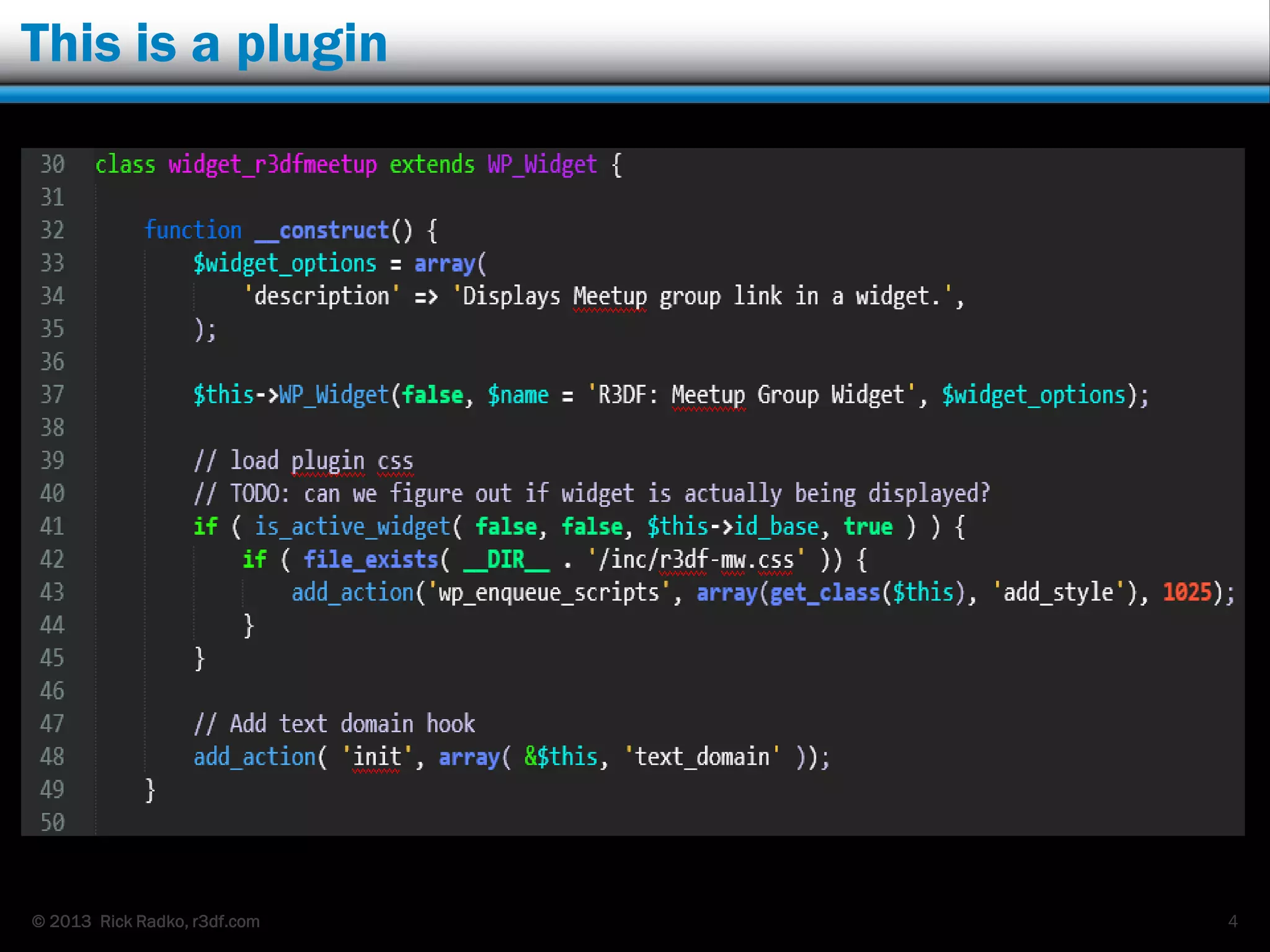
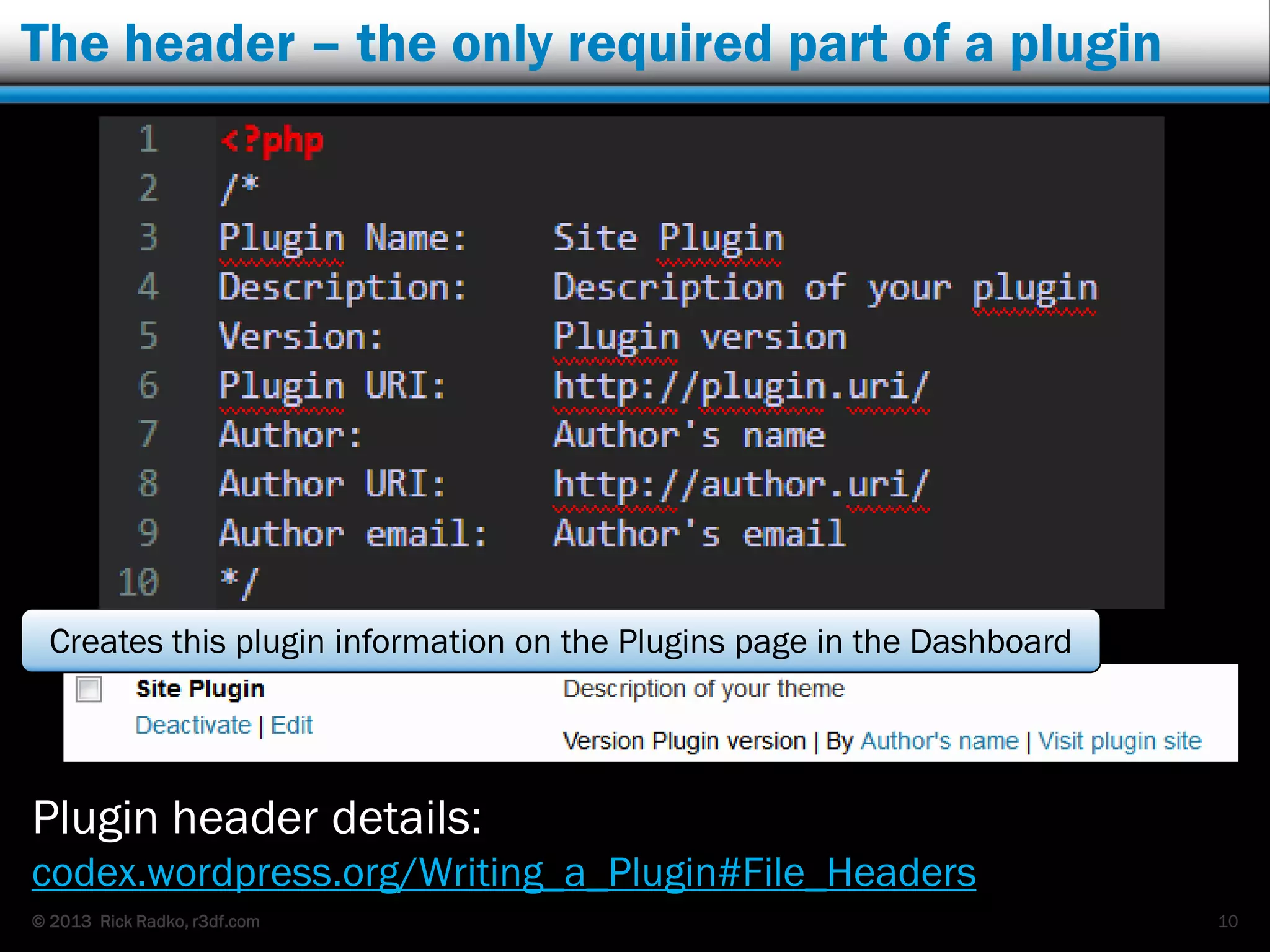
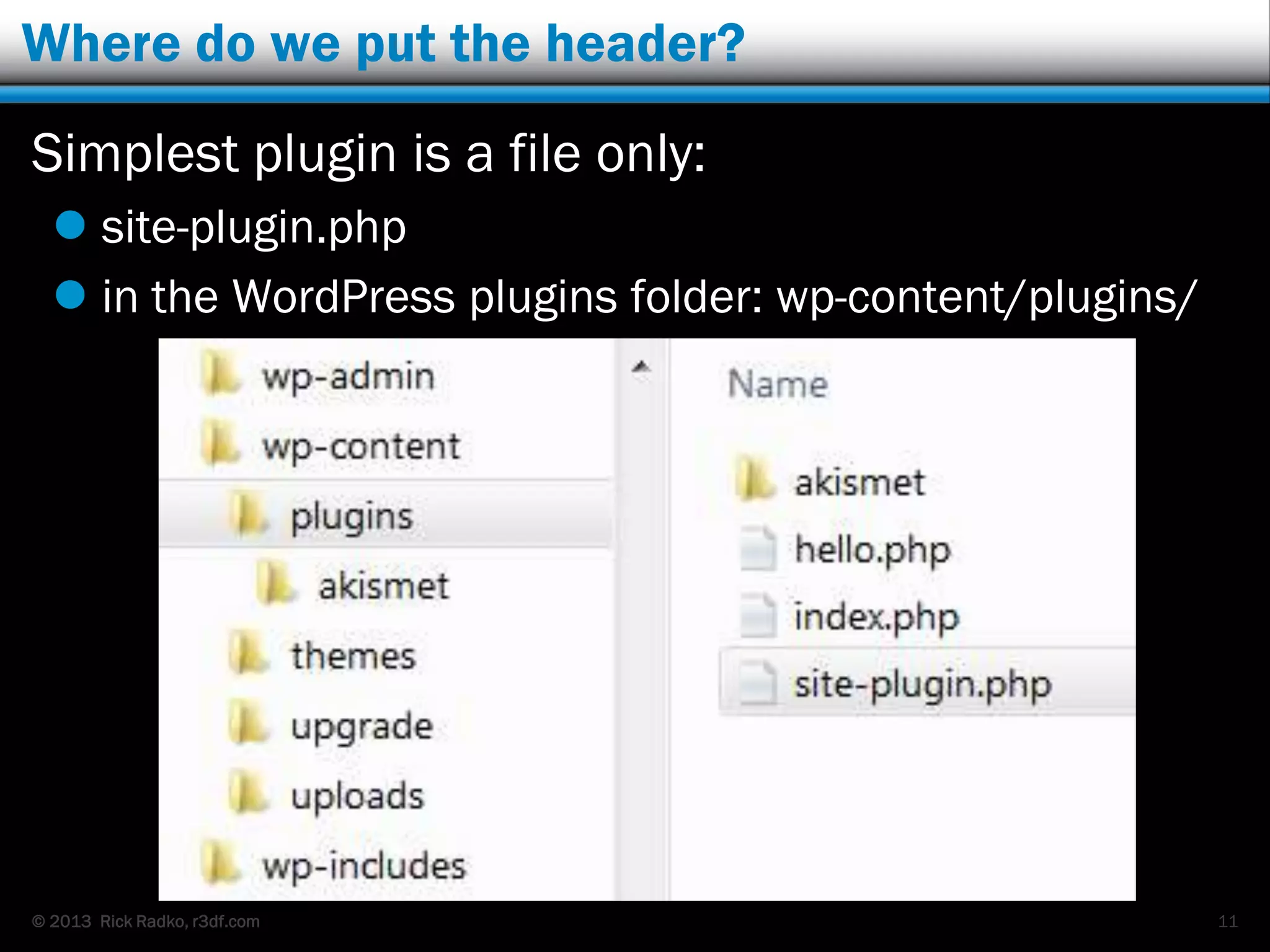
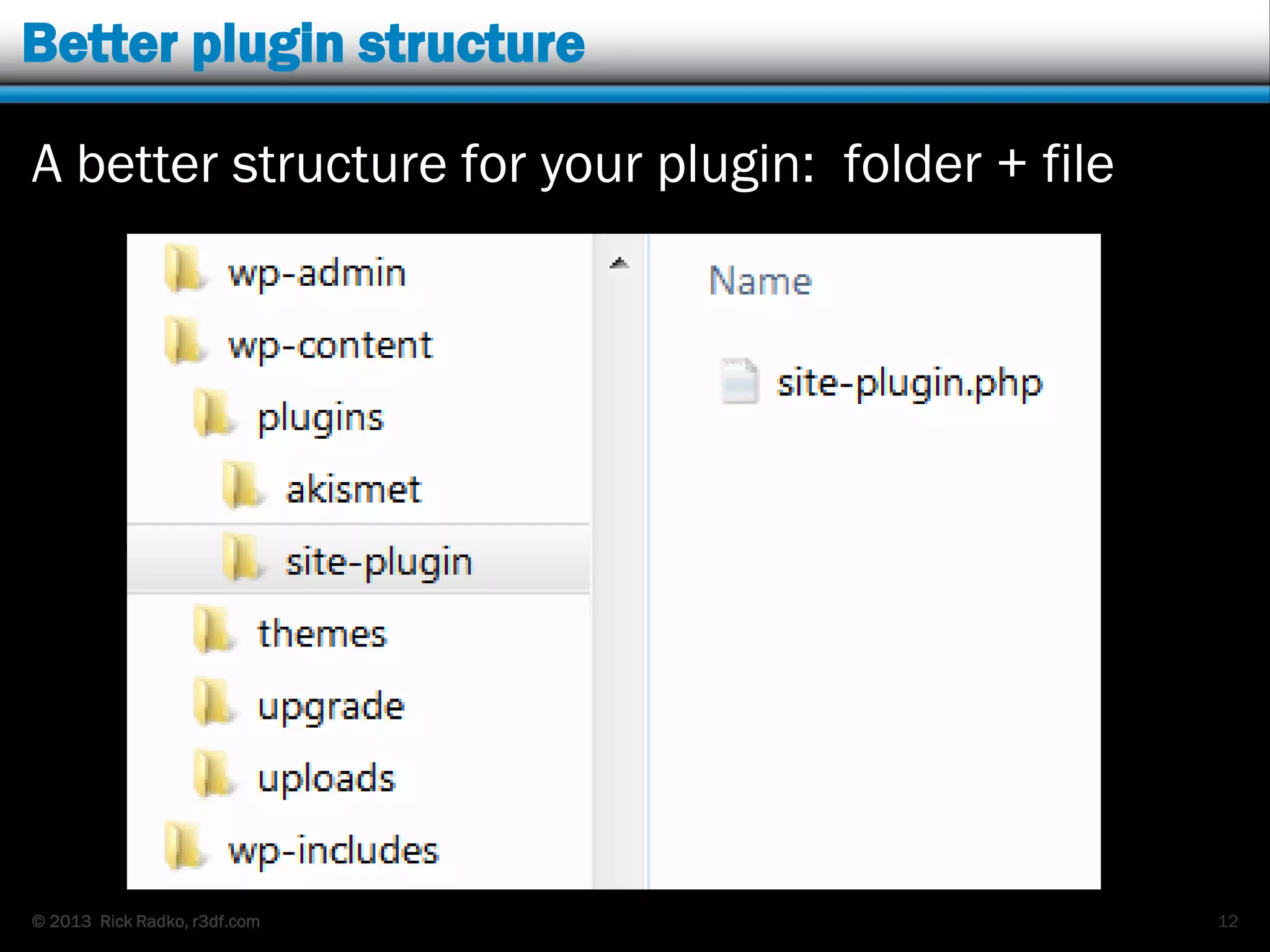
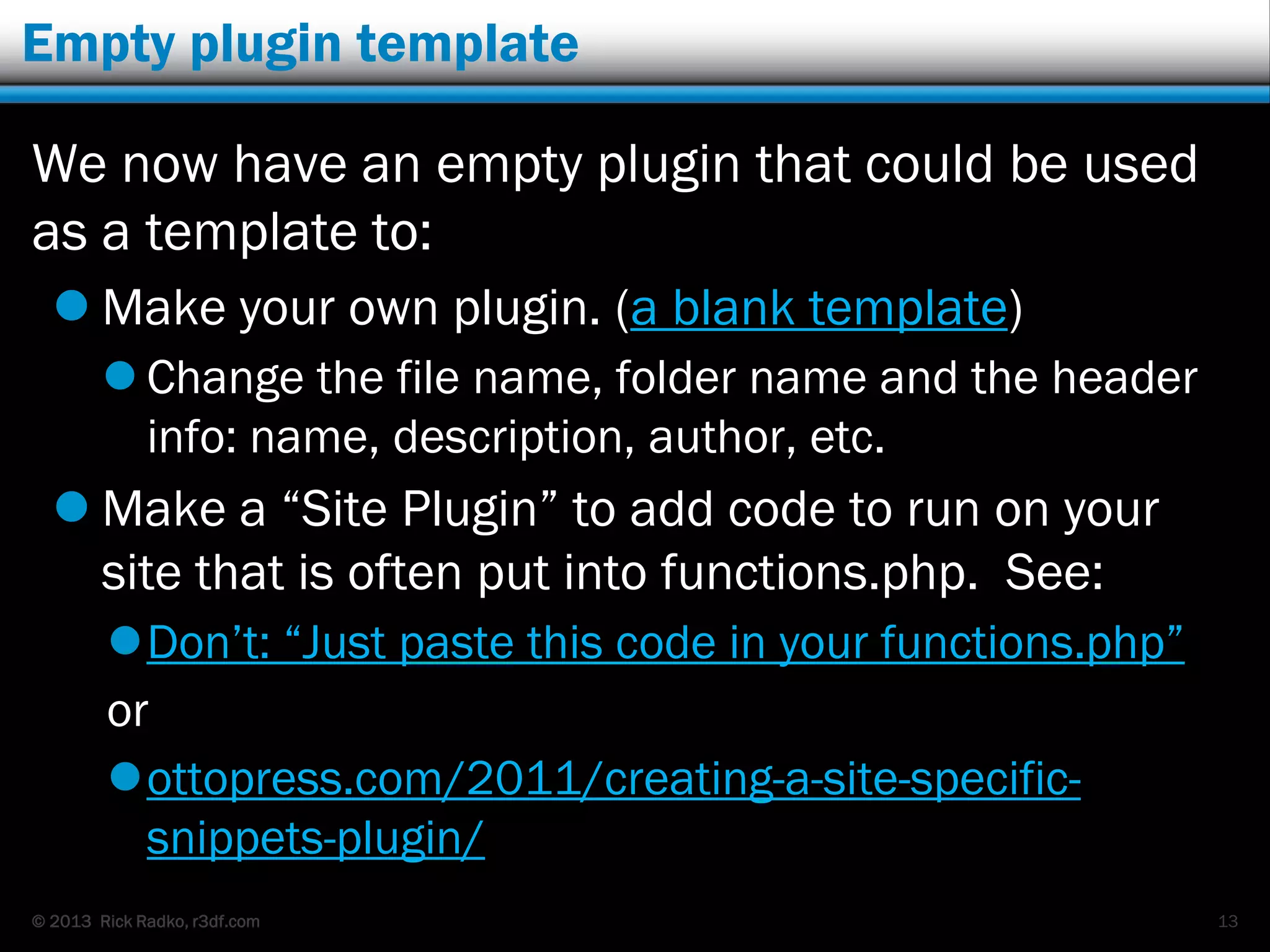
