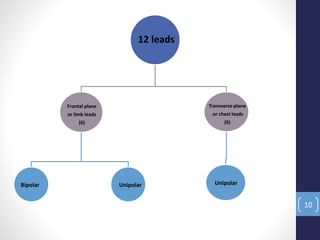
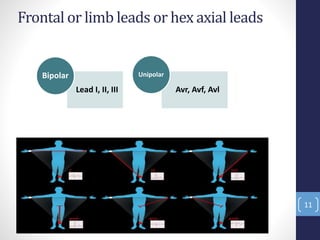
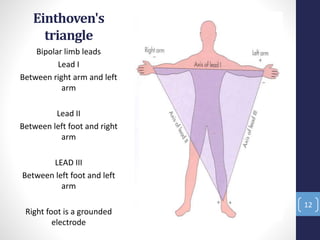
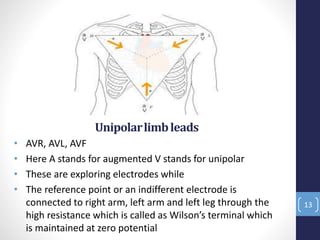
The document discusses an electrocardiogram (ECG), which is a graphic recording of the electrical activity of the heart. An ECG is obtained by placing electrodes on the body surface to record voltage differences generated by the heart. It can provide information about the heart's anatomy, chambers, rhythm, conduction, ischemia, and myocardial infarction. The document outlines some key terminologies used in ECG recording, including electrodes, leads, the 12-lead system, and frontal or limb leads that record from different planes. It also notes some cases where a dentist may advise a patient to get an ECG done in their dental office.