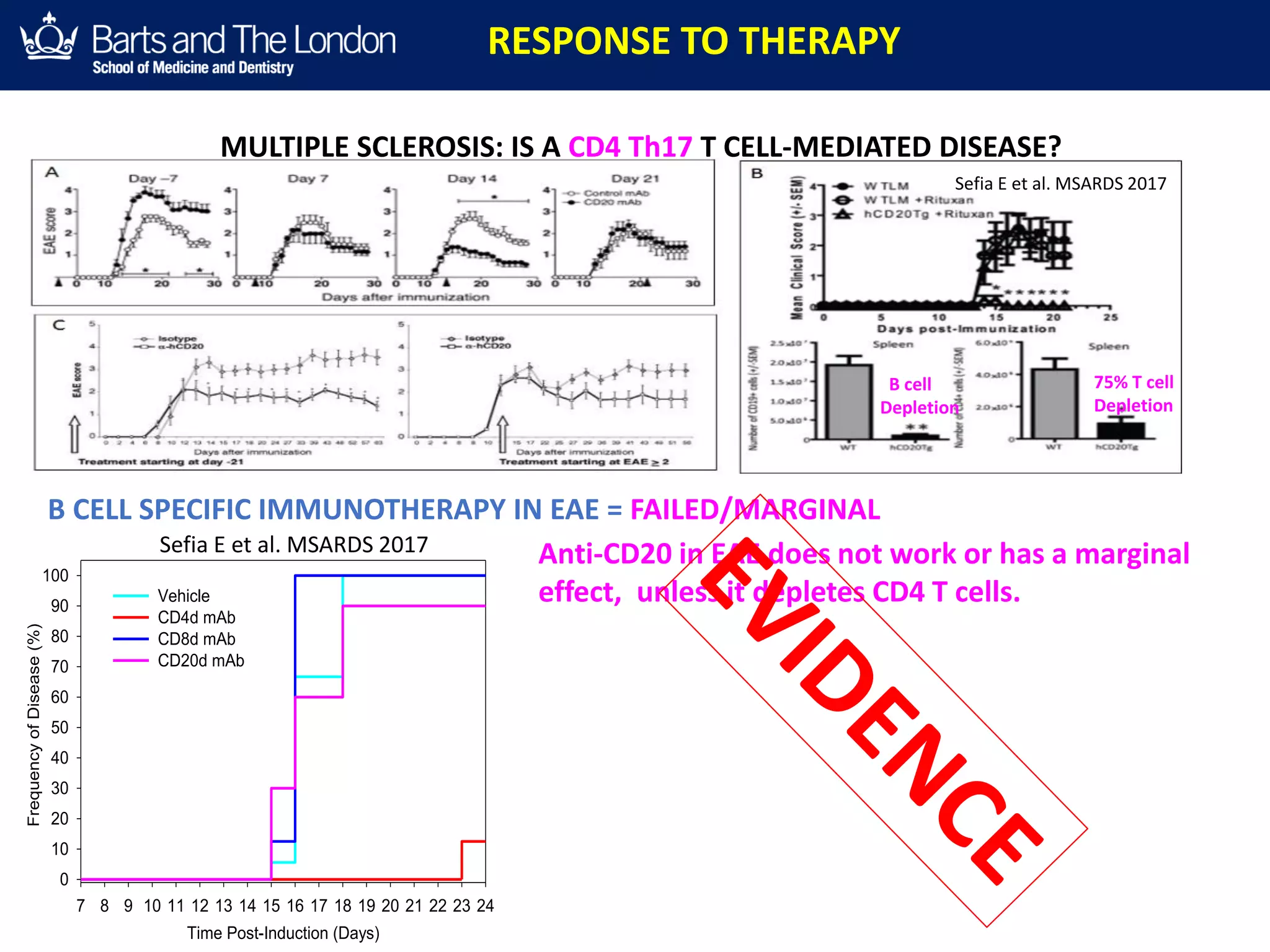
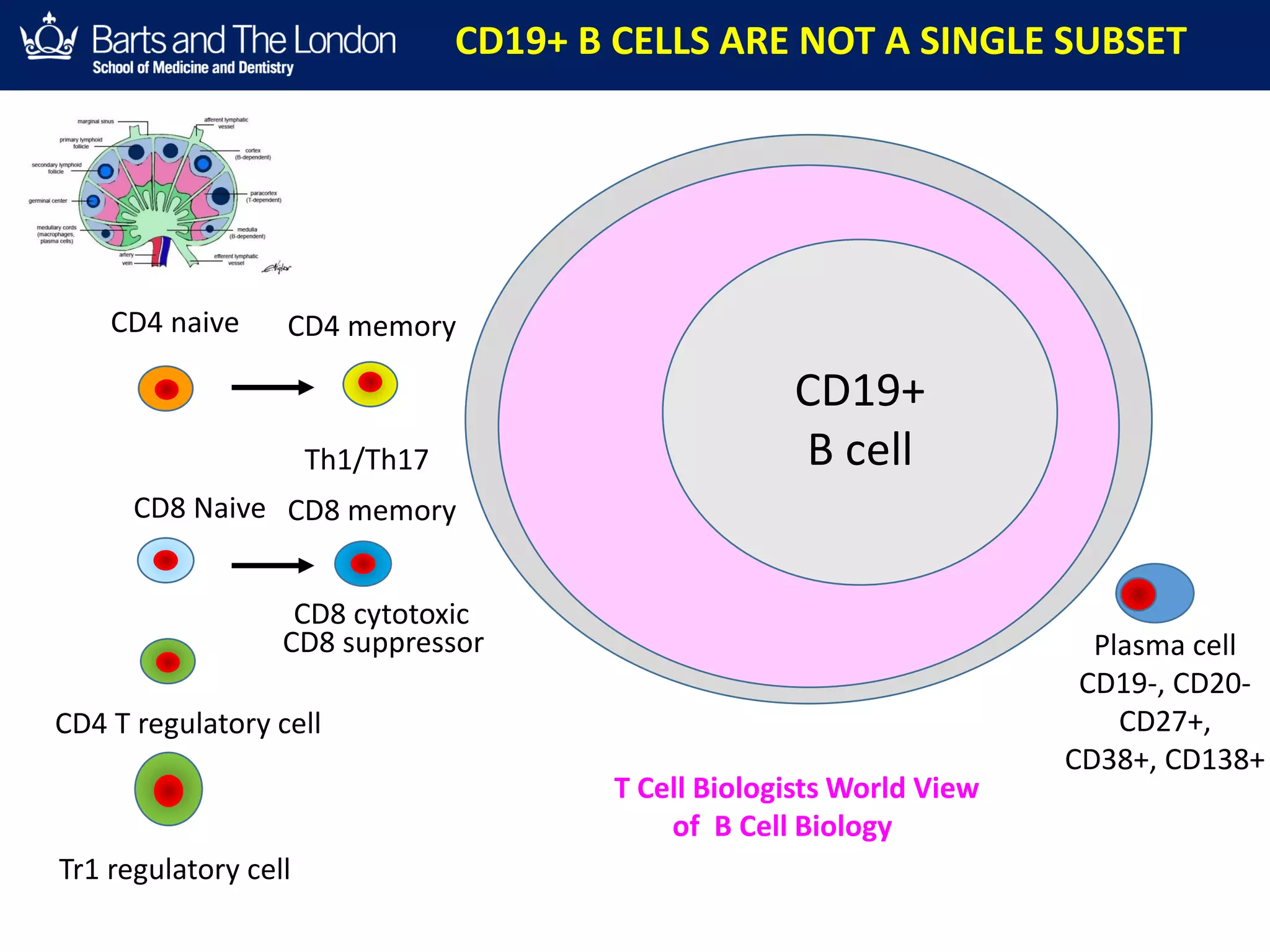
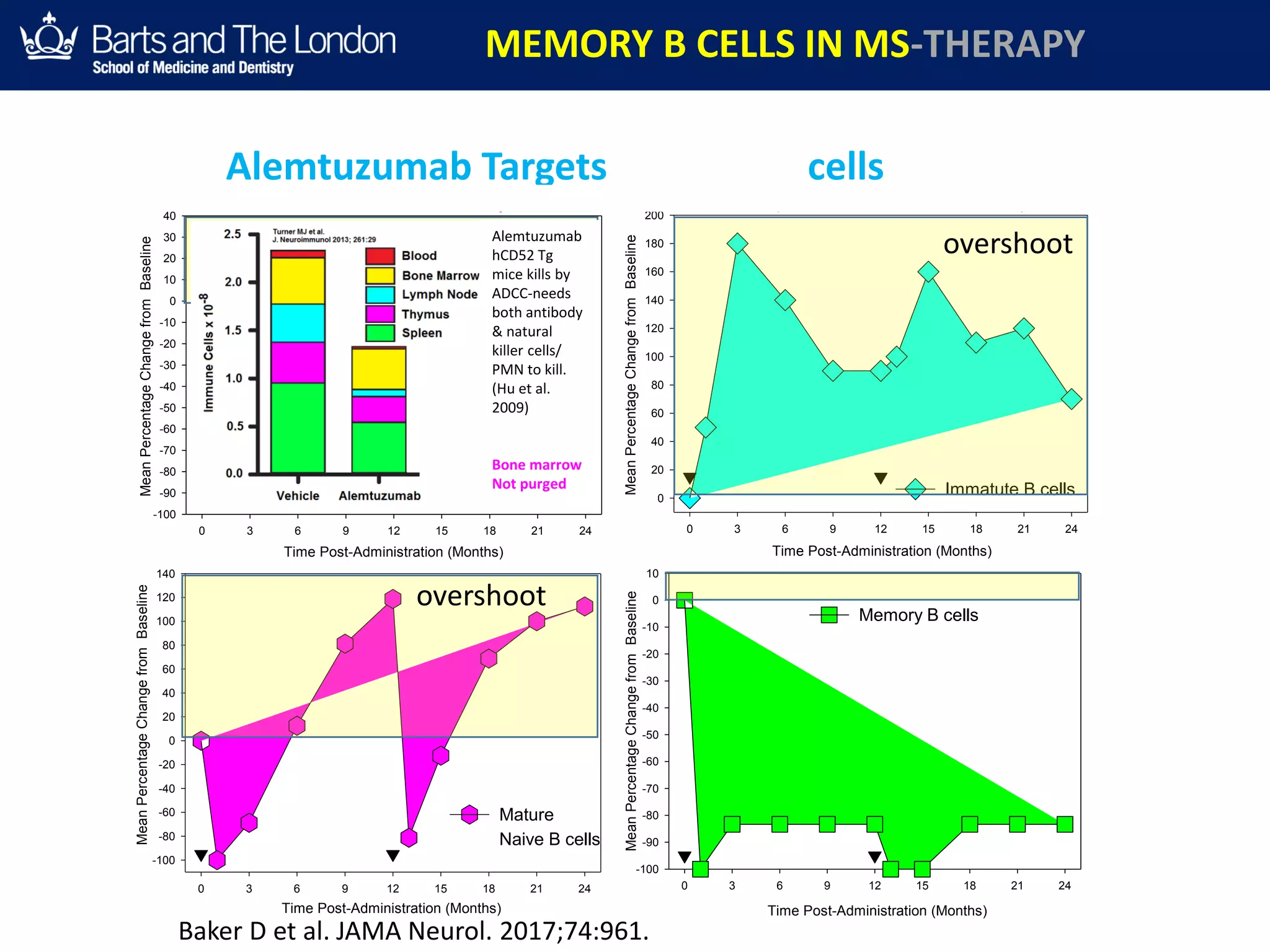
