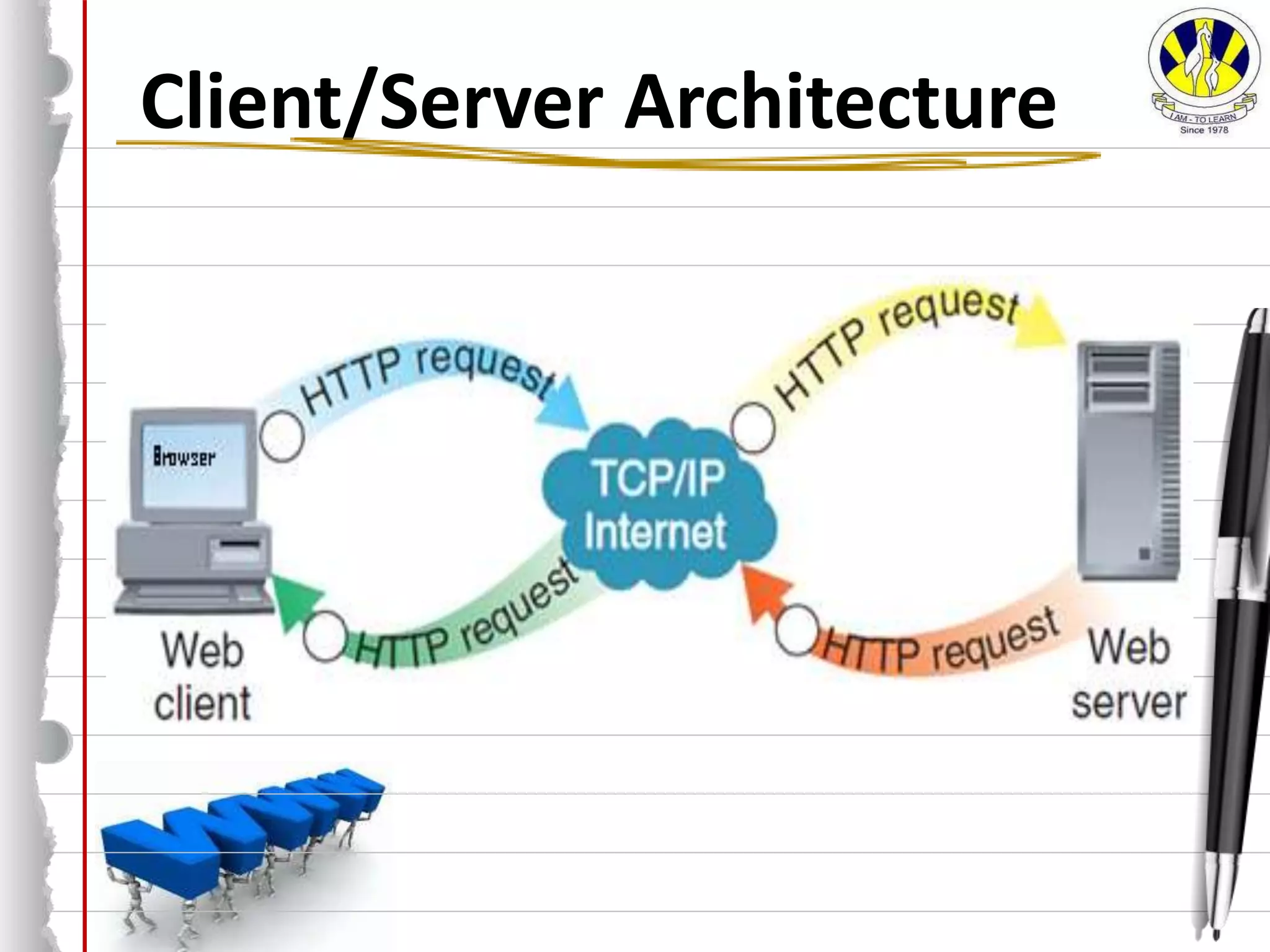
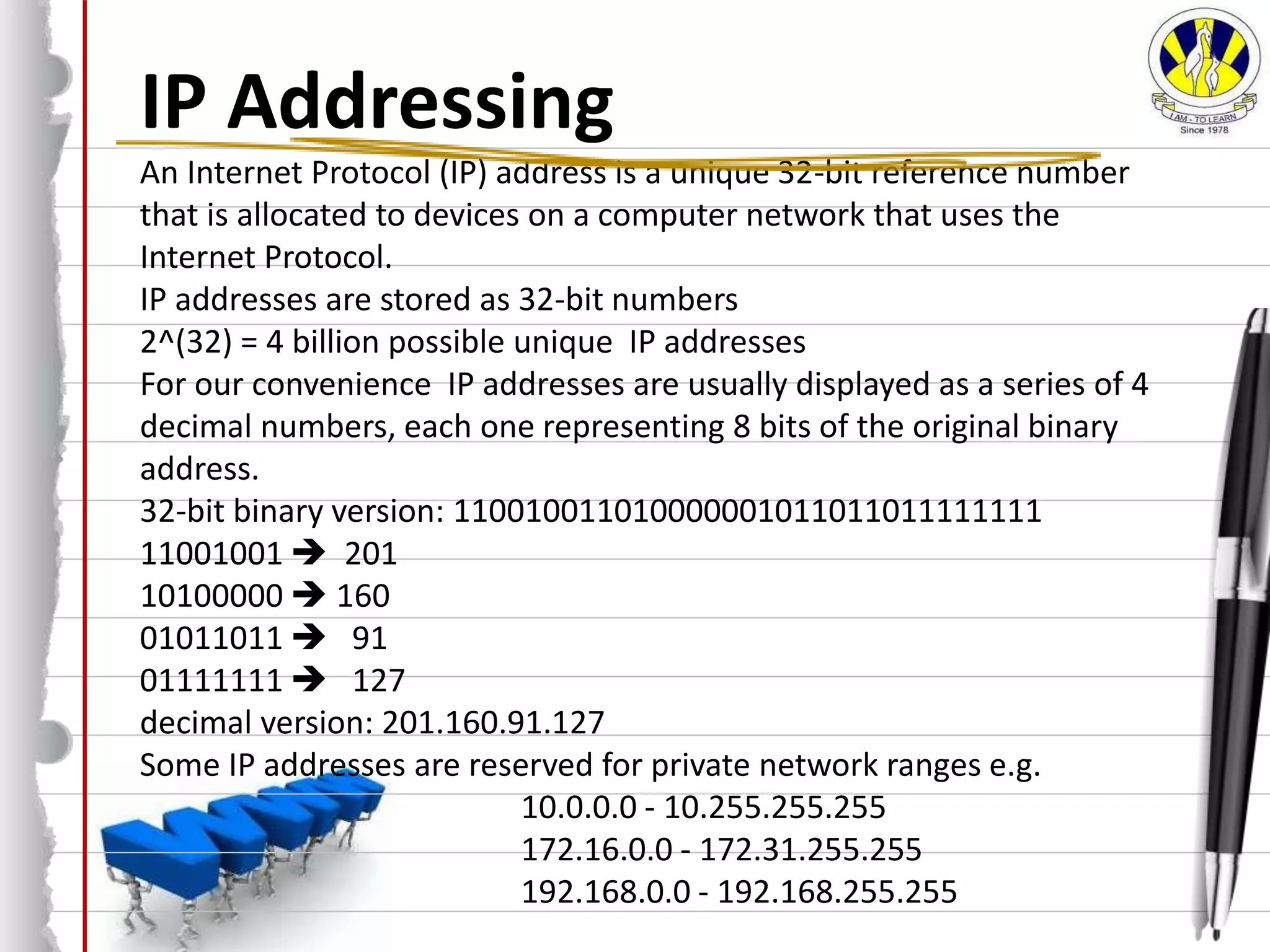
The document discusses key concepts related to how the internet works. It defines the internet as a global network of interconnected computer networks that uses TCP/IP to serve billions of users. It describes the client/server model where clients access web servers to retrieve web pages, images, and files. It also explains important protocols like HTTP and HTML that allow communication and formatting of web pages, and concepts like IP addresses, MAC addresses, and cookies that enable identification and functionality on the internet.