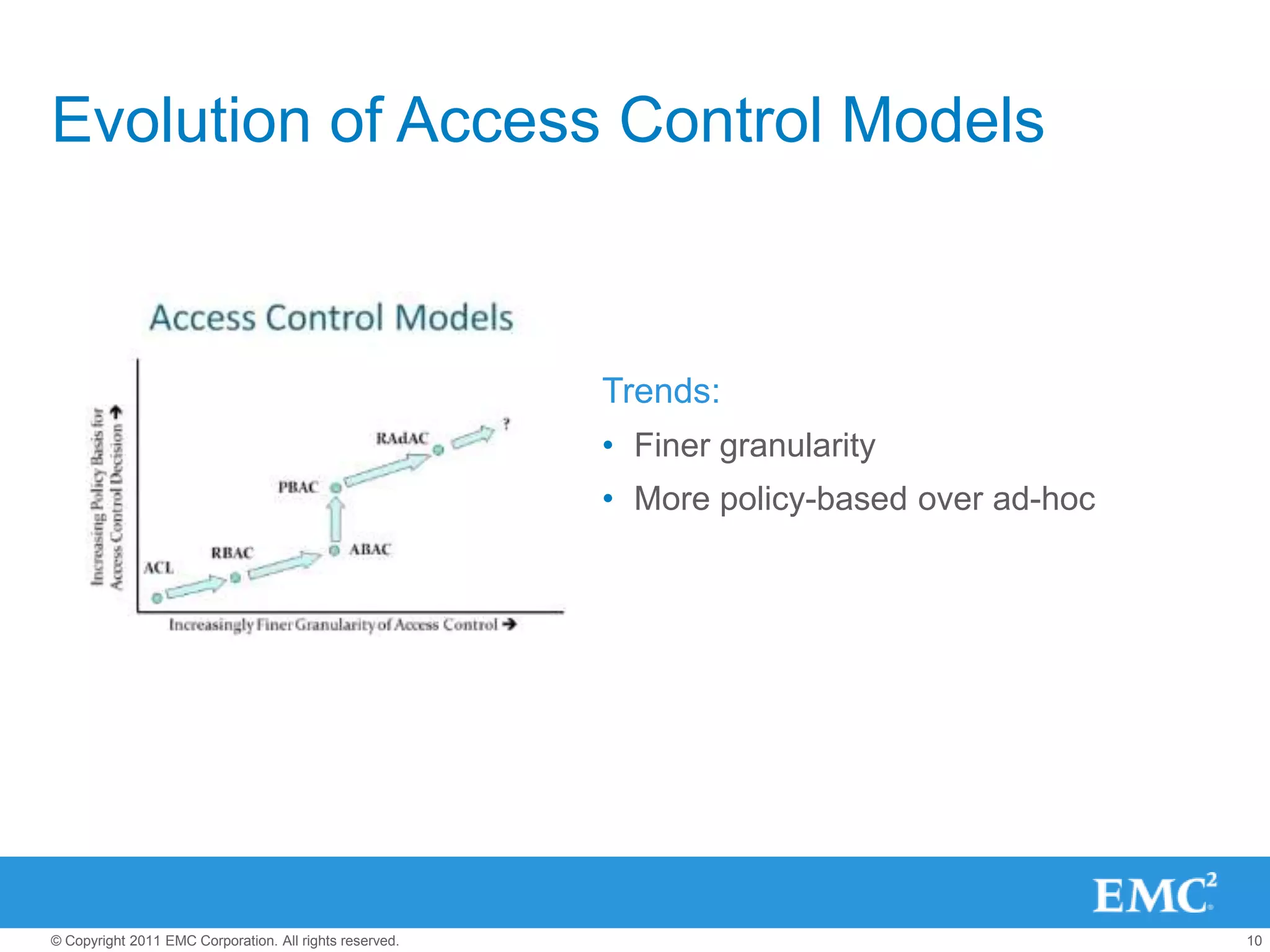
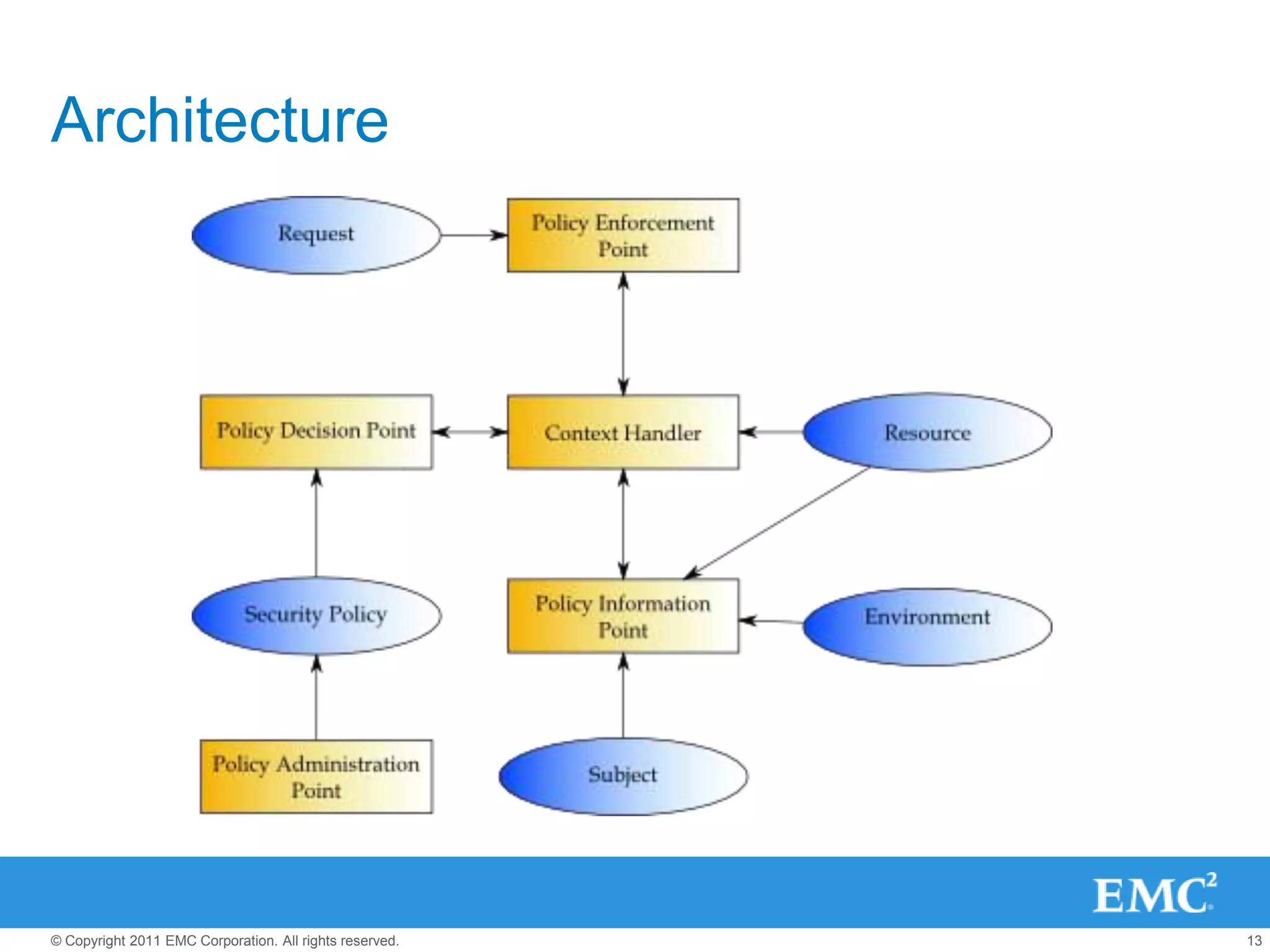
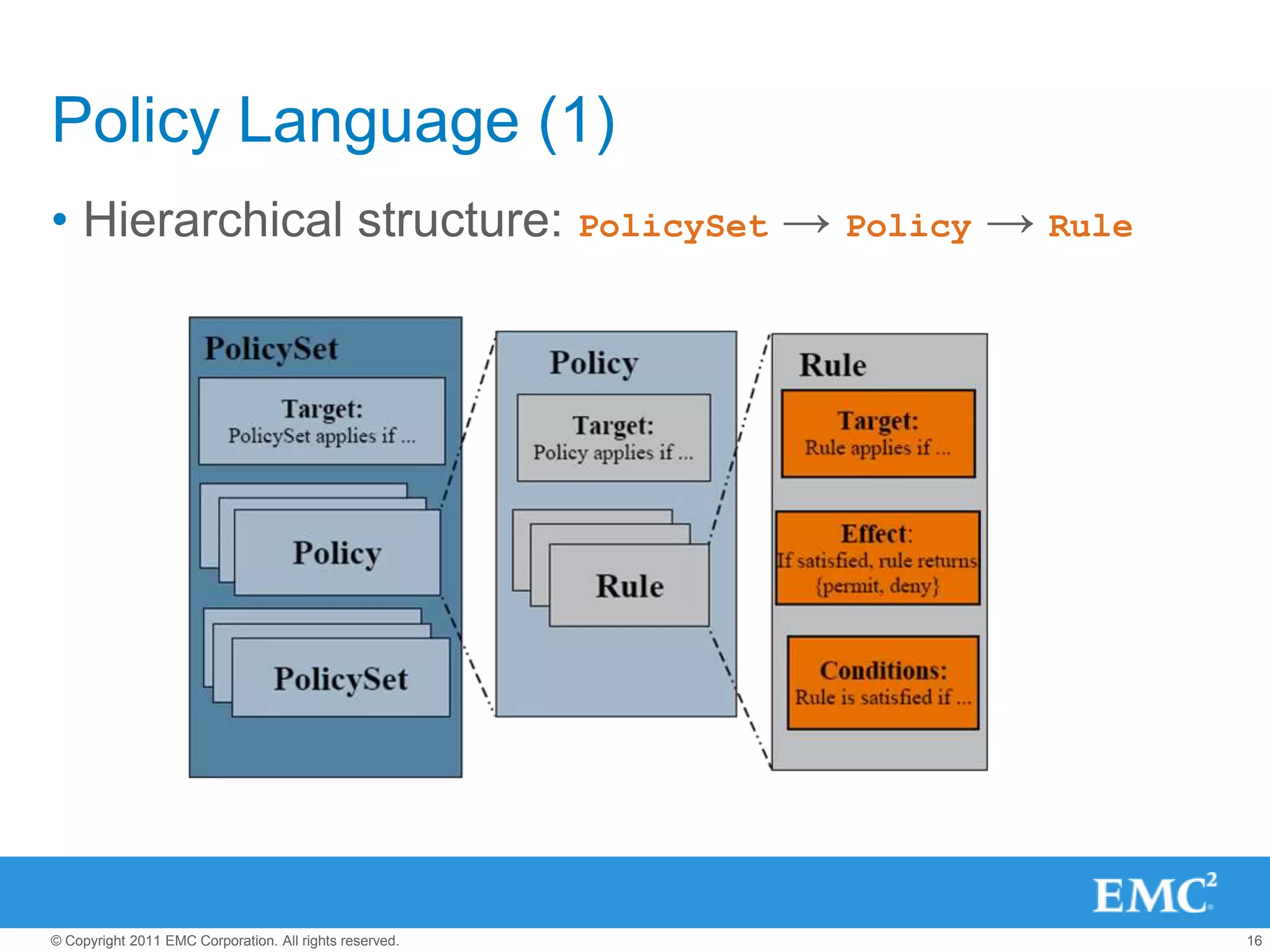
