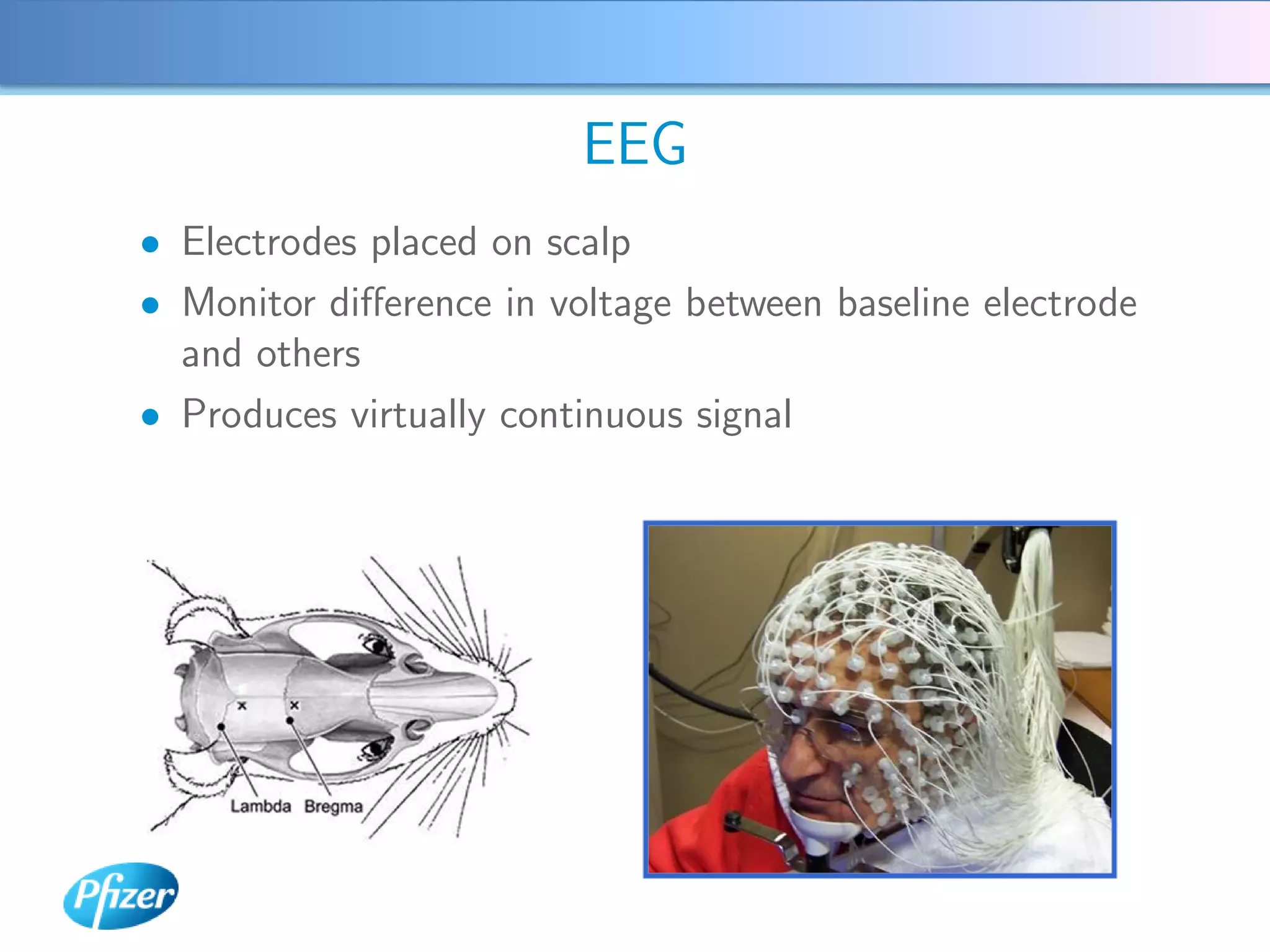
