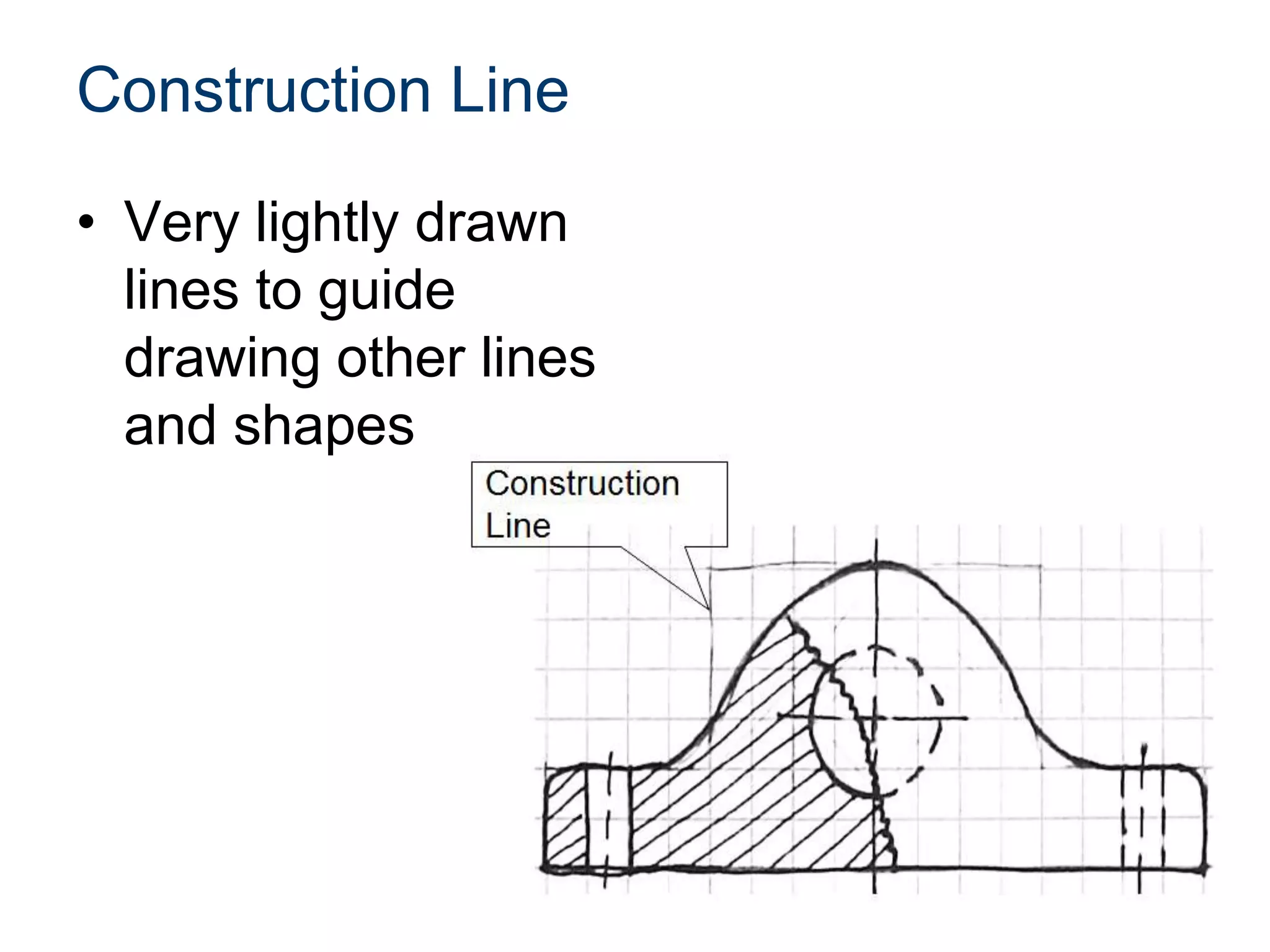
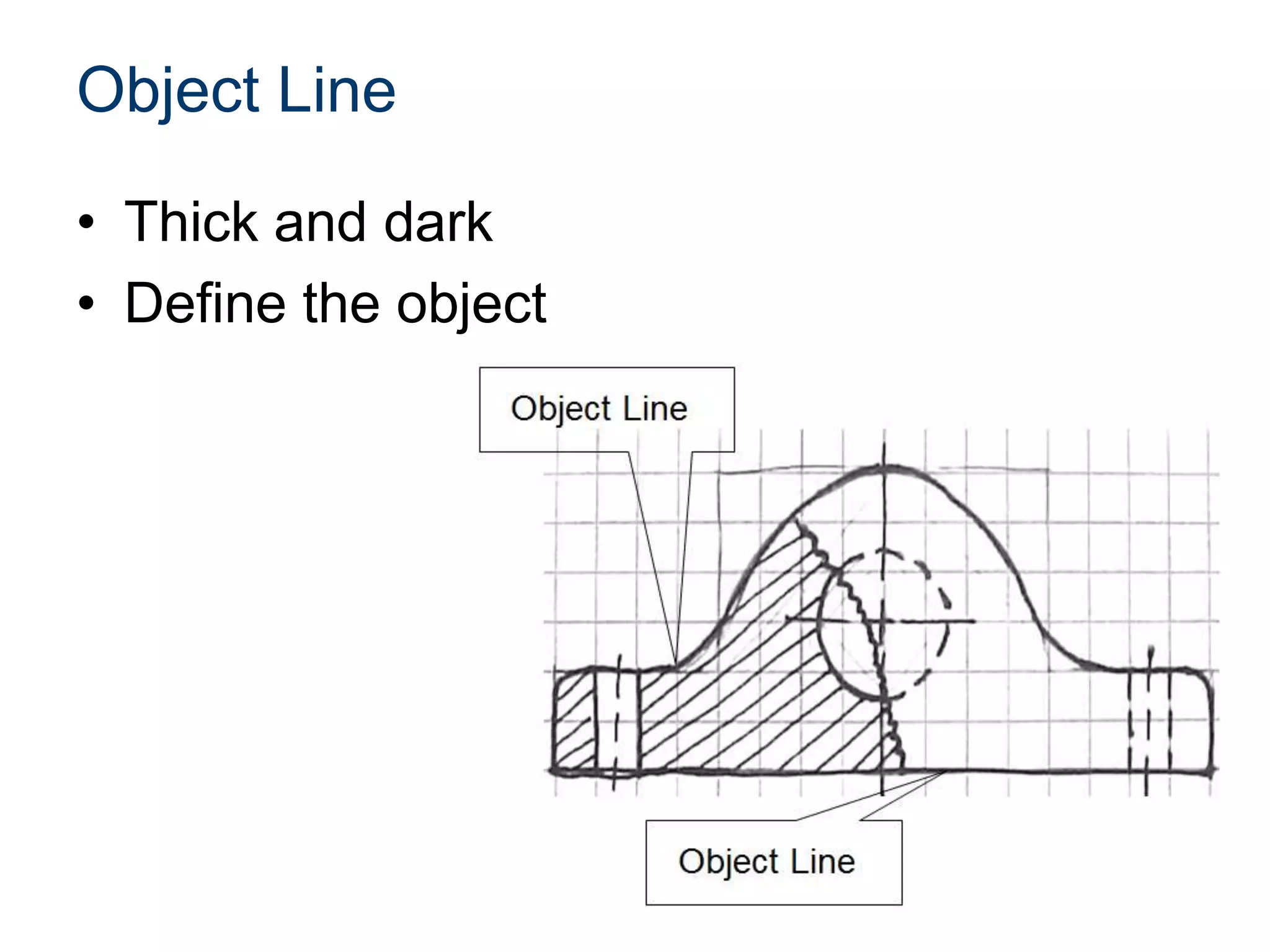
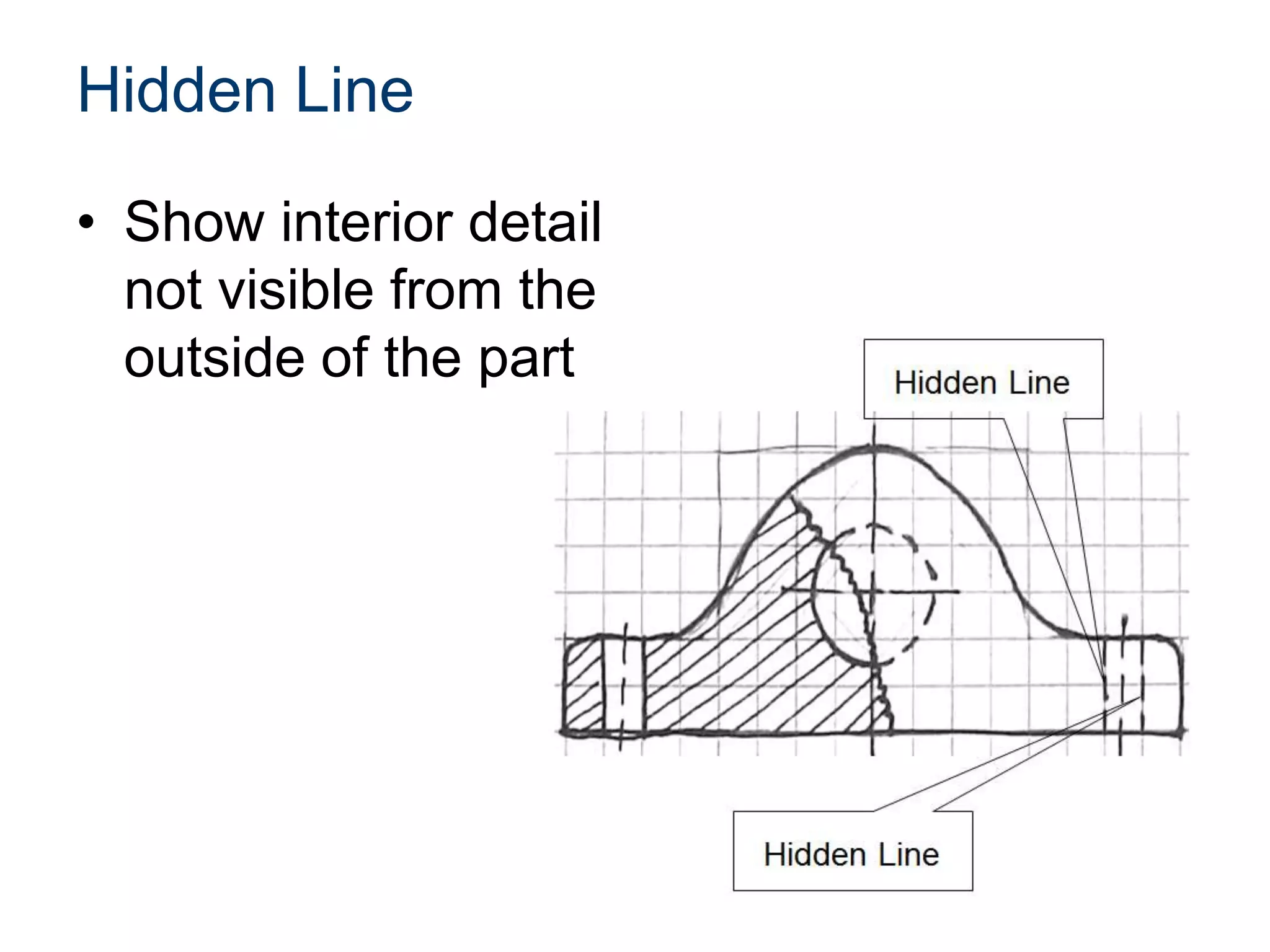