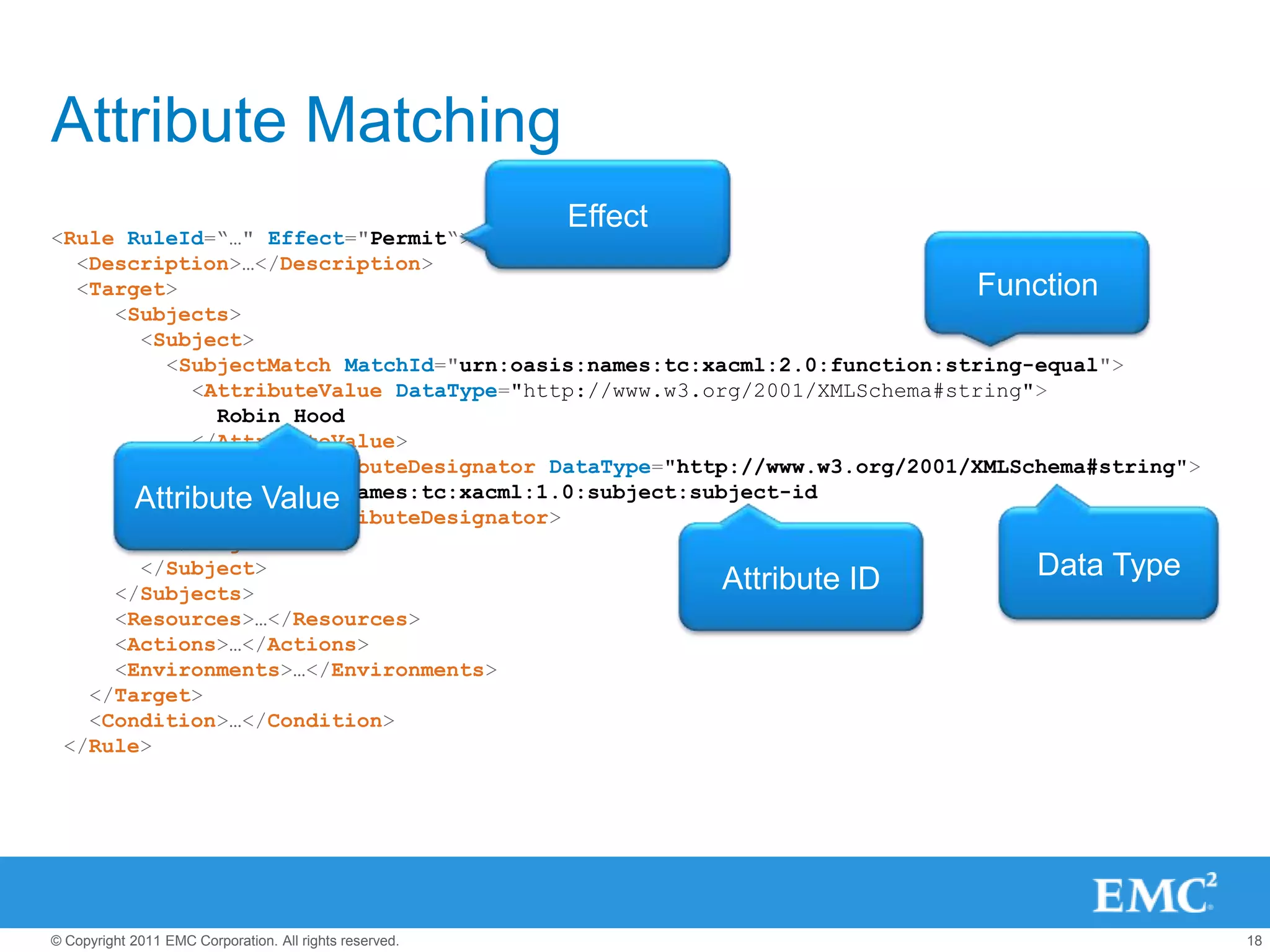
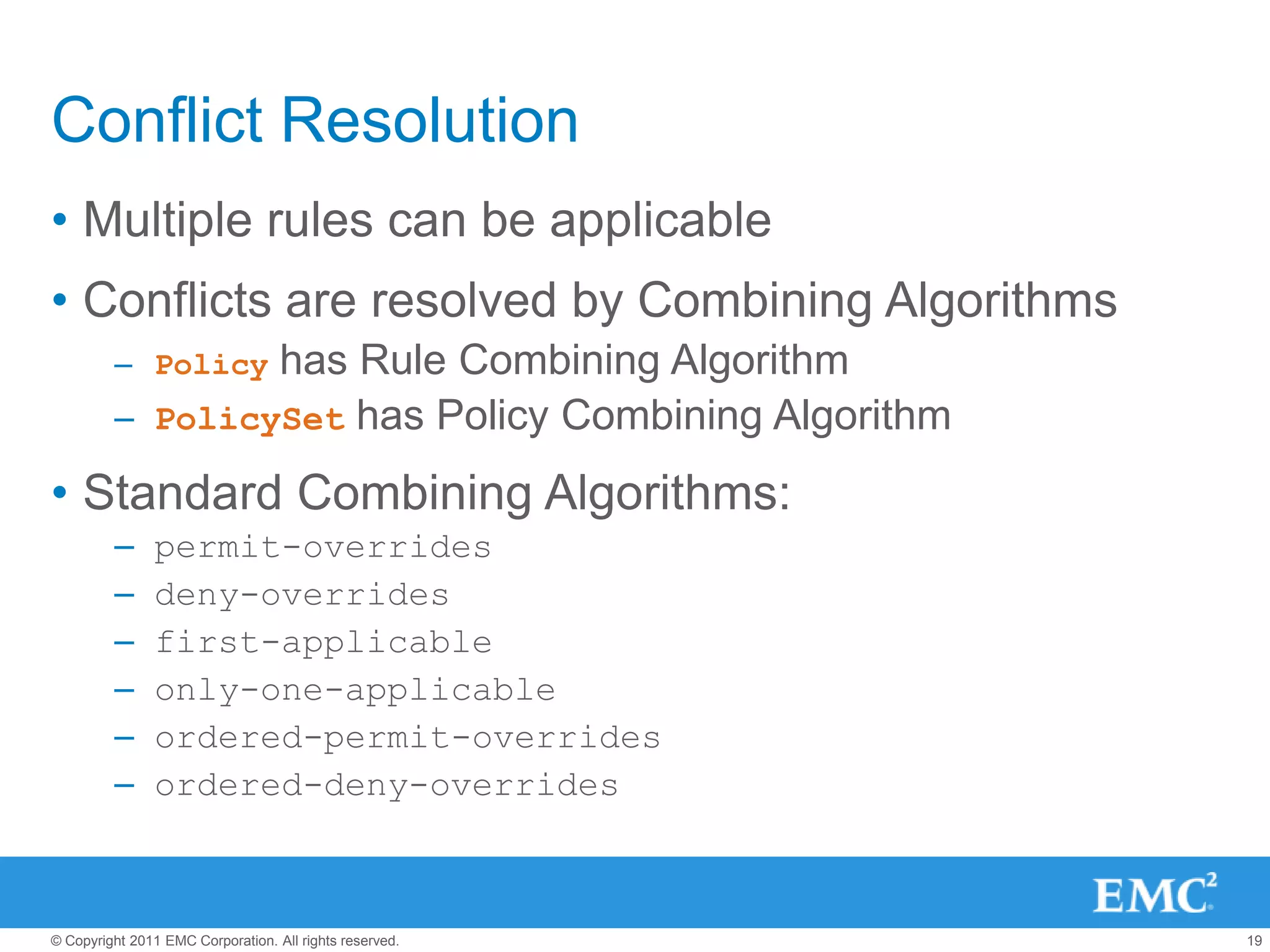
This document summarizes the eXtensible Access Control Markup Language (XACML). It discusses access control models like ACL, RBAC, ABAC and how XACML supports all of them. The document outlines the key components of XACML including its architecture, request/response protocol, policy language, optional profiles, and what is new in version 3.0. It also briefly mentions some XACML implementations.