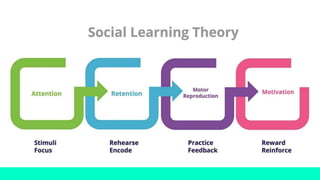
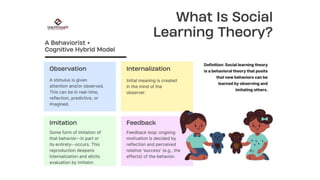
Bandura's social learning theory posits that personality and behavior are shaped by observing and imitating others. According to the theory, we learn new behaviors by watching significant others or role models, and imitating their actions, especially if reinforcement is present. The process of observational learning involves paying attention to a model, retaining what is observed, reproducing the behavior physically, and being motivated to imitate the model. Bandura's theory suggests that personality develops through social interaction and environmental influences rather than innate traits.









![EYE ON THE EXAM
1. Using practical examples
and referring to
Bandura's model, explain
the process of
observational learning
when it is used for
acquiring movement
skills. Discuss the
factors that affect
successful modeling when
learning motor skills in
sport[10]
Complete the answers on a
Google sheet and hand in
for marking.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-231004143750-db34a547/85/3-Bandura-s-social-learning-_-observational-learning-theory-pptx-12-320.jpg)