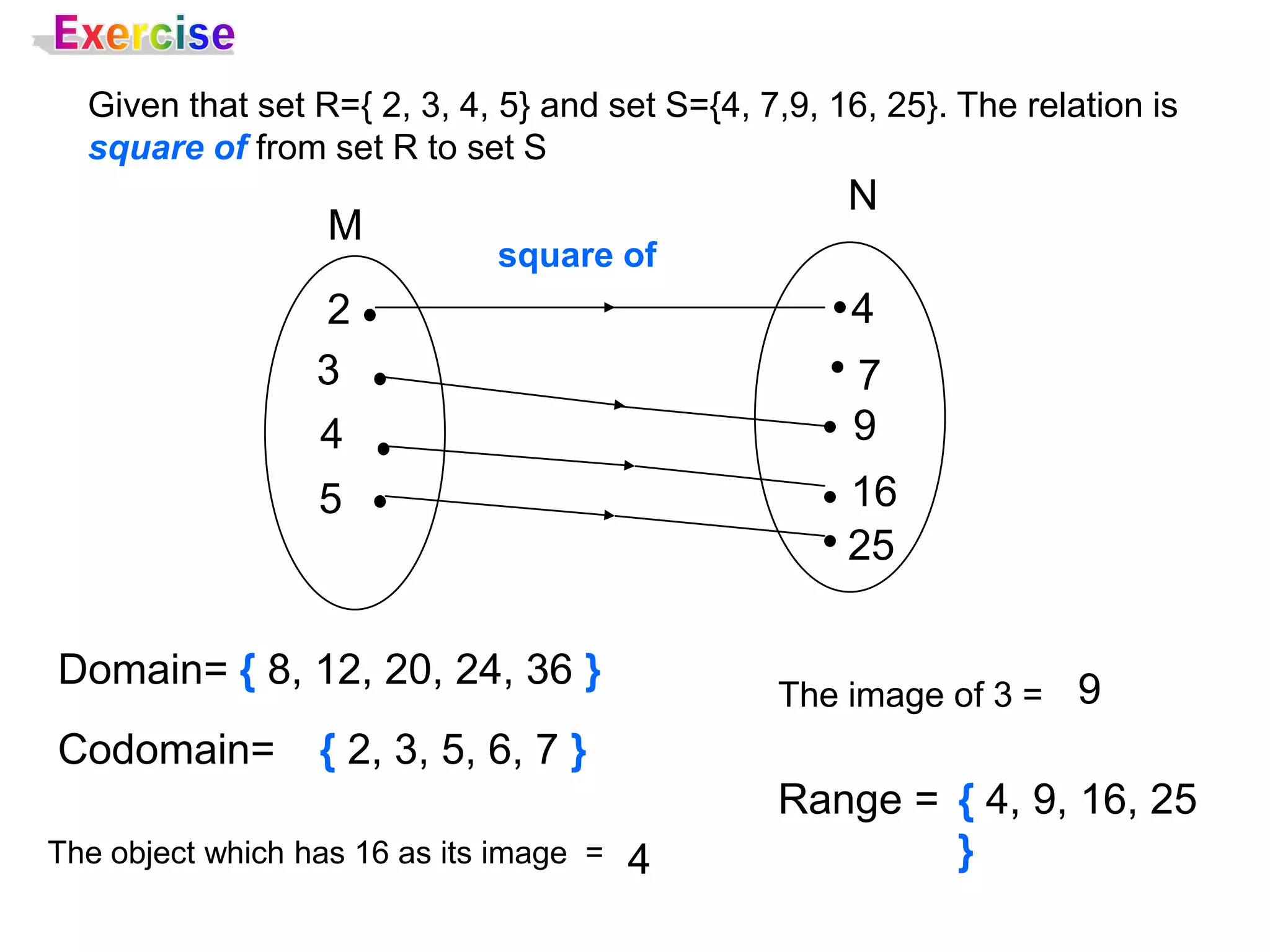
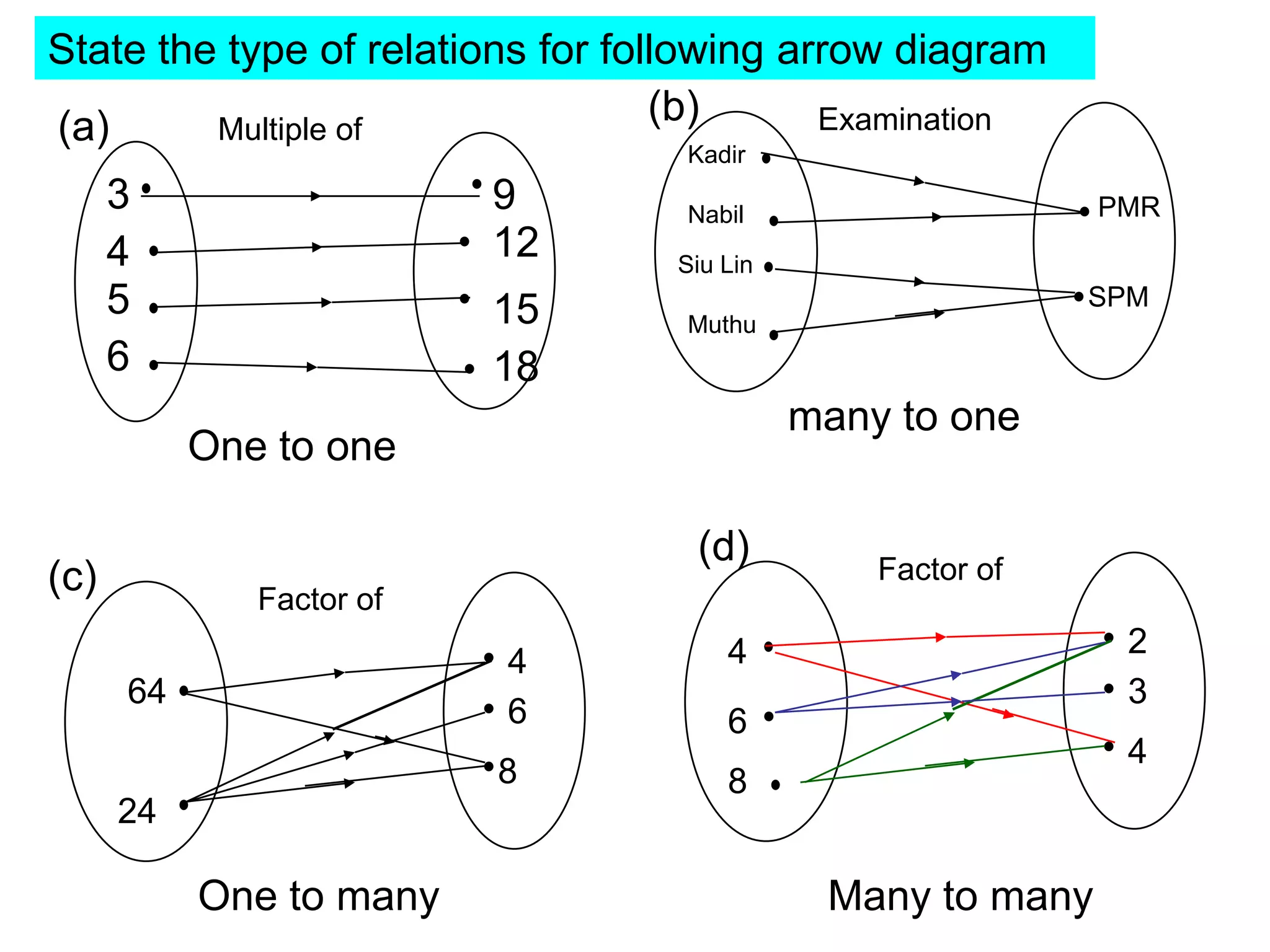
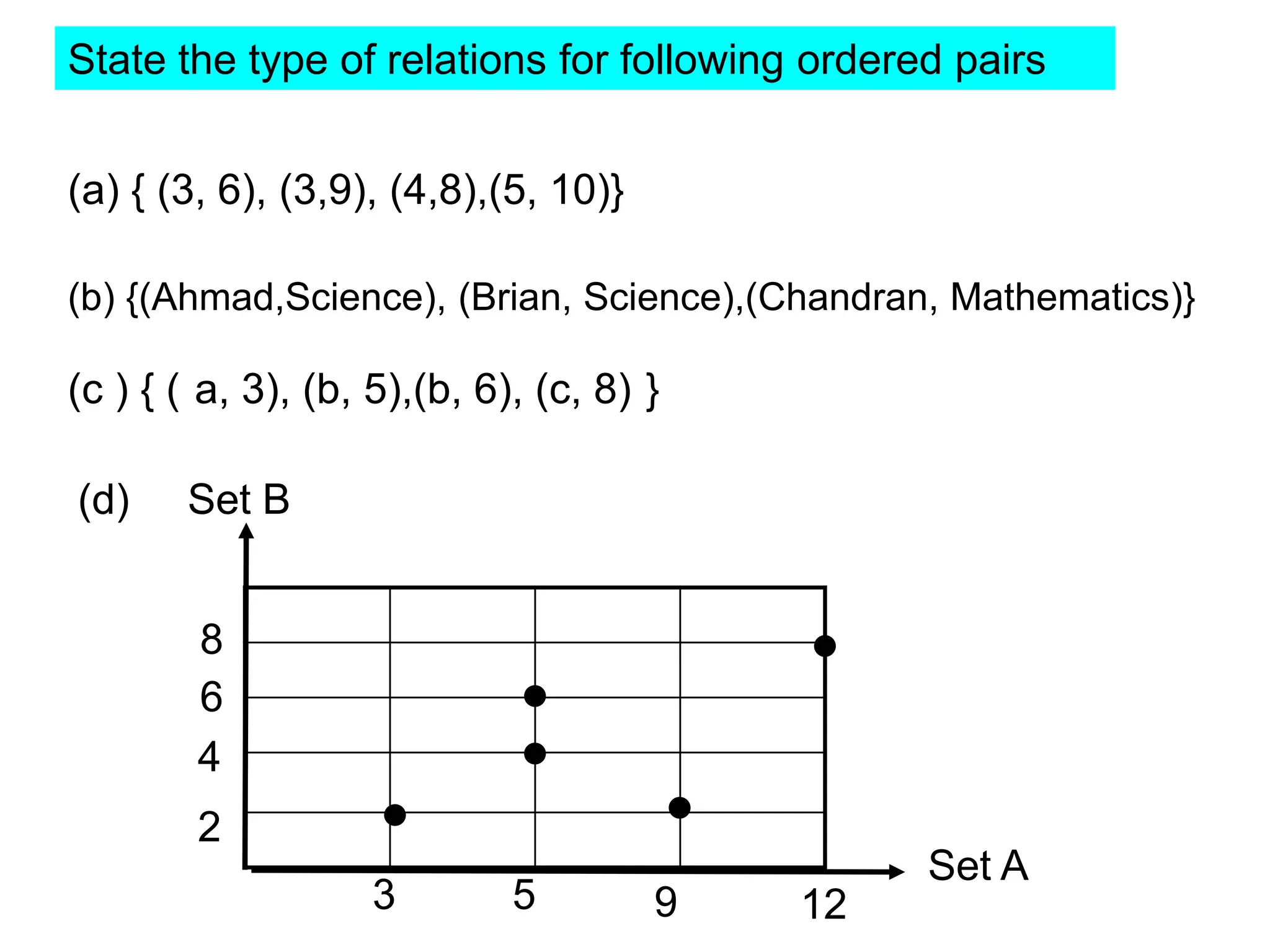