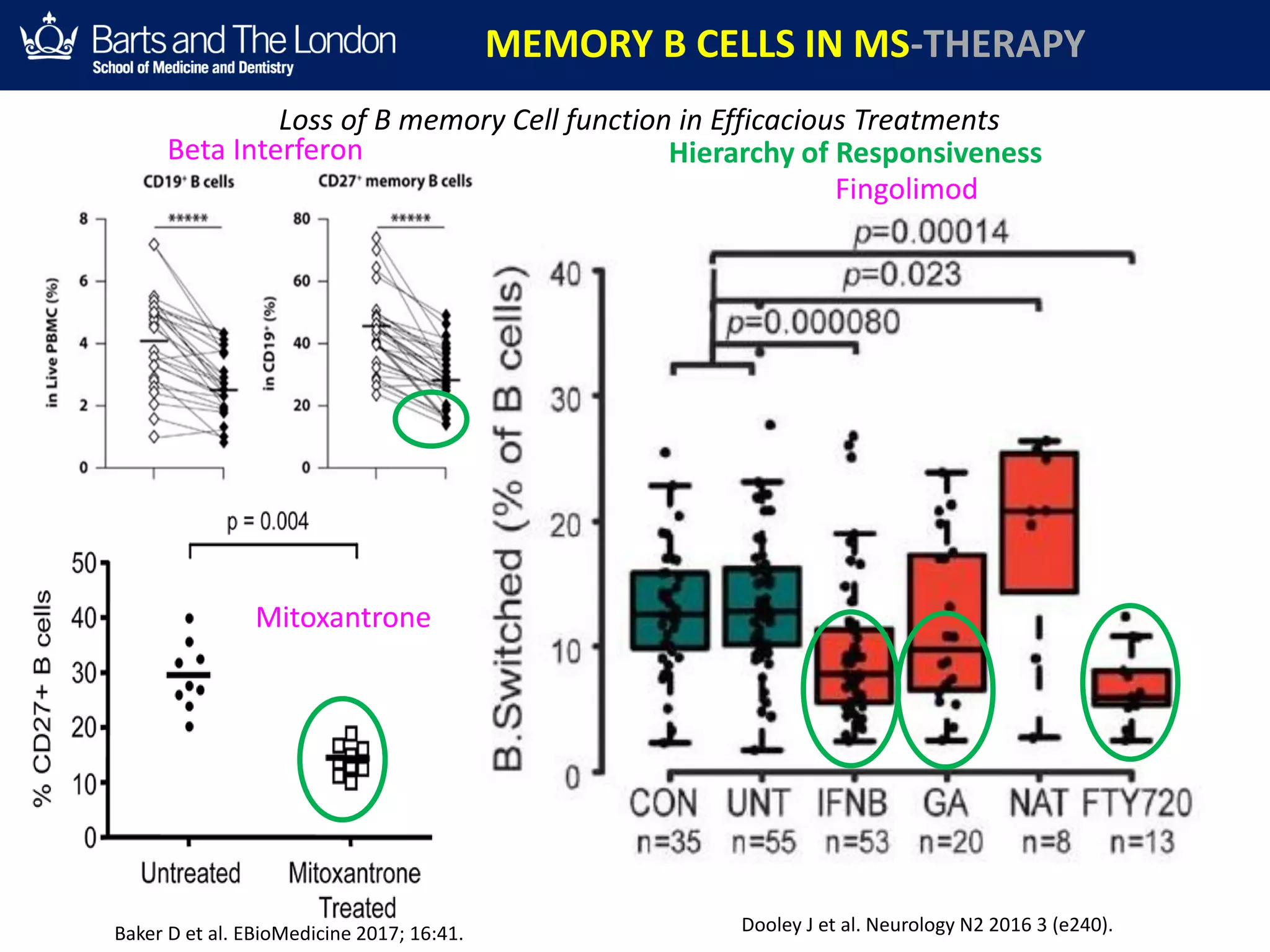
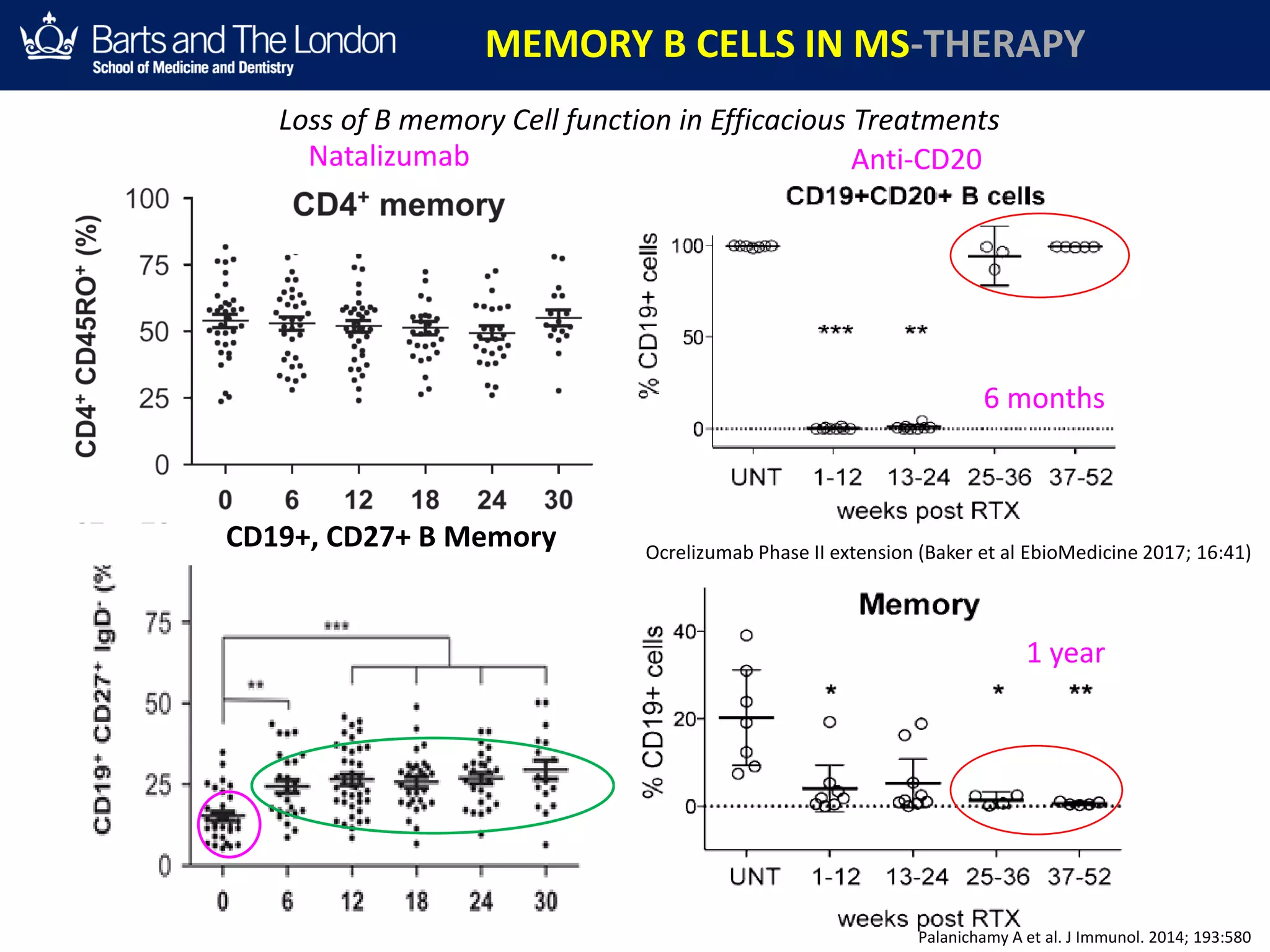
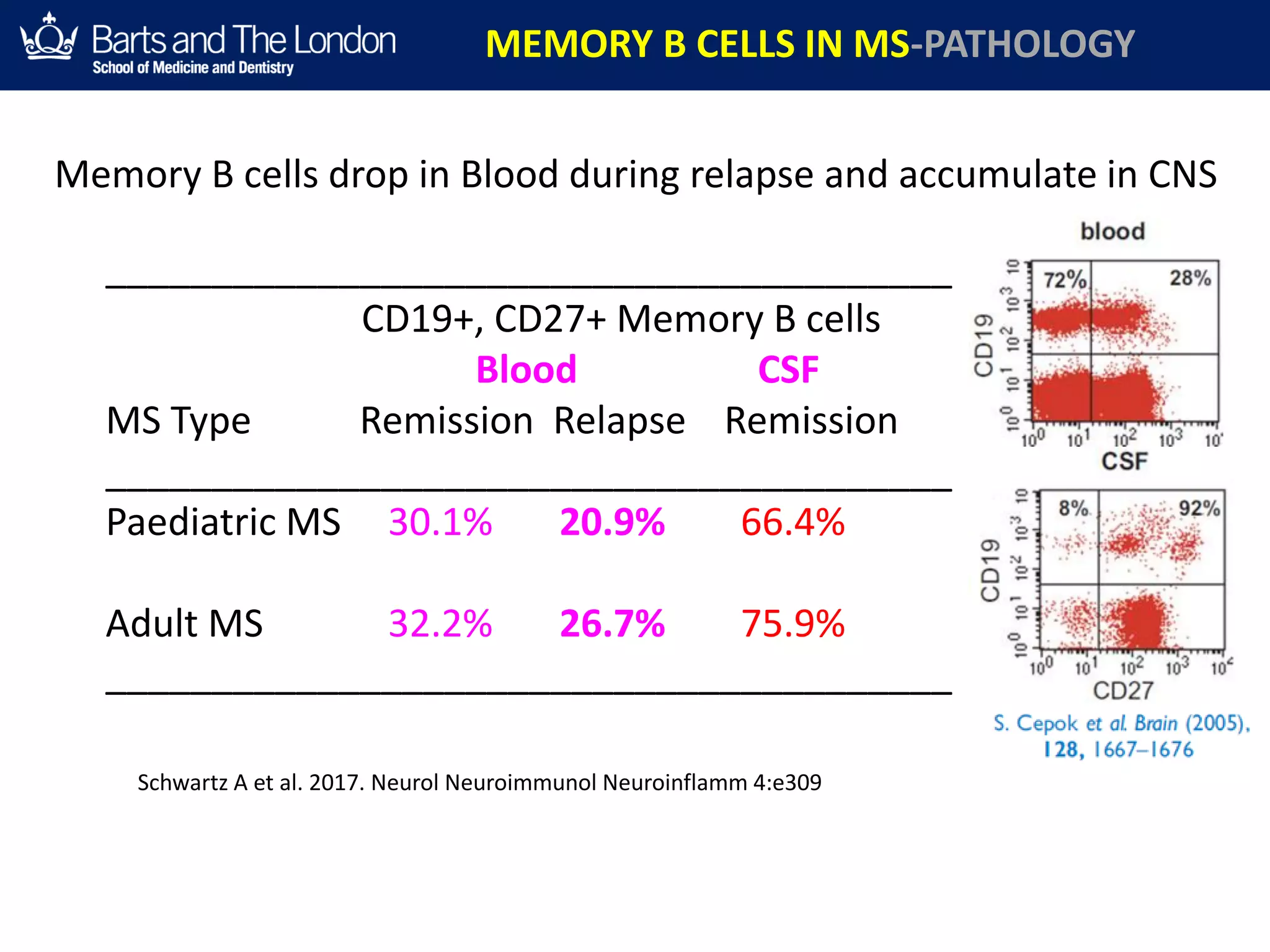
