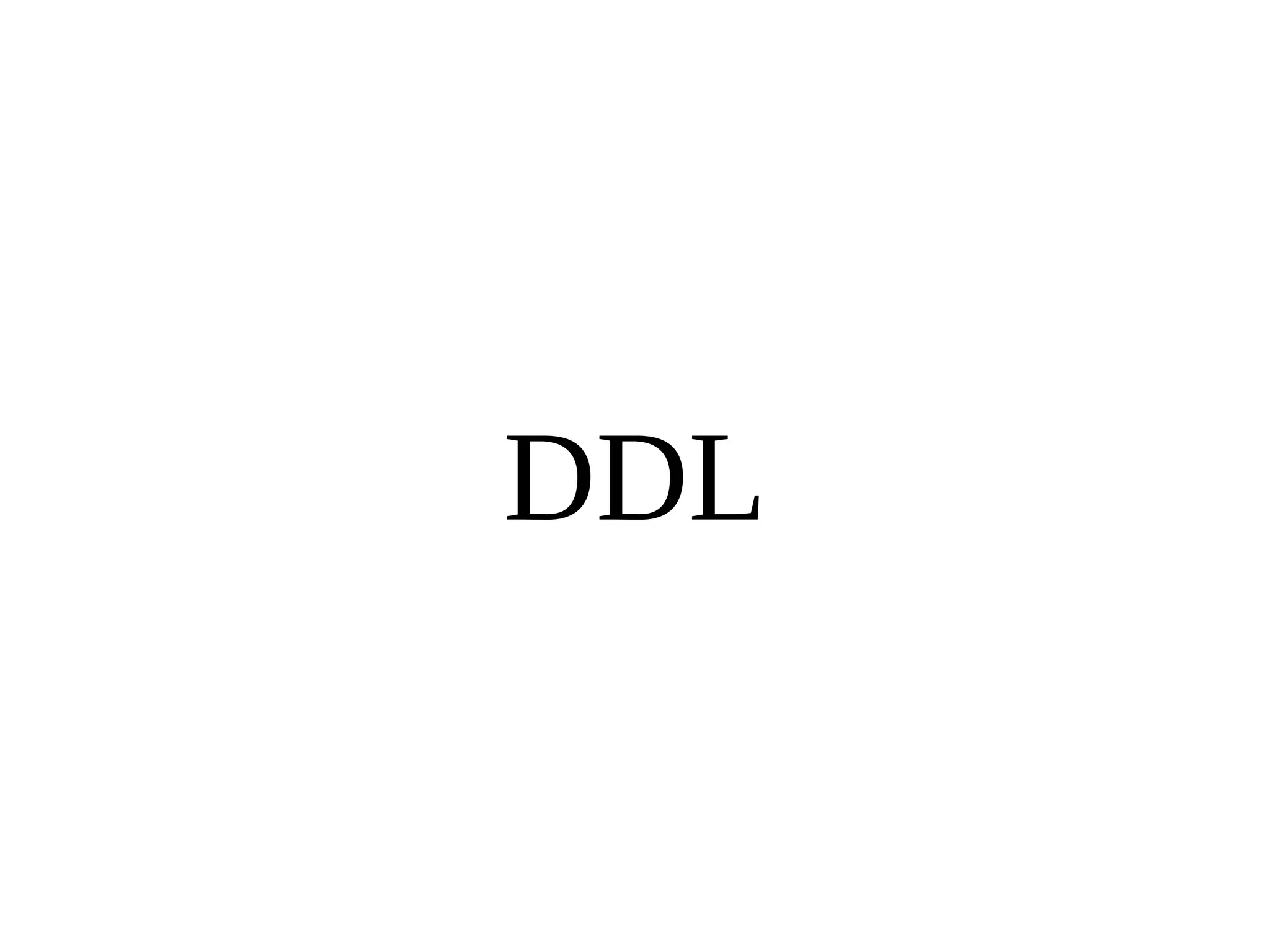
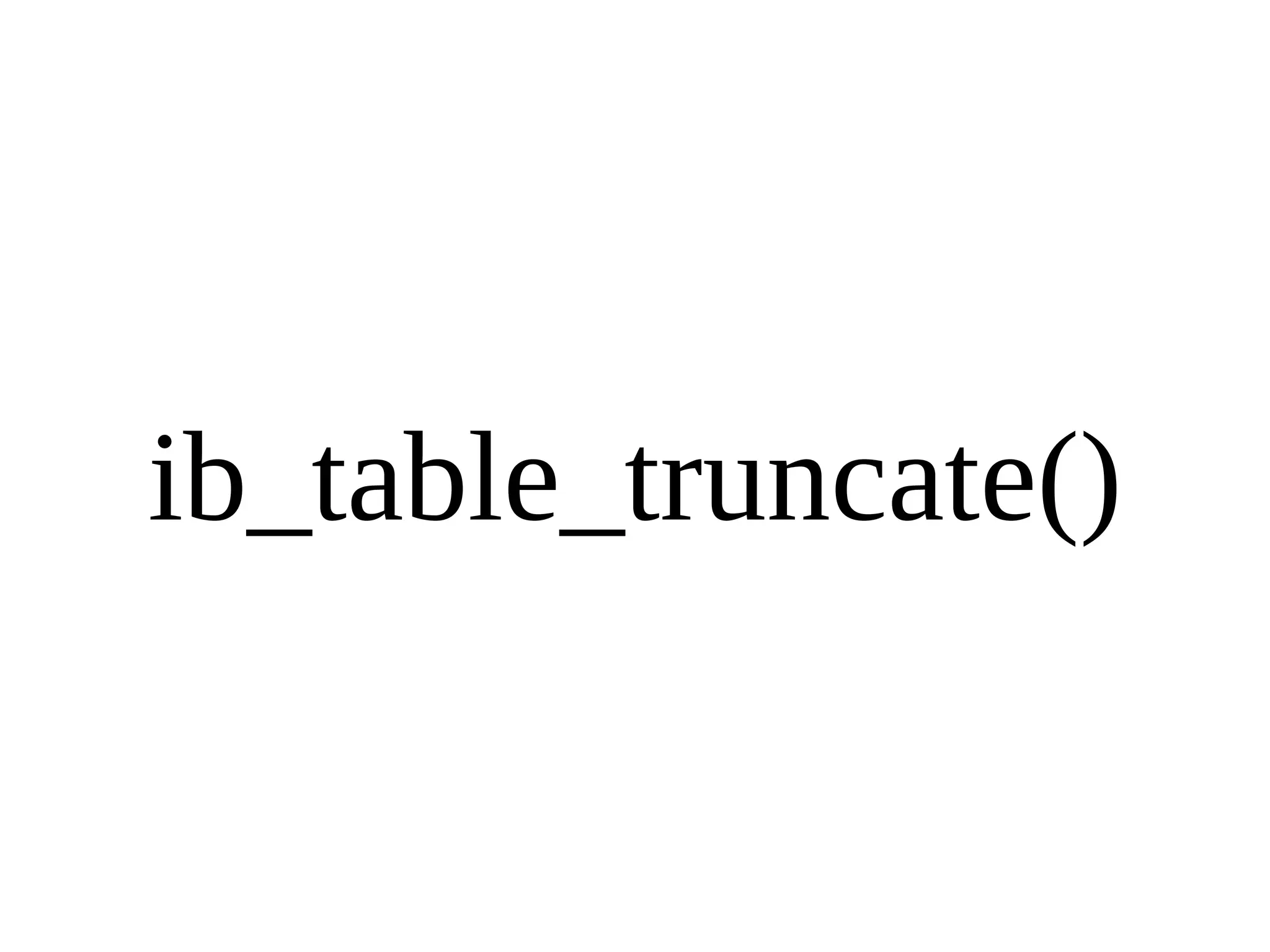
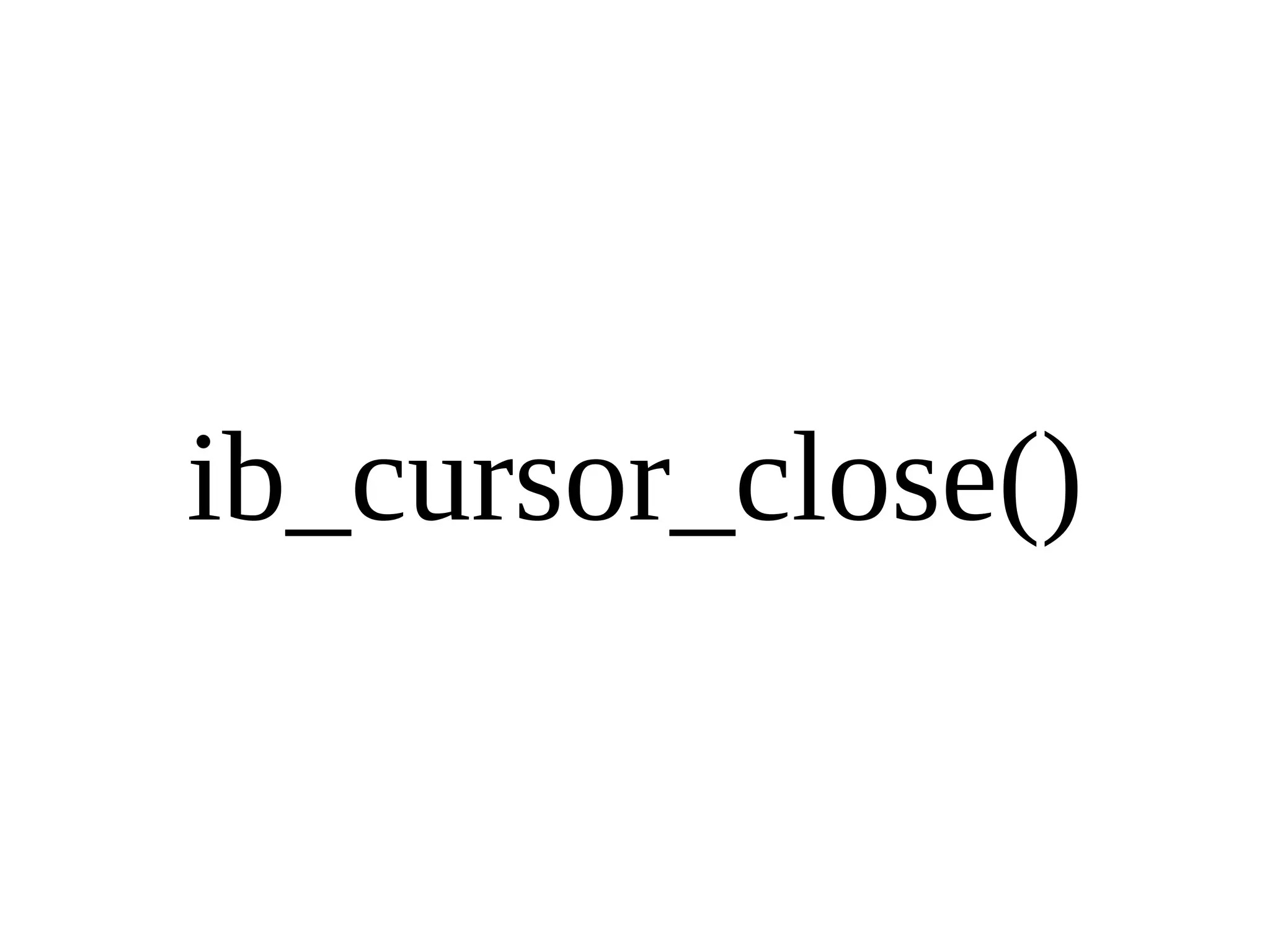
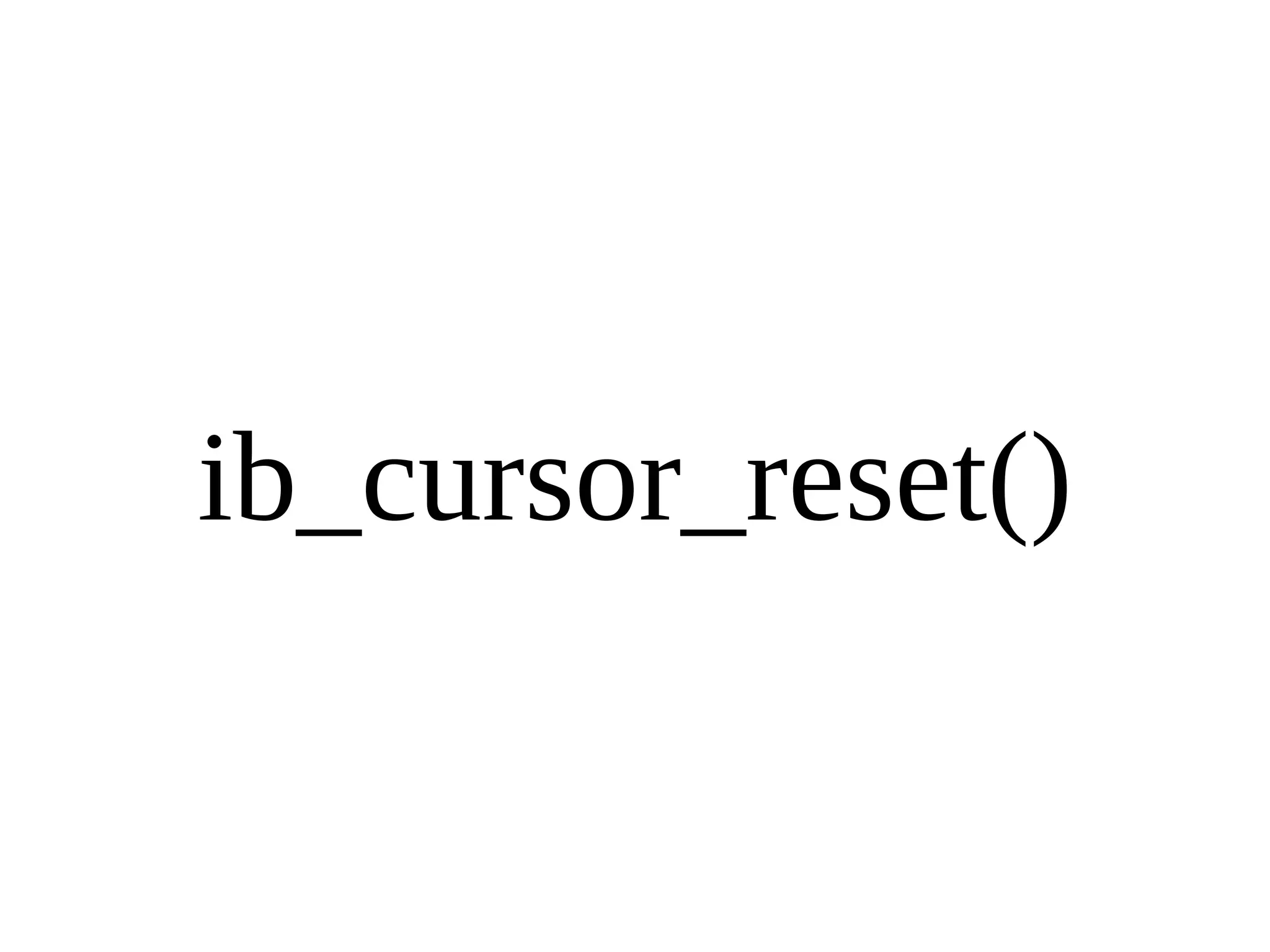