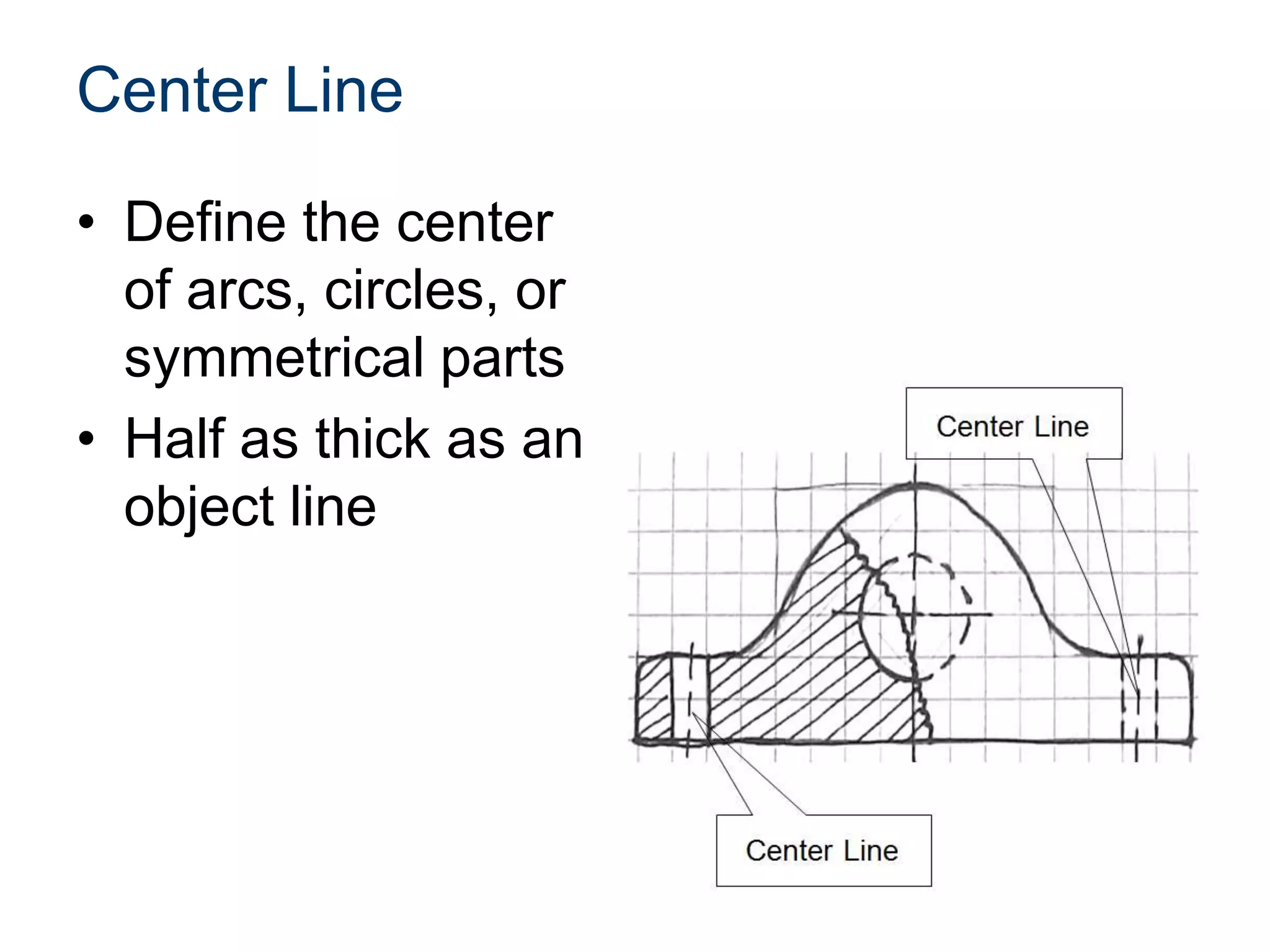
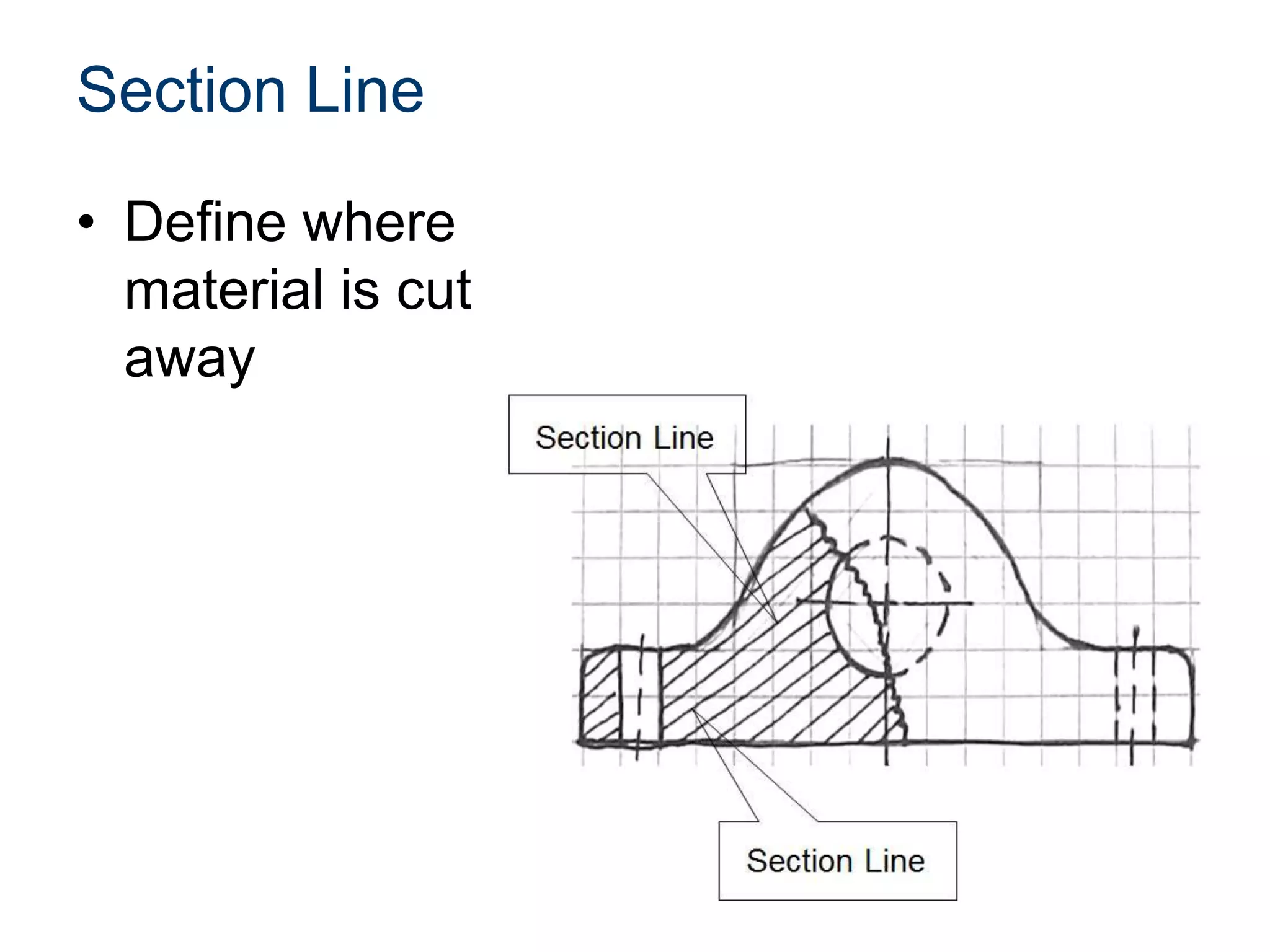
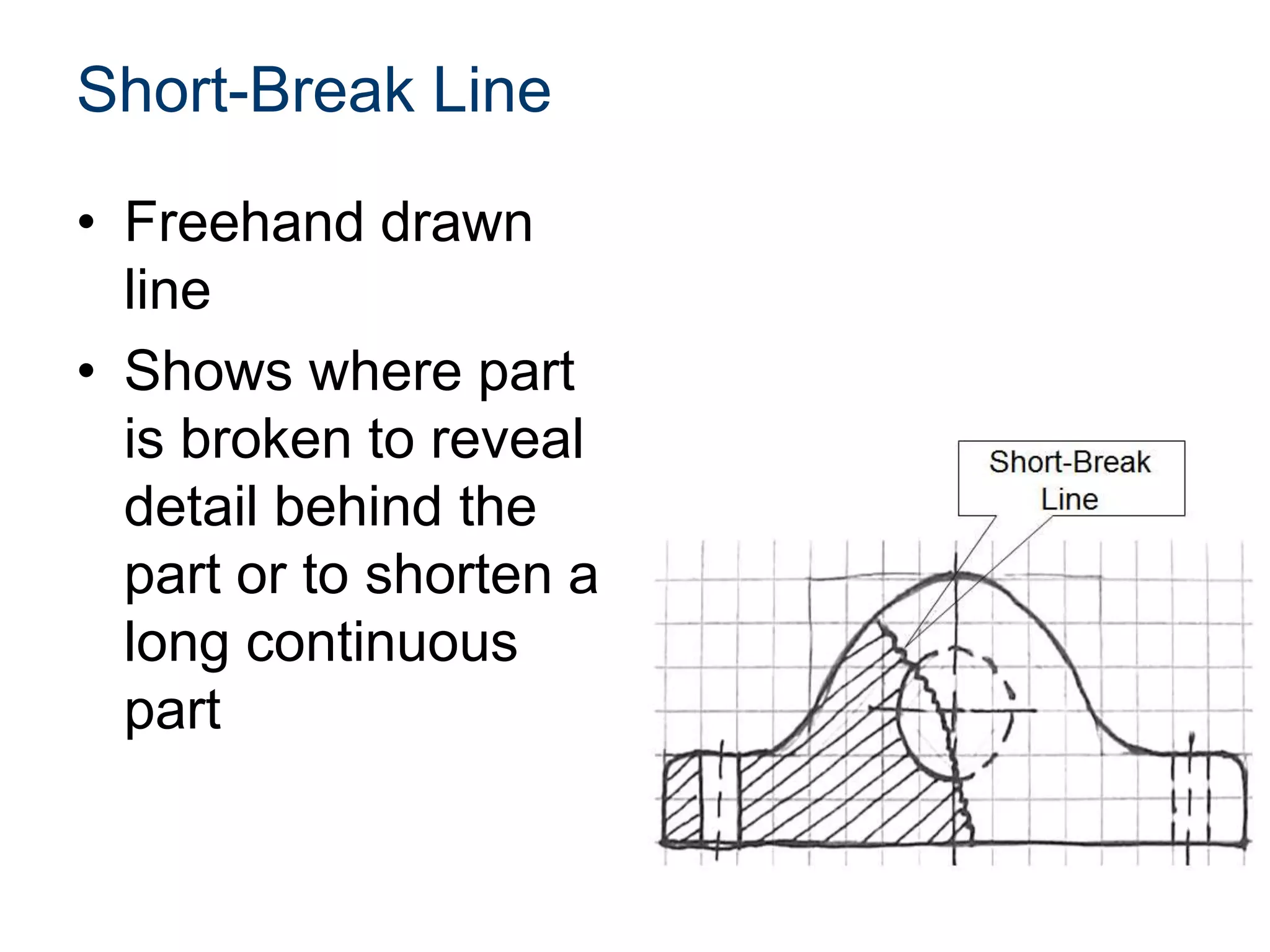
