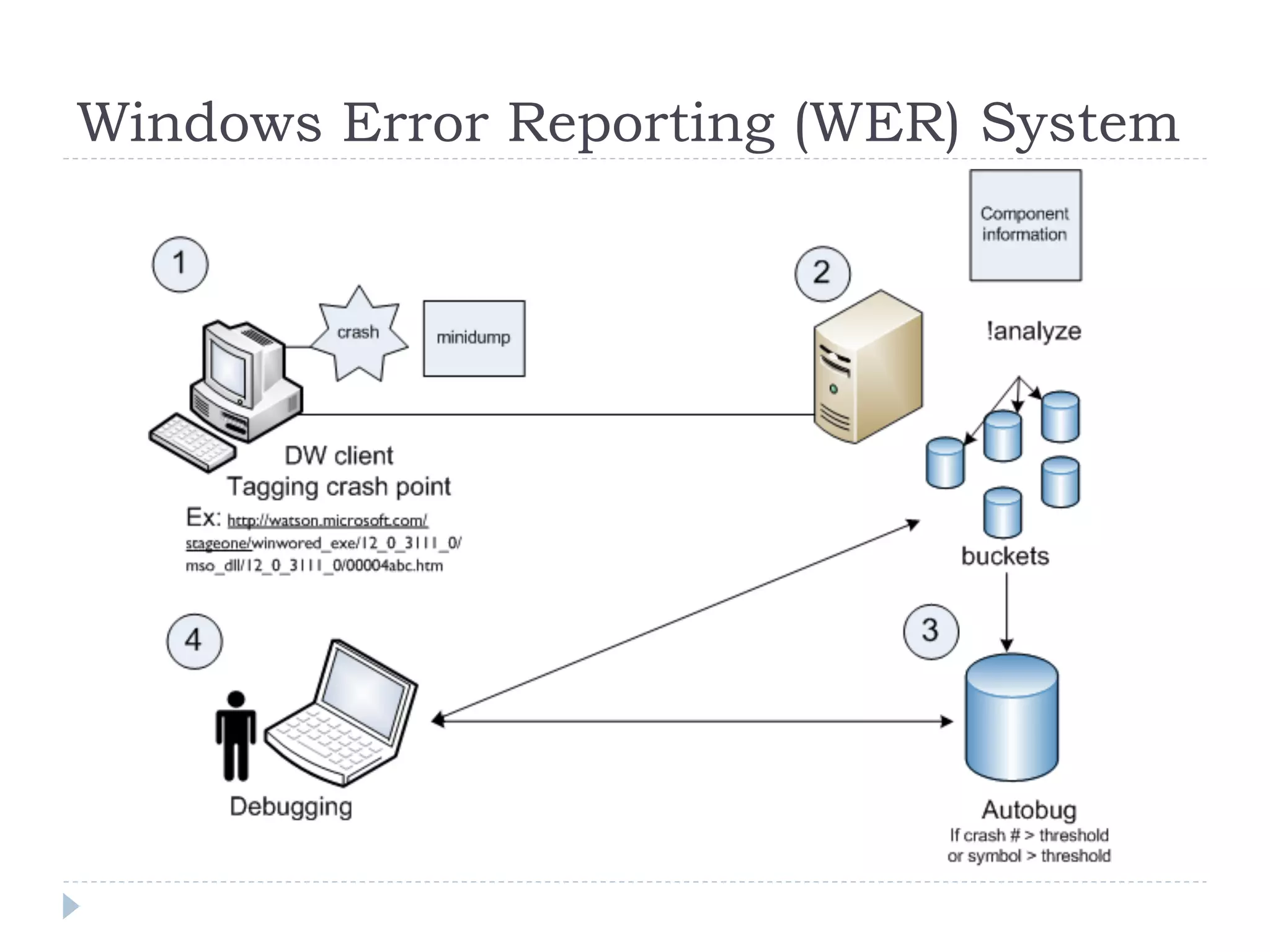
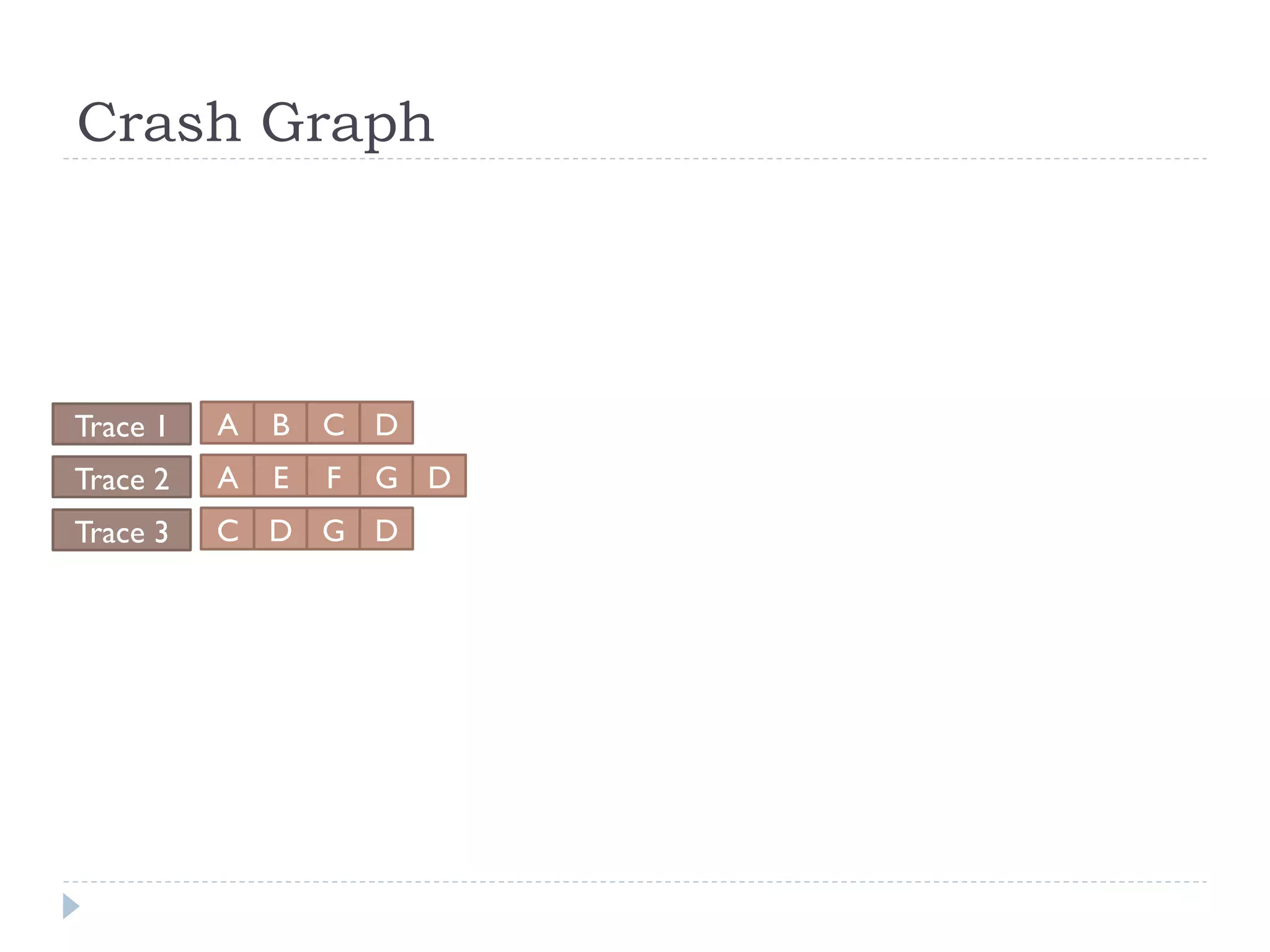
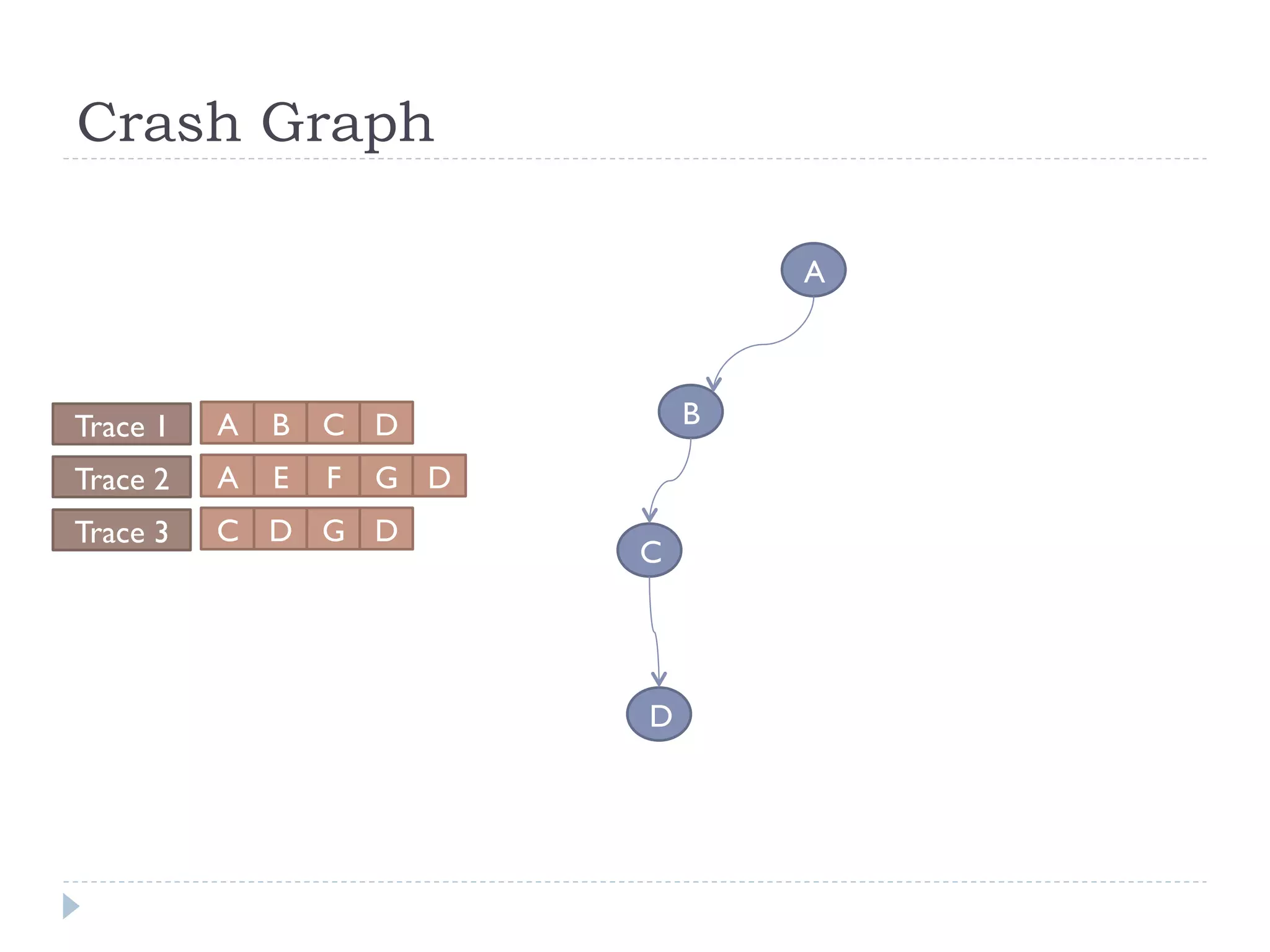
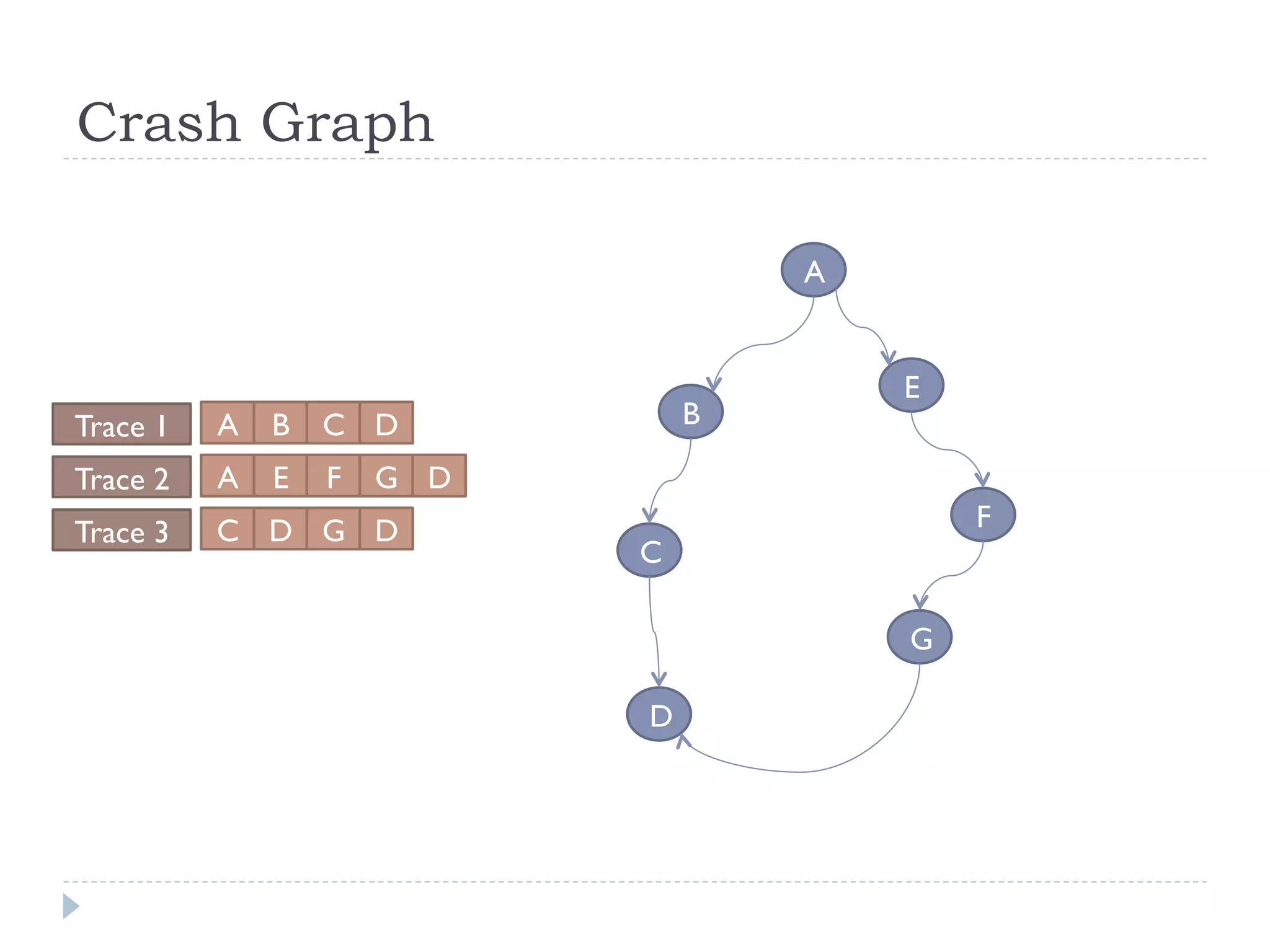
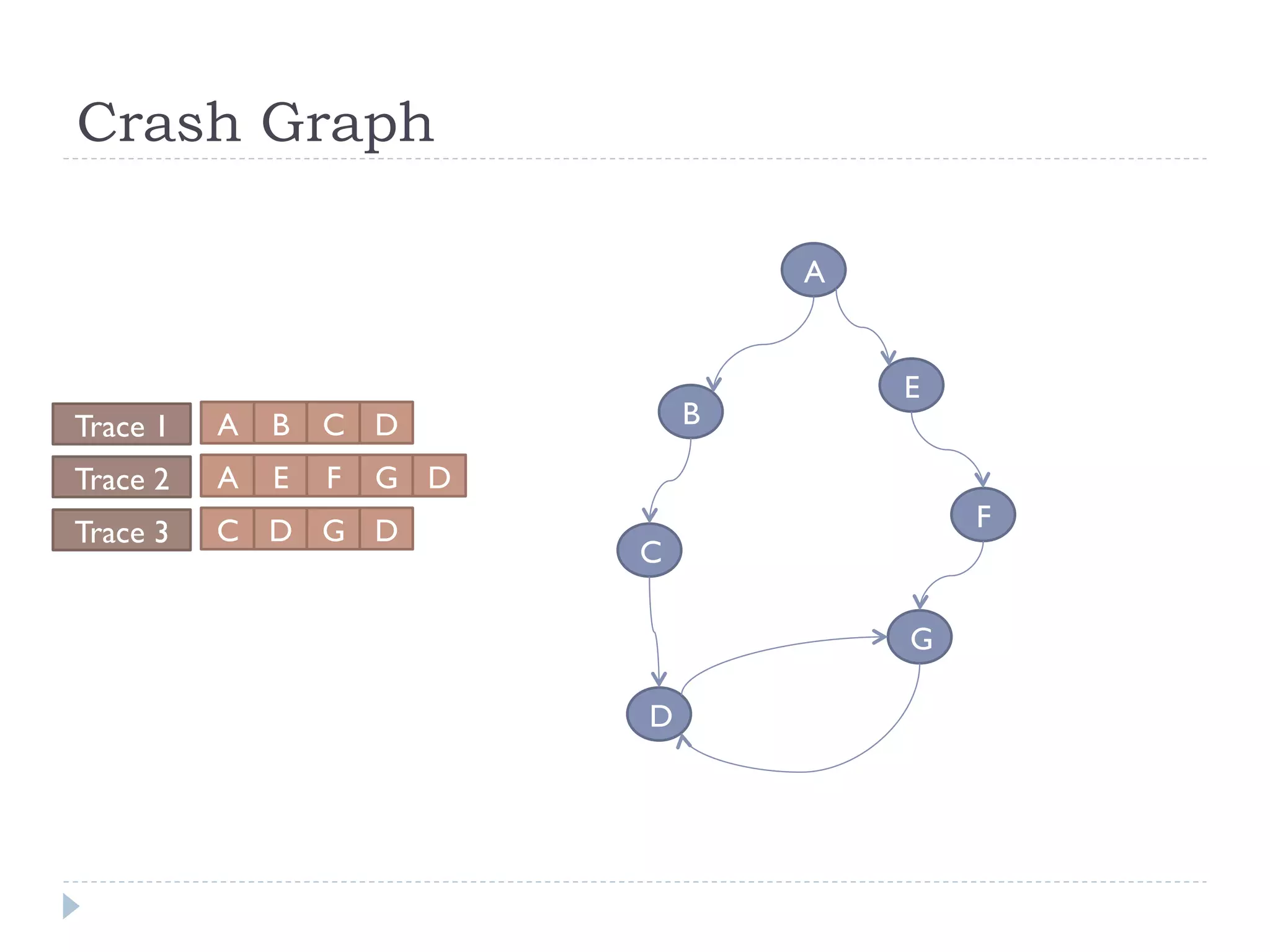