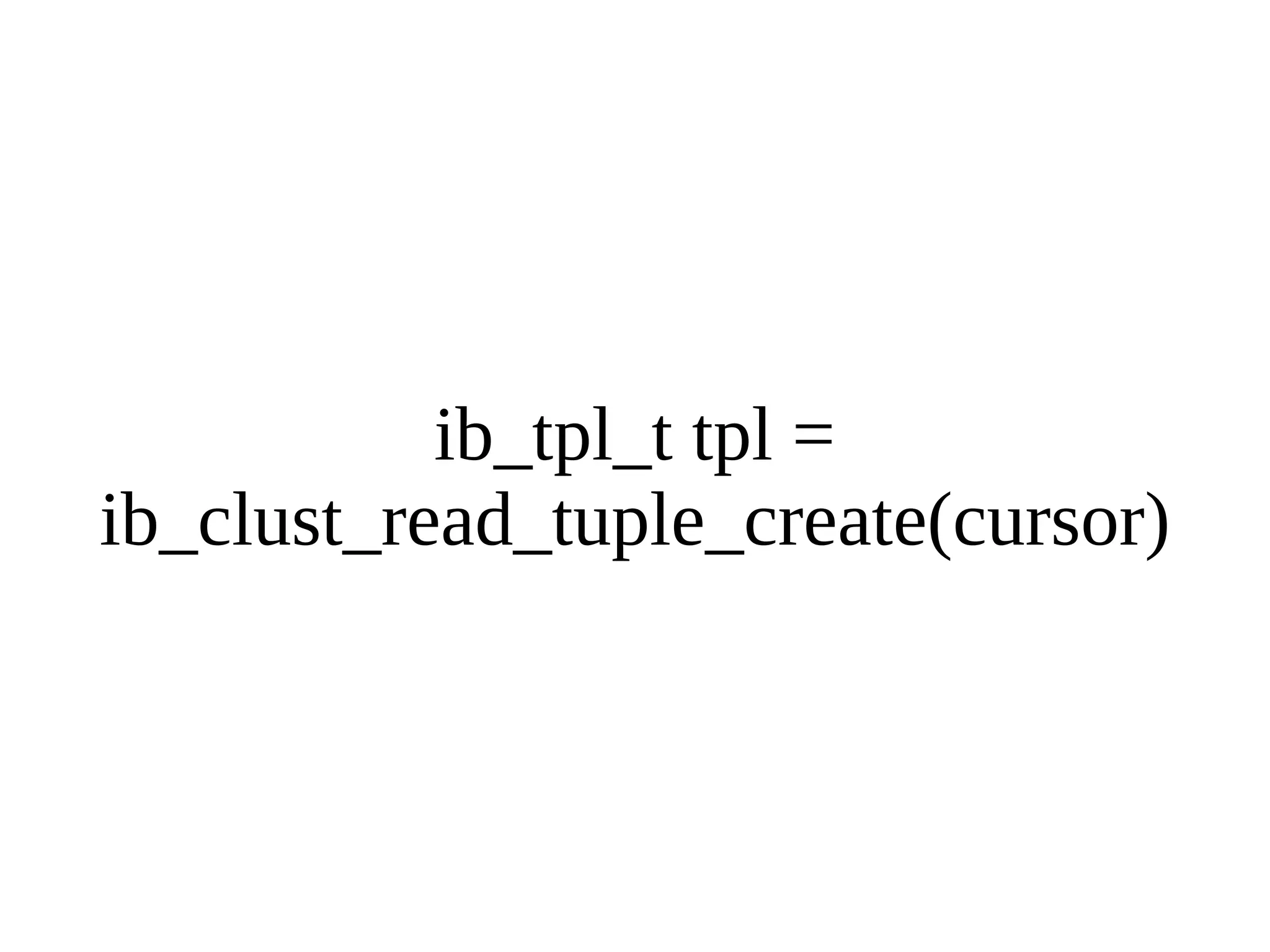
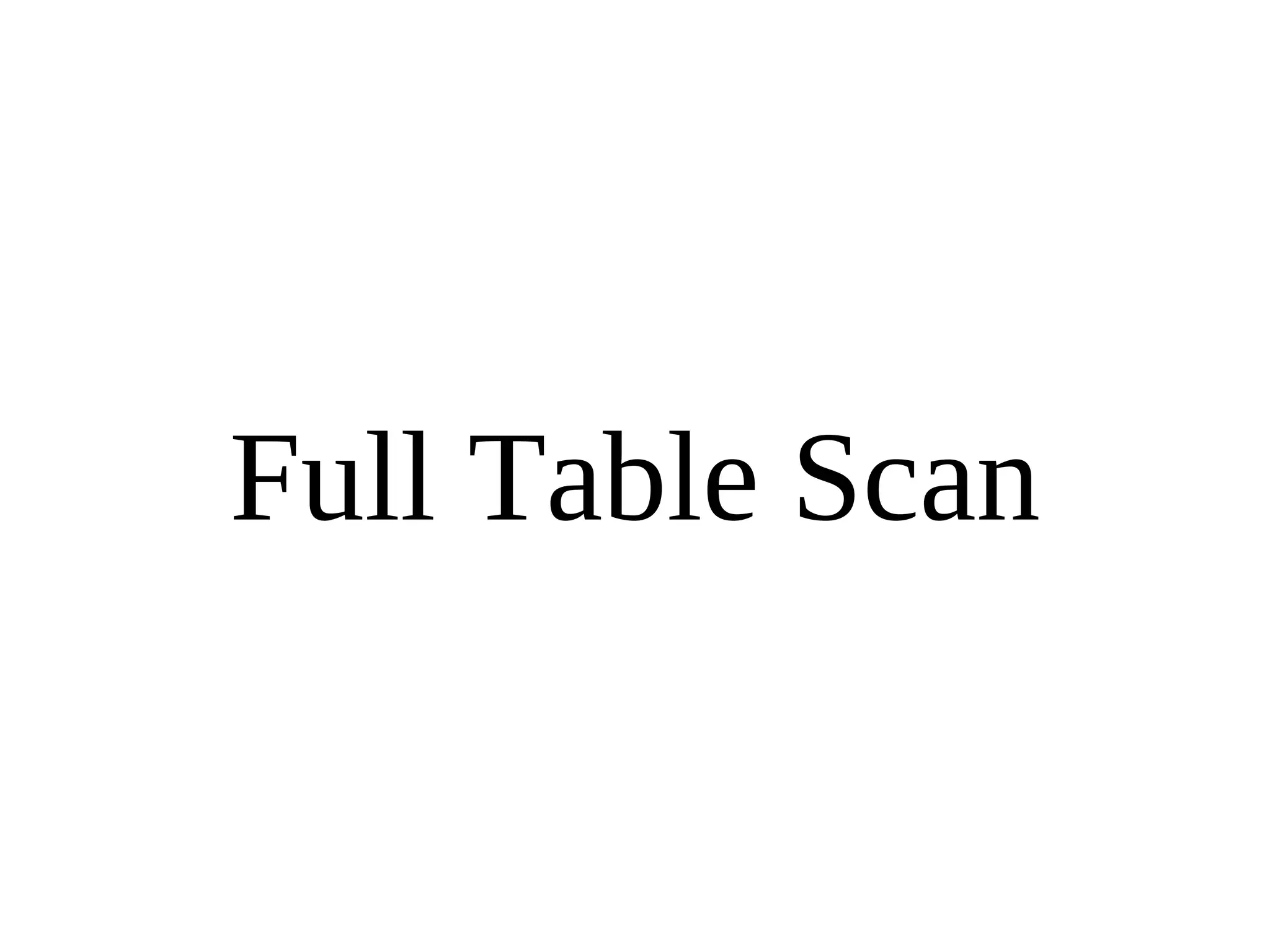
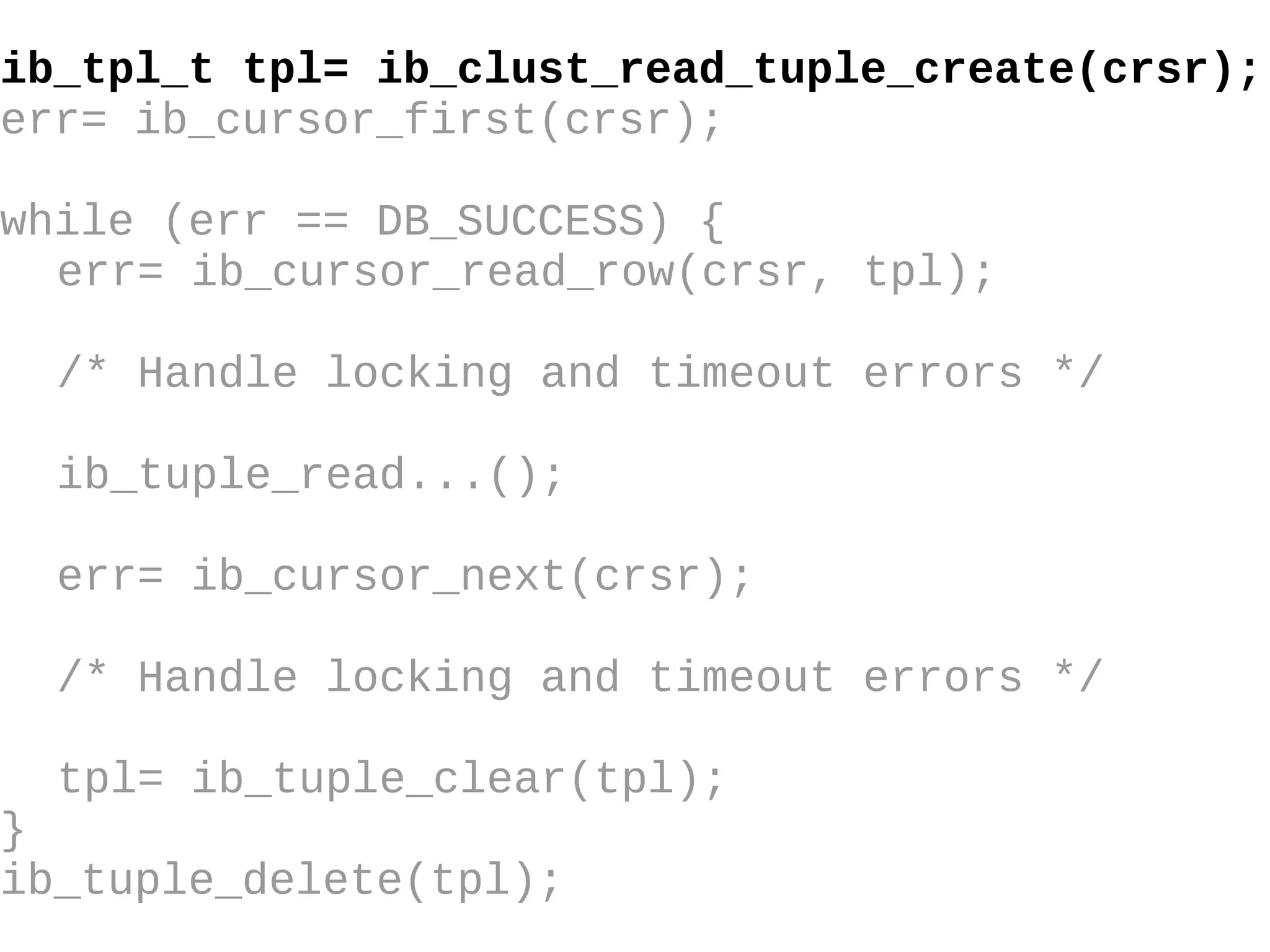
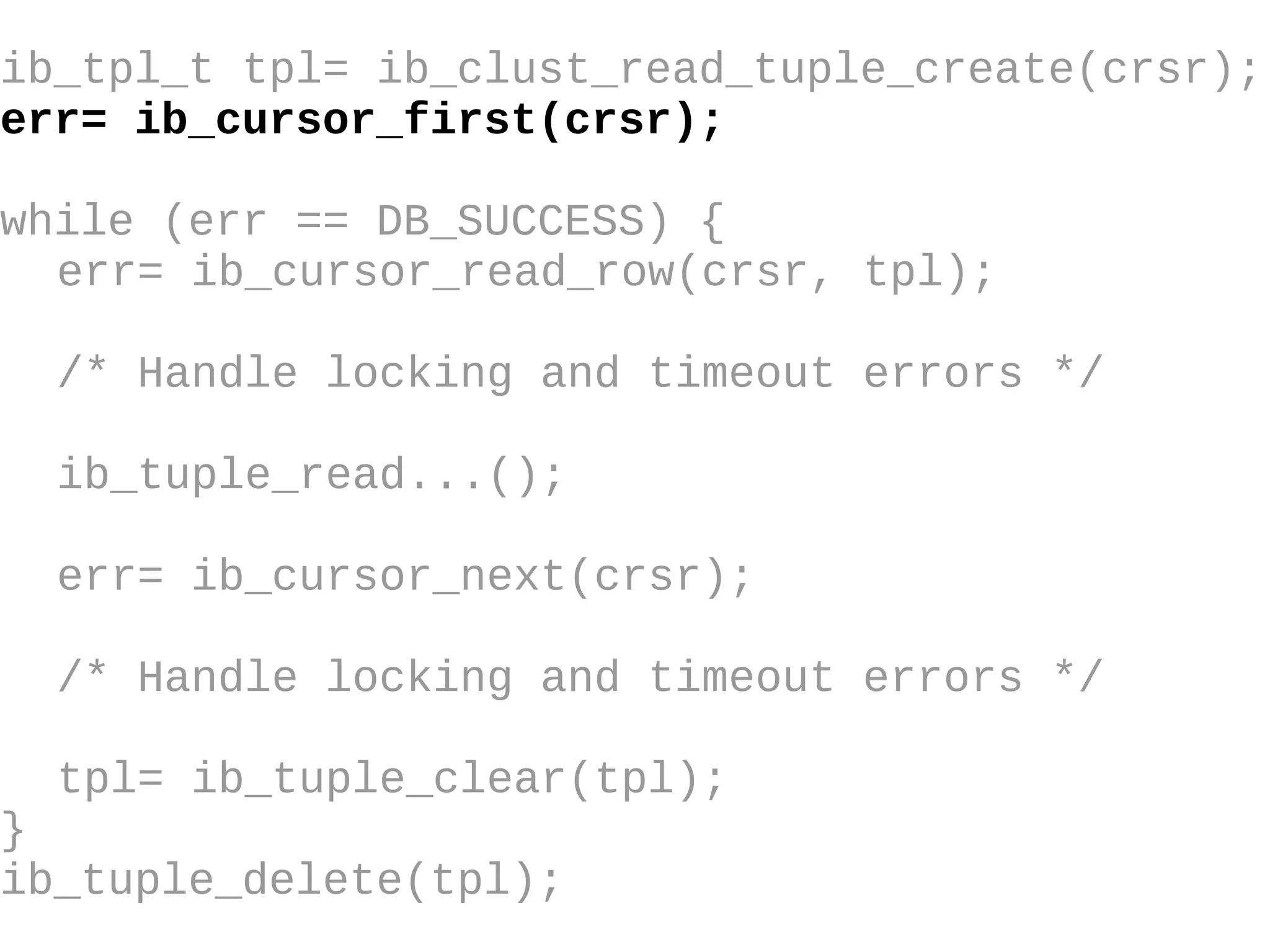
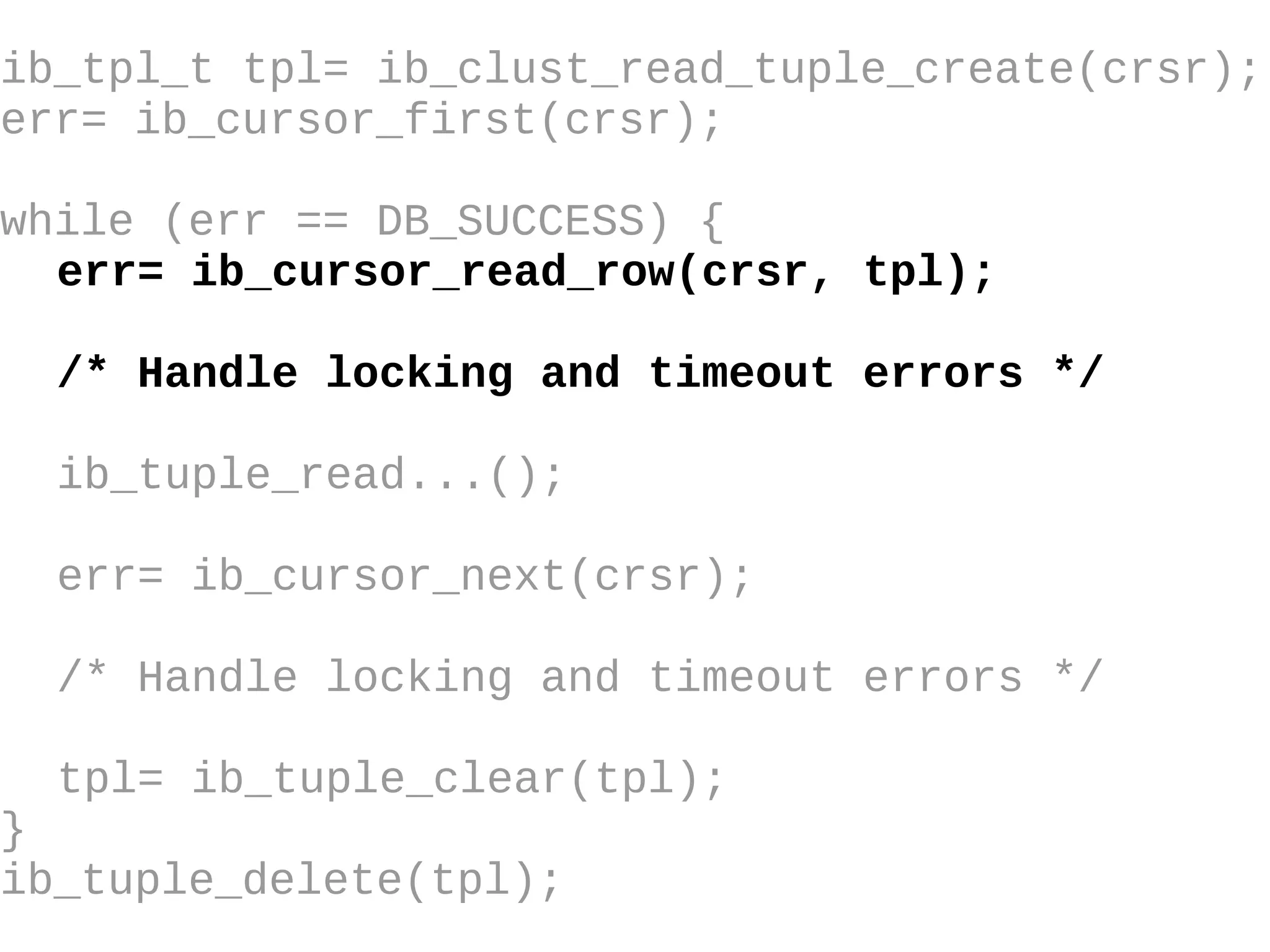
