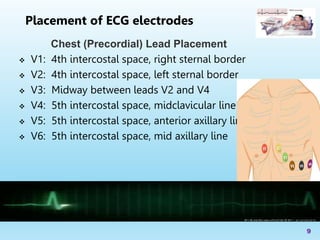
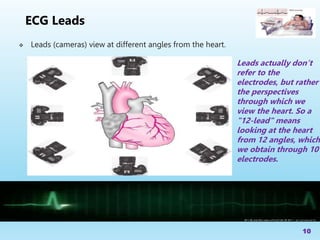
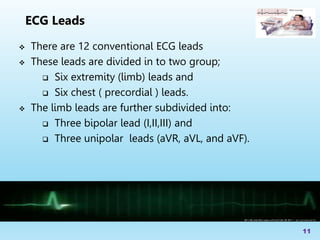
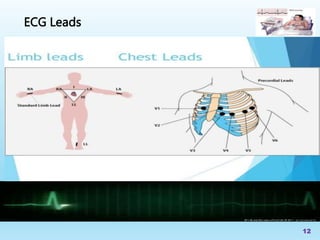
The document serves as an educational guide on electrocardiography (ECG), describing its significance in diagnosing cardiac conditions and detailing the anatomy of the cardiac conduction system. It outlines the placement of electrodes, types of ECG leads, and the importance of prehospital ECGs in improving patient outcomes. The lecture aims to equip participants with the knowledge to interpret ECG waveforms and recognize various heart issues.