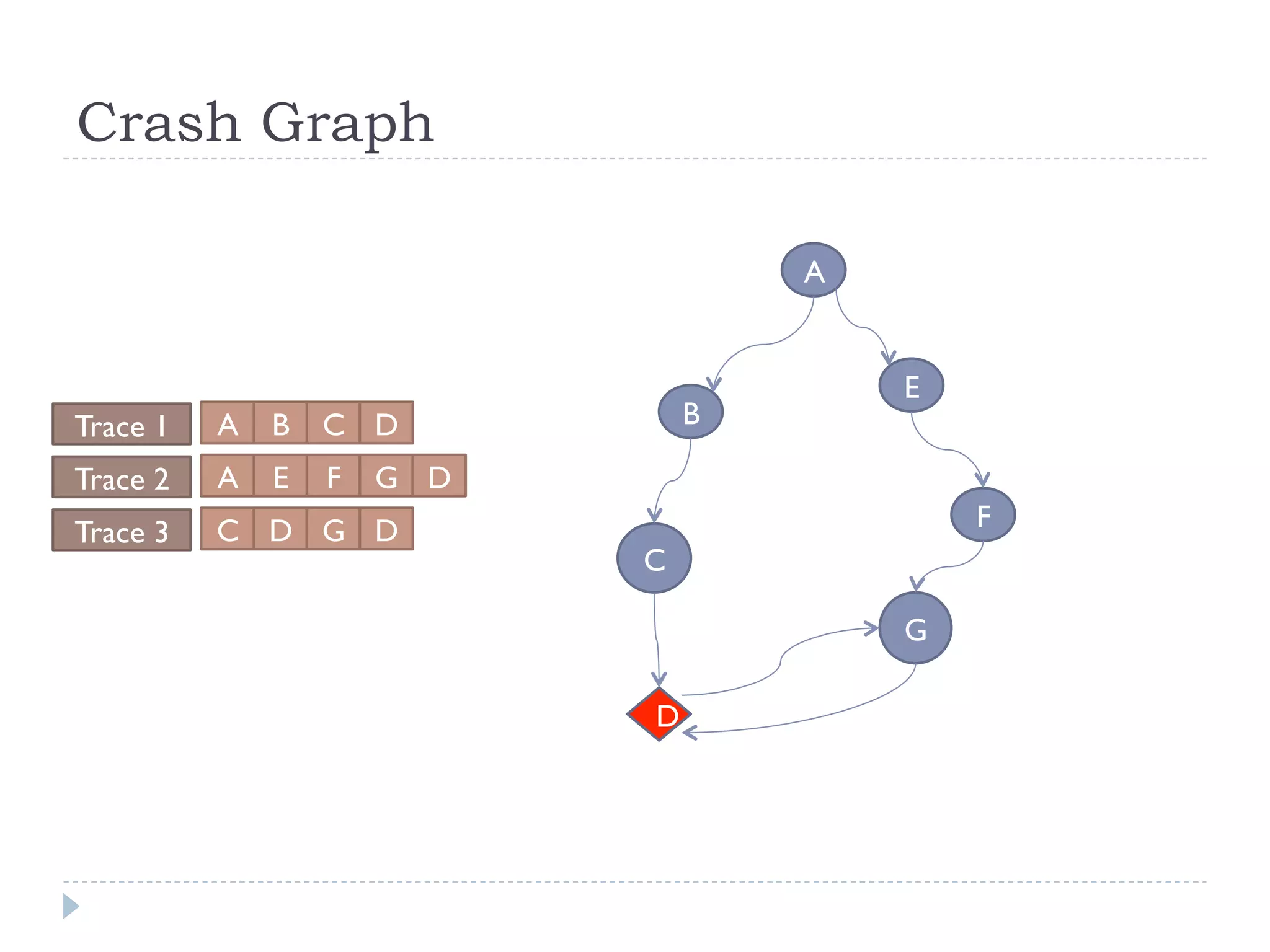
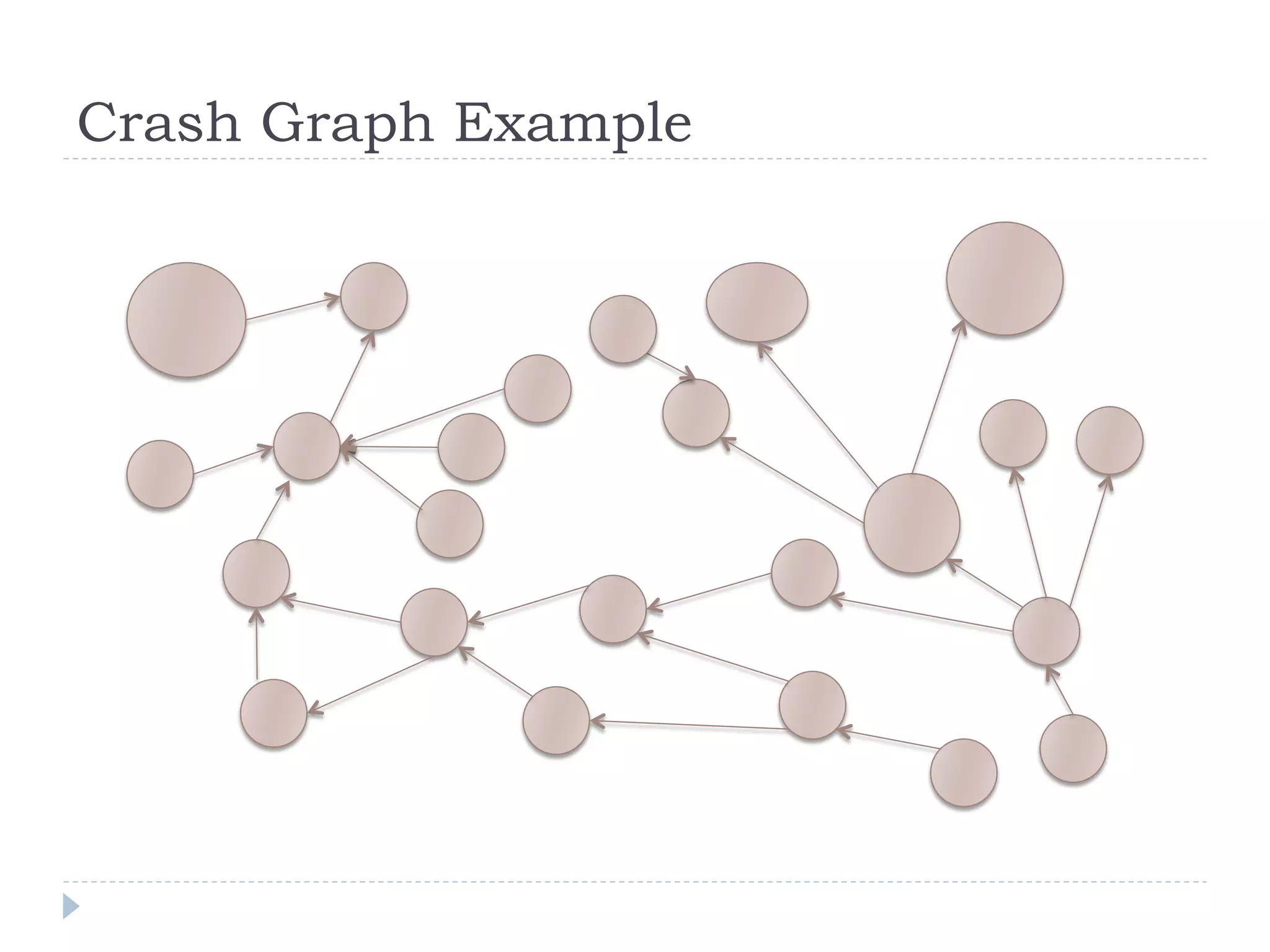
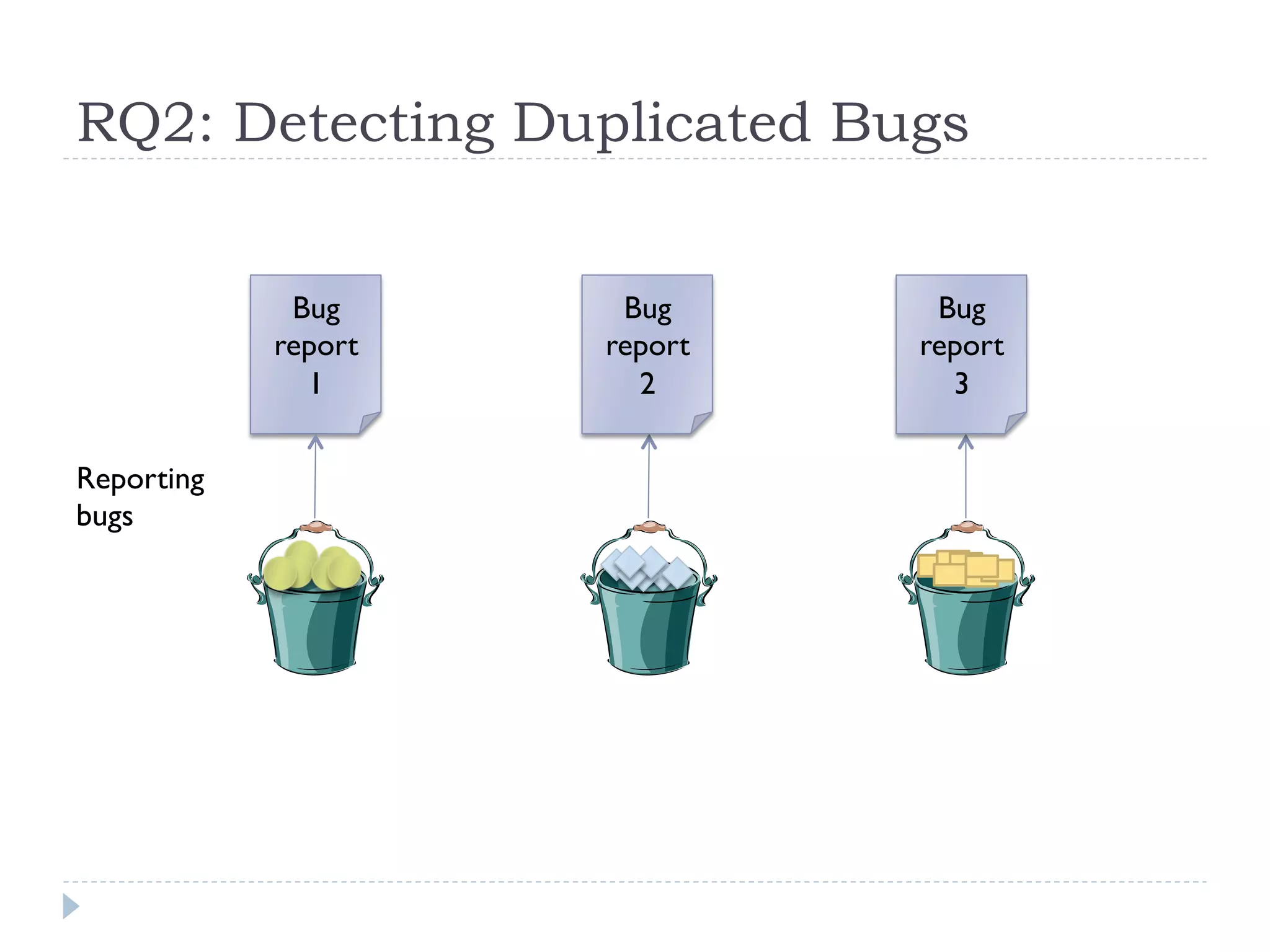
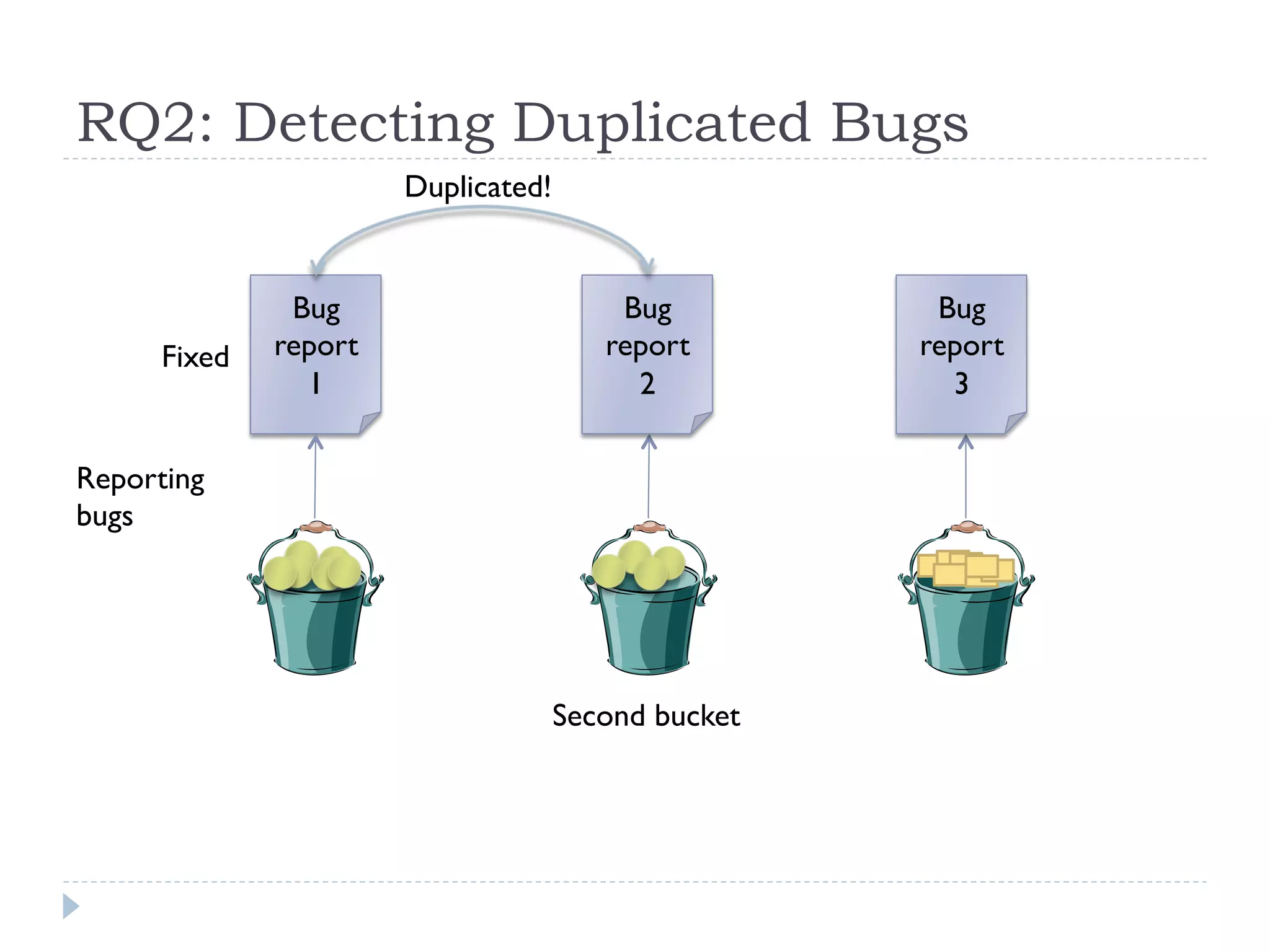