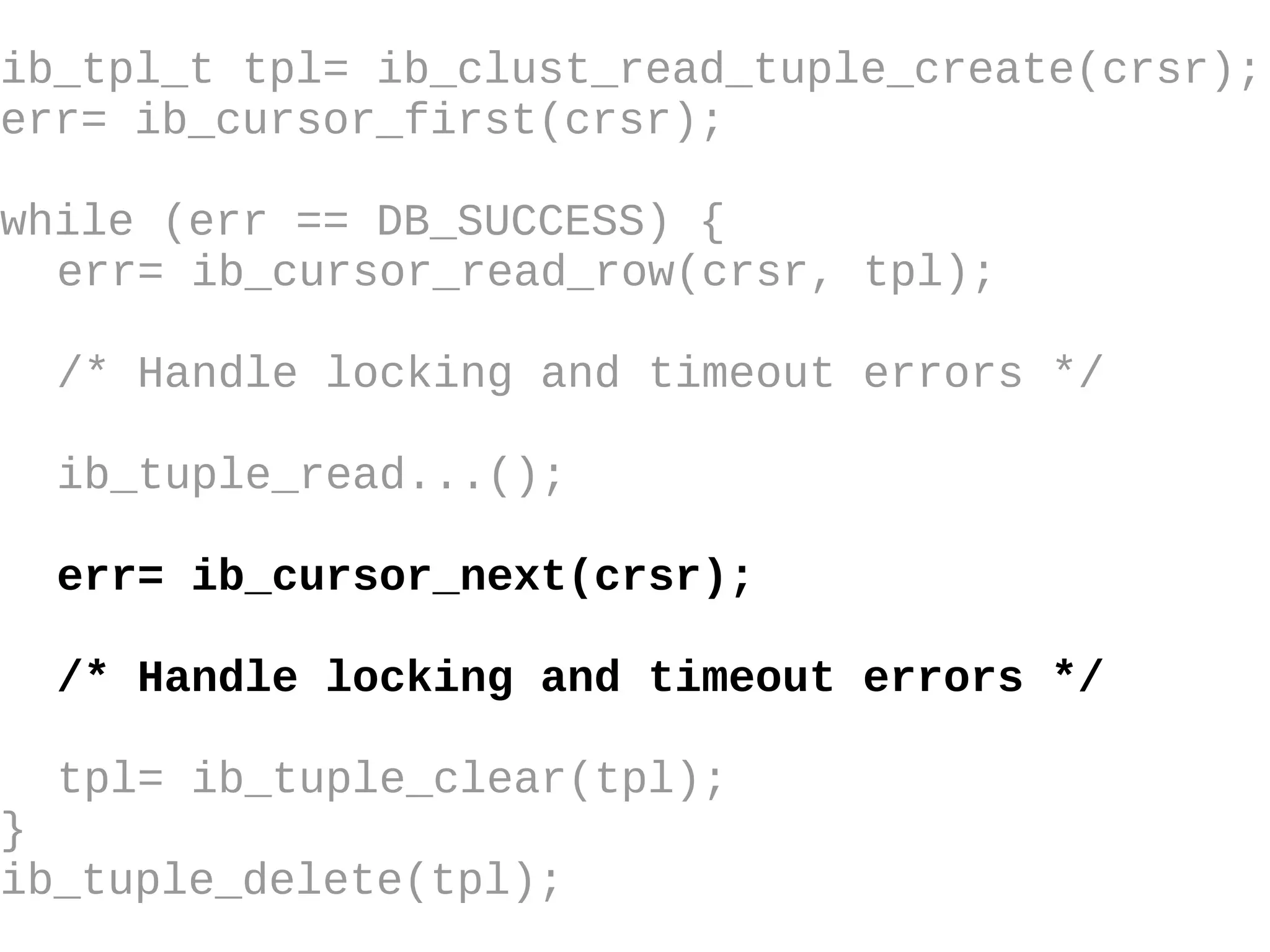
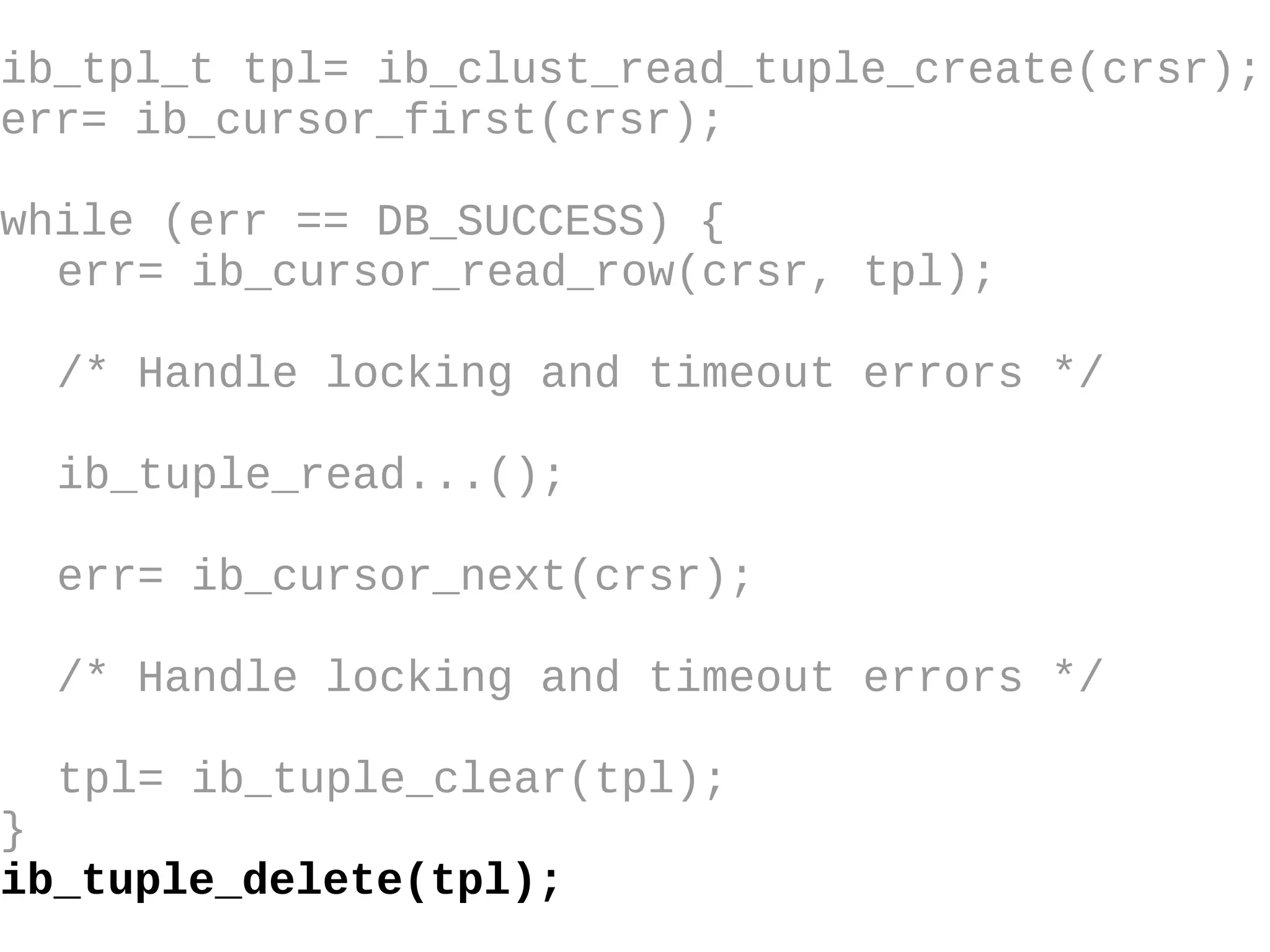
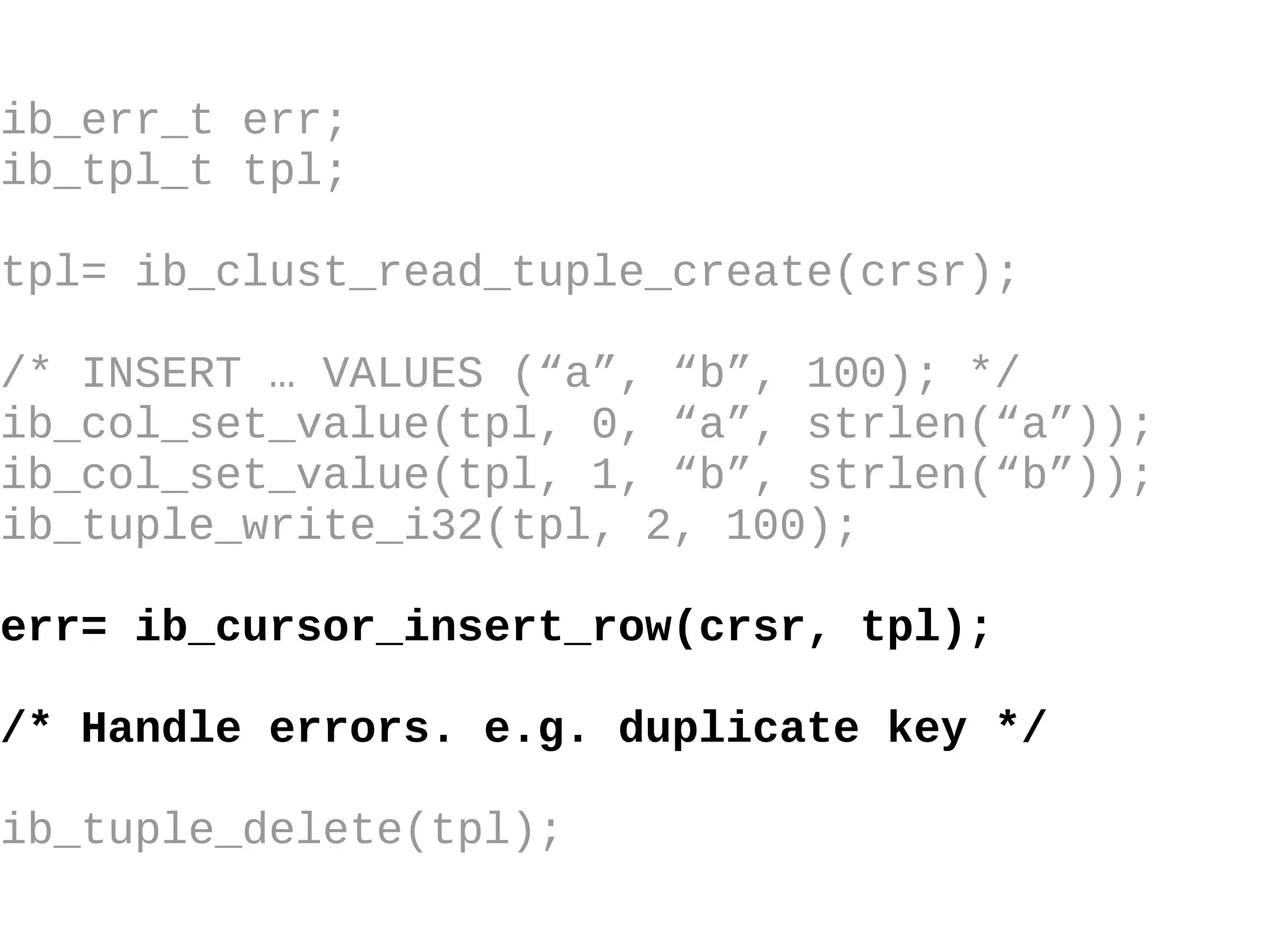
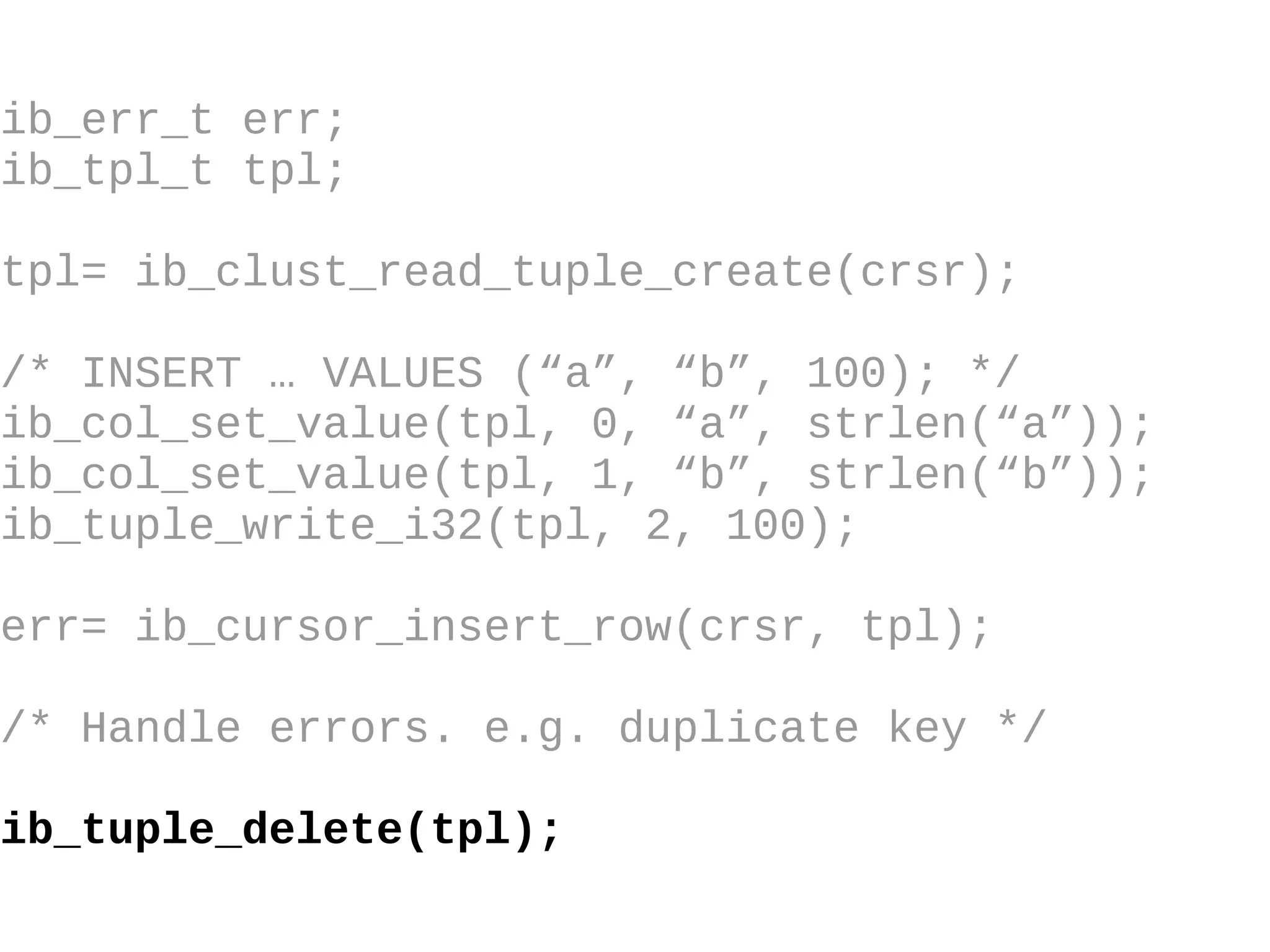