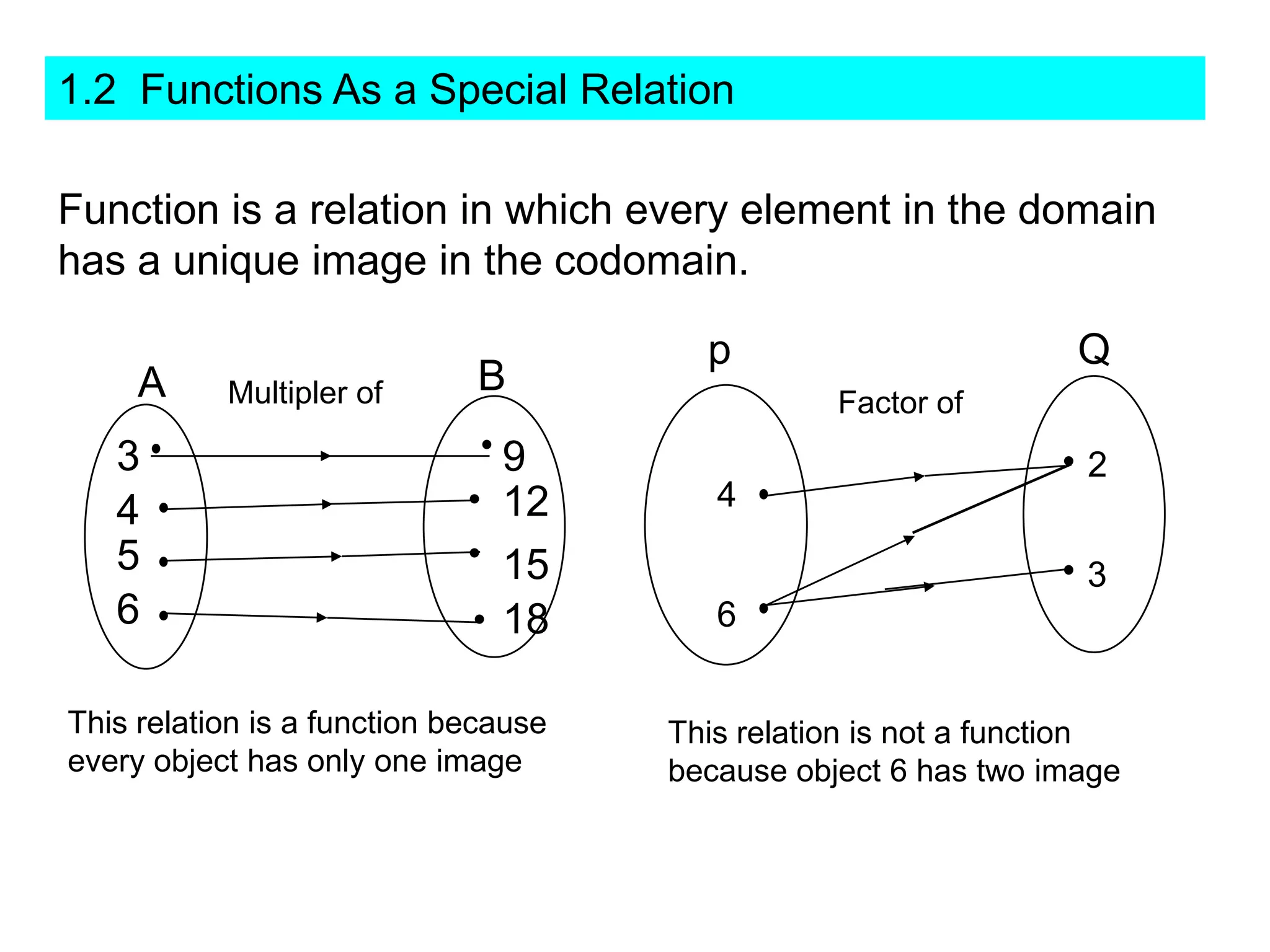
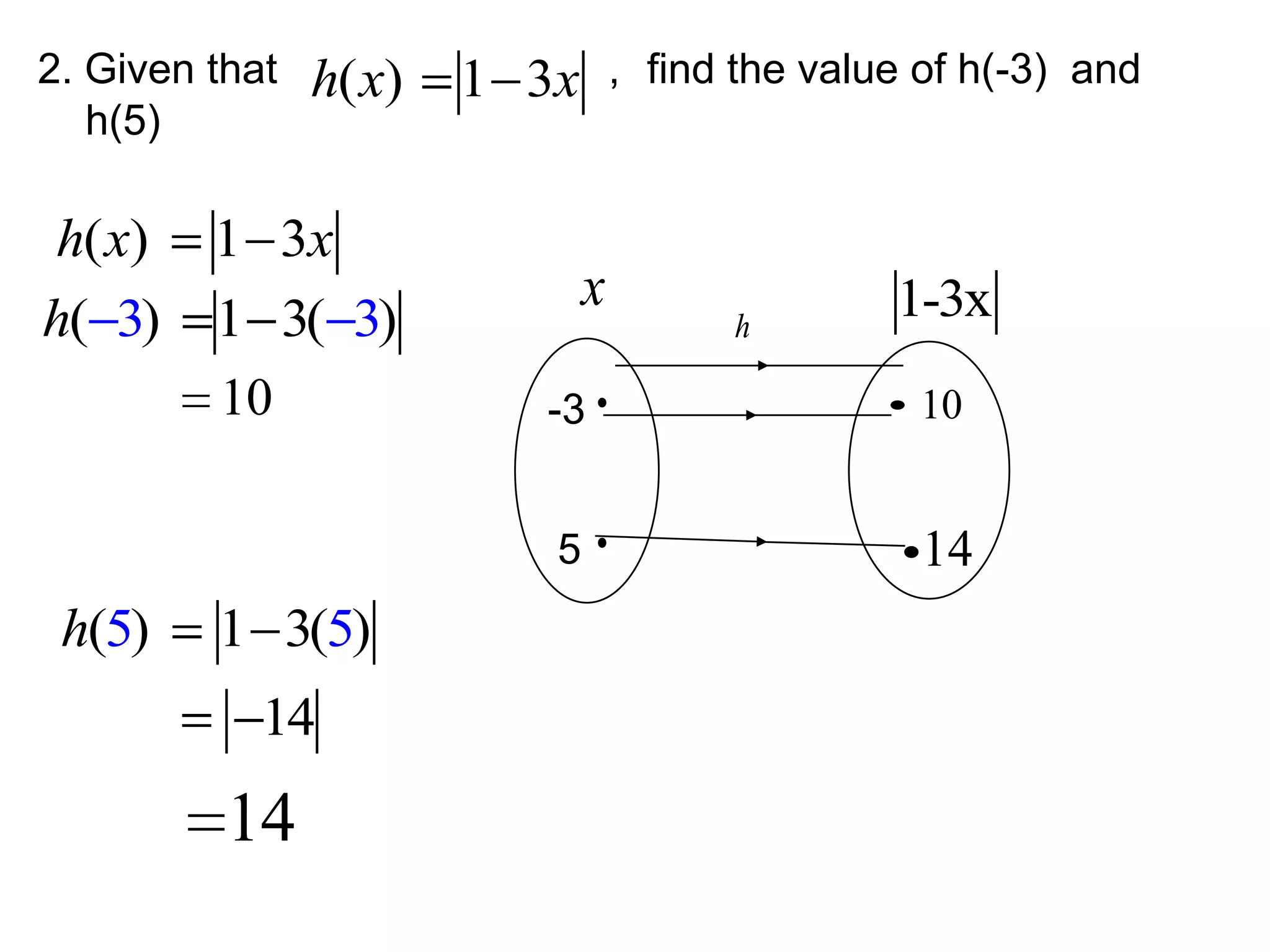
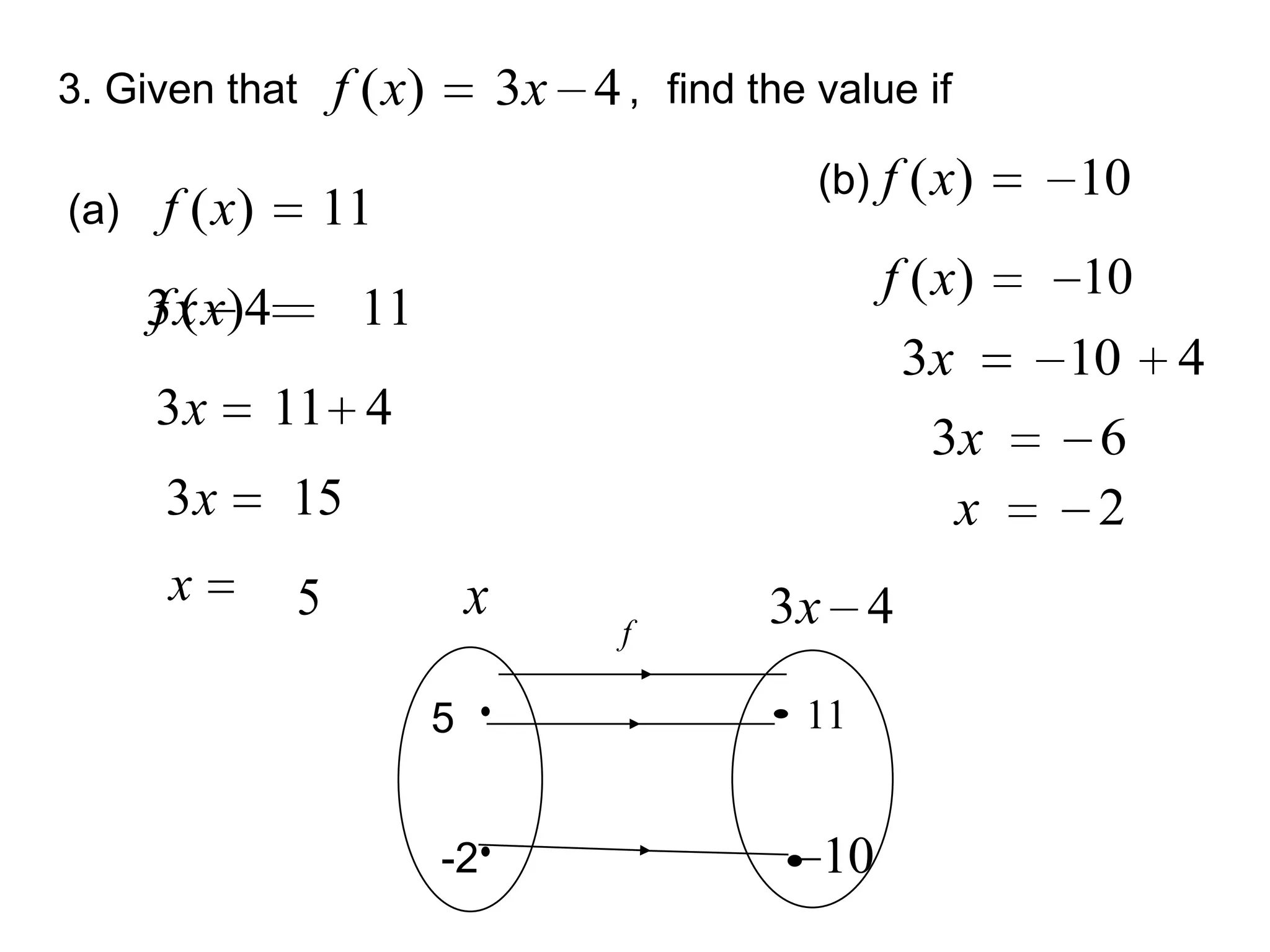
(1) The functions f and g are given as:
f(x) = x + 1
fg(x) = x^2 + 2x - 4
(2) The functions f and g are given as:
f(x) = x^2 - 5
gf(x) = 2x^2 - 9
(3) The question asks to find the function g such that the composite functions equal the given functions.