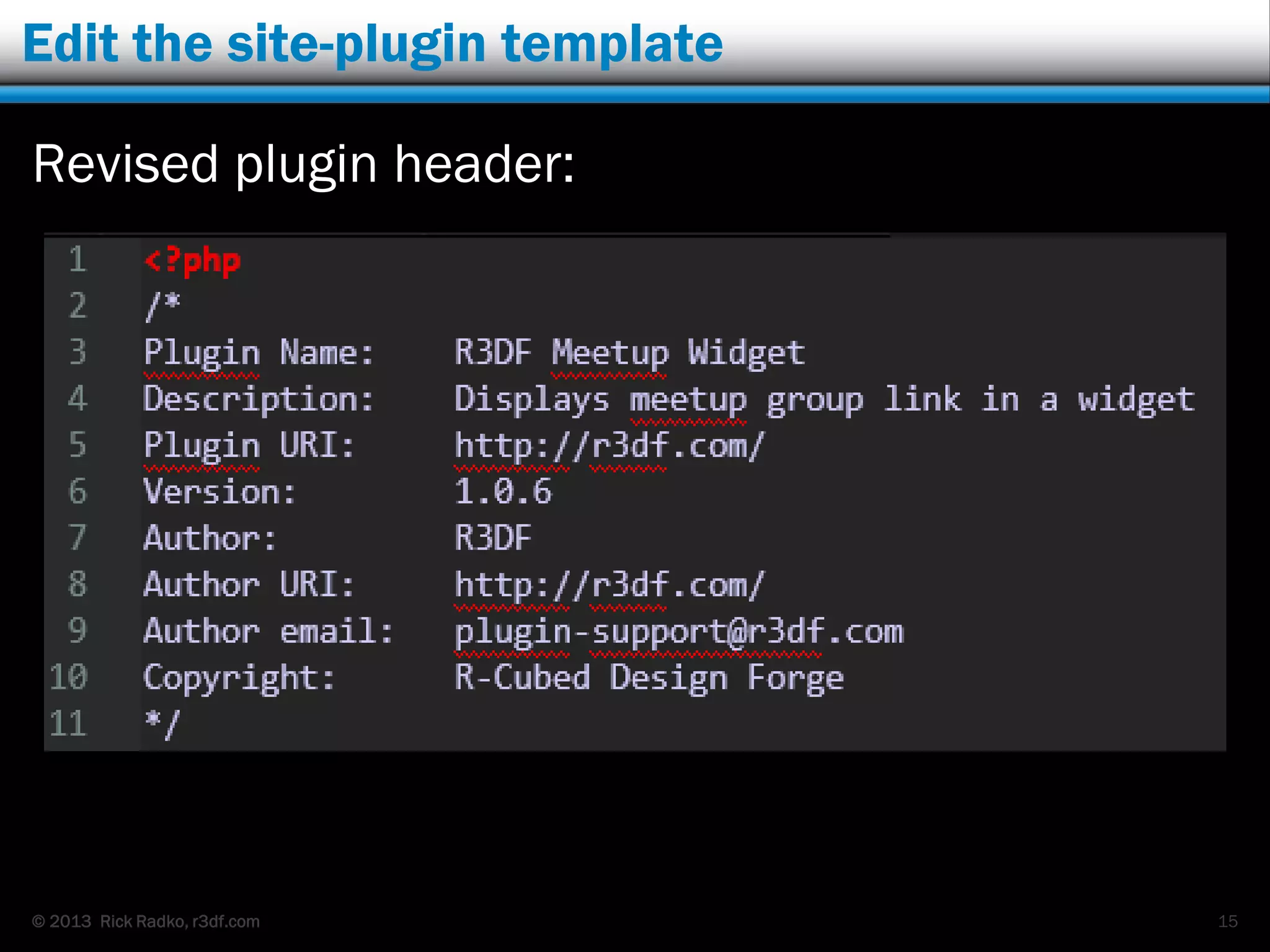
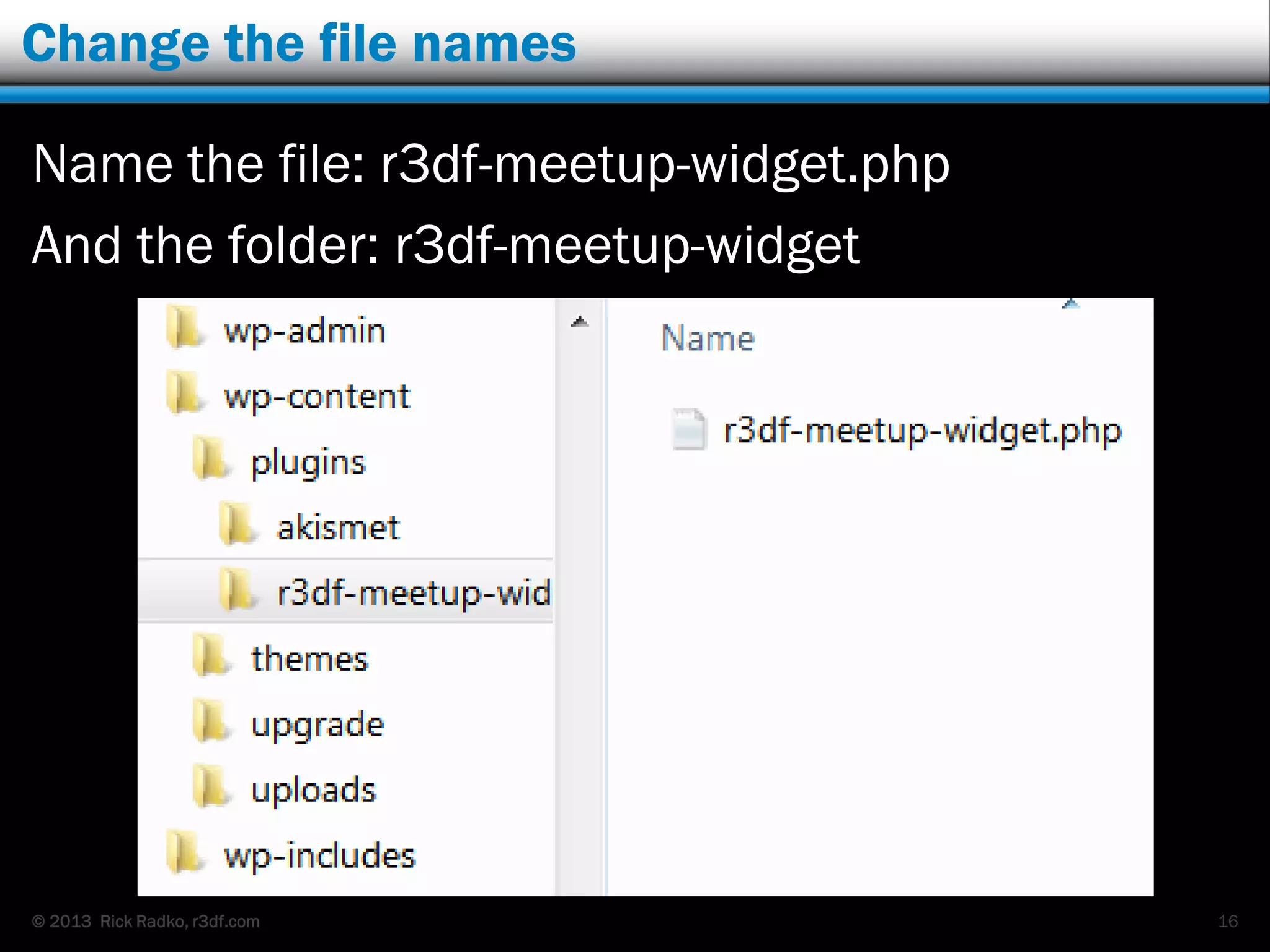
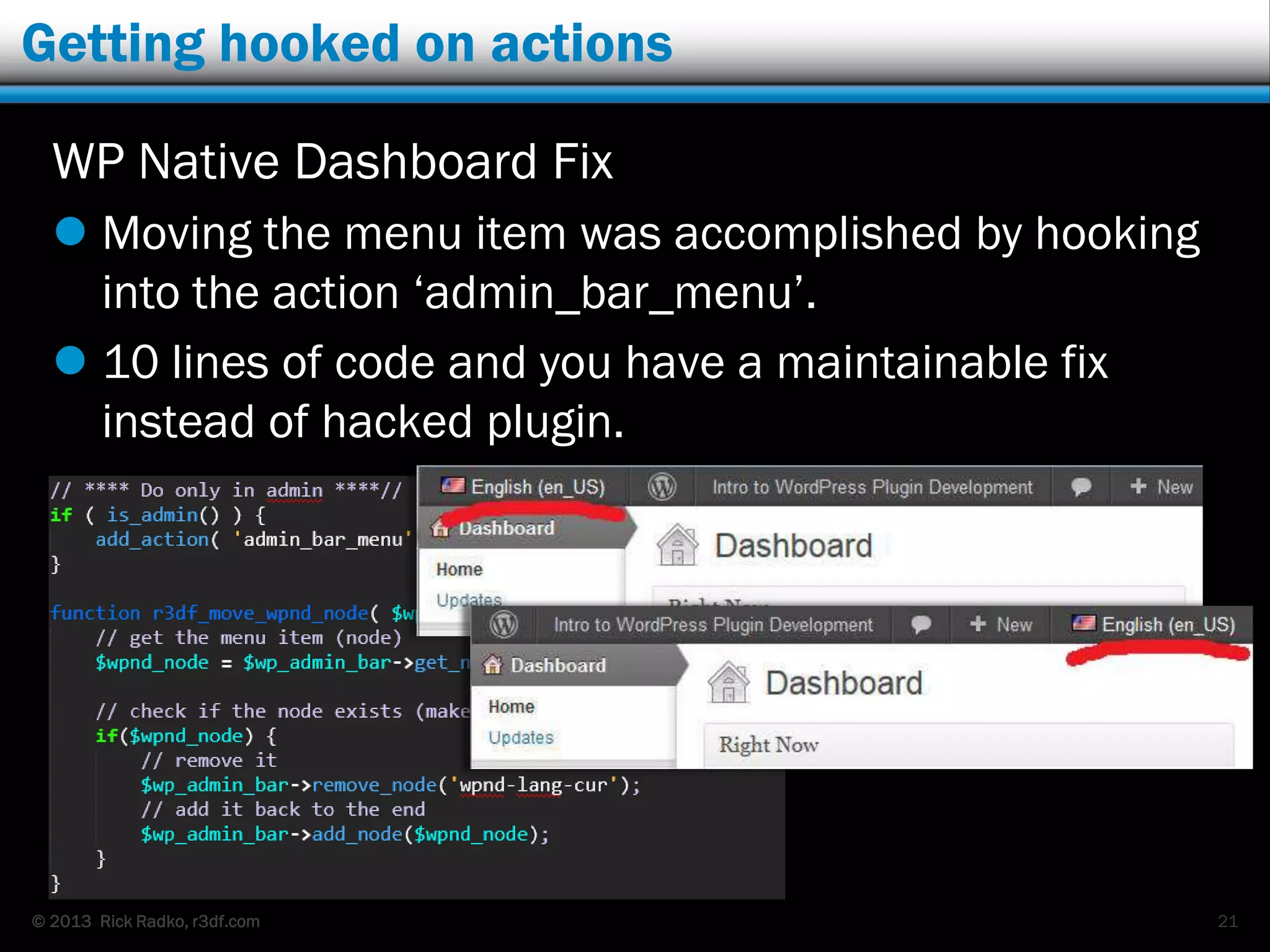
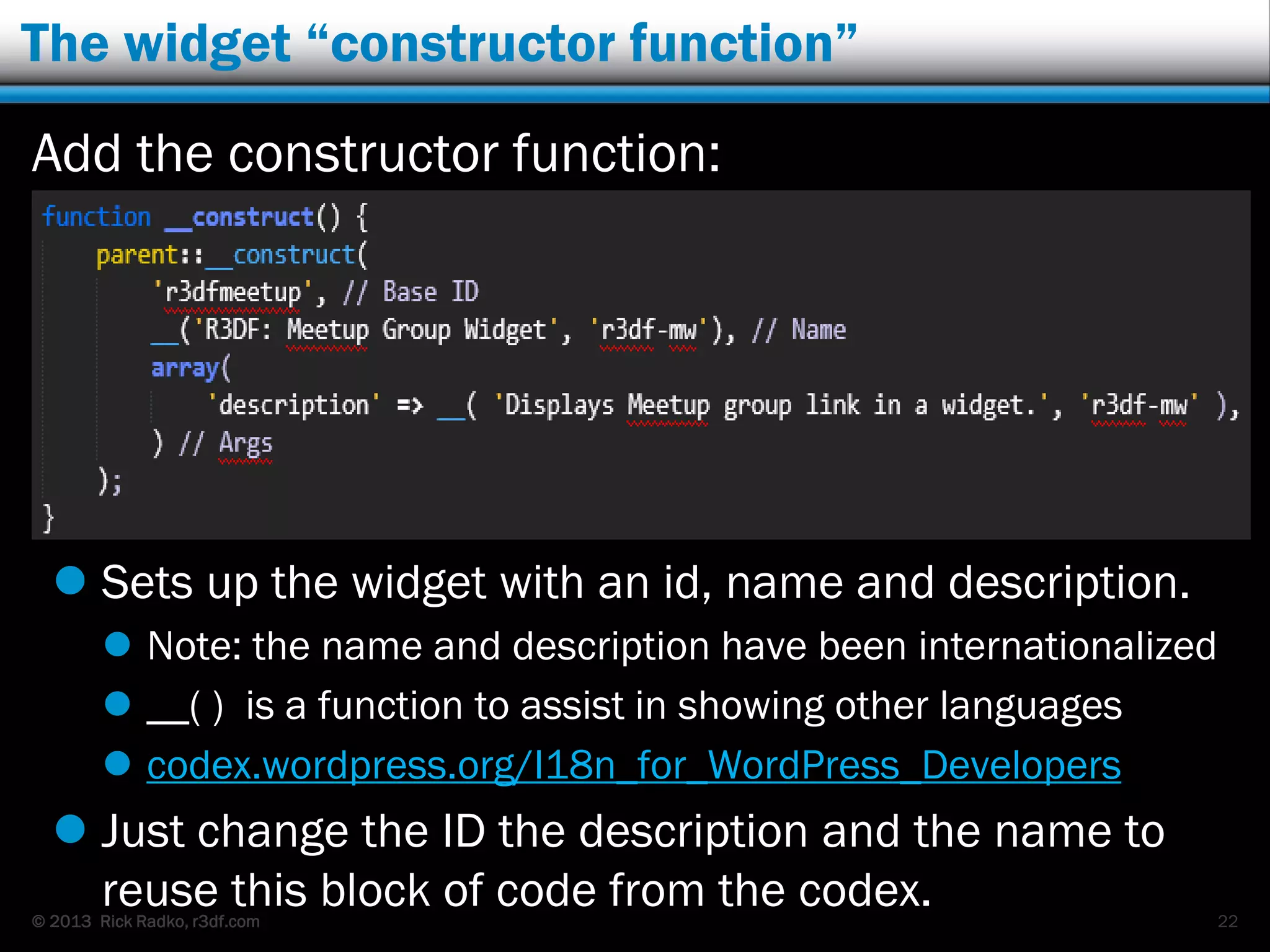
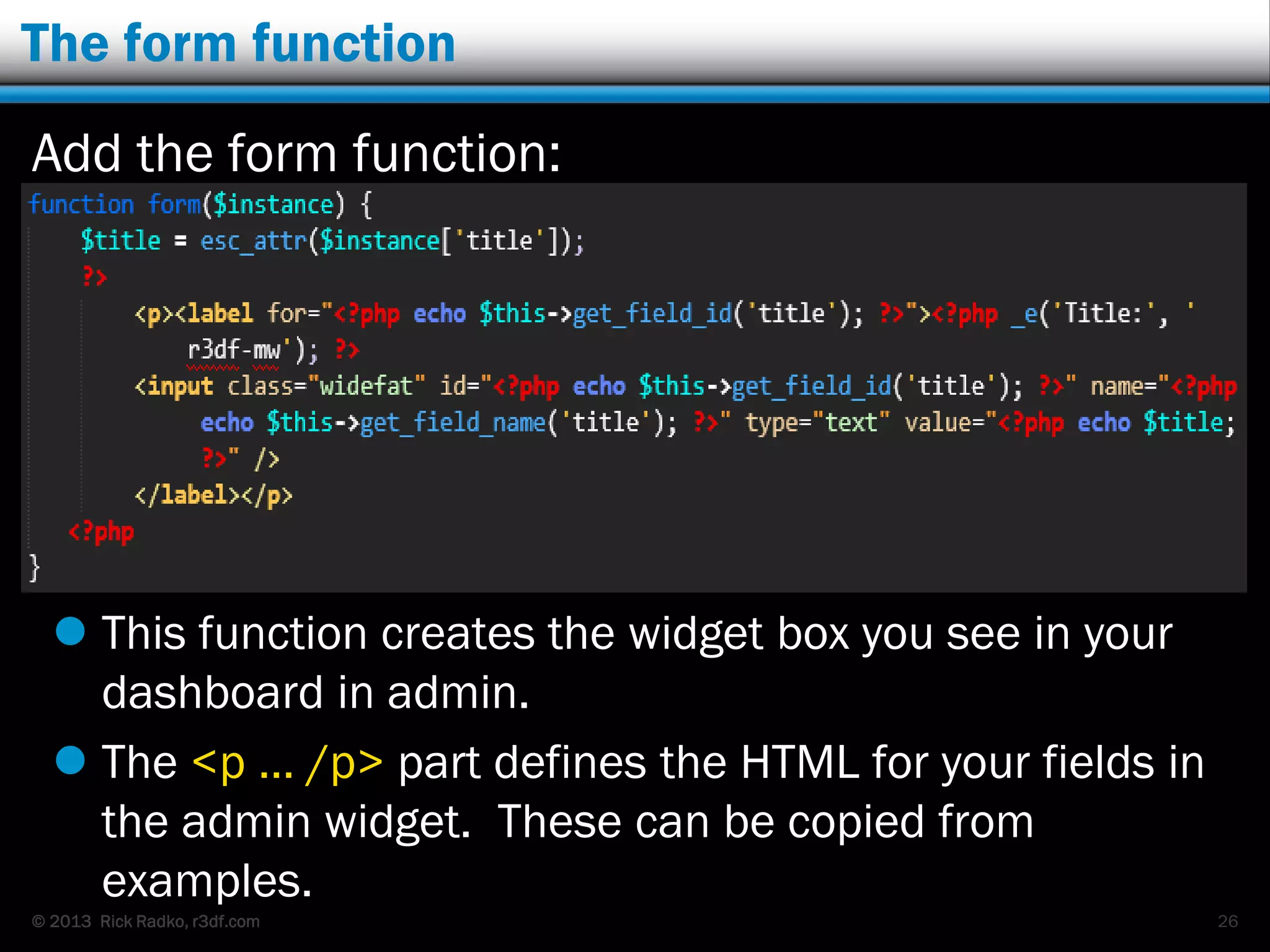
