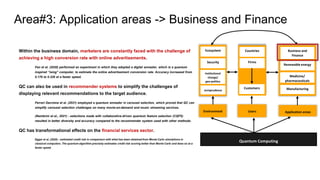
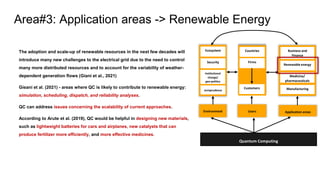
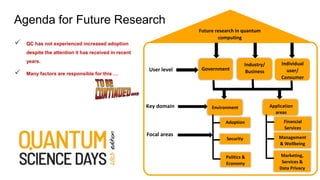
The document discusses a proposed framework for understanding quantum computing (QC) use cases from a multidisciplinary perspective, highlighting the potential impacts on areas such as the Internet of Things, cryptography, and finance. It outlines the critical need for an integrated approach that includes business, legal, and policy considerations, as current research predominantly focuses on technical facets of QC. The paper also emphasizes the importance of ecosystem collaboration and user adoption factors that will affect the widespread applicability and implementation of QC technologies.




![Things change as technological development becomes entangled with political power.
Data and Information security is crucial for both governments, their administrations,
such as ministries or subordinate federal authorities, social institutions, such as the
free market, as well as every individual market participant and, of course, every
individual citizen.
Central categories of politics, such as security, freedom, or economic activity, are
affected by these radical developments, where political science and economics speak
of institutional change [the concept developed by Nobel Prize winner Douglass C. North (1991)]
Geopolitics: QC is a central part of the Chinese power strategy, yet other countries
emphasize technological supremacy as a sign of power in the international arena
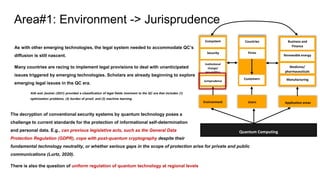
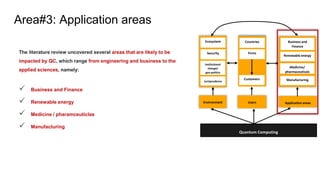
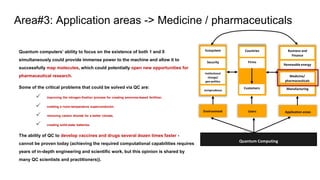
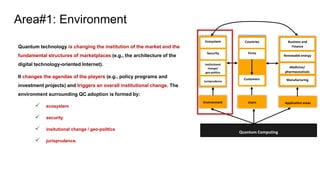
Area#1: Environment -> Institutional Change and geopolitics
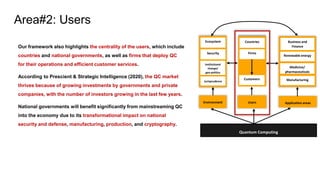
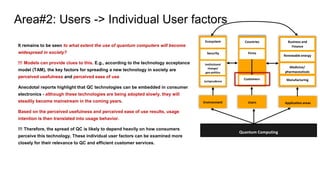
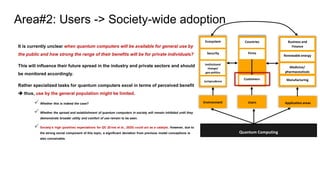
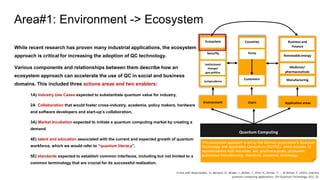
Environment Users Application areas
Quantum Computing
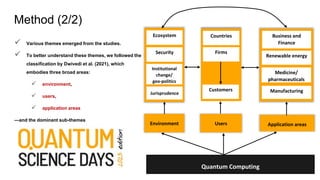
Ecosystem
Security
Institutional
change/
geo-politics
Jurisprudence
Countries
Firms
Customers
Business and
Finance
Renewable energy
Medicine/
pharmaceuticals
Manufacturing
“the key question in the global contest of QC, quantum technology, and artificial intelligence [AI] is whether a technocracy with (e.g., Chinese) state
capitalism and Confucian ethics will prevail over Western market economics and democracy, in which quantum technology and AI systems are
understood as a service of individual liberties" (Mainzer, 2020, p. 236).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qworld2023an-230530155043-b8159a70/85/Framework-for-understanding-quantum-computing-use-cases-from-a-multidisciplinary-perspective-and-future-research-directions-8-320.jpg)