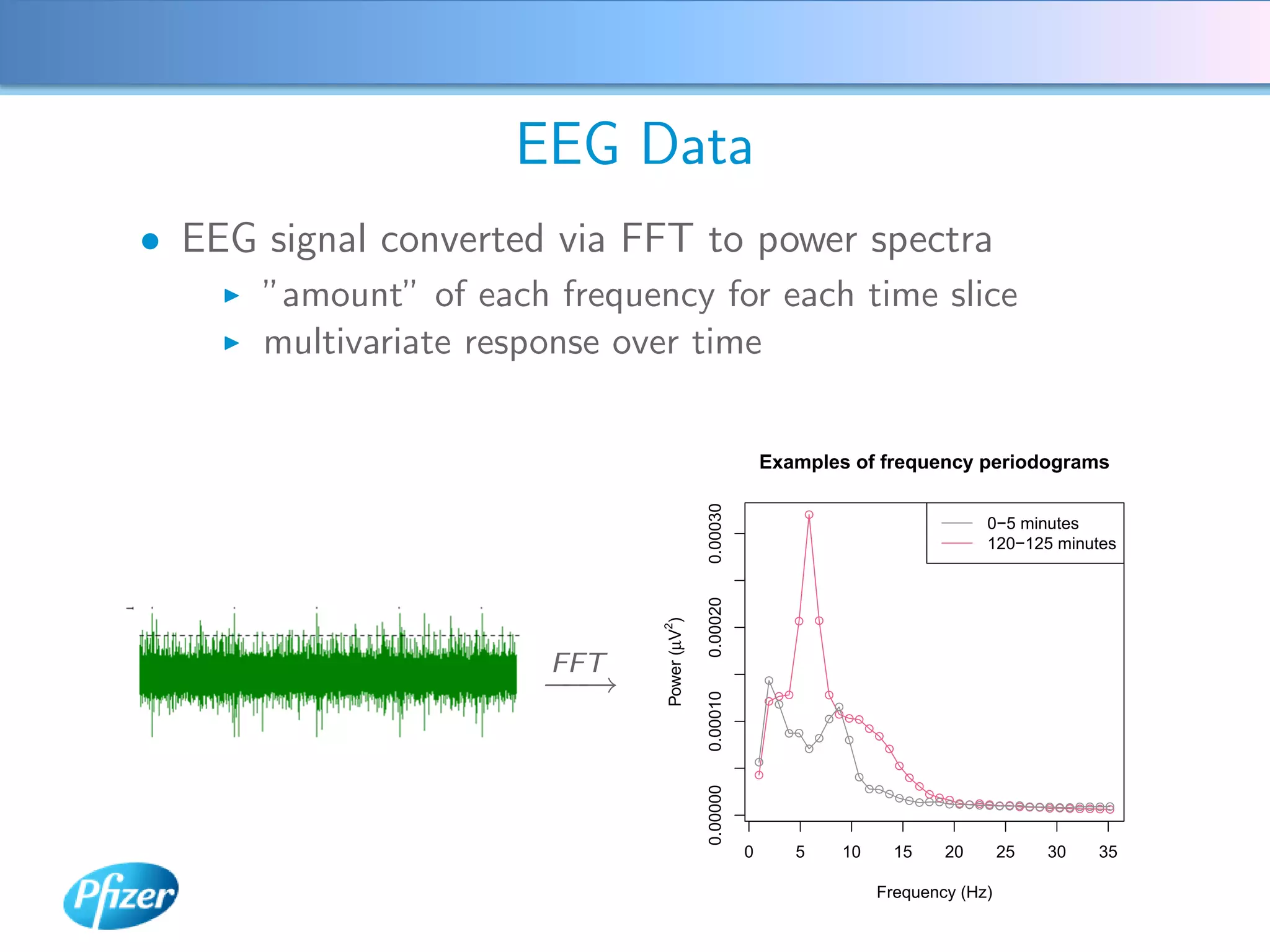