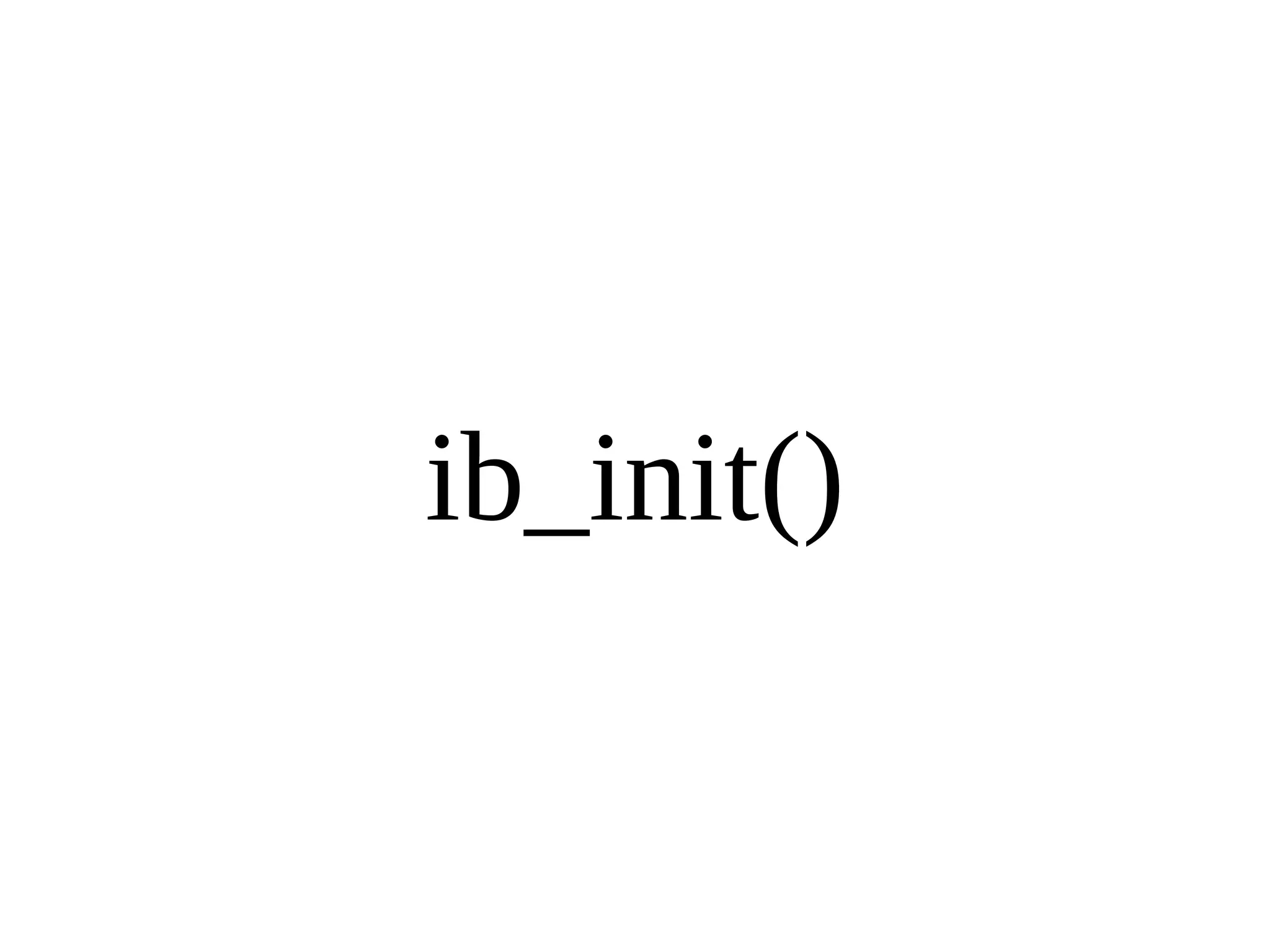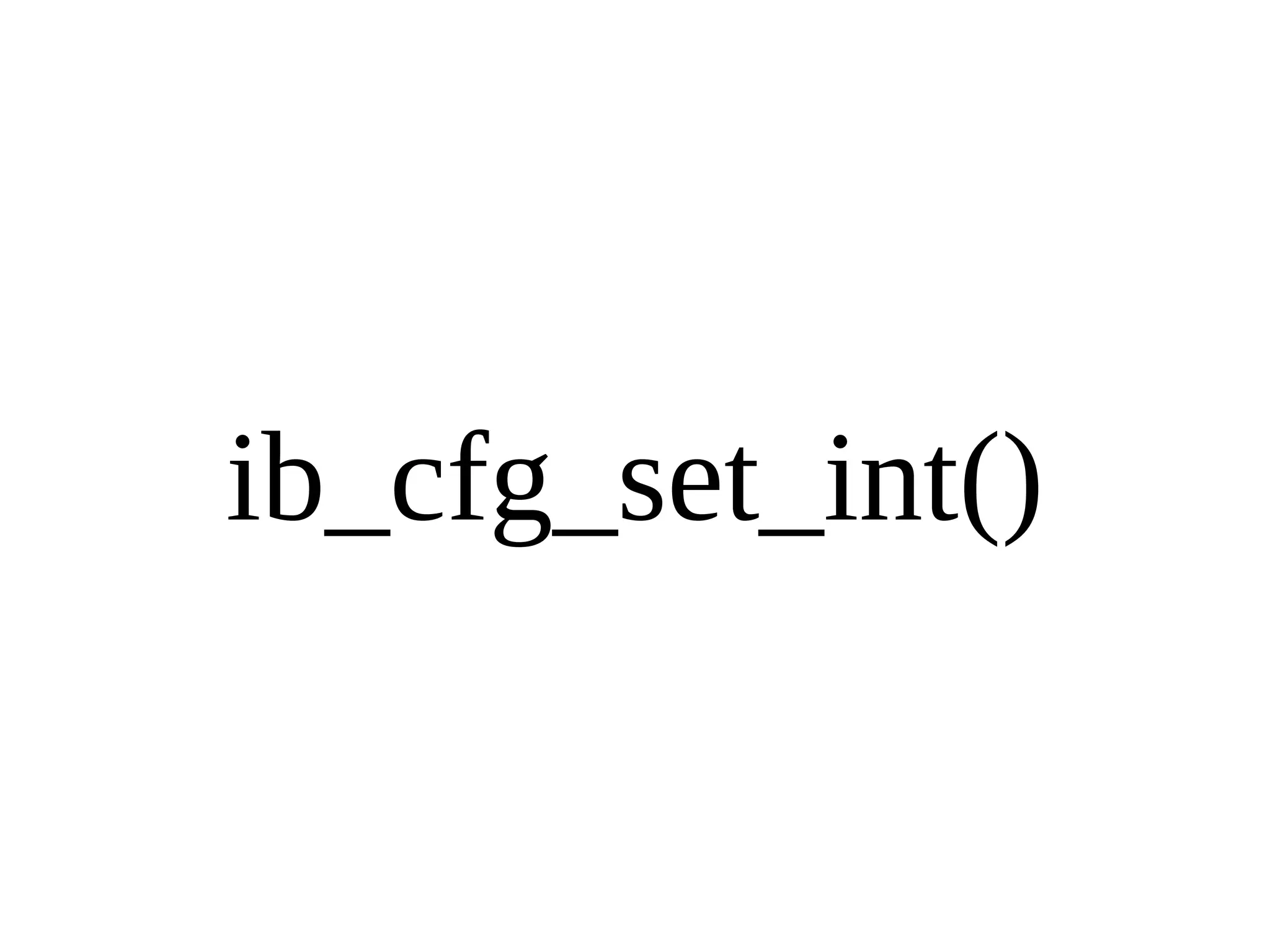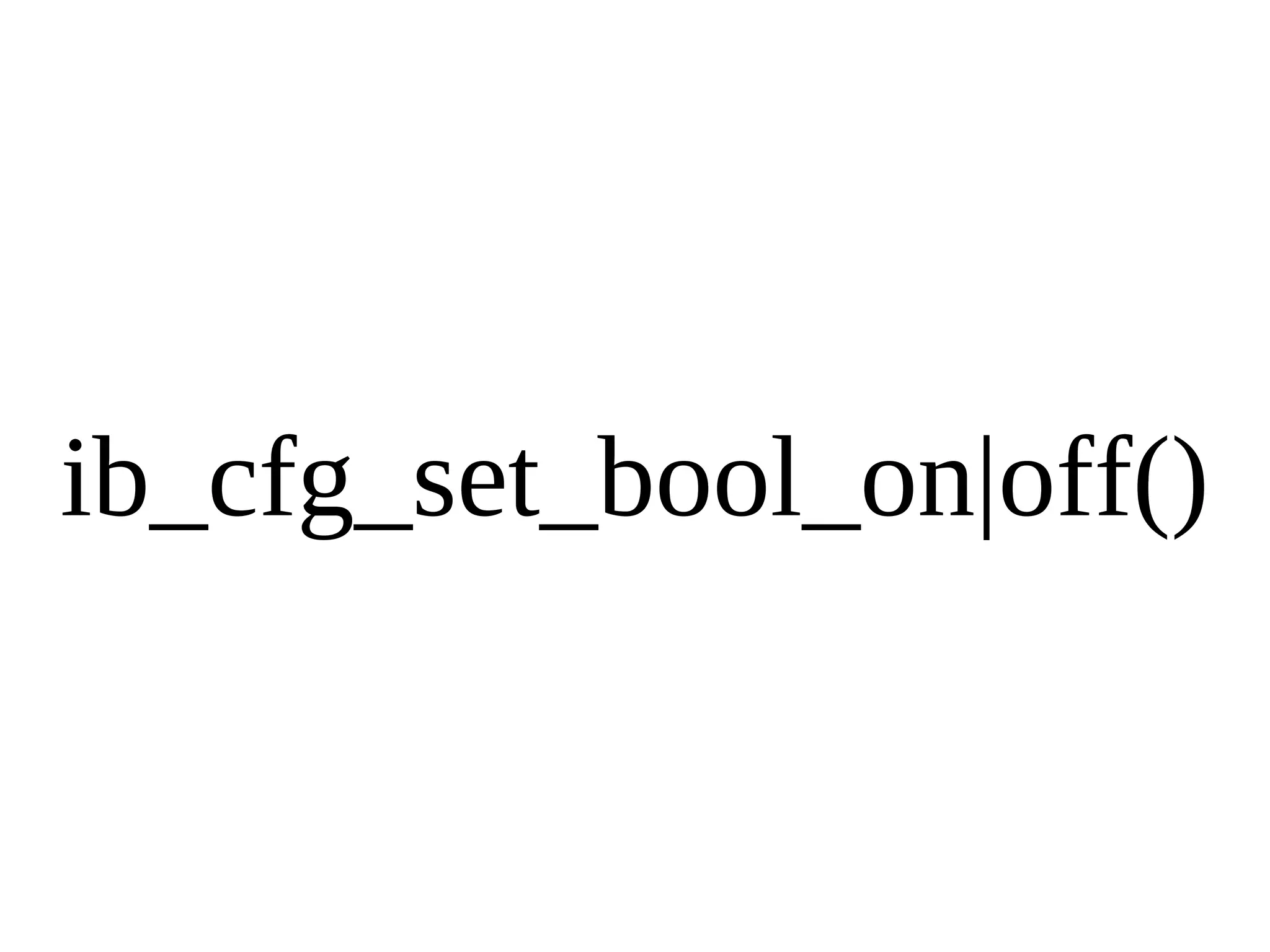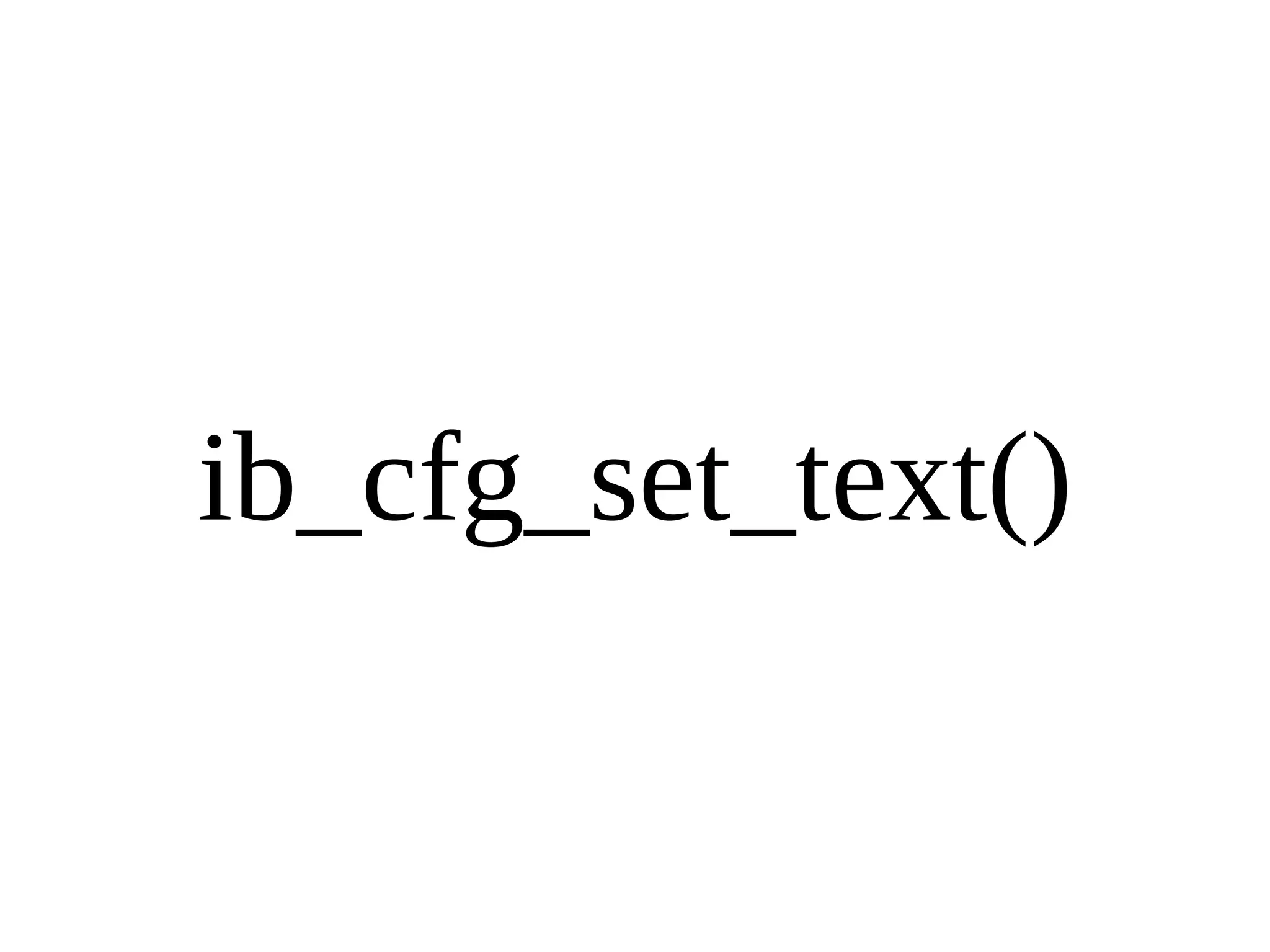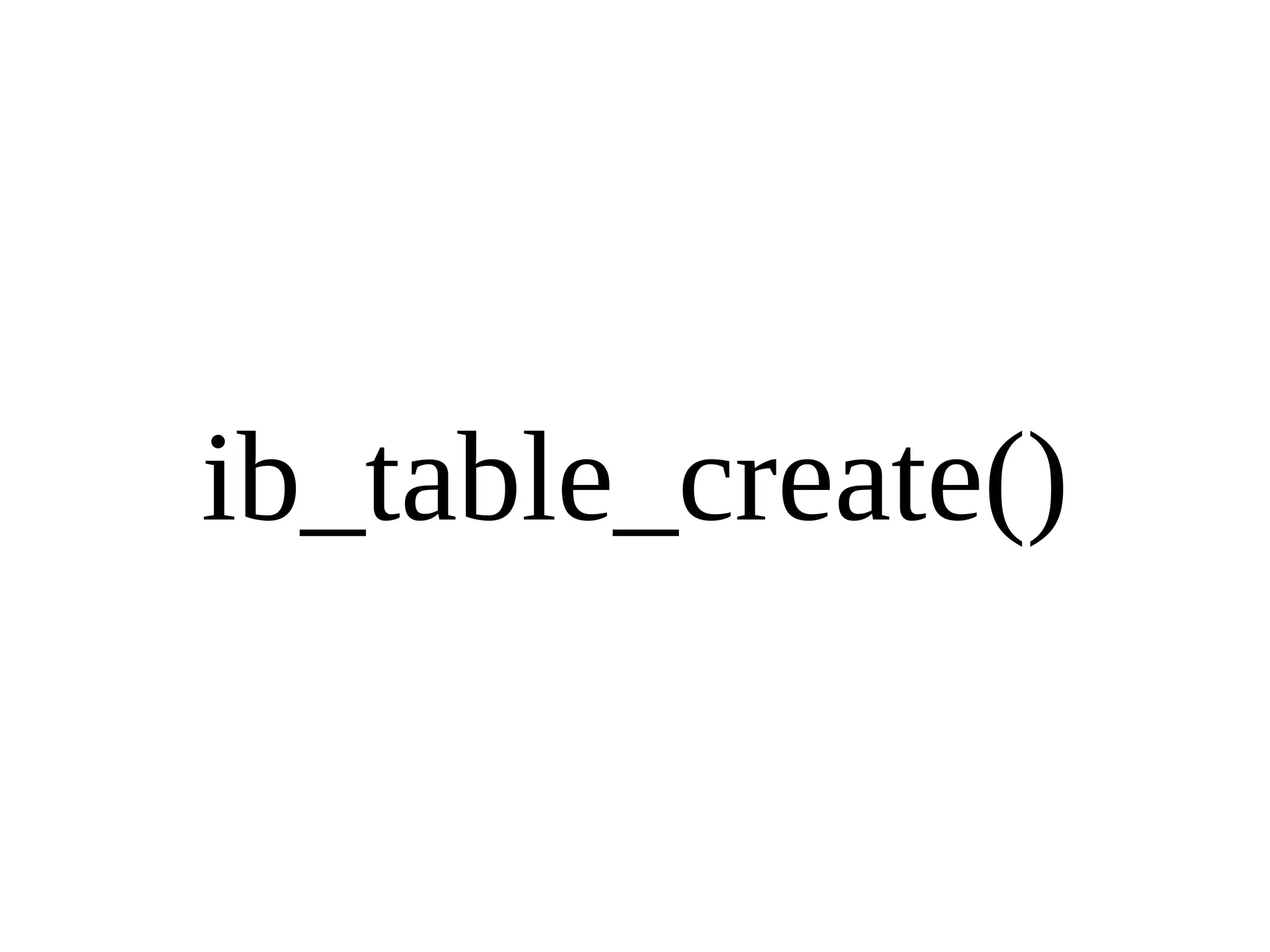