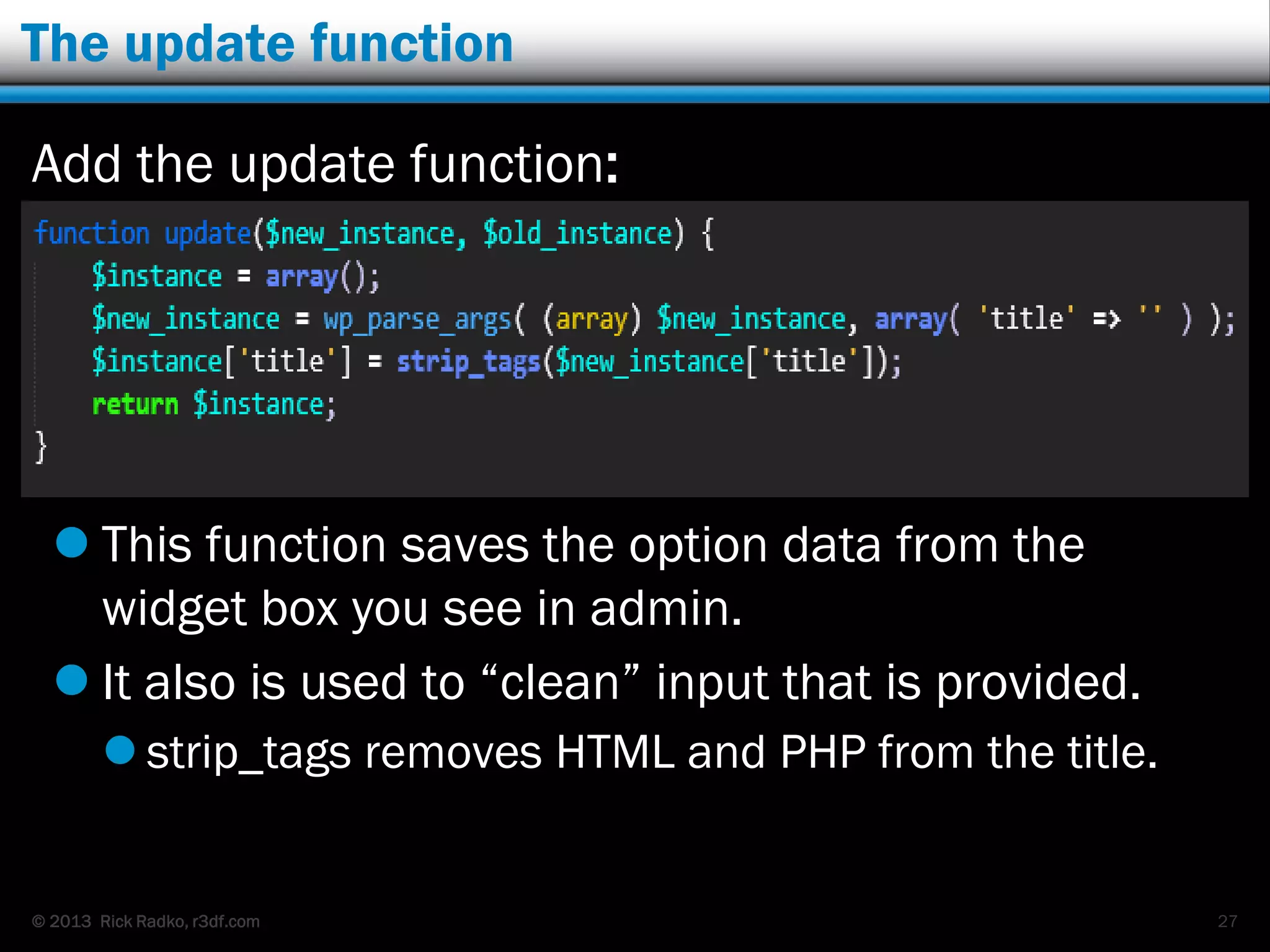
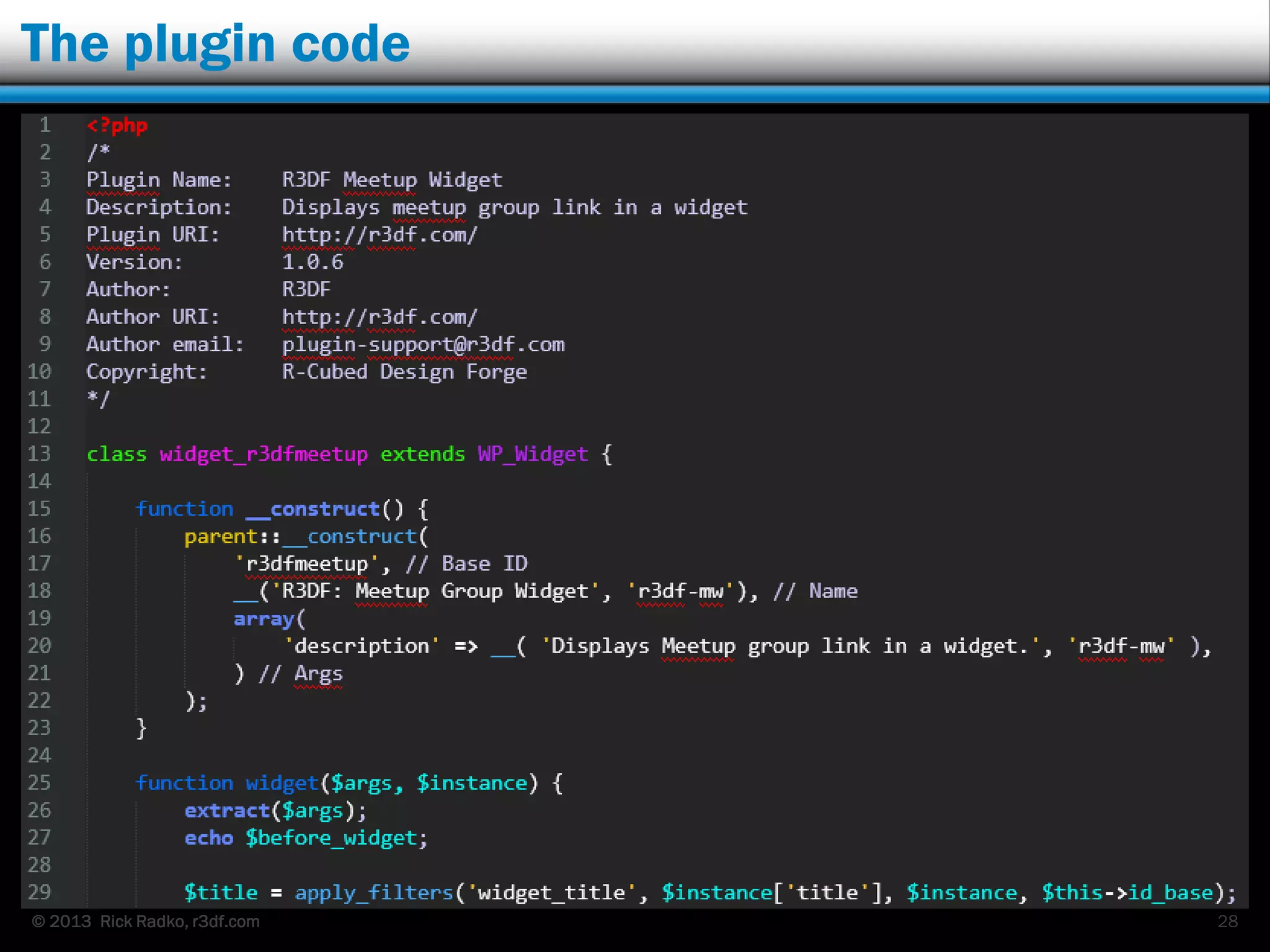
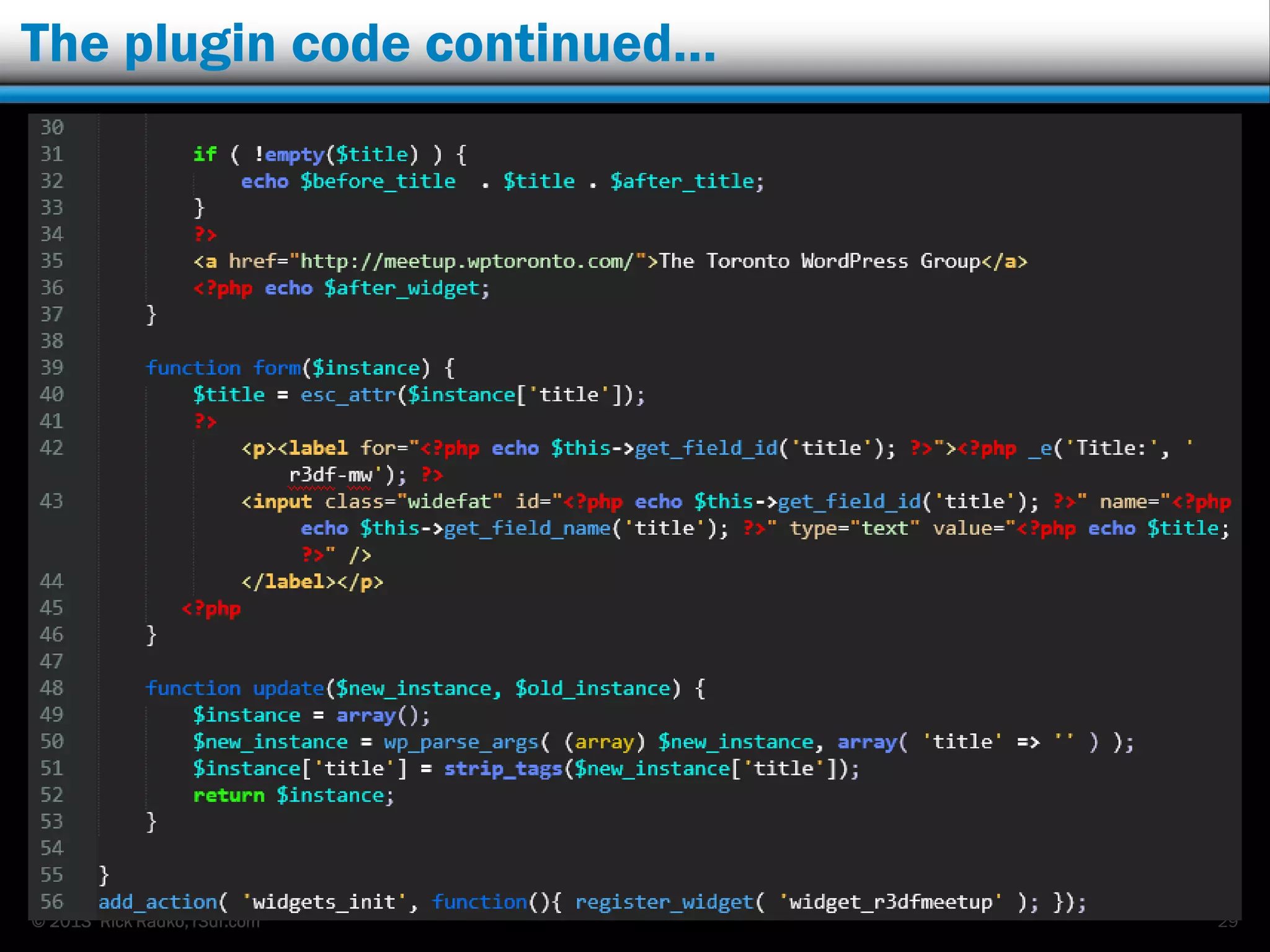
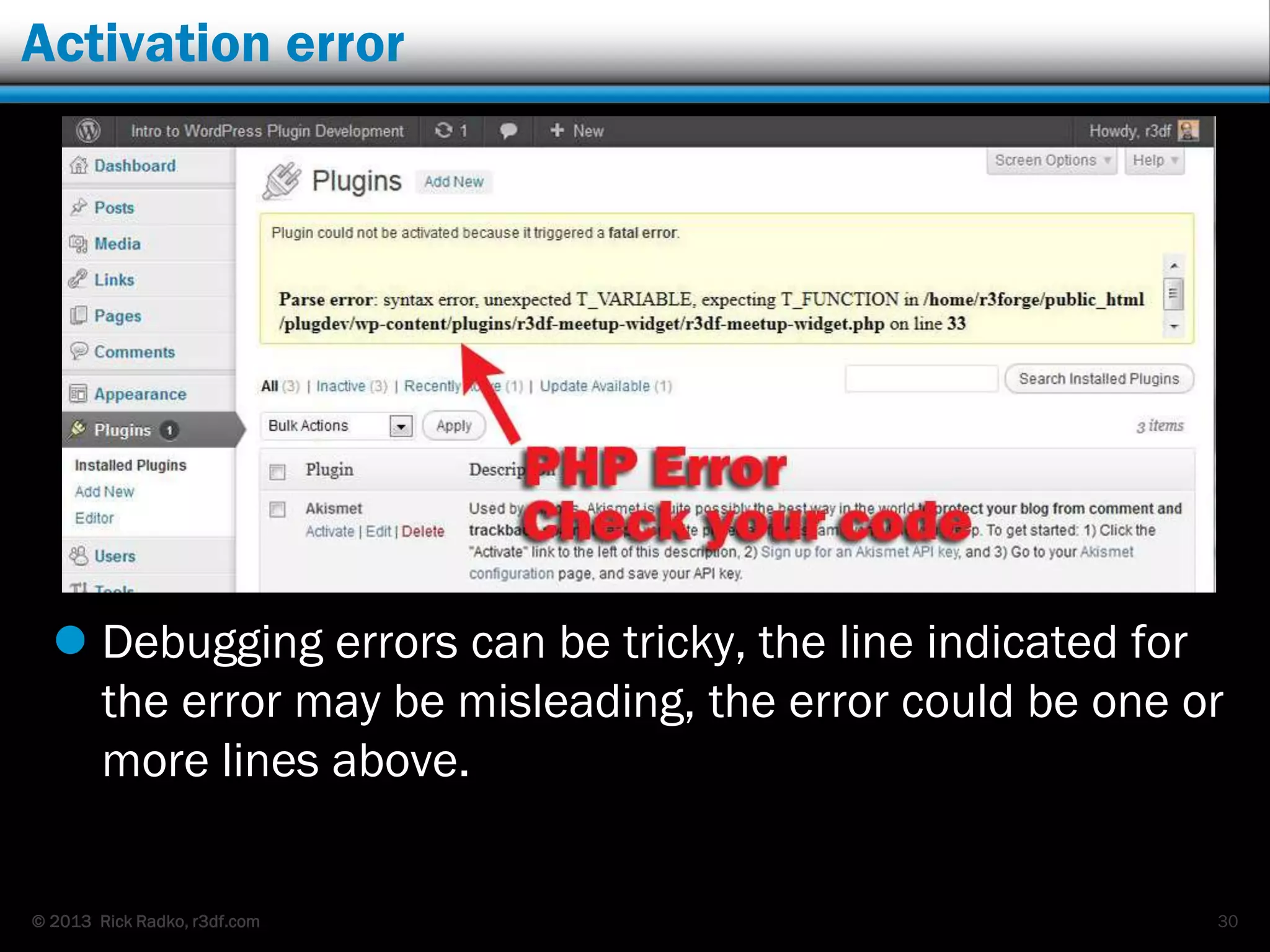
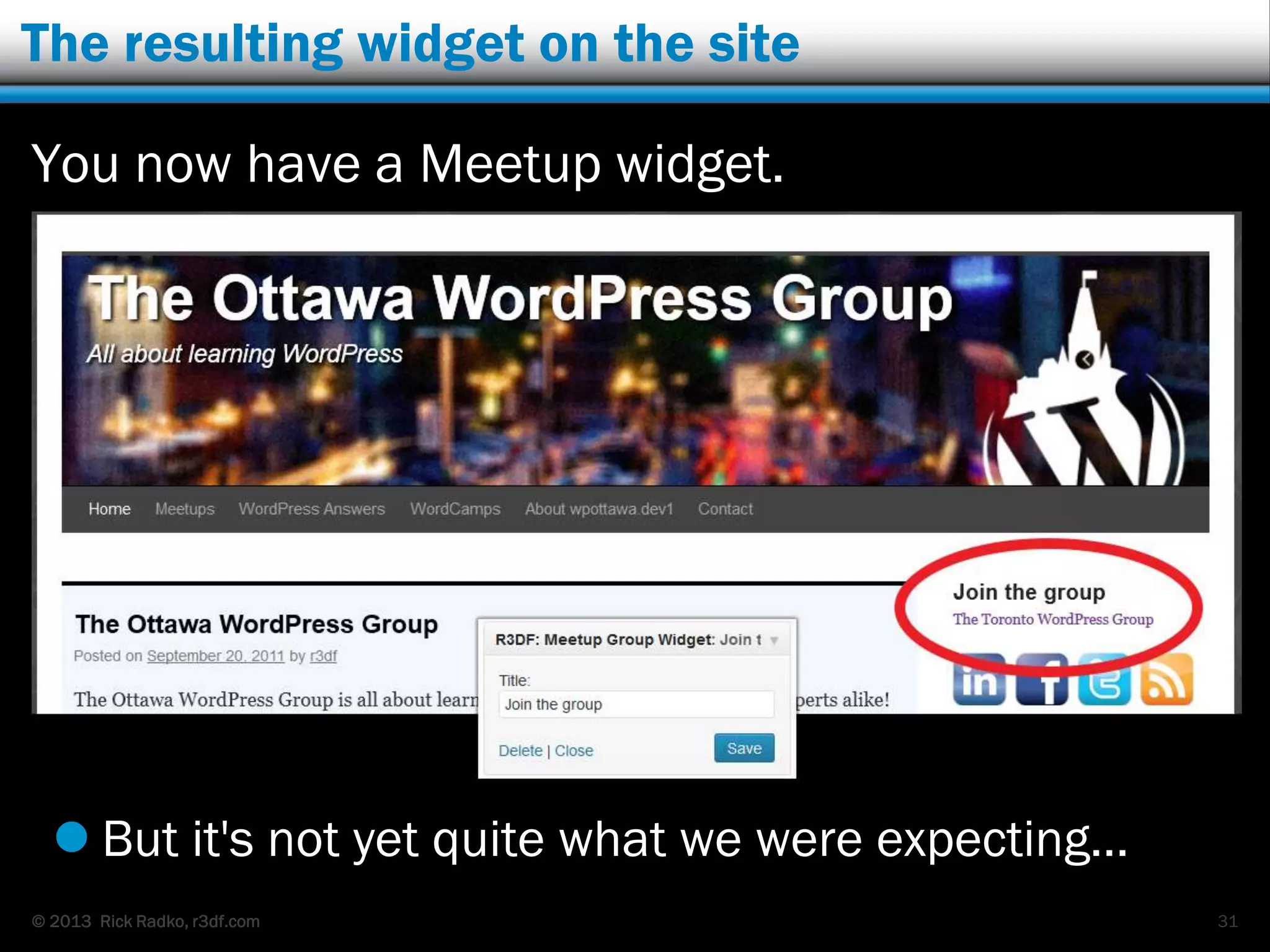