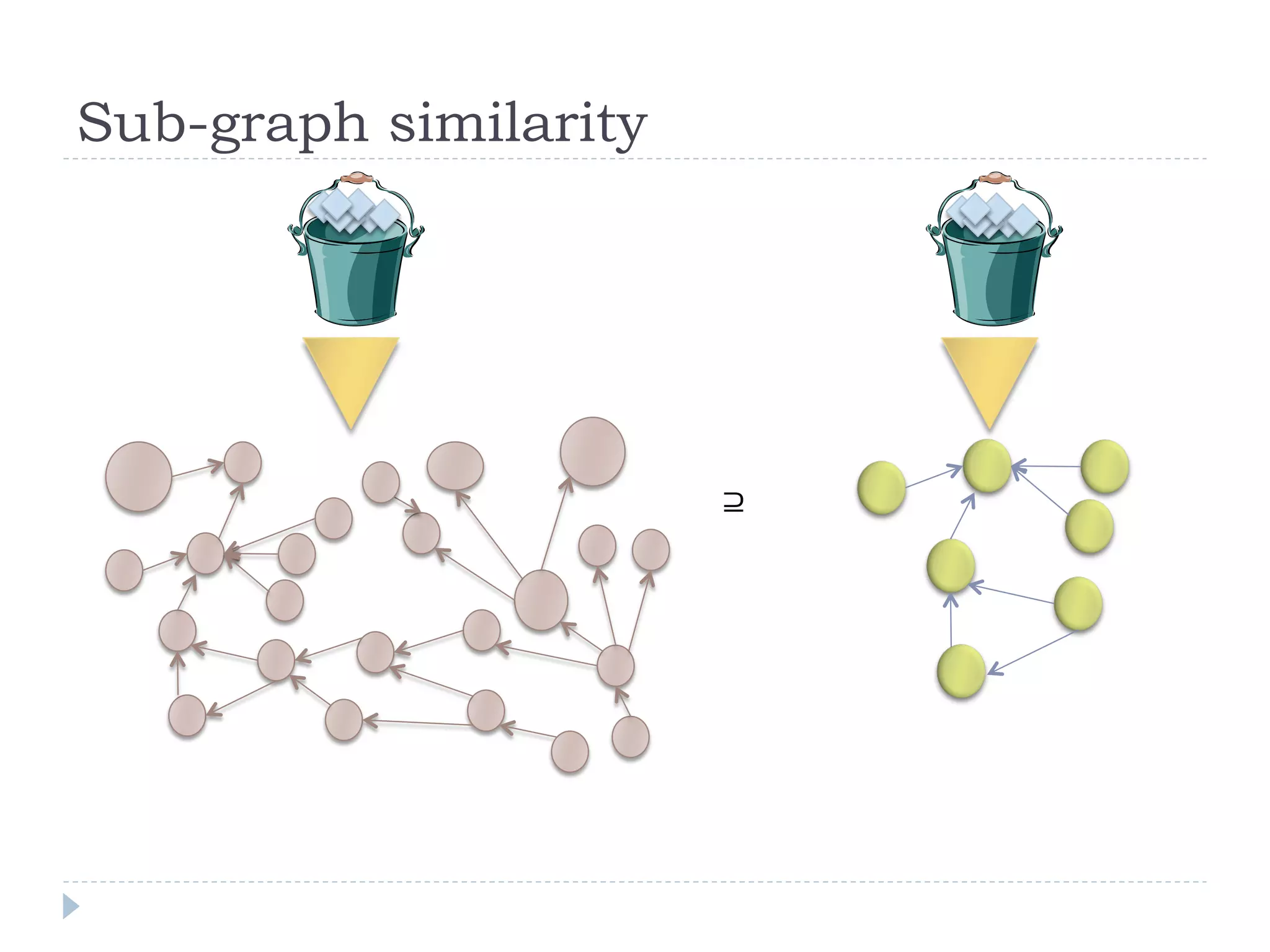
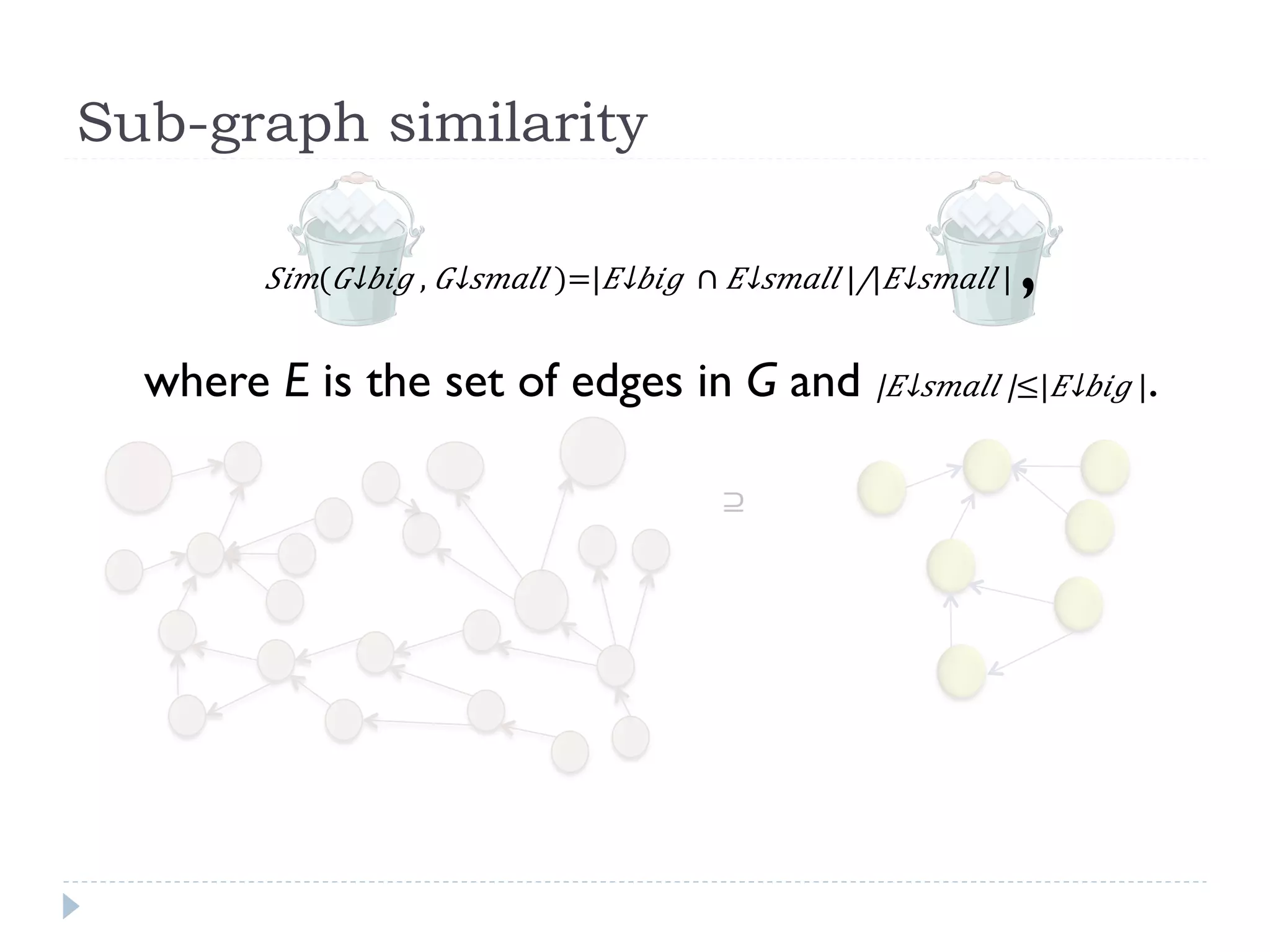
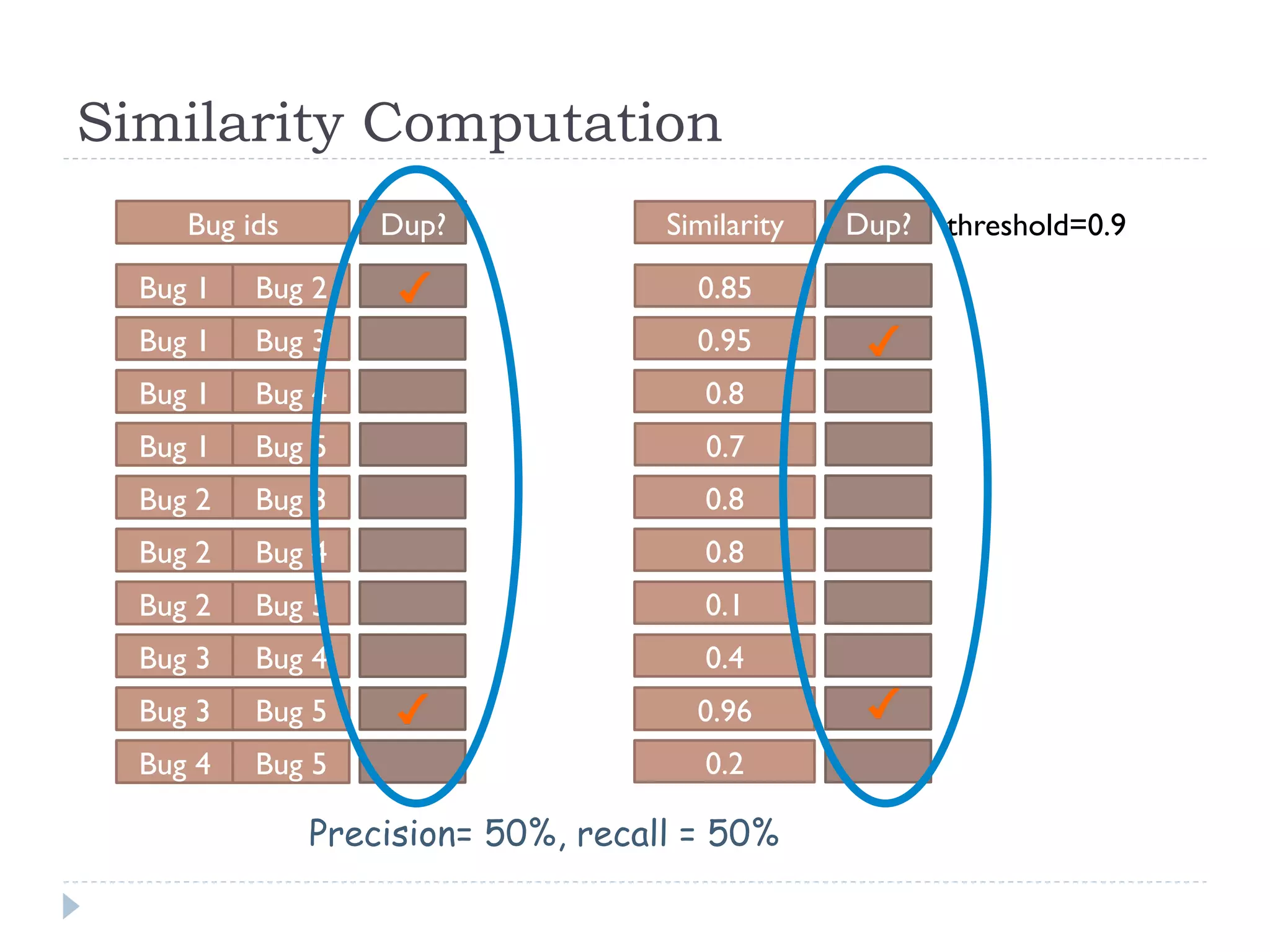
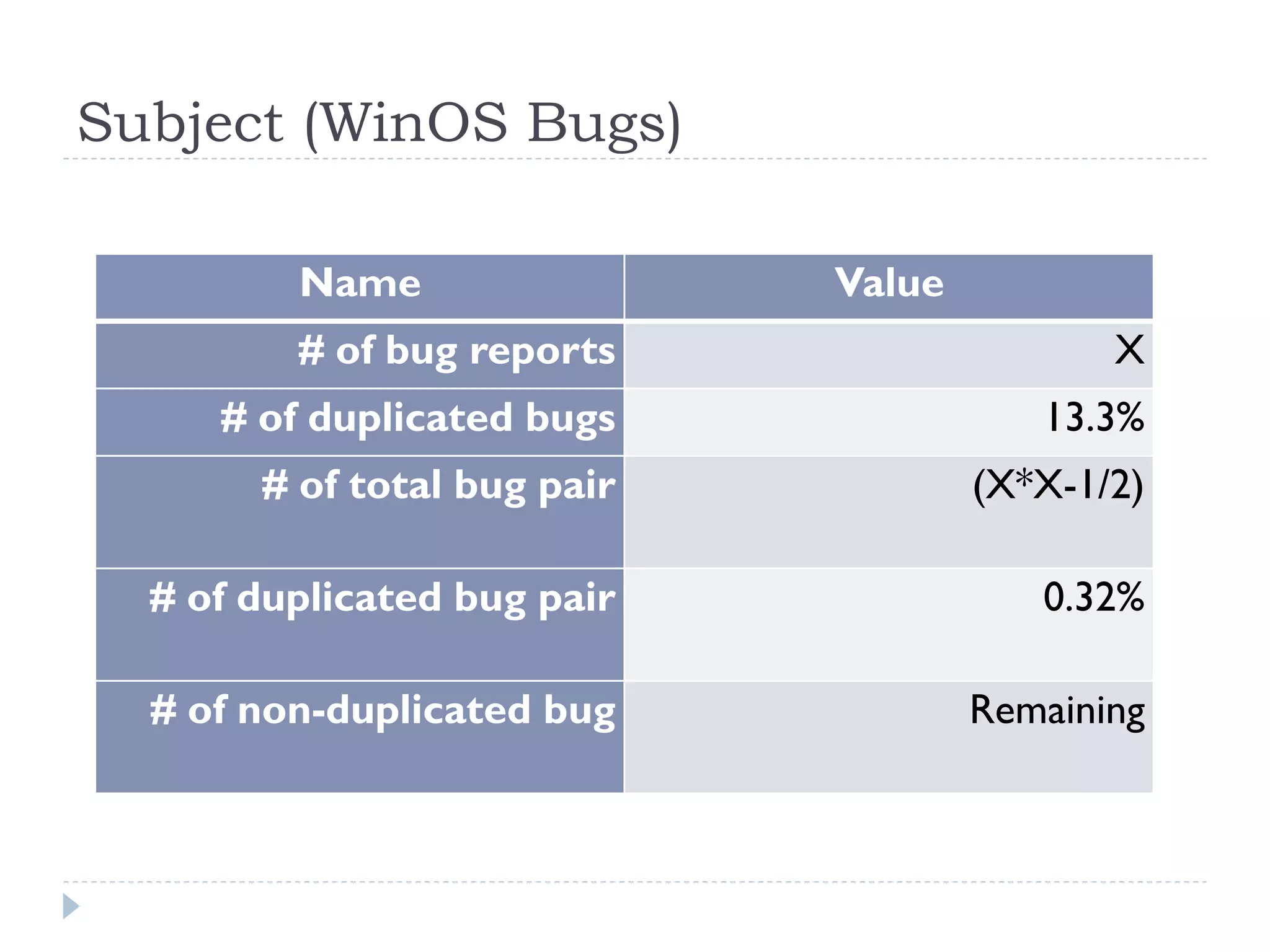
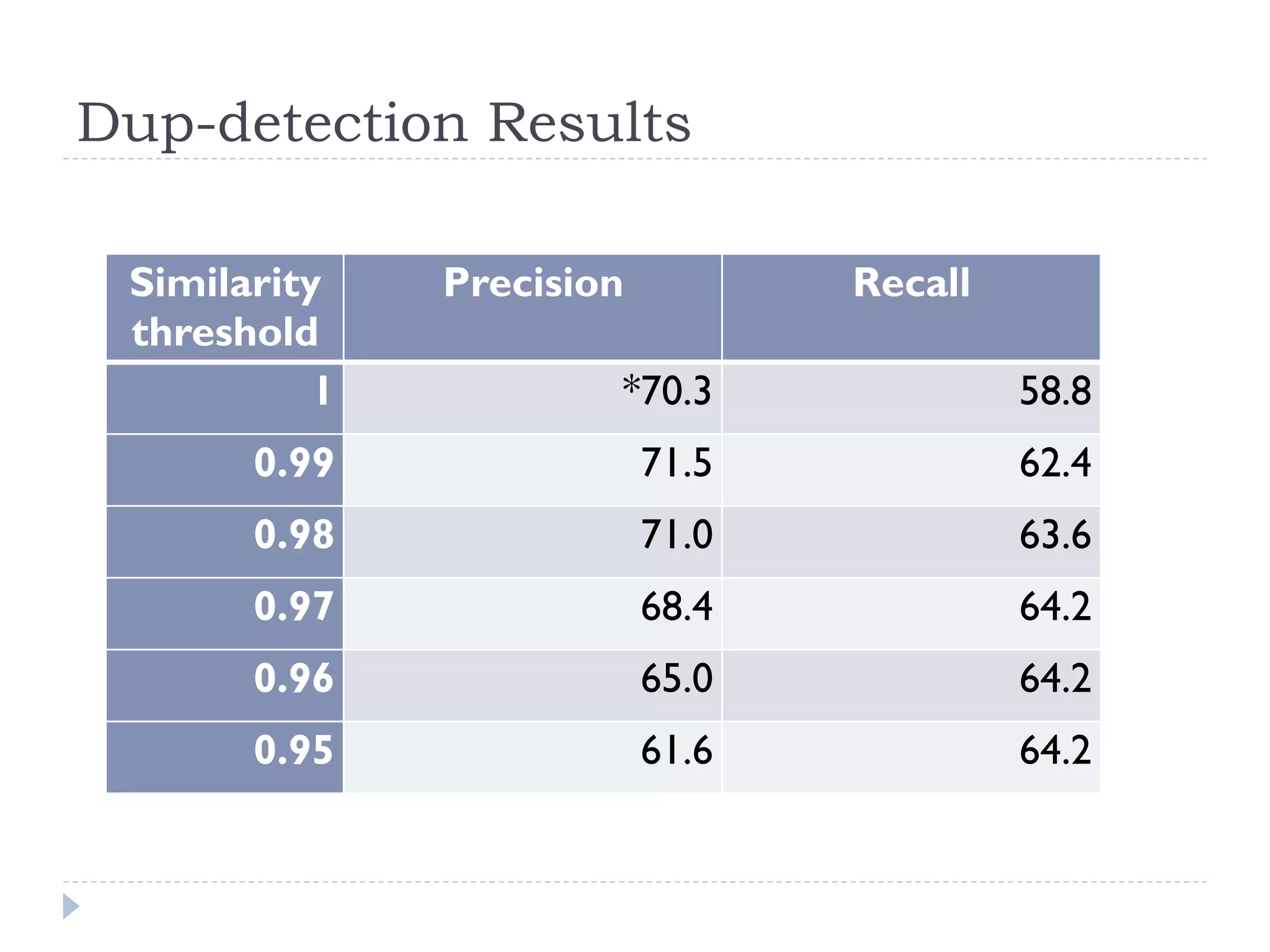