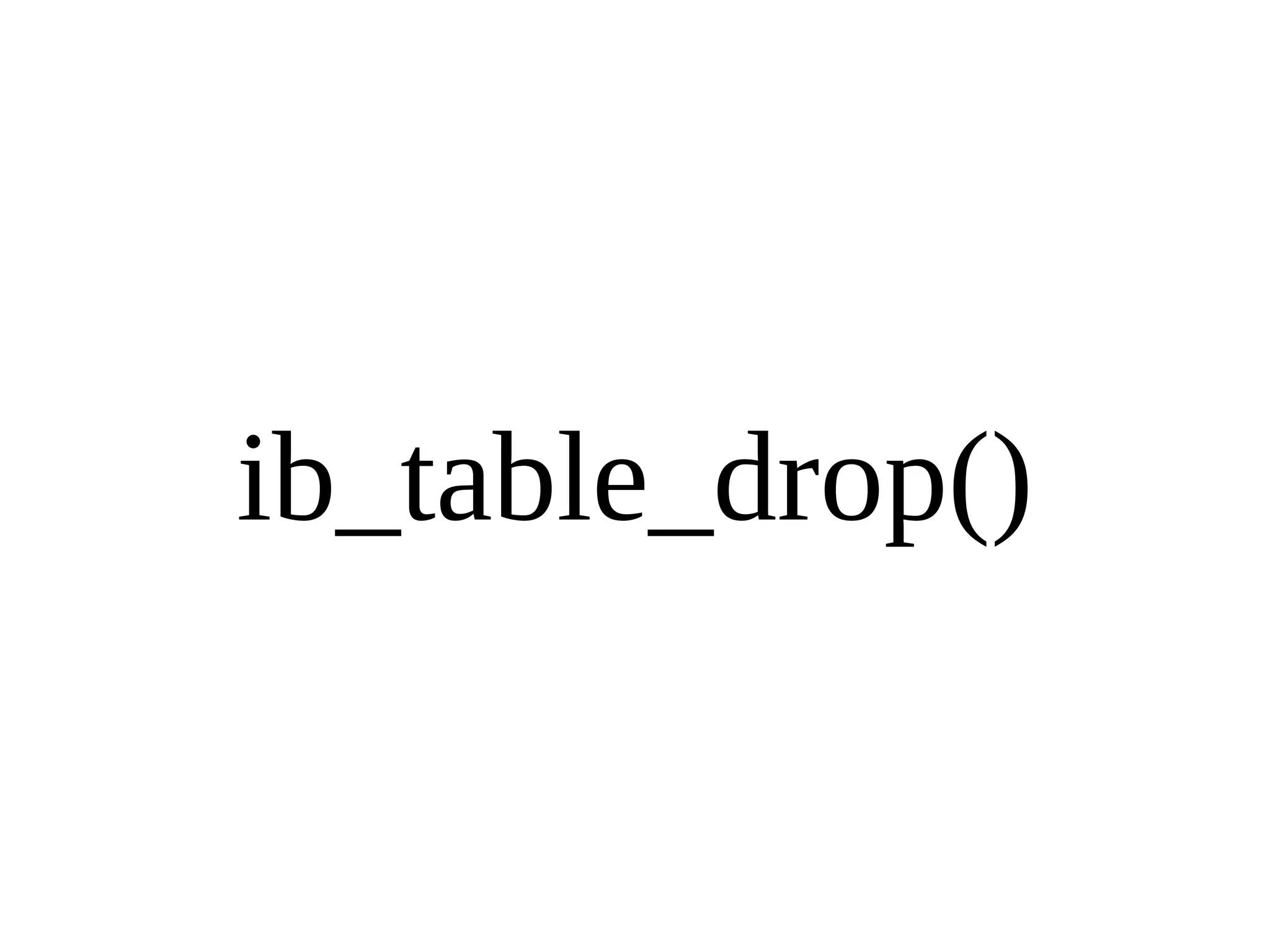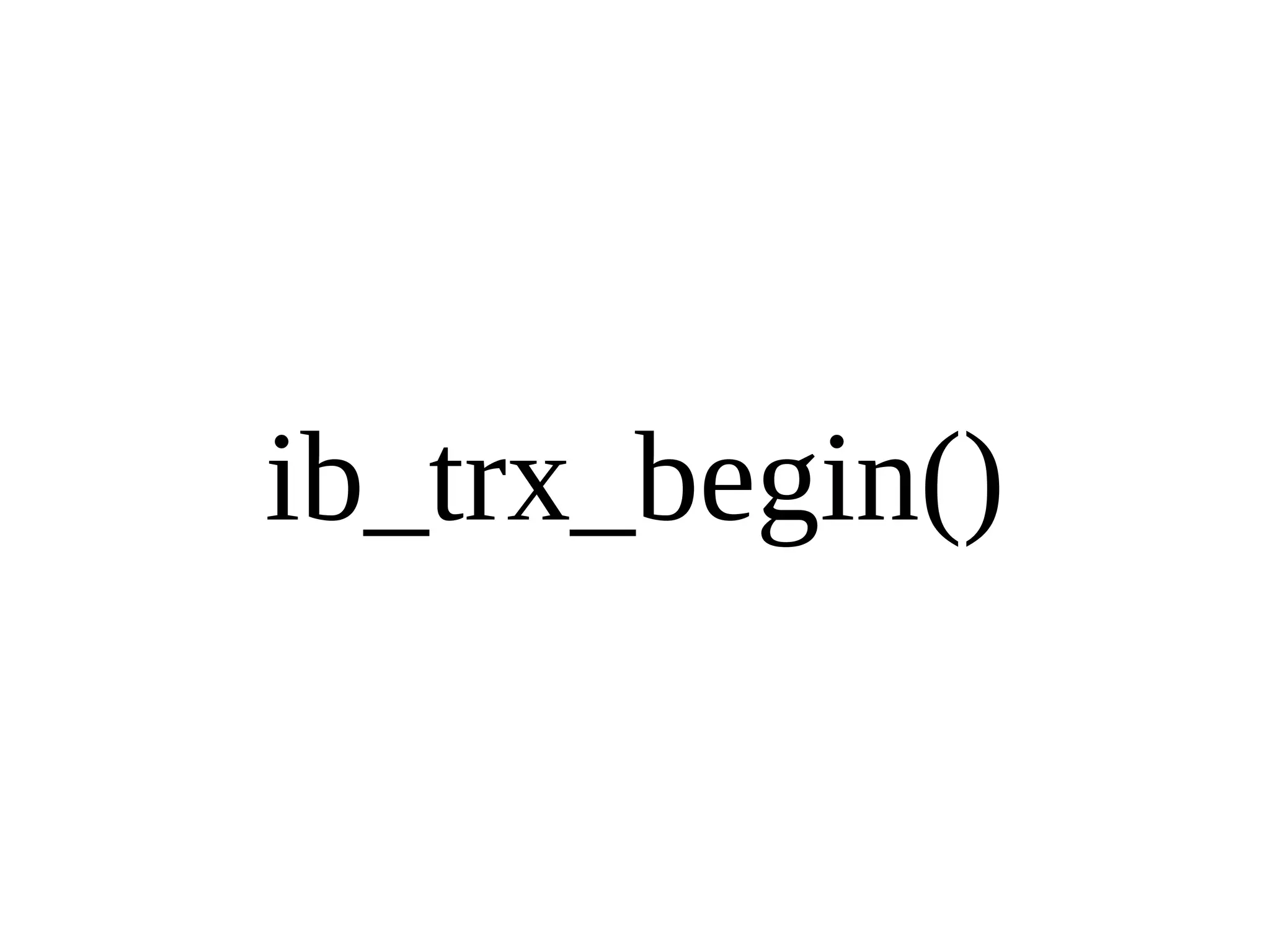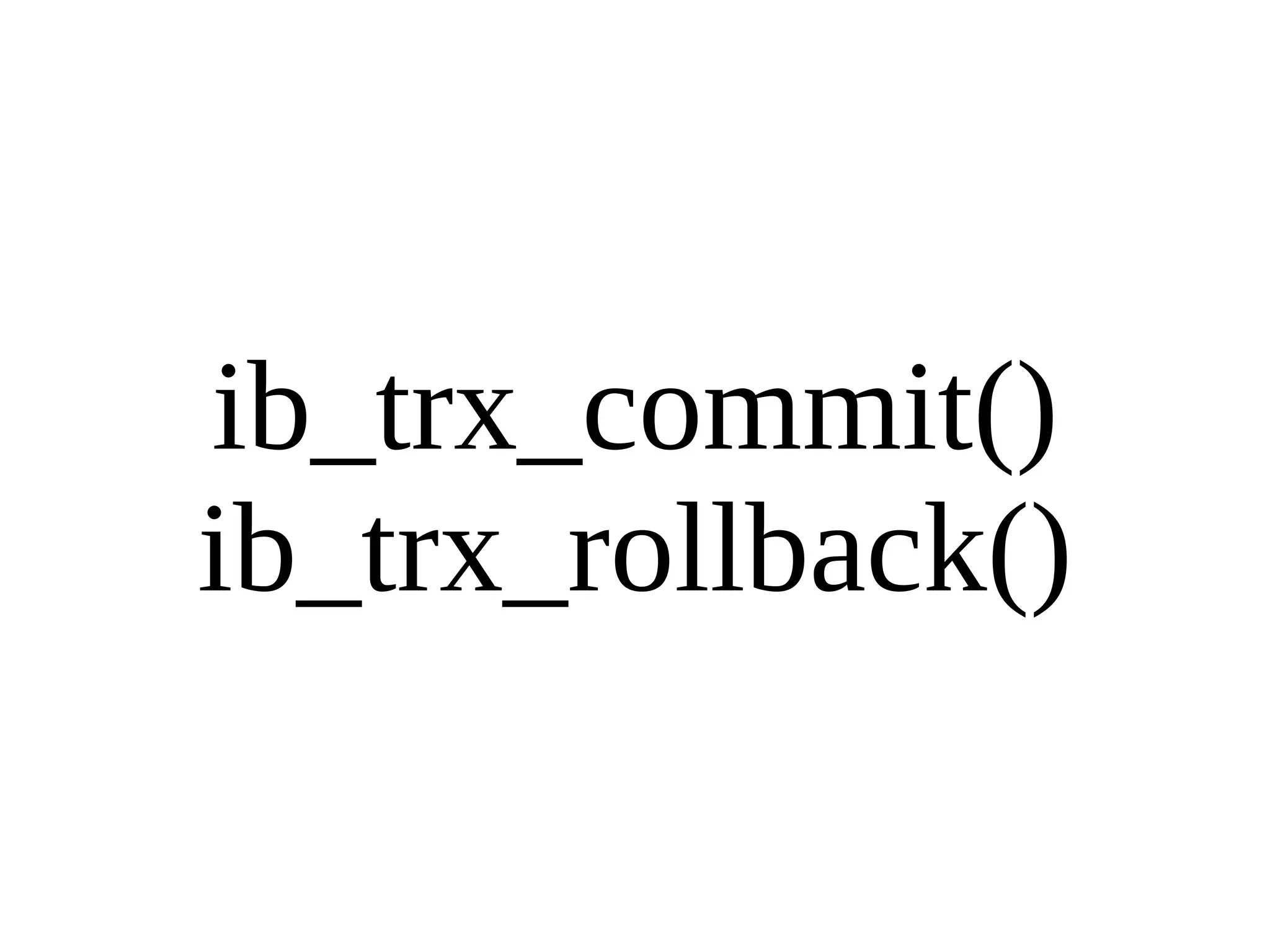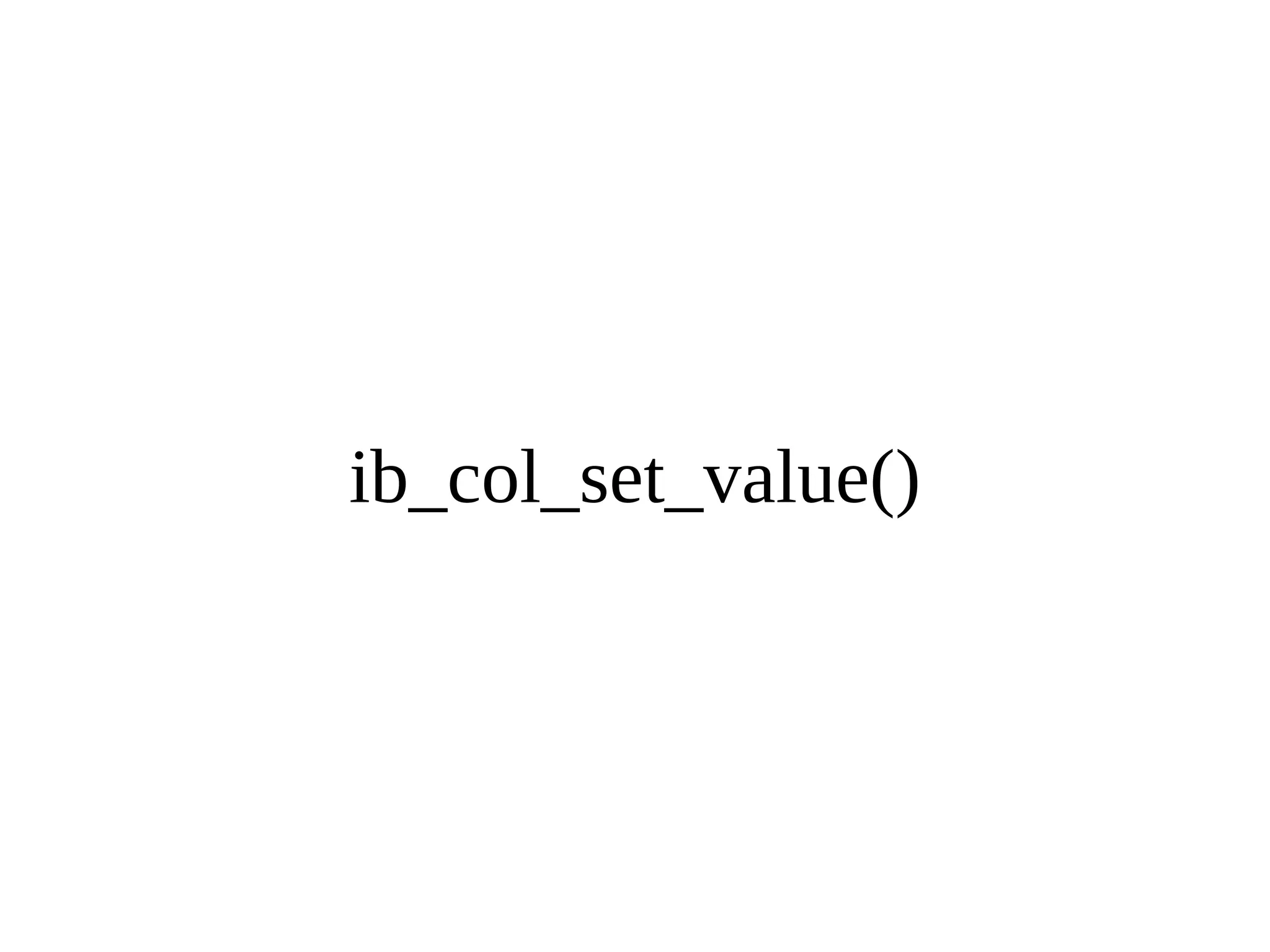