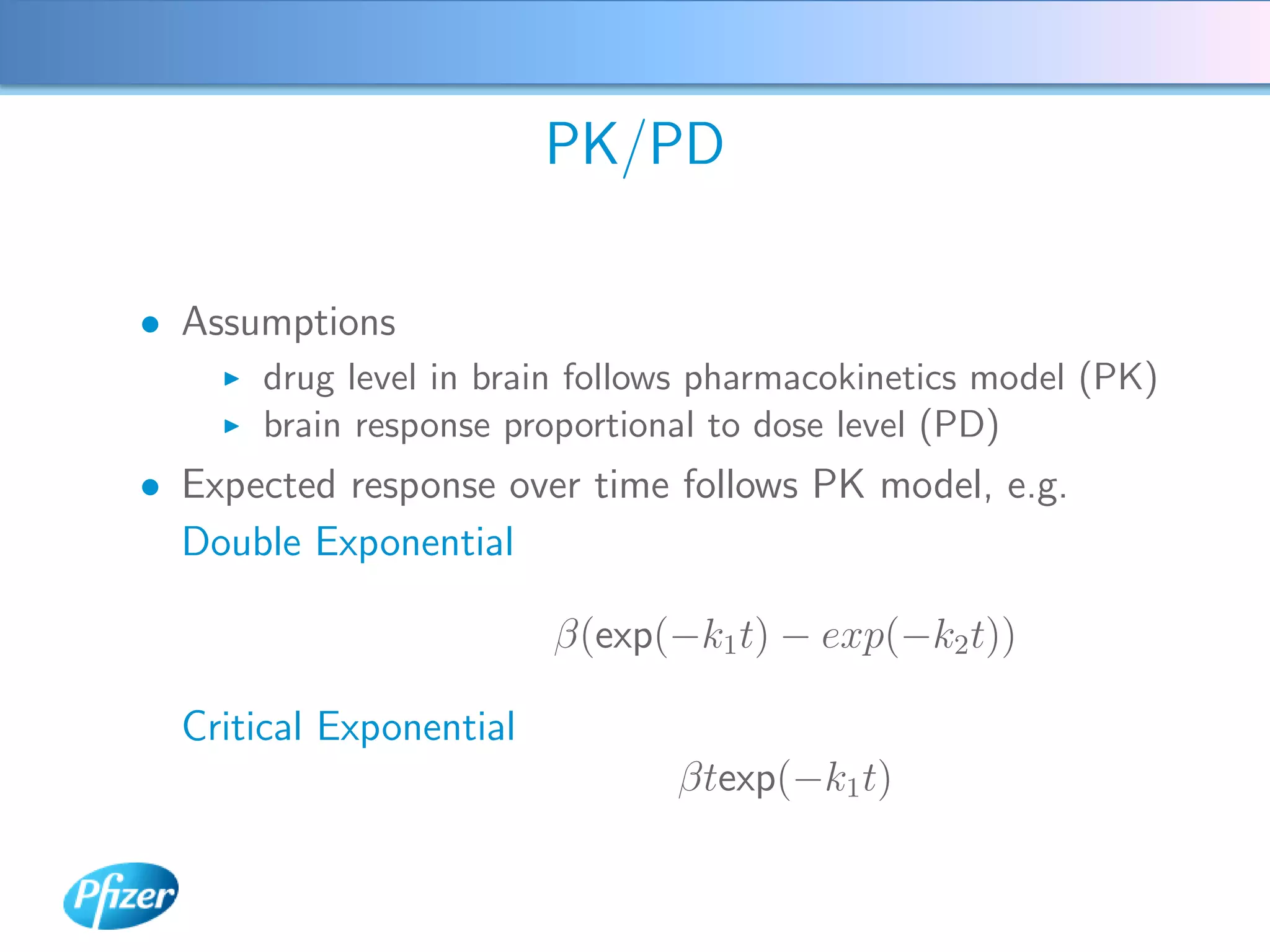