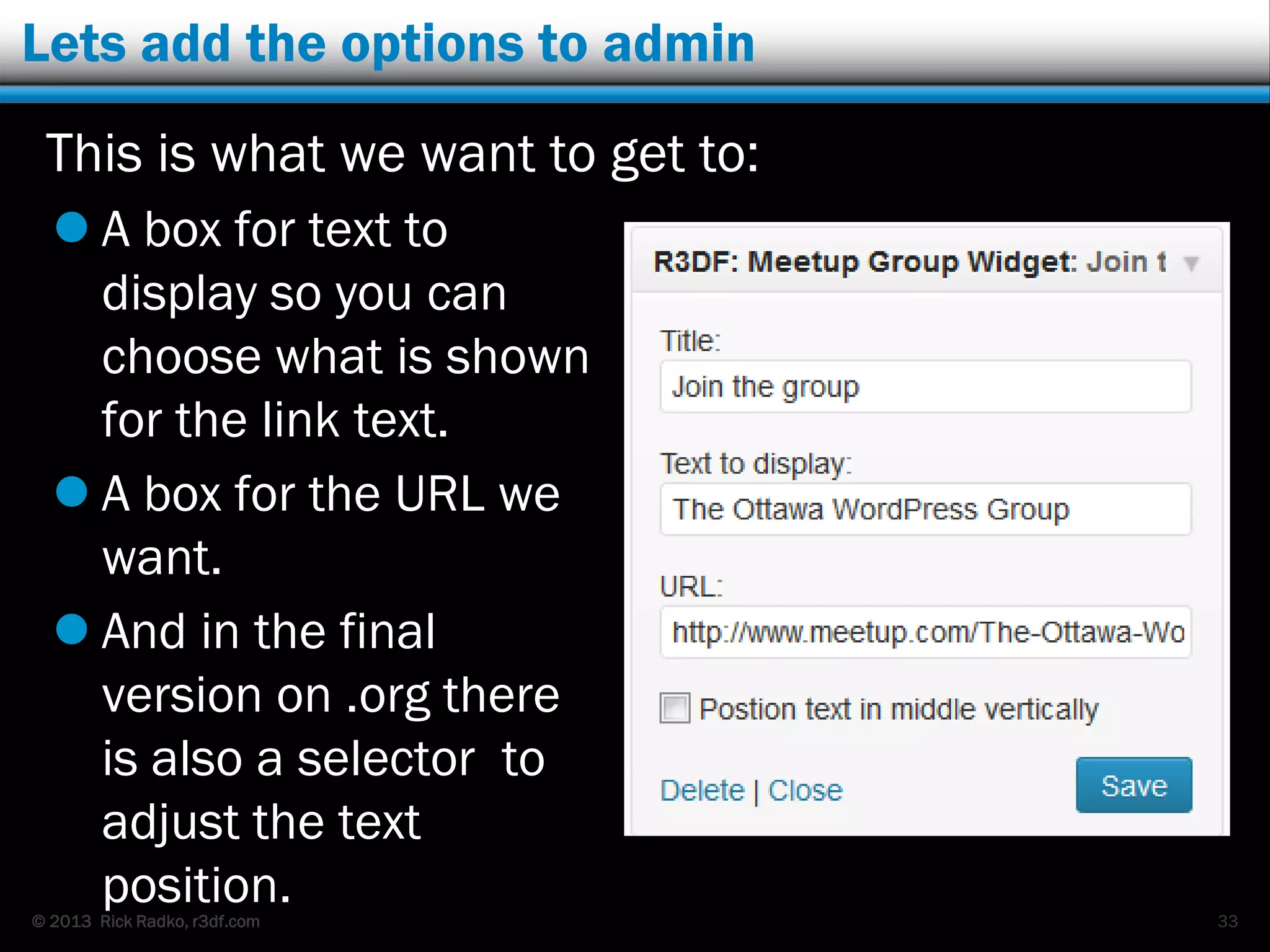
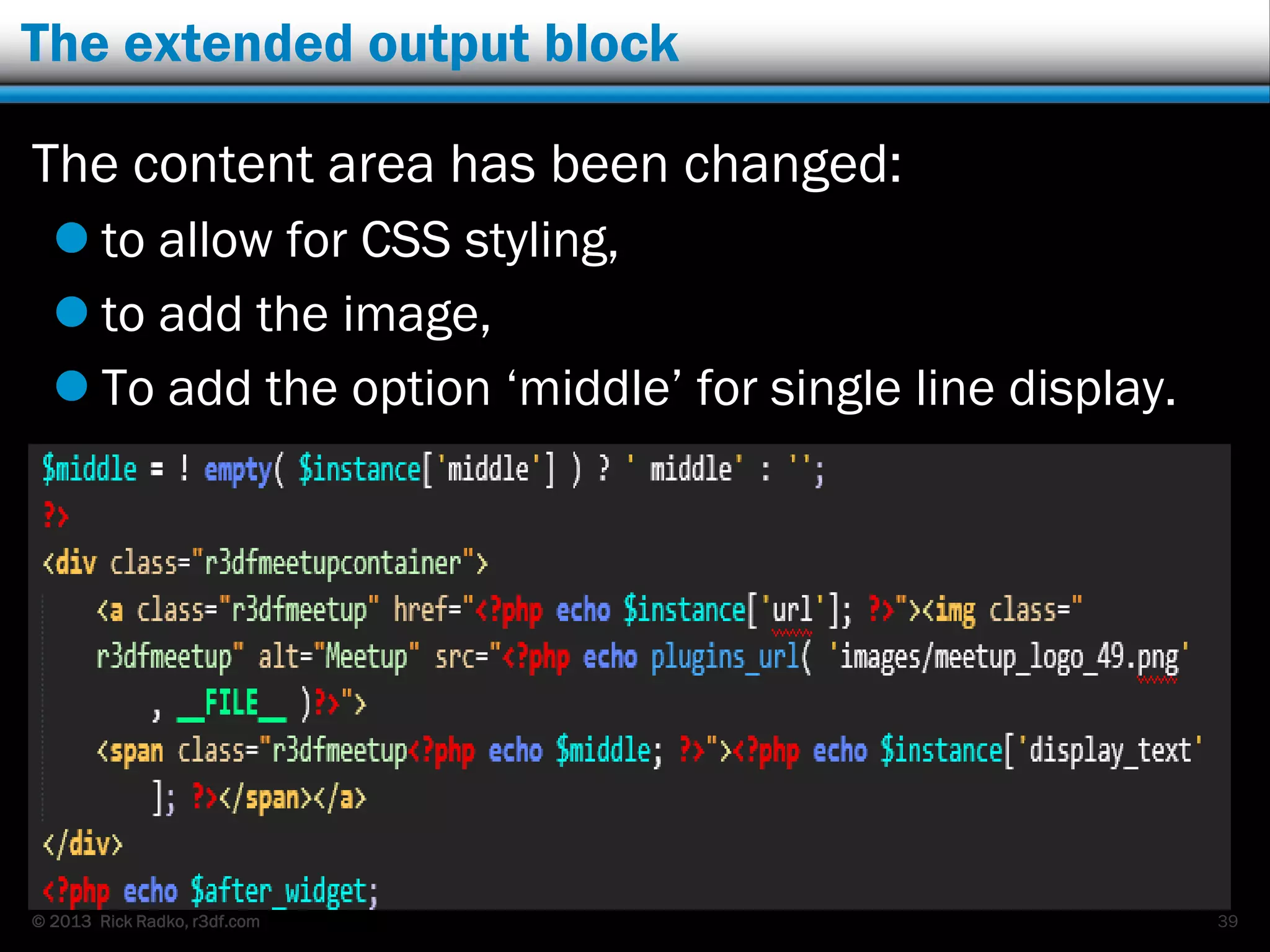
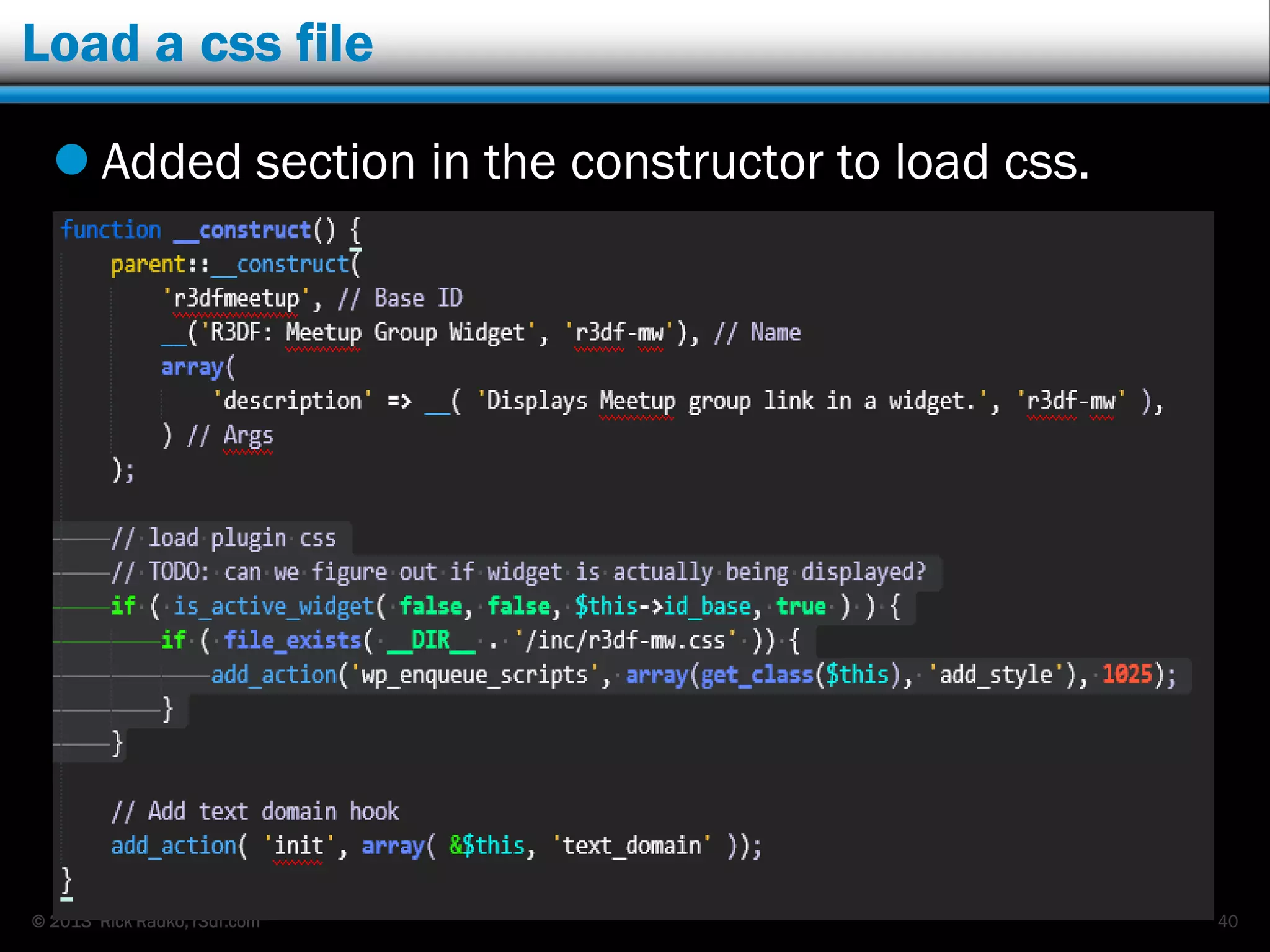
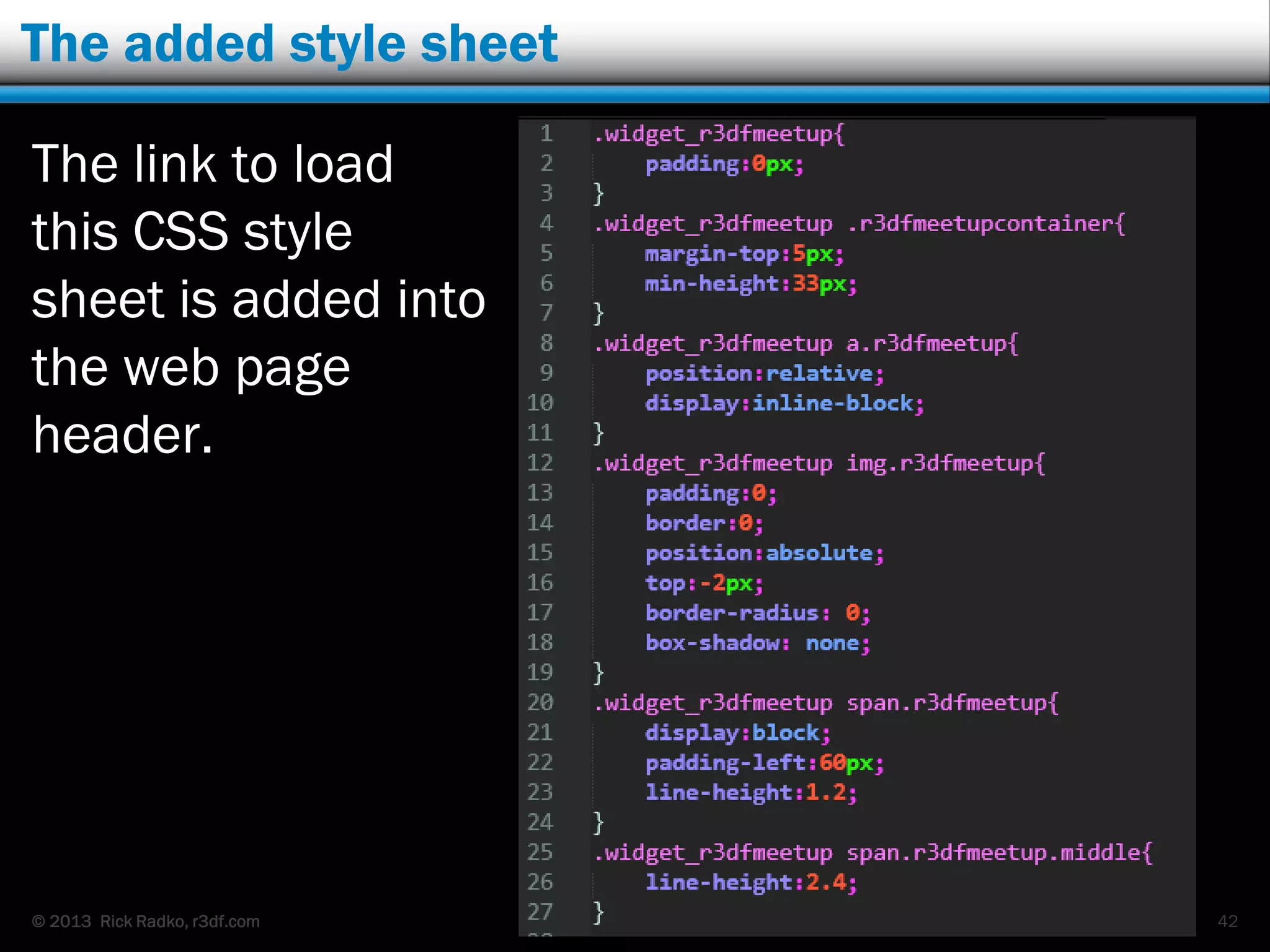