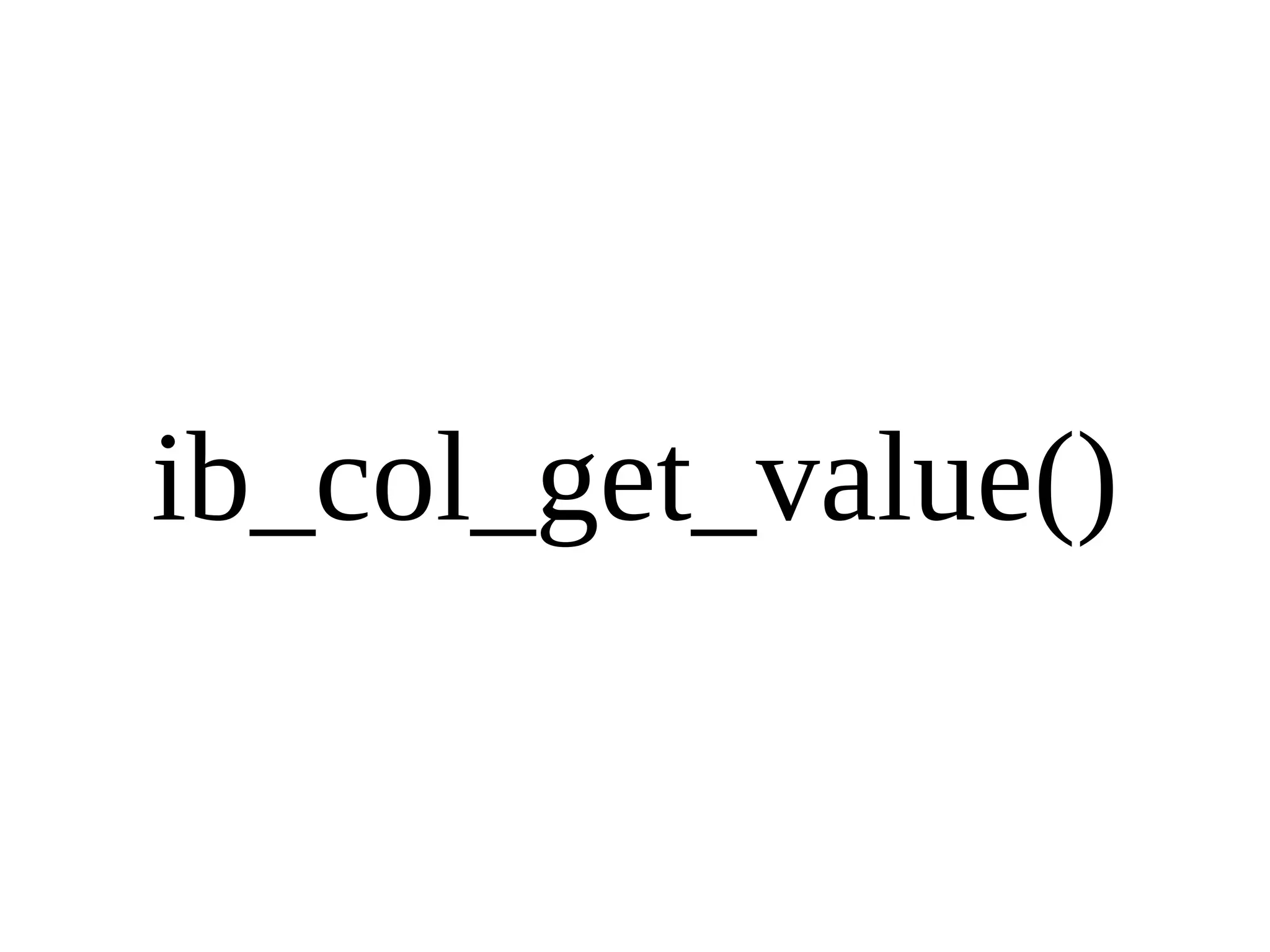HailDB is an open source project that provides a NoSQL API directly to InnoDB. It exposes the internal InnoDB API through cursor-based functions for transactions, key lookups, index scans, updates, inserts, and deletes. HailDB can be used to build embedded, fast, concurrent relational databases or as the storage engine for SQL databases by using the API instead of SQL. The API provides functions for initialization, configuration, DDL statements, transactions, cursors, tuples, full table scans, inserts, and updates.