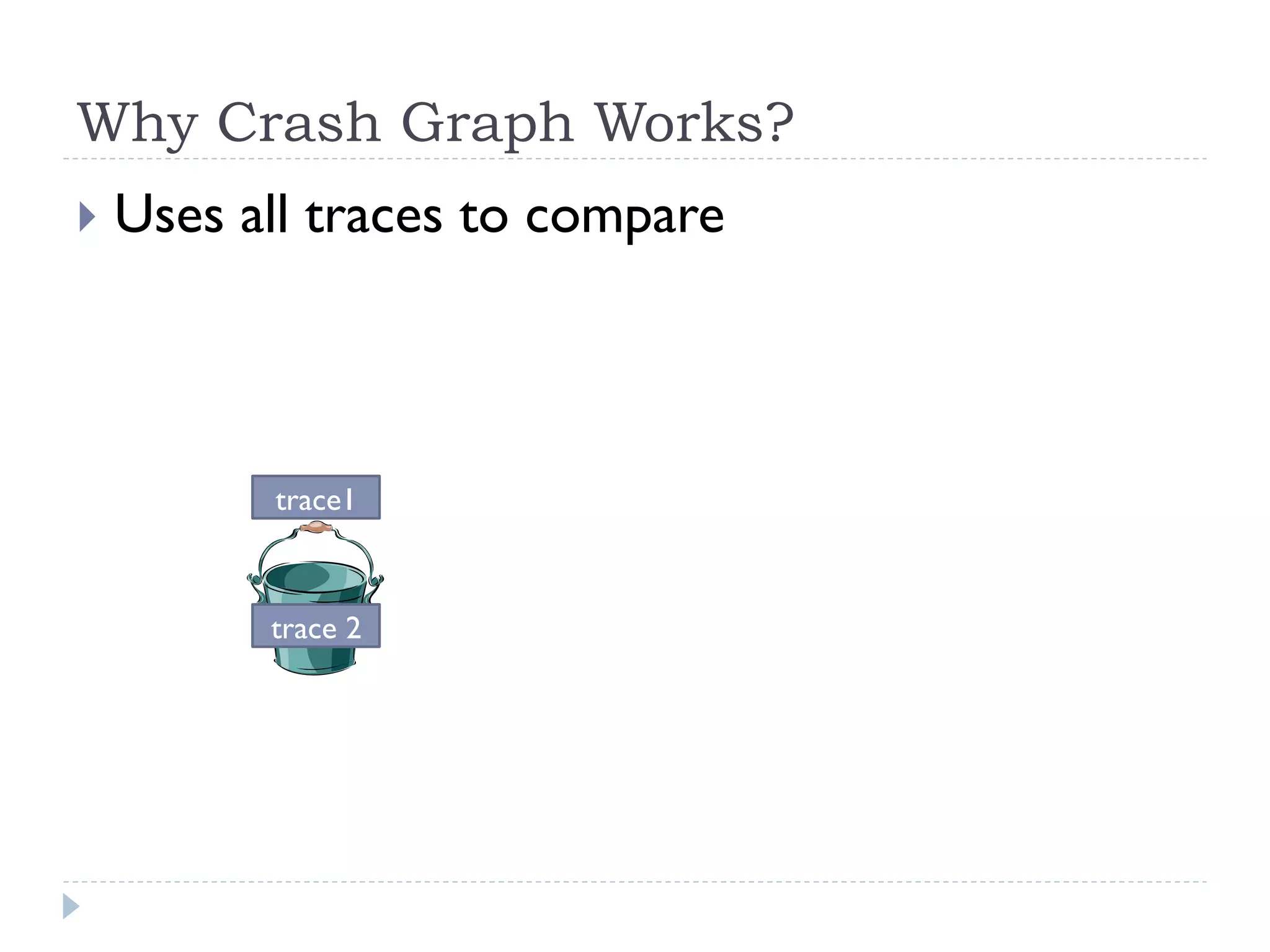
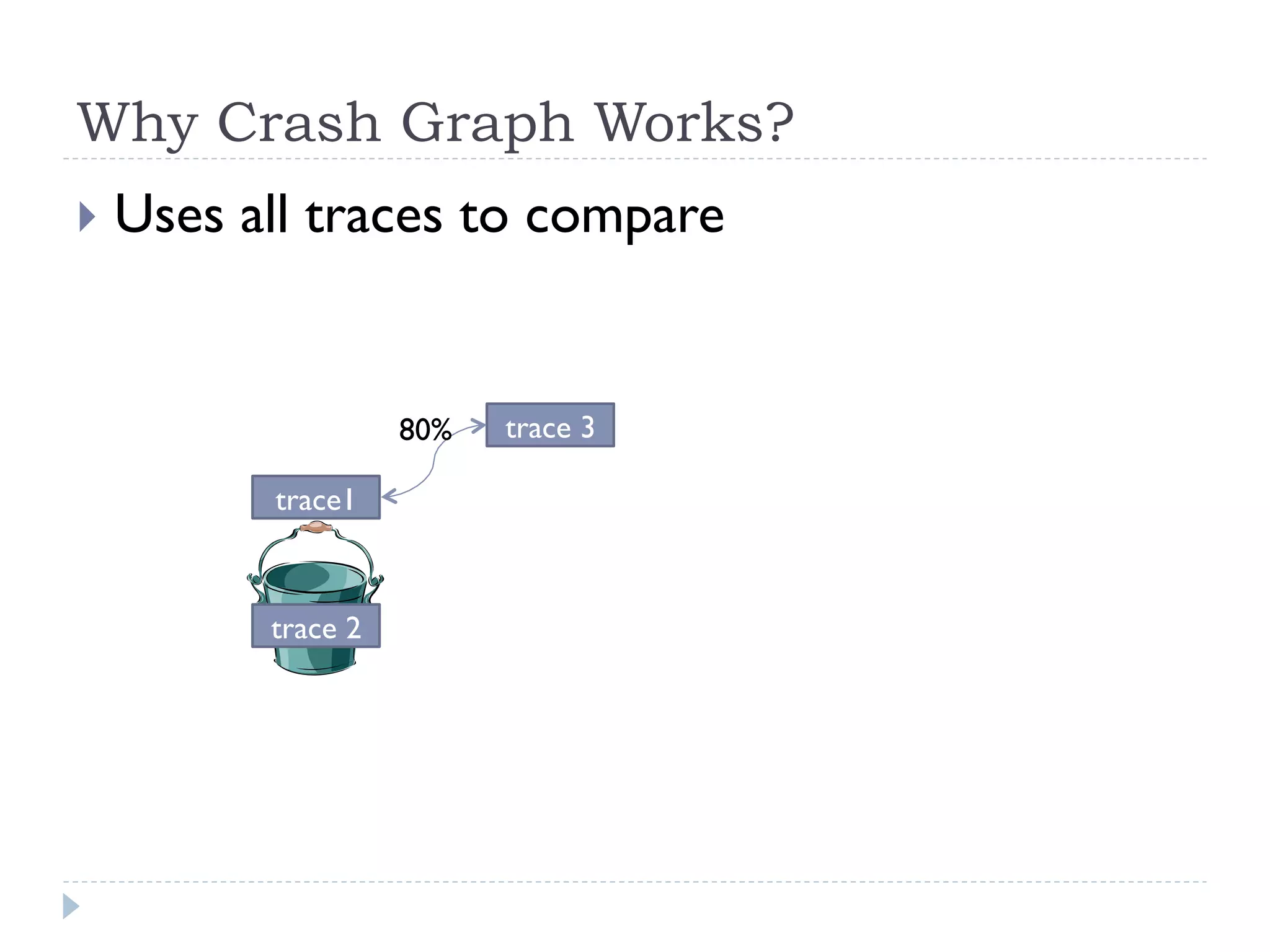
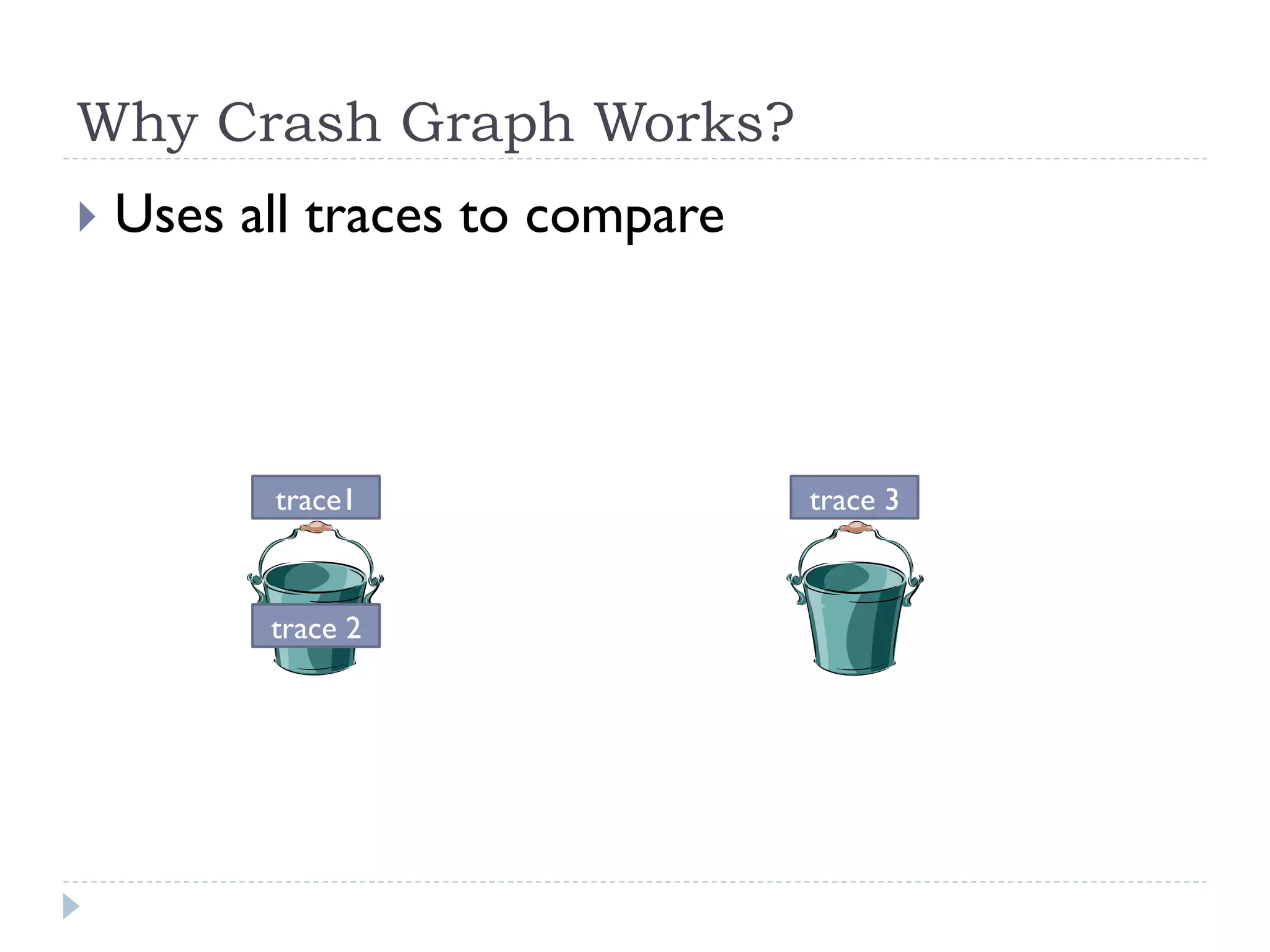
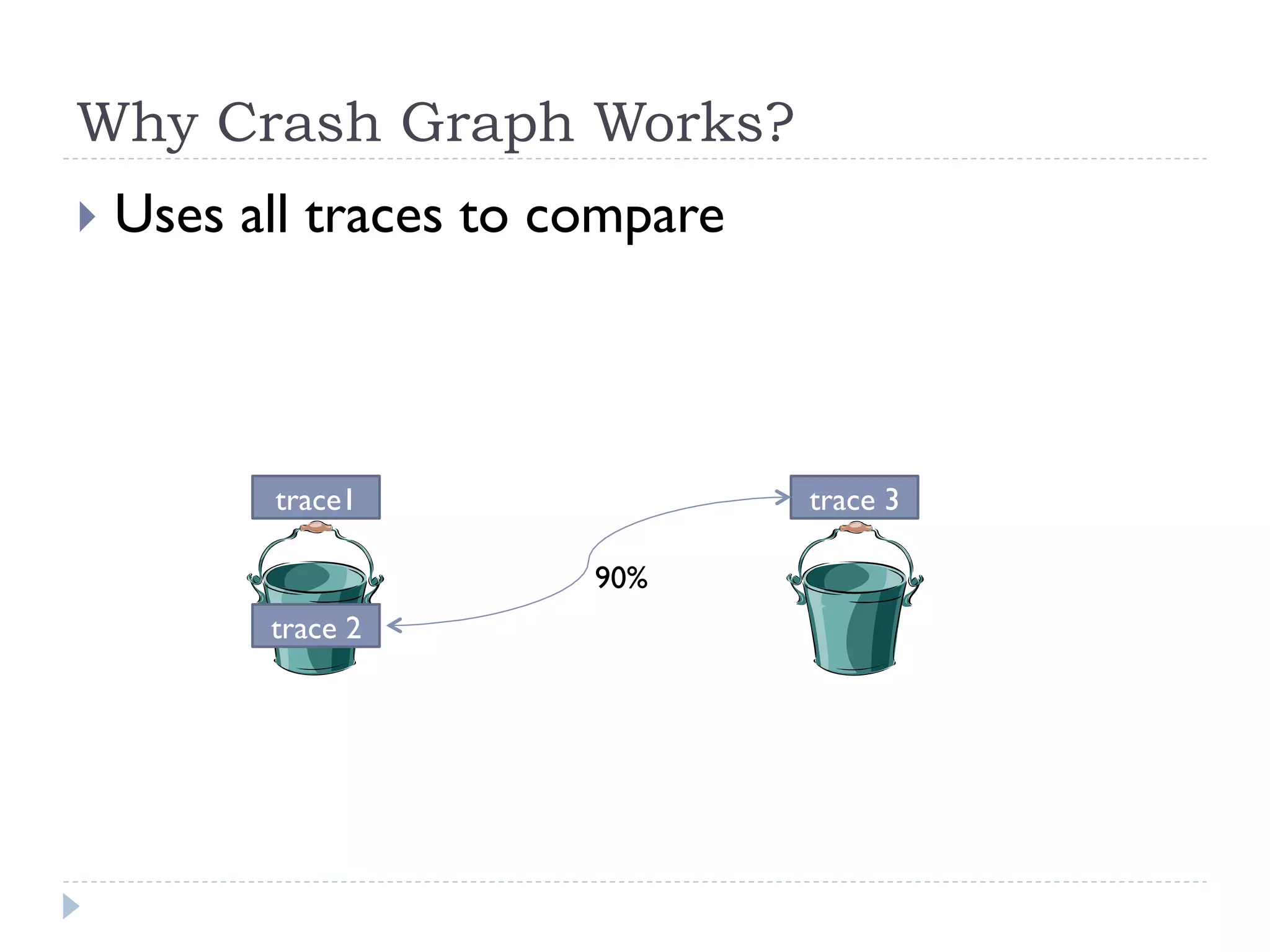