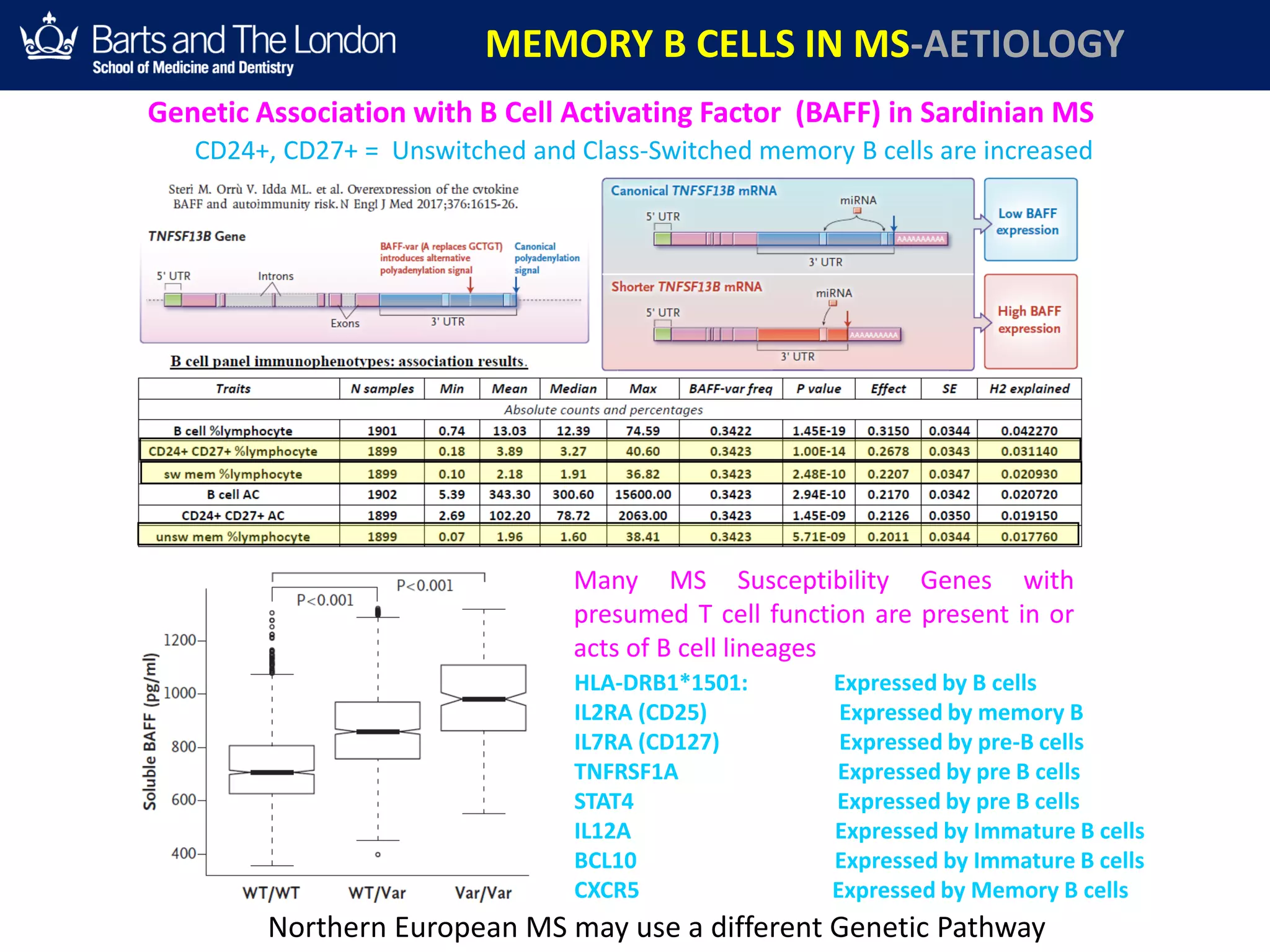
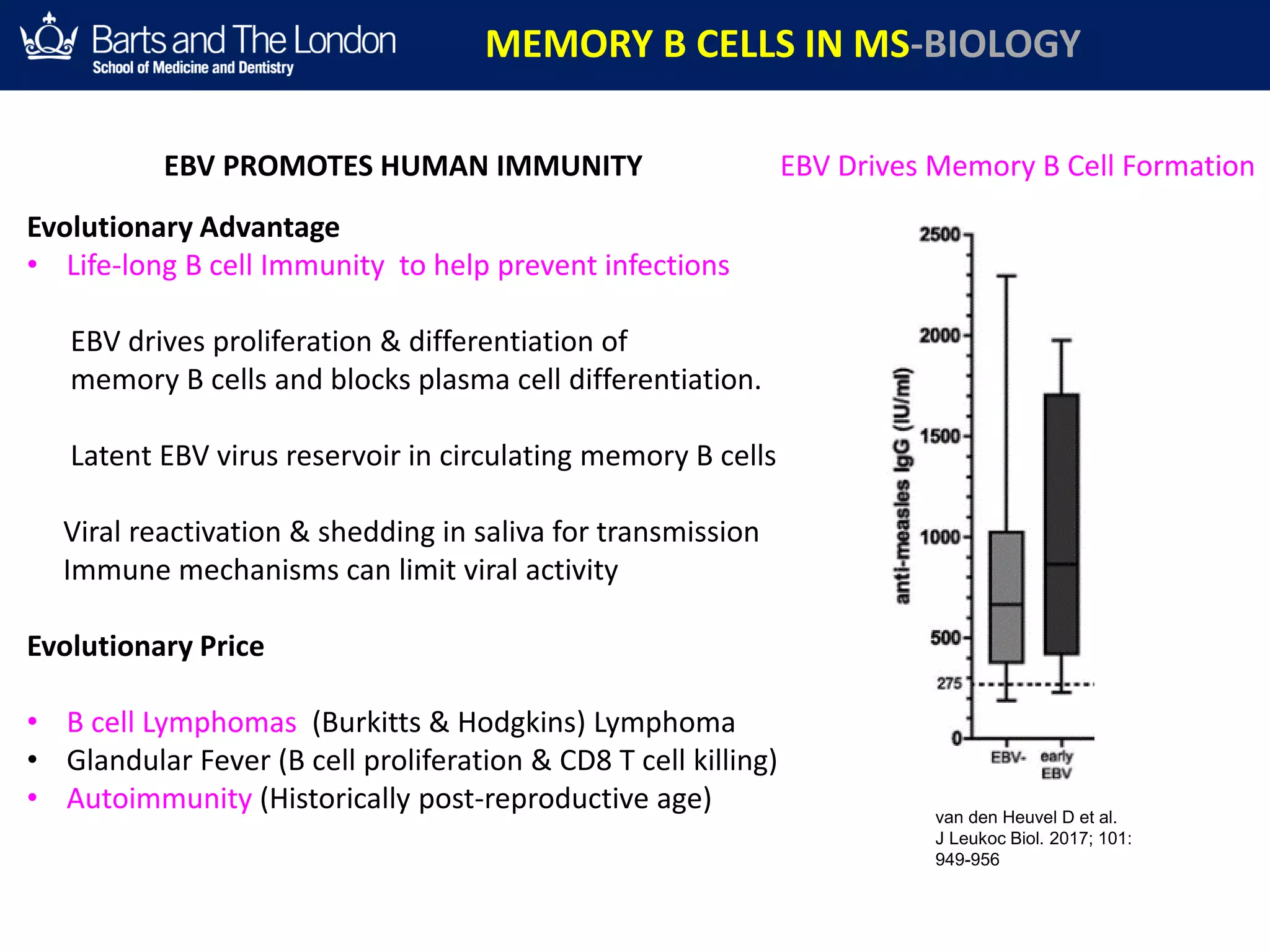
This document summarizes a debate about whether B cells or T cells are the key pathogenic cell in multiple sclerosis (MS). It provides evidence from MS therapies, animal models, and human data that memory B cells may drive MS pathology. Studies show that effective MS treatments like alemtuzumab, rituximab, and ocrelizumab strongly deplete memory B cells and reduce relapse rates. Memory B cell levels are also higher in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients during MS relapses. While T cells outnumber B cells in MS lesions, B cells may have an important role in antigen presentation and driving inflammation. Genetic studies also link MS risk genes to B cell functions. Overall, the document argues that