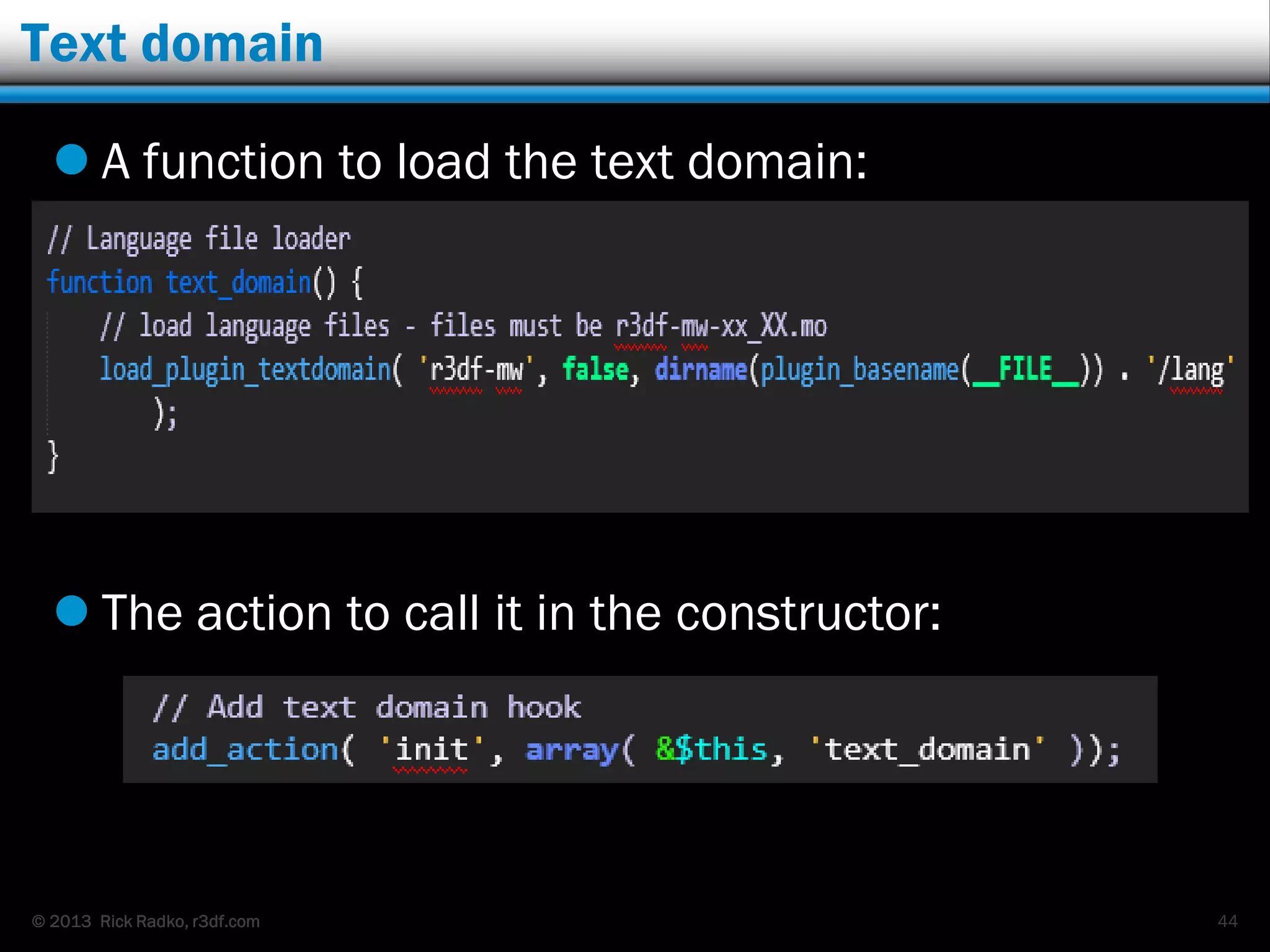
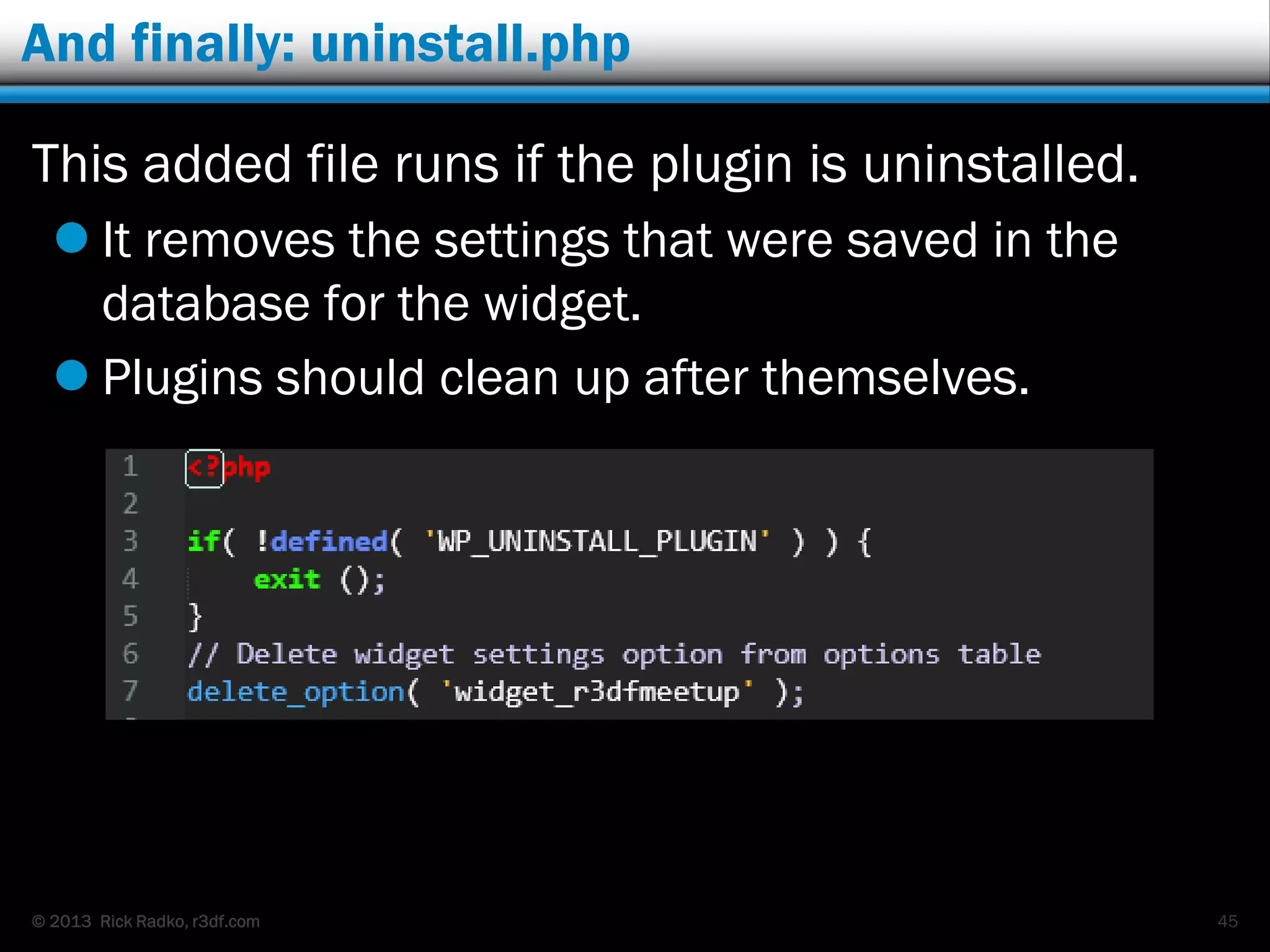
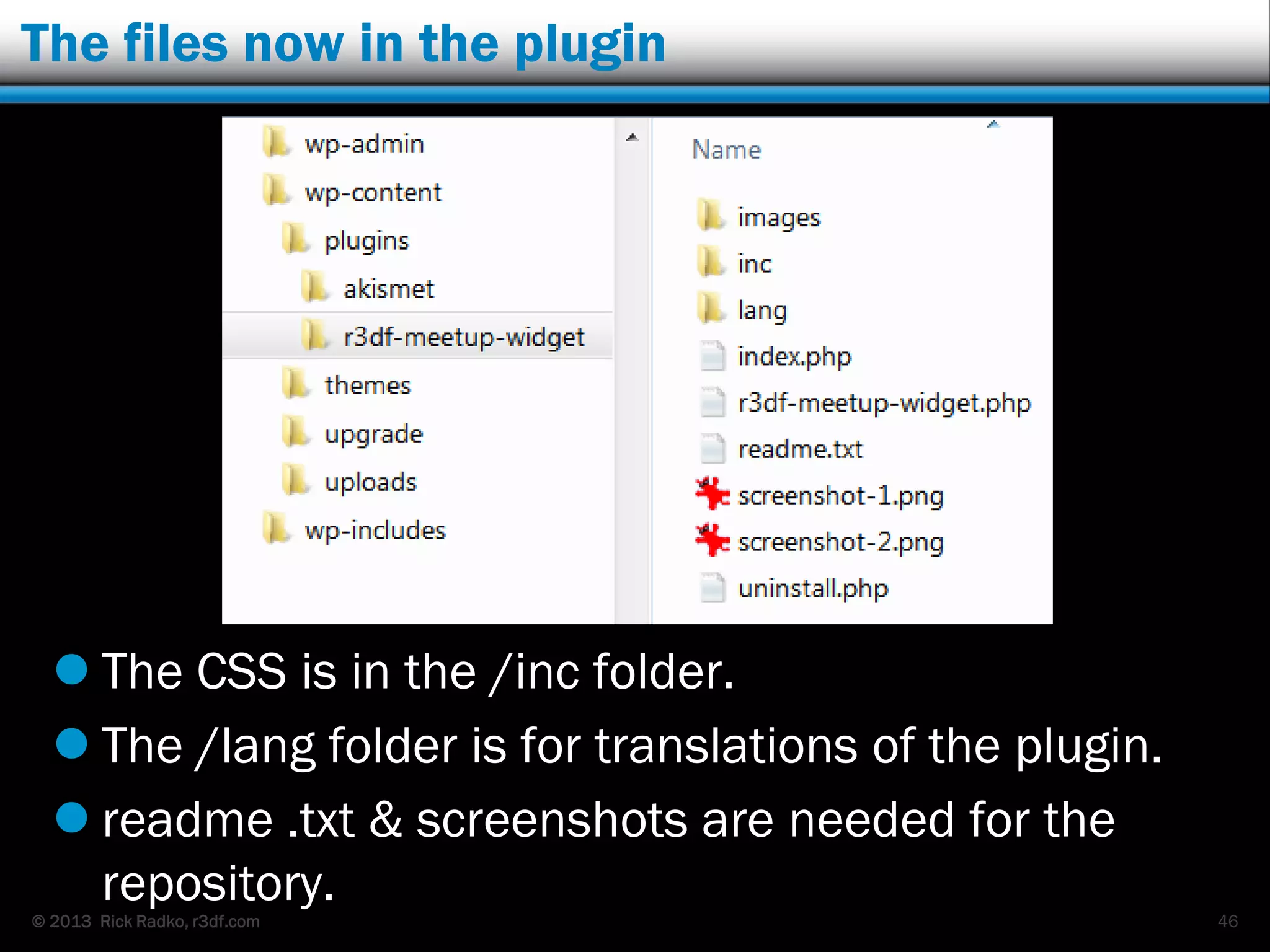
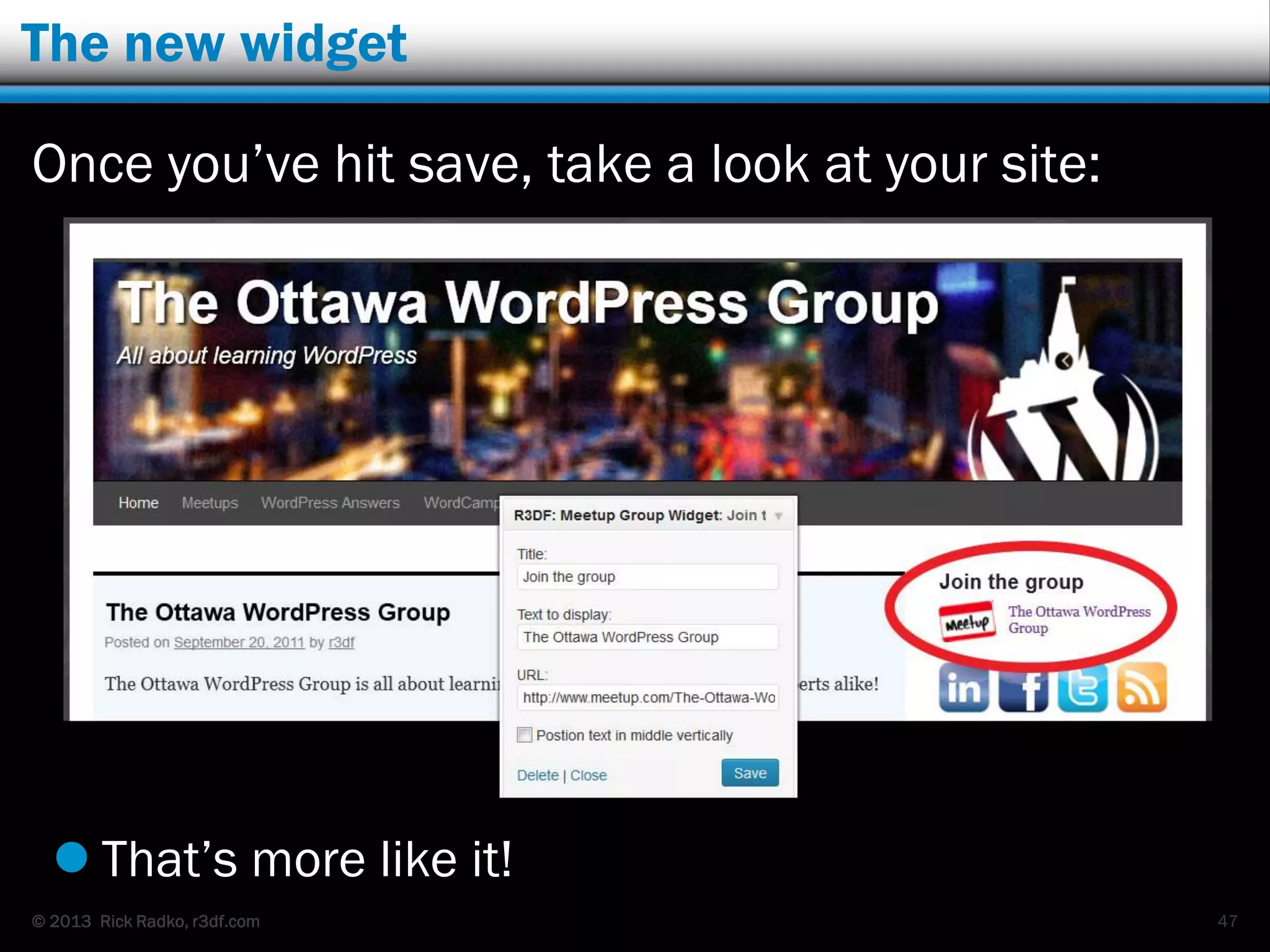
This document provides an overview of developing WordPress plugins. It begins with introductions and defines what plugins are. It then discusses the necessary tools for plugin development like code editors, development environments, and the WordPress Codex. The document walks through creating a basic Meetup widget plugin, starting with the required plugin header and basic structure. It demonstrates how to register and output a widget using the Widgets API. It also introduces actions and filters. The document expands on this basic plugin by adding options to the widget form, saving the options, and updating the widget output to use the new options.