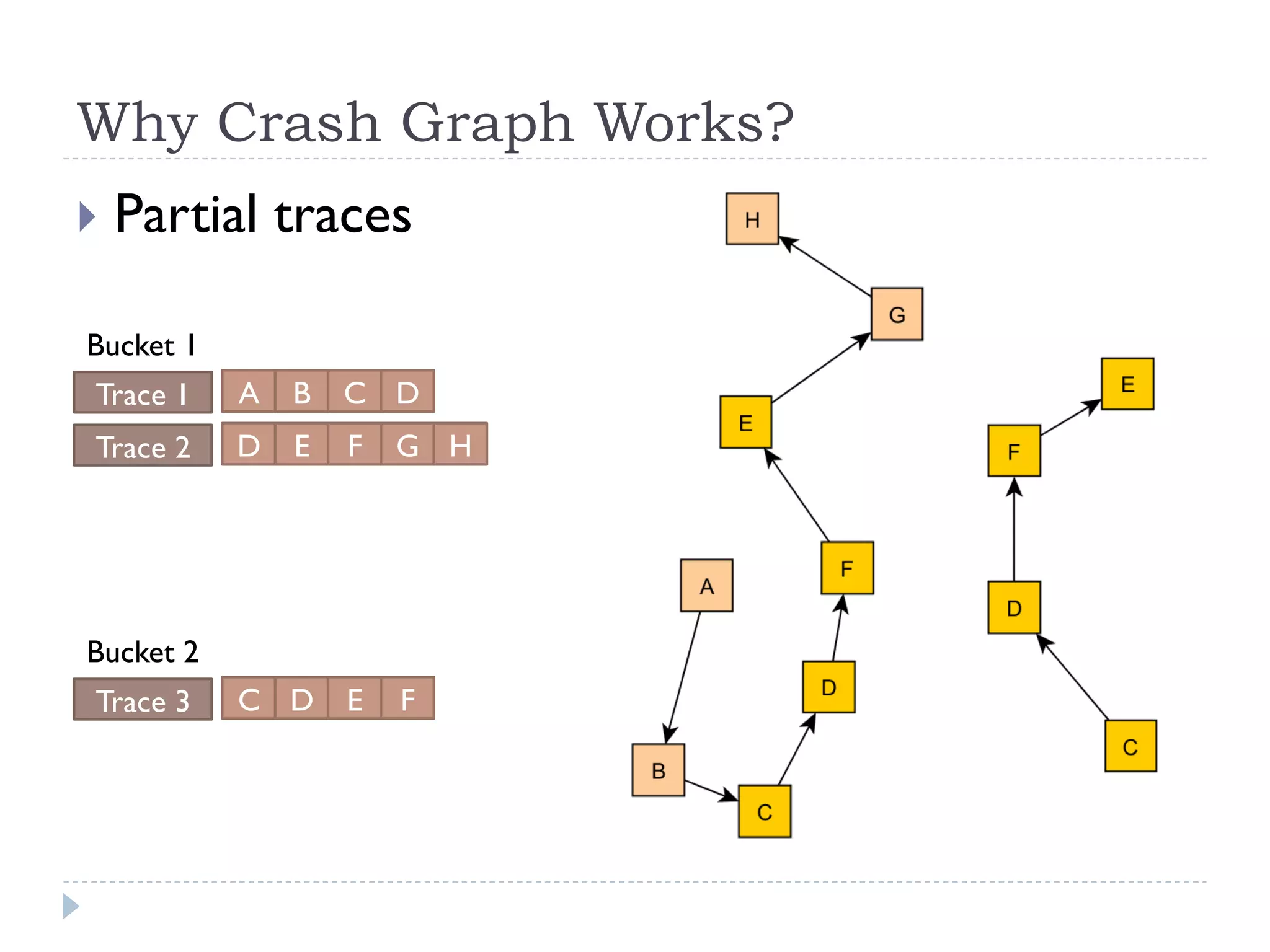
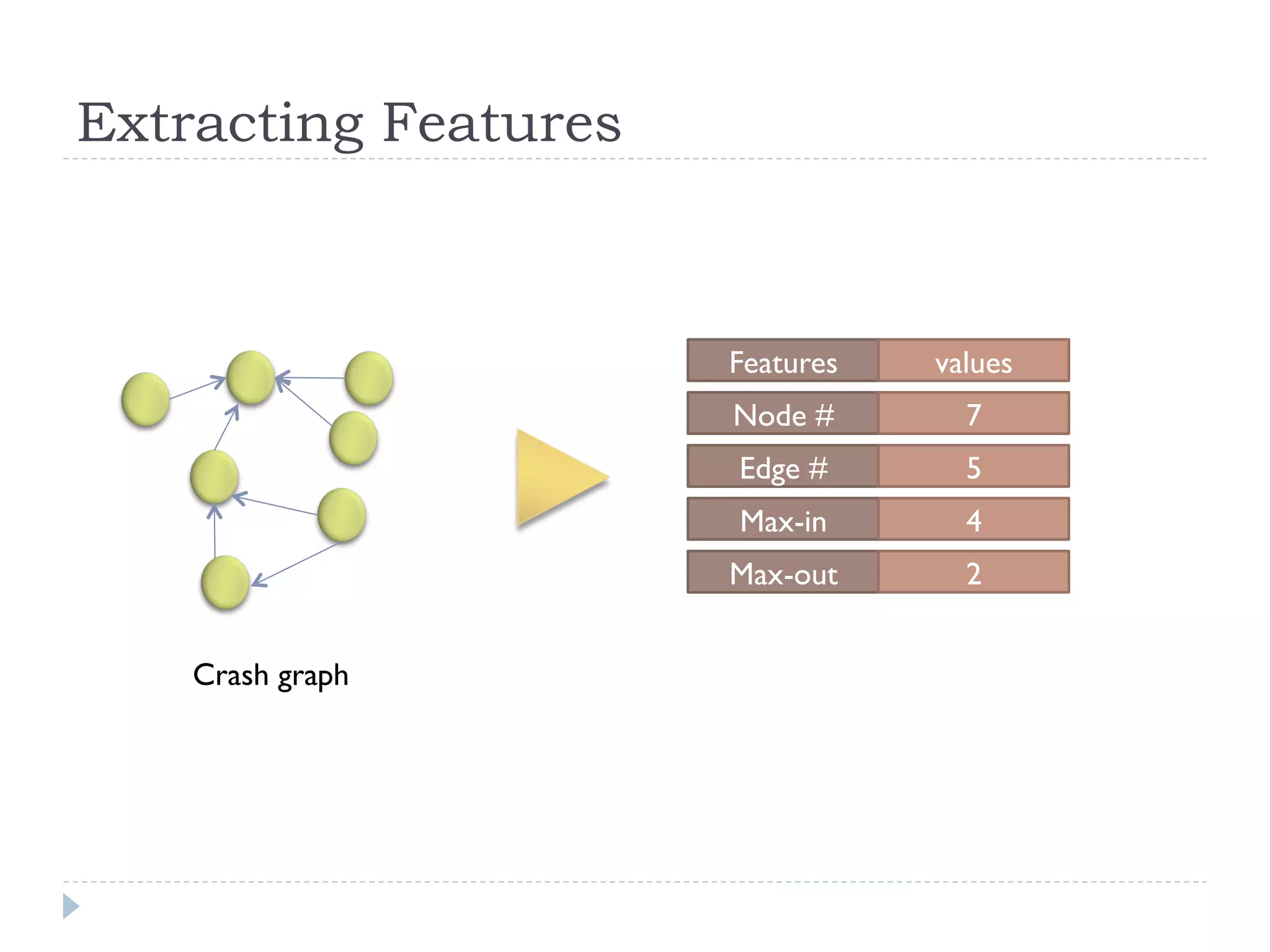
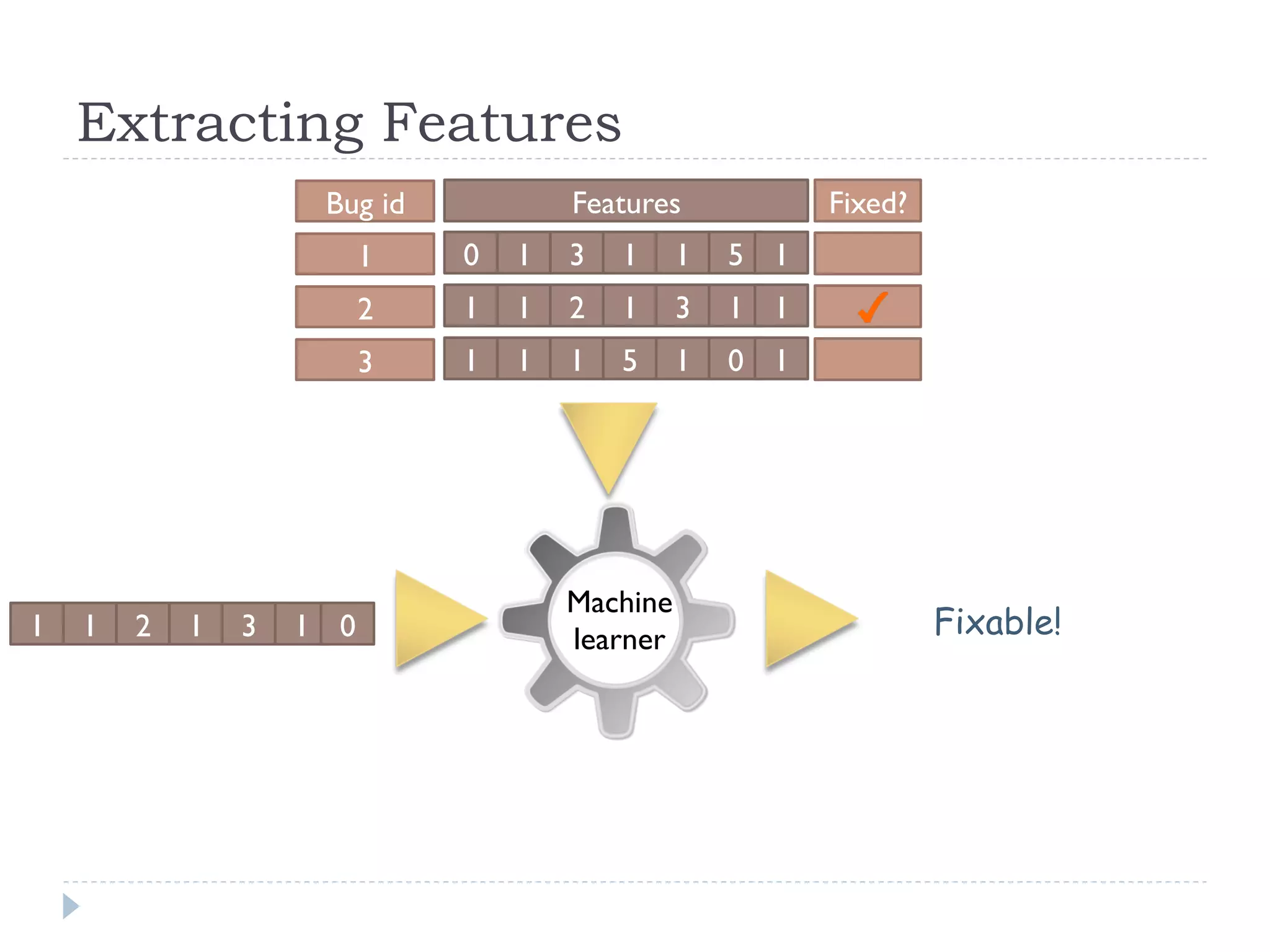
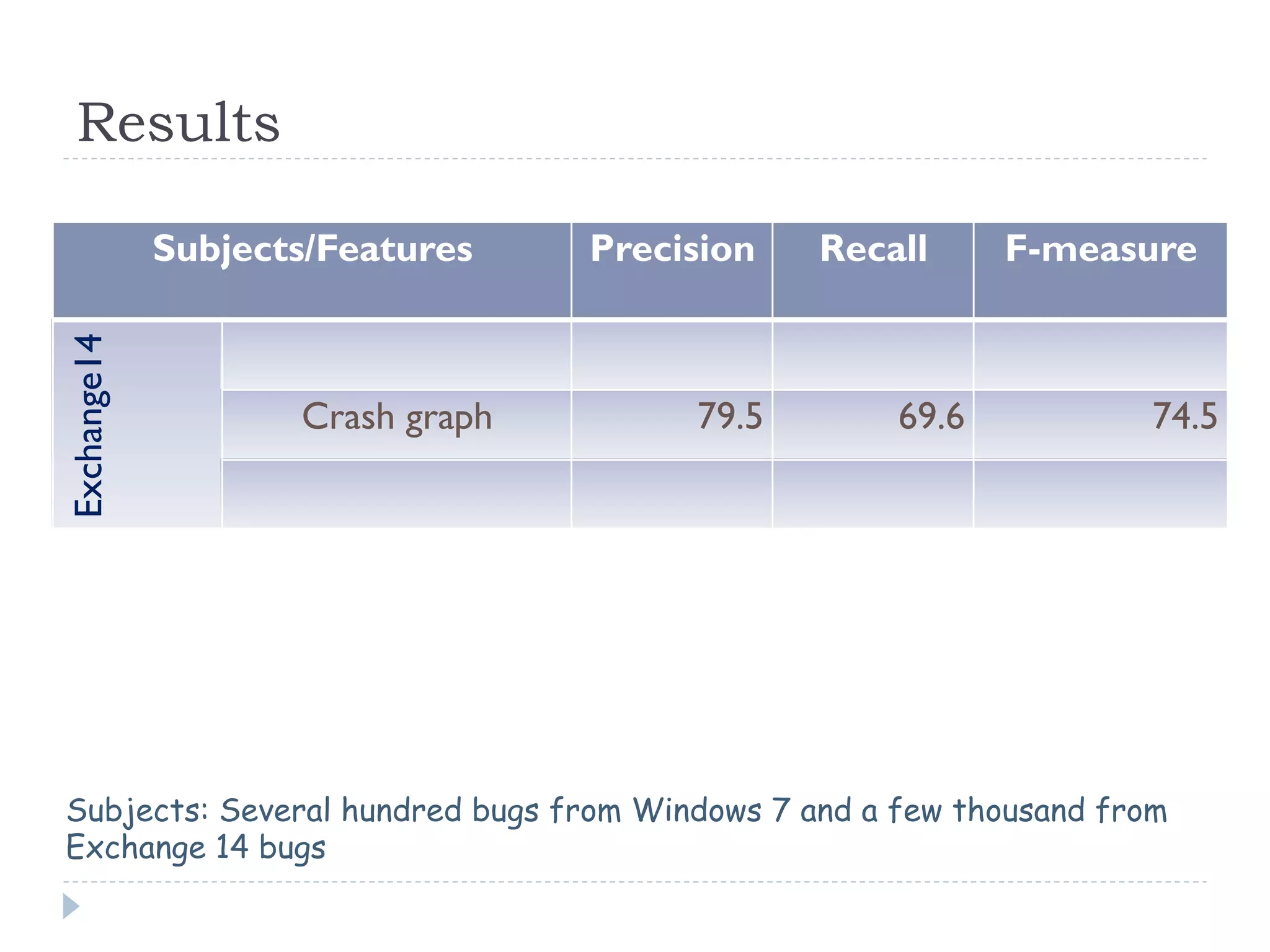
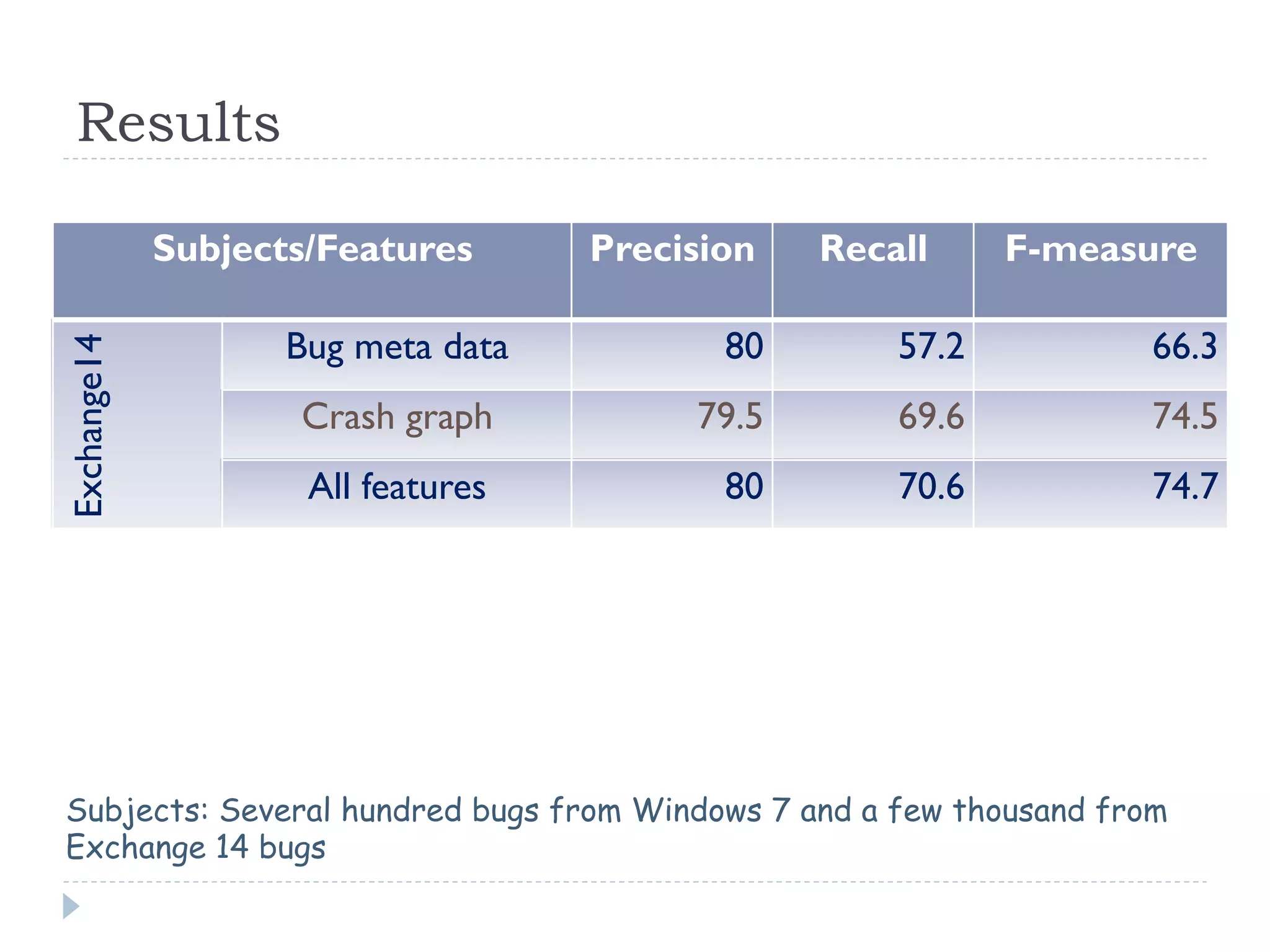