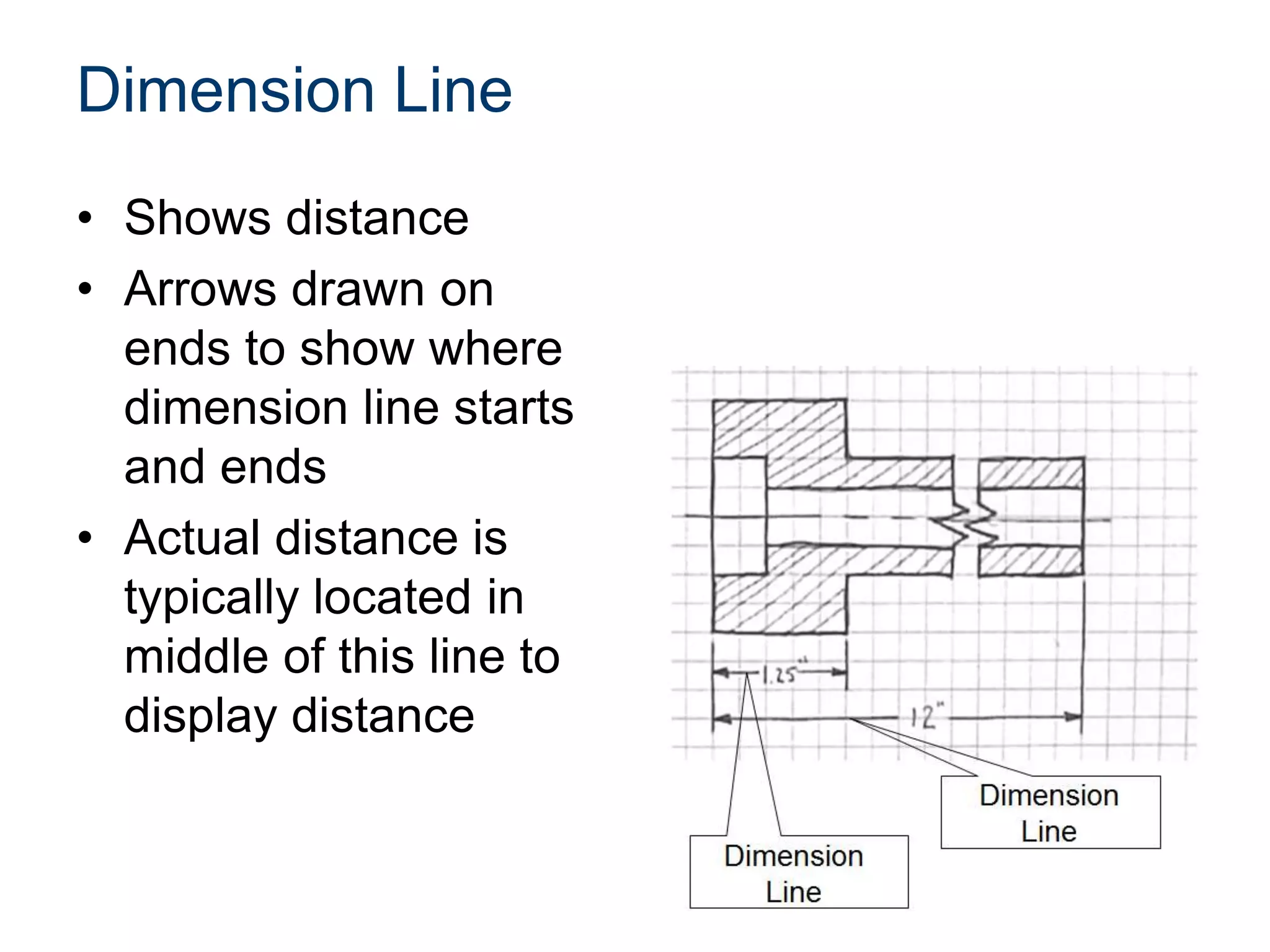
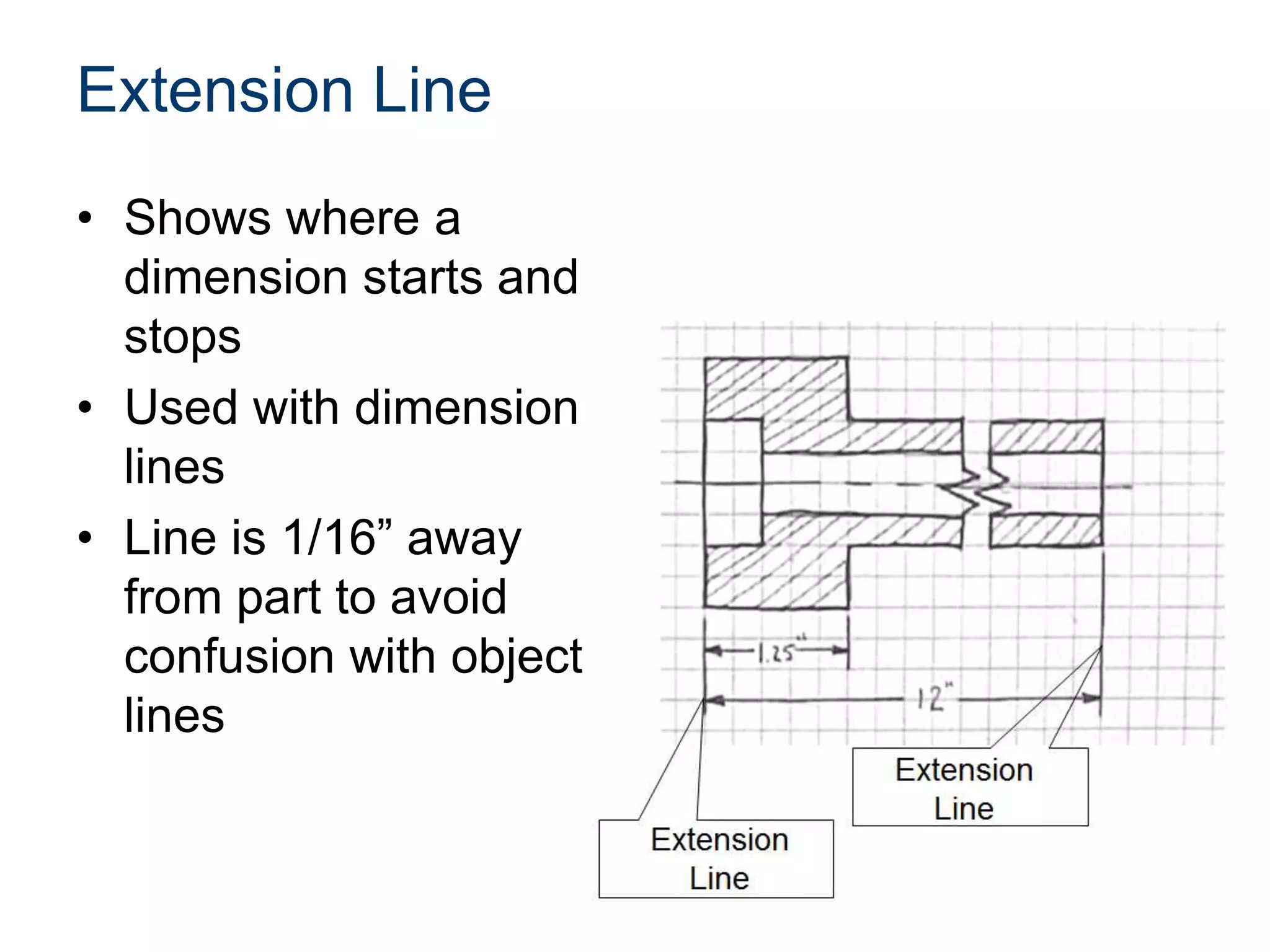
