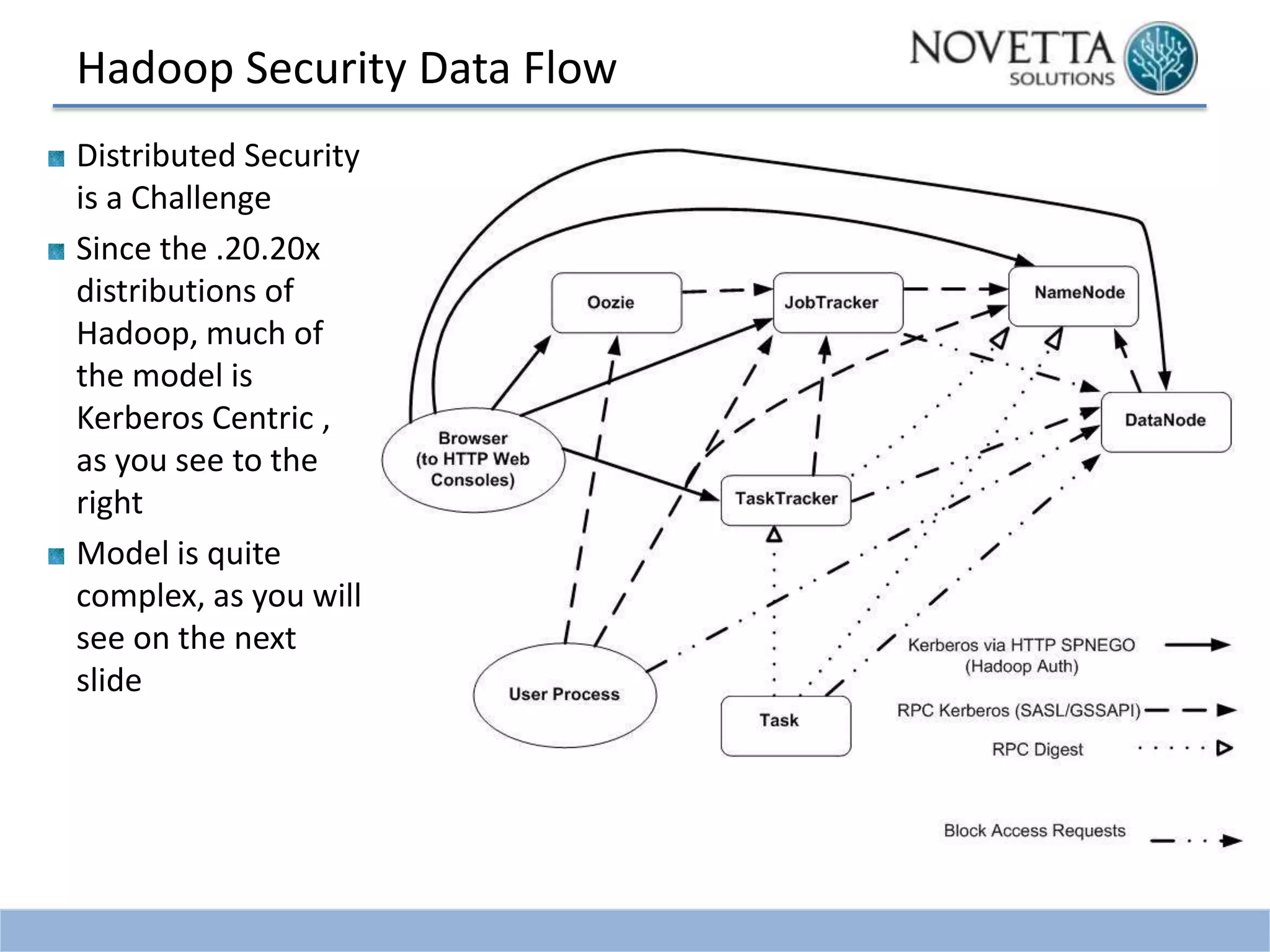
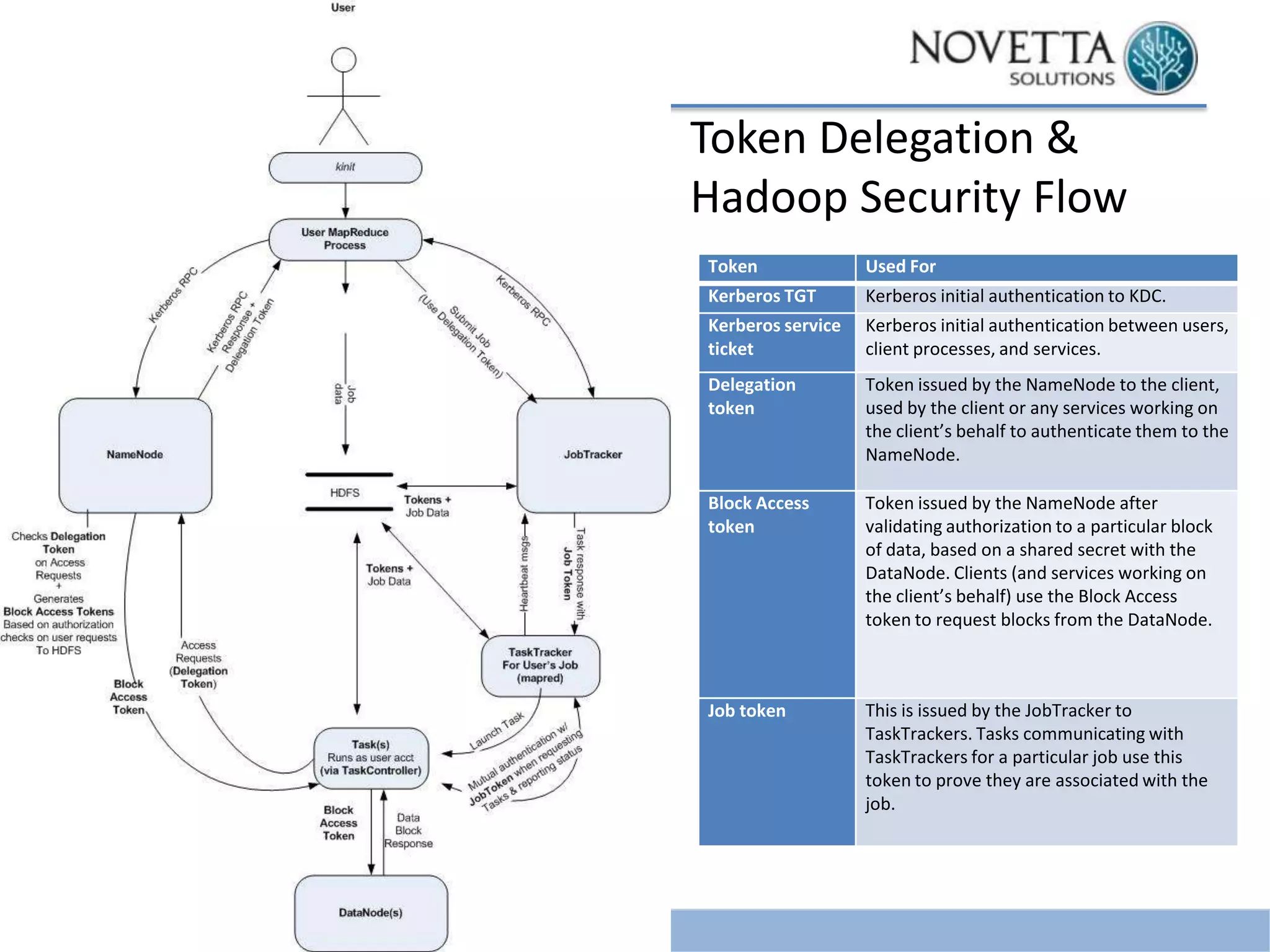
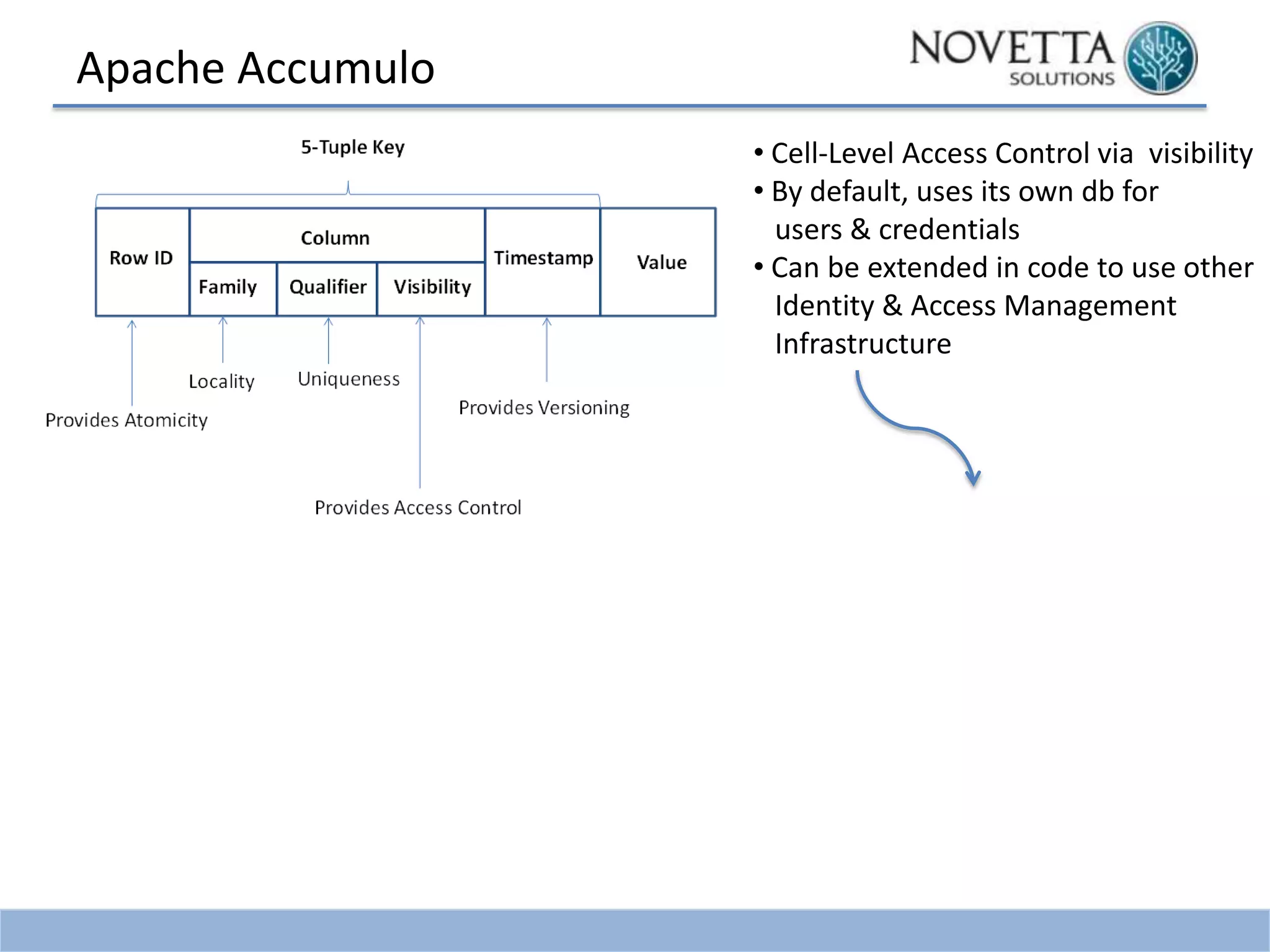
This document discusses security challenges related to big data and Hadoop. It notes that as data grows exponentially, the complexity of managing, securing, and enforcing privacy restrictions on data sets increases. Organizations now need to control access to data scientists based on authorization levels and what data they are allowed to see. Mismanagement of data sets can be costly, as shown by incidents at AOL, Netflix, and a Massachusetts hospital that led to lawsuits and fines. The document then provides a brief history of Hadoop security, noting that it was originally developed without security in mind. It outlines the current Kerberos-centric security model and talks about some vendor solutions emerging to enhance Hadoop security. Finally, it provides guidance on developing security and privacy