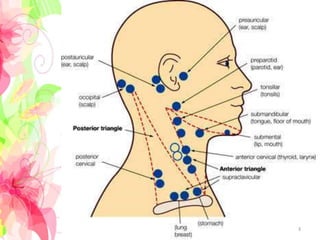
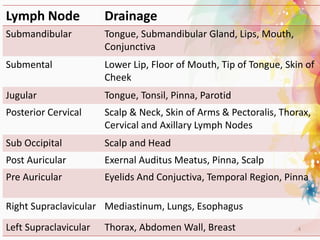
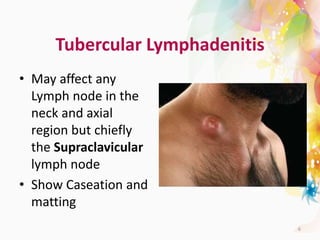
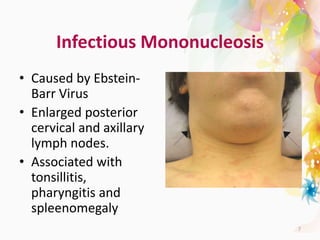
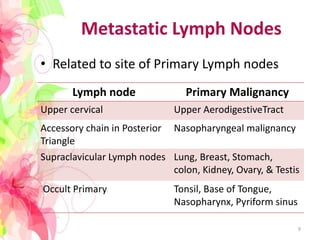
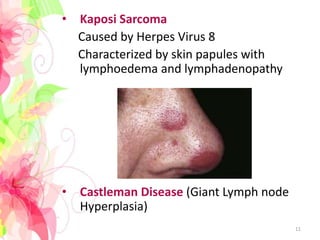
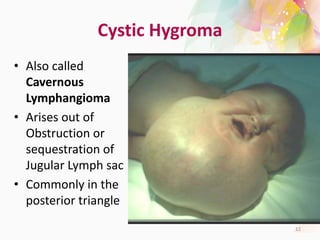
The document discusses the differential diagnosis of enlarged cervical lymph nodes, outlining various causes including infections, neoplasms, and other conditions. Key infections mentioned include bacterial, viral, and mycobacterial infections, while neoplastic conditions like lymphomas and metastatic lymph nodes are also highlighted. Moreover, it provides insights on diagnostic factors, treatment options, and specific diseases associated with lymph node enlargement.