![Composite Functions
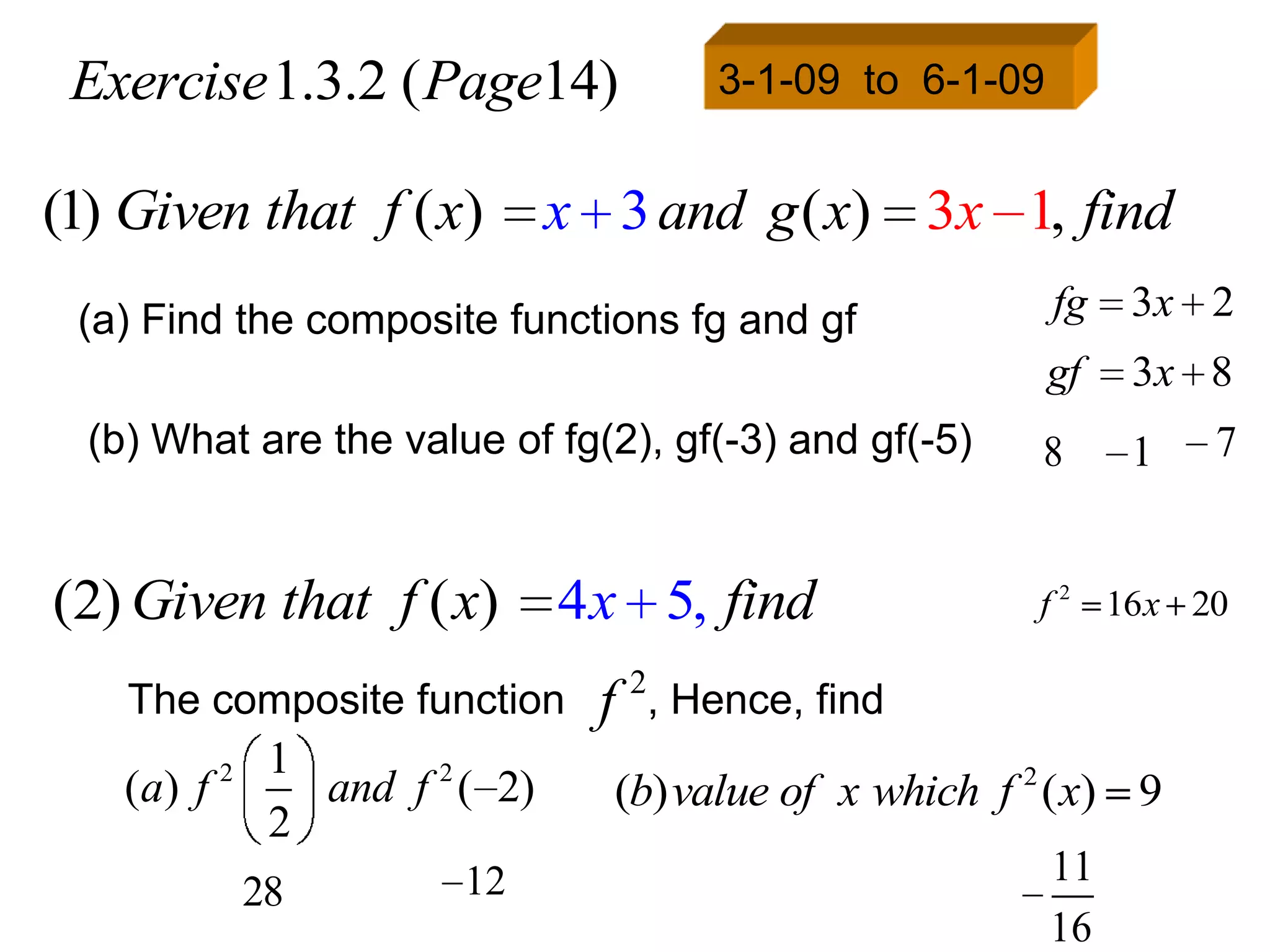
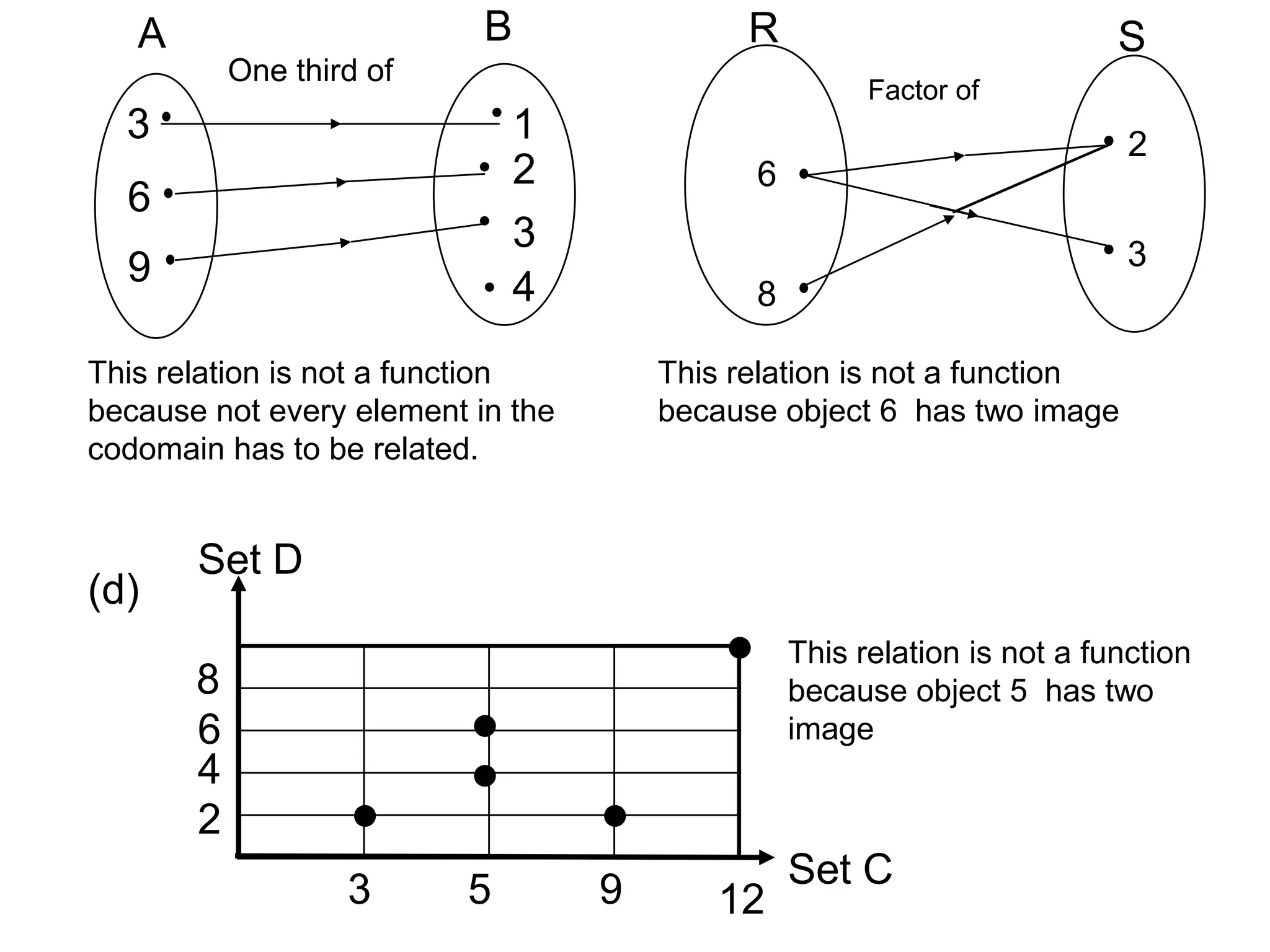
Given that f ( x) x 3 and g ( x) 2 x 1, find
(a) fg
fg f [ g ( x)]
f [ g ( x)] x
g ( x) 3
f(2 x( x1])
g ) 2x 1 3
2x 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functions-101208210331-phpapp02/75/Functions-29-2048.jpg)
![Composite Functions
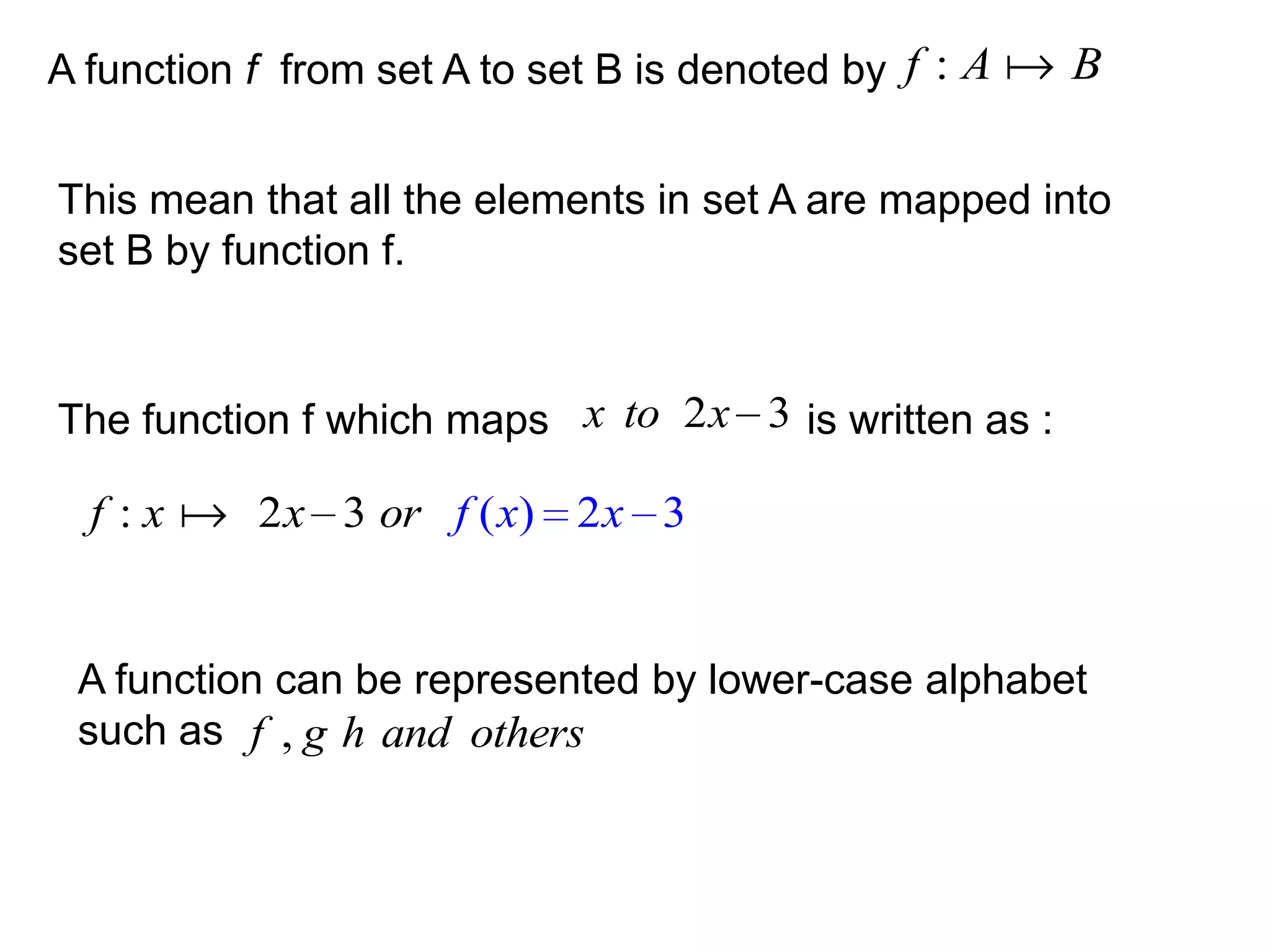
Given that f ( x) x 3 and g ( x) 2 x 1, find