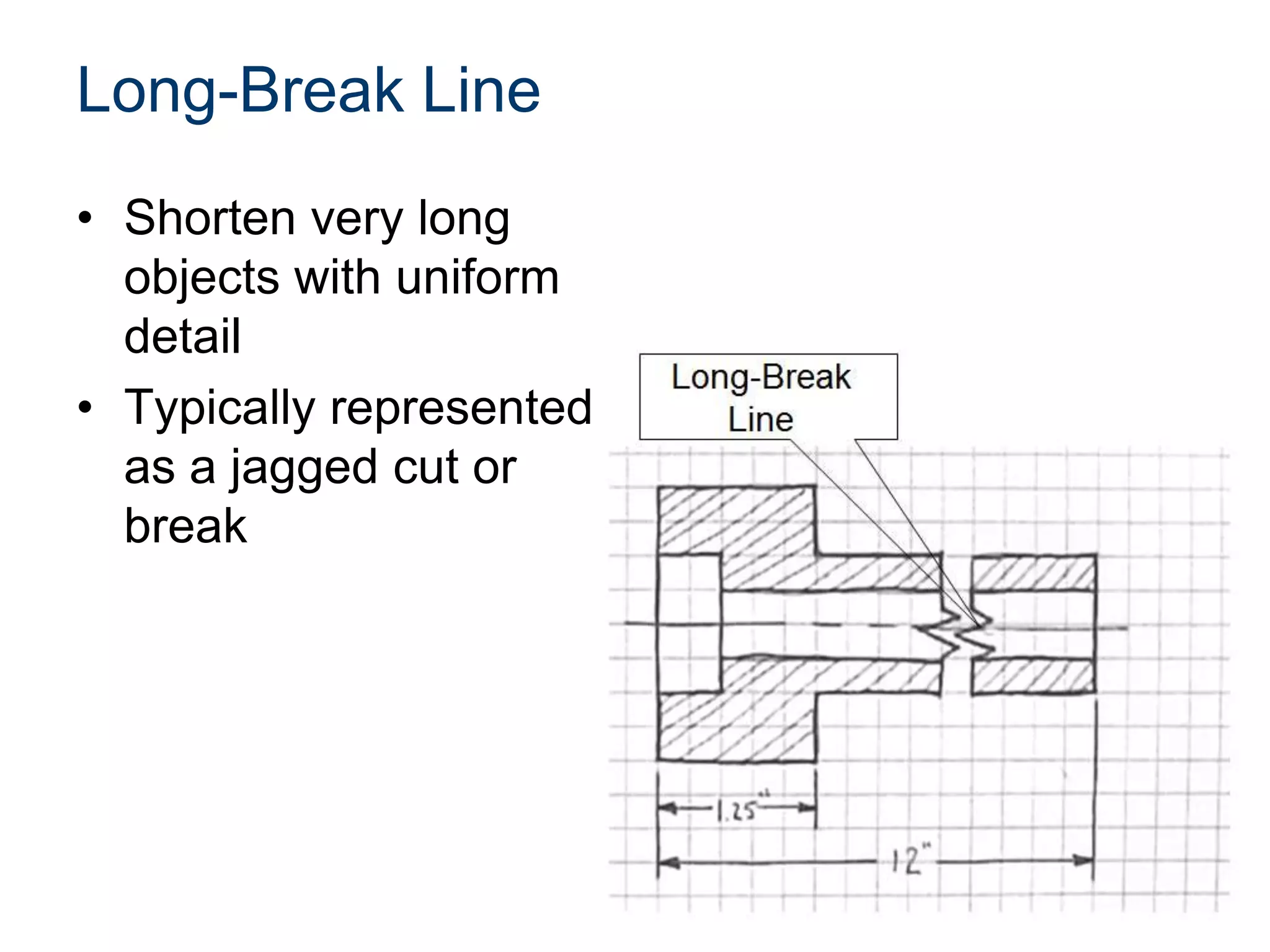
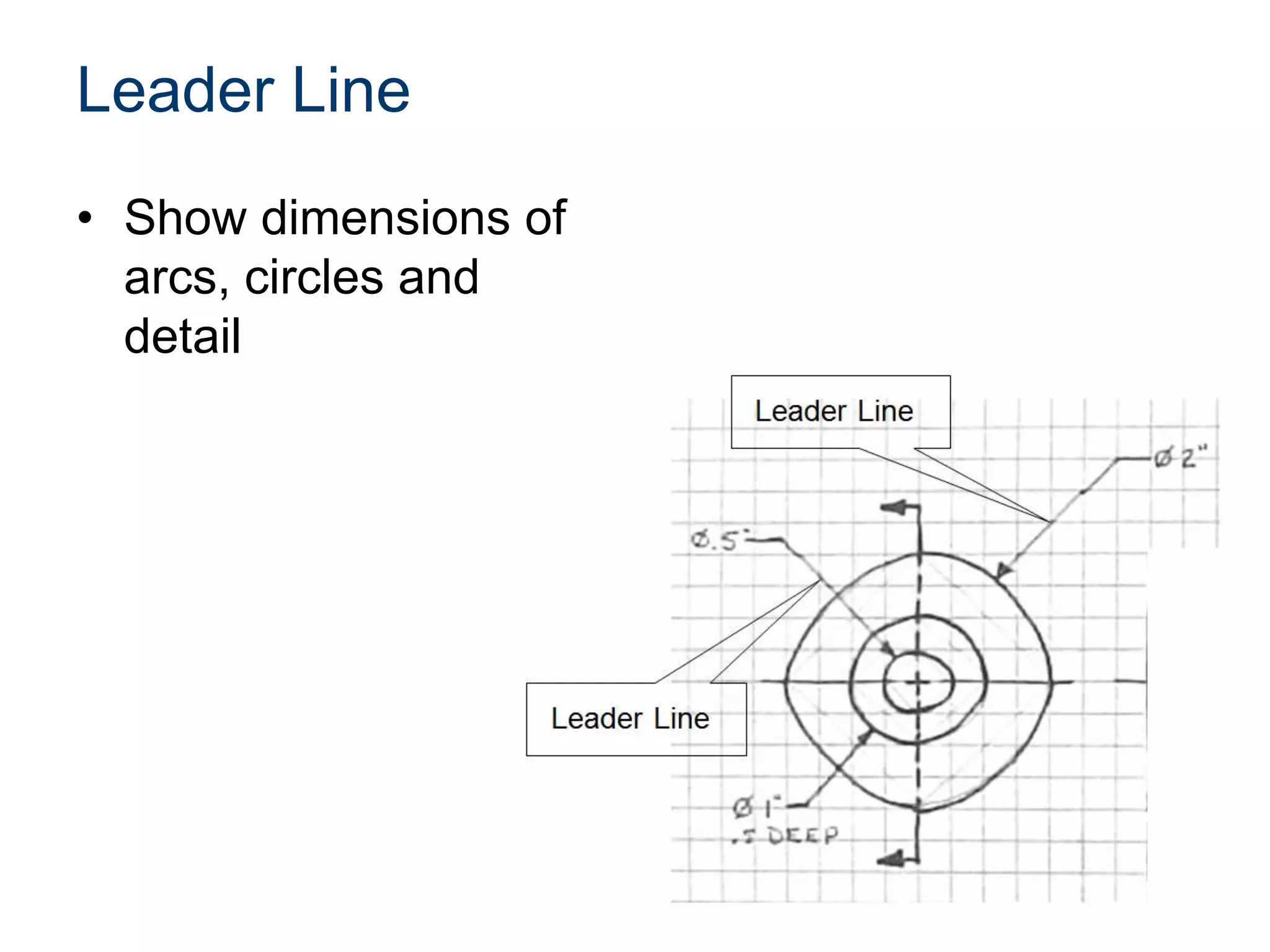
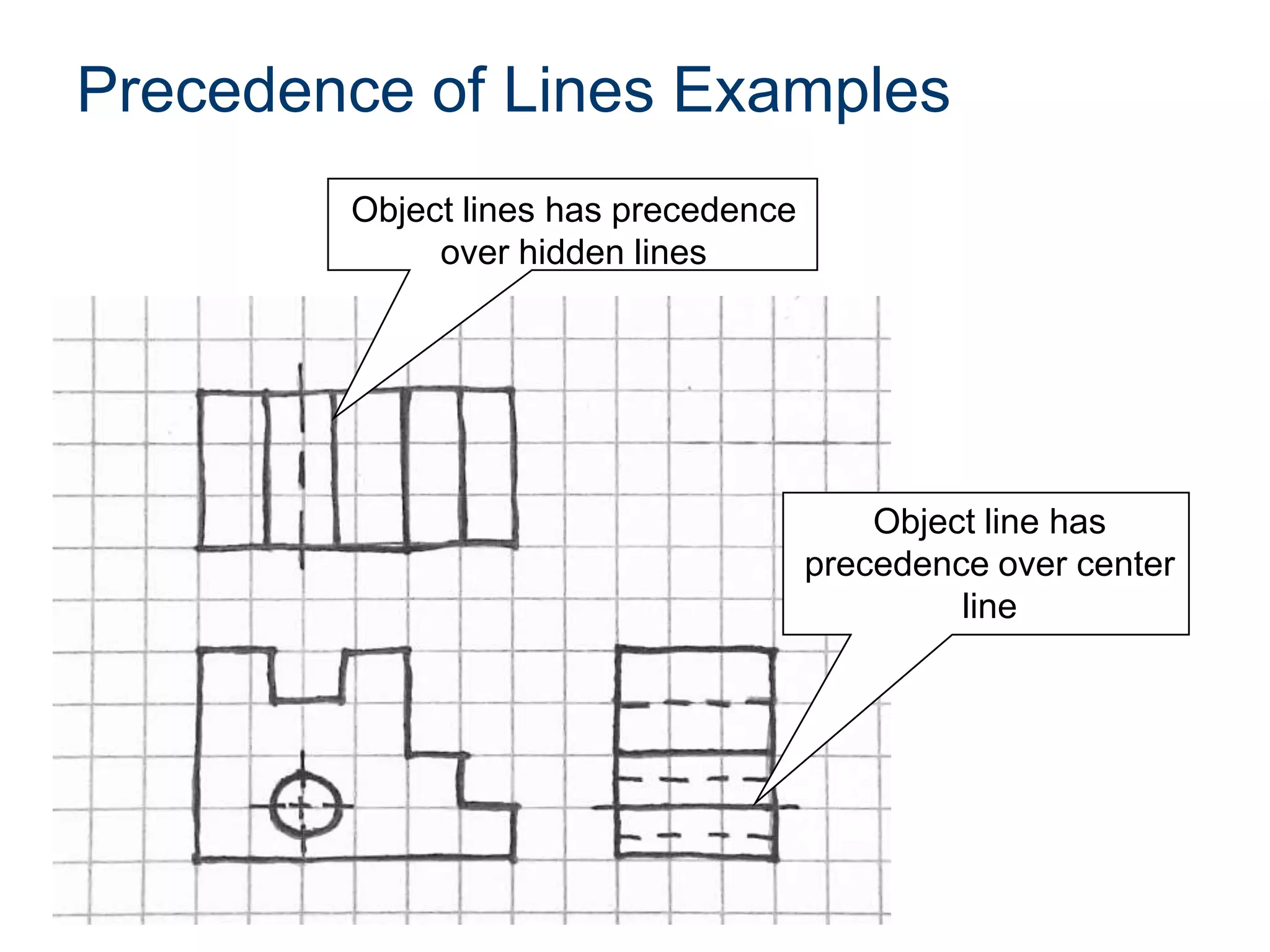
The document discusses various line conventions used in technical drawings to develop and communicate geometric information. It describes line types such as construction lines, object lines, hidden lines, center lines, section lines, and dimension lines; and indicates how they are drawn and what purpose each serves. Guidelines are provided for using the appropriate line conventions and precedence when multiple line types overlap in a complex sketch.