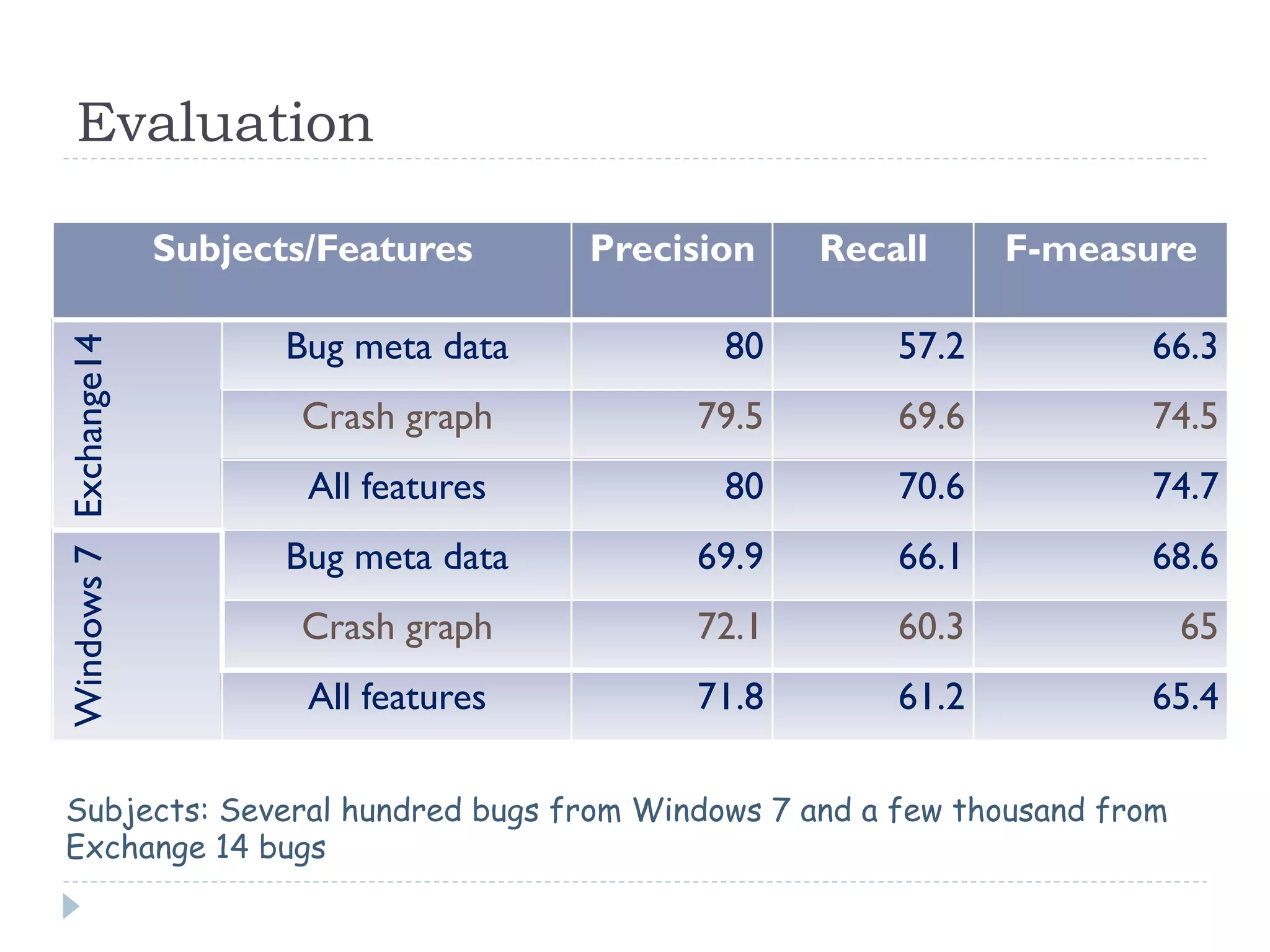
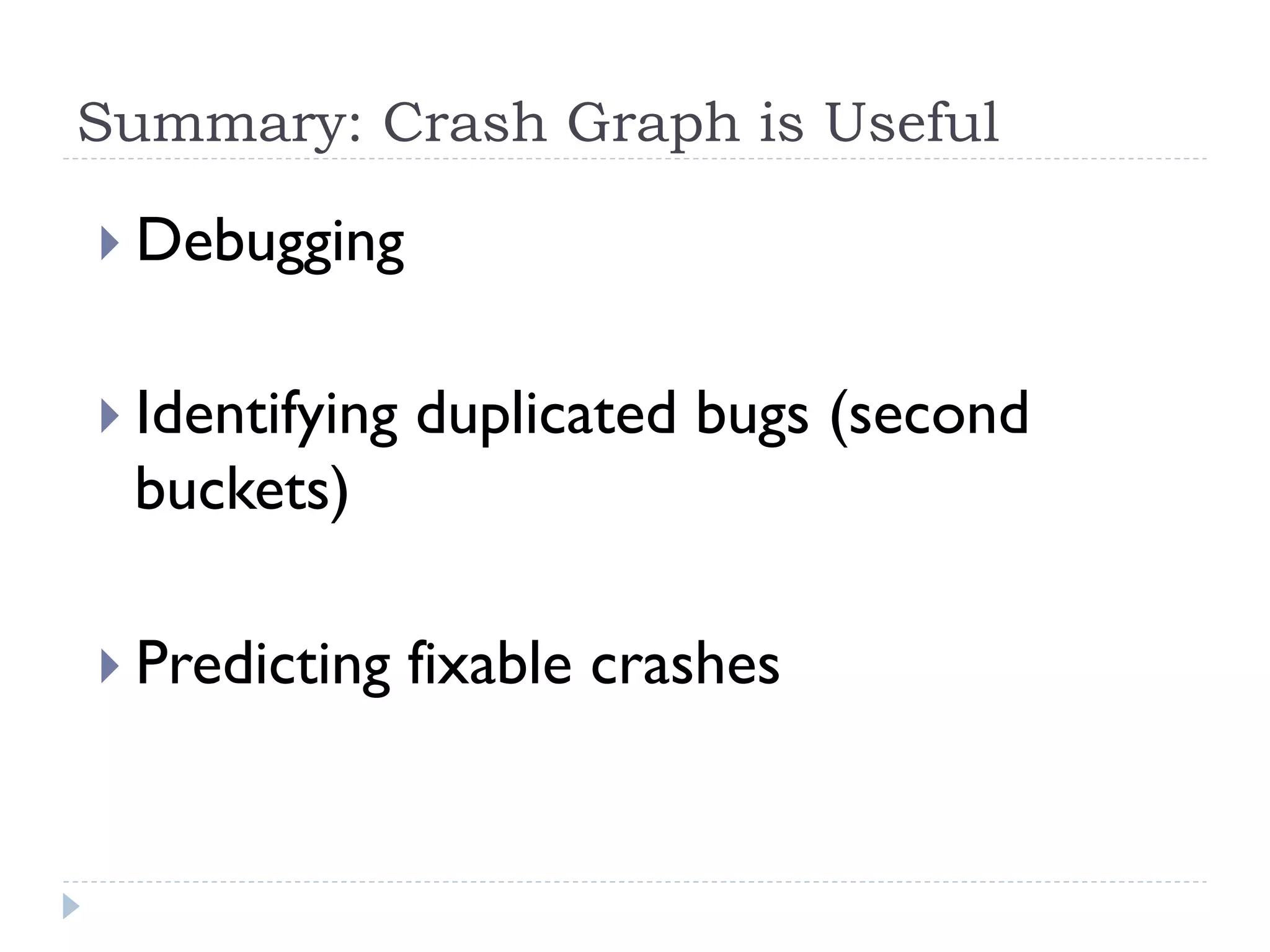
The document discusses the development and application of crash graphs, which aggregate multiple crash reports to aid in debugging, prioritize fixable crashes, and identify duplicate bugs. It evaluates the effectiveness of crash graphs in providing insights to developers and improving bug triage through quantitative measures like precision and recall. The future work outlined includes enhancing the interactivity of crash graphs and exploring other algorithms for trace clustering.