(a) gf
gf g[ f ( x)]
g [ f ( x)] 2 x 1
(x
[ f 3) 2x 3) 1
g ( x ( x)]
2x 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functions-101208210331-phpapp02/75/Functions-30-2048.jpg)
![Composite Functions
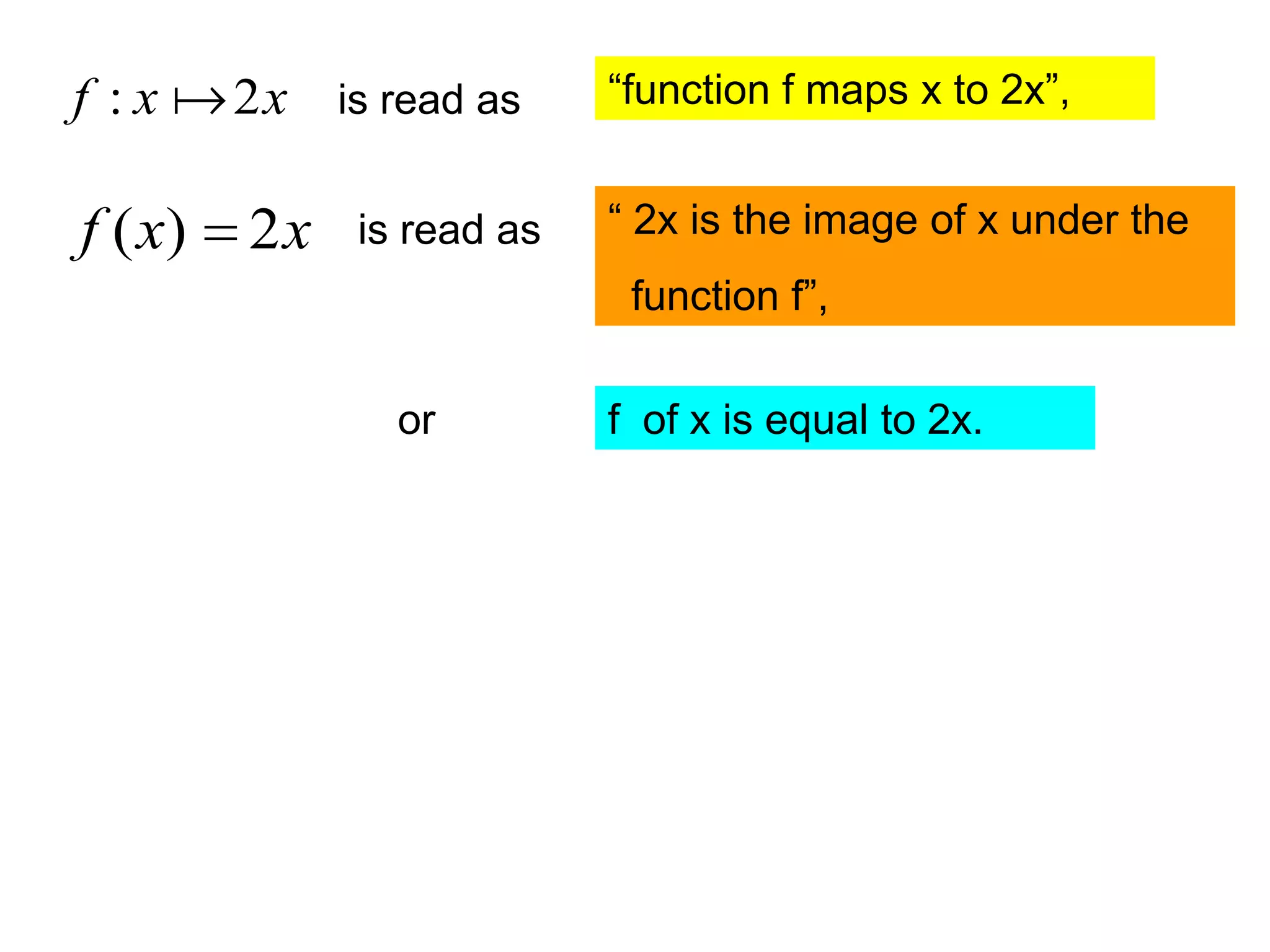
Given that f ( x) x 3 and g ( x) 2 x 1, find
(a) f 2 (b) f 4
f 2
f f f 4
f 2f 2
2 2
f [ f ( x)] f [ f ( x)]
2
f ( x 3) f ( x 6)
xx 3 3 xx 6 6
2 4
f x 6 f x 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functions-101208210331-phpapp02/75/Functions-31-2048.jpg)
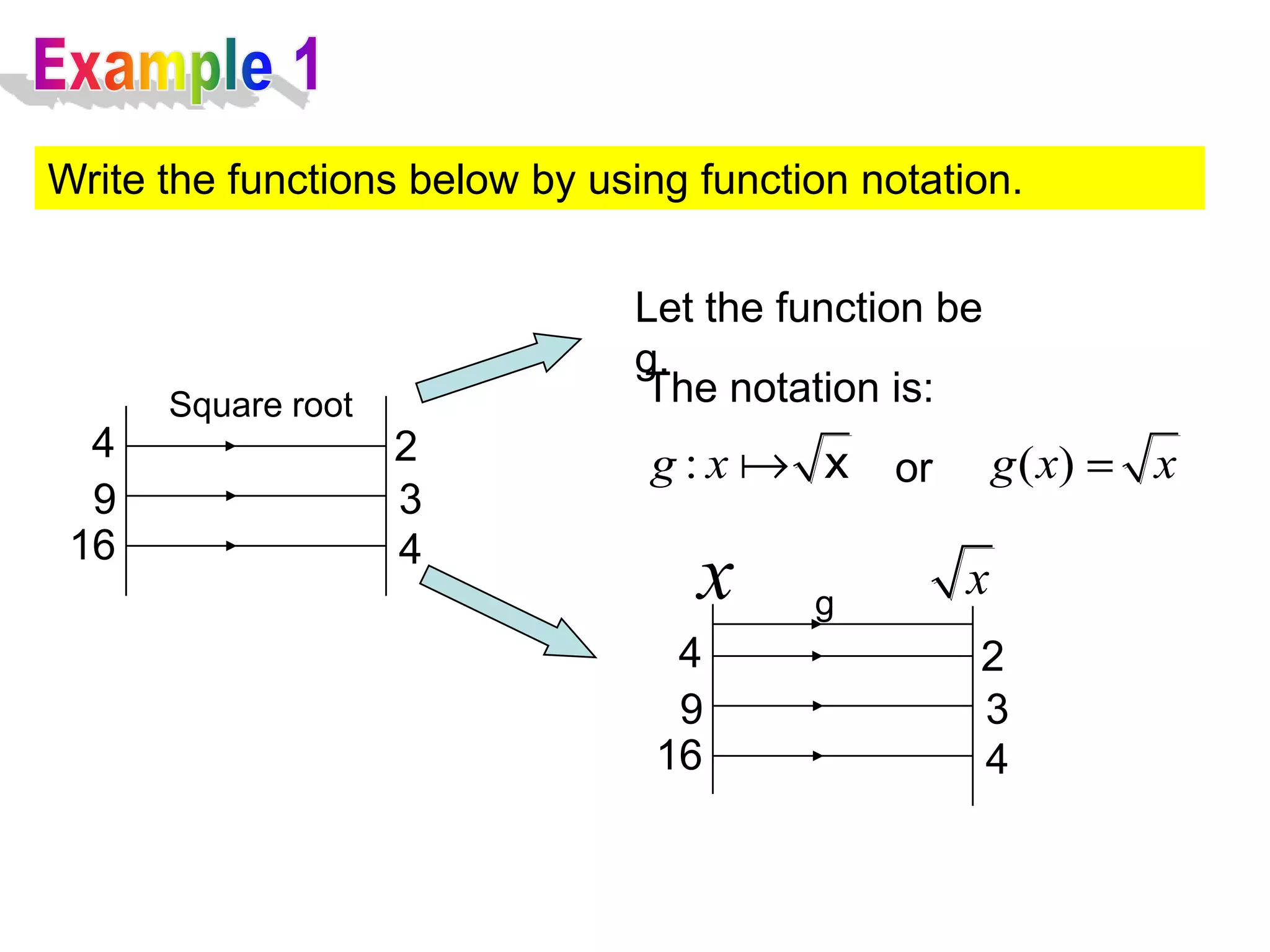
![Given that f ( x) 2 x and g ( x) 3 2 x, find
(a) fg (2) (b) gf ( 2)
fg ( x) f [ g ( x)] gf ( x) g[ f ( x)]
f (3 2 x) g ( 2 x)
x
2 (3 2x)
3 2 x)
(2 x
fg ( x) 6 4x gf ( x) 3 4x
fg (2) 6 4(2) gf ( 2) 3 4( 2)
2 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functions-101208210331-phpapp02/75/Functions-32-2048.jpg)
![Determine one of the Functions when the Composite
Function and Other Function are Given
A function f is defined by . Find the function g
f :xx 1
in each of the following
(a) fg : x 2x 2
3 (b) gf : x2 3x 5
2
2
g[ f ( x)] x 3x 5
f [ g ( x)] 2x 3
Let y x 1
2
g (x ) 1
x 2x 3 x y 1
2 g ( y) ( y 1)2 3( y 1) 5
g ( x) 2x 2
g ( y) y2 2 y 1 3y 3 5
g ( y) y2 y 3
g ( x) x2 x 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functions-101208210331-phpapp02/75/Functions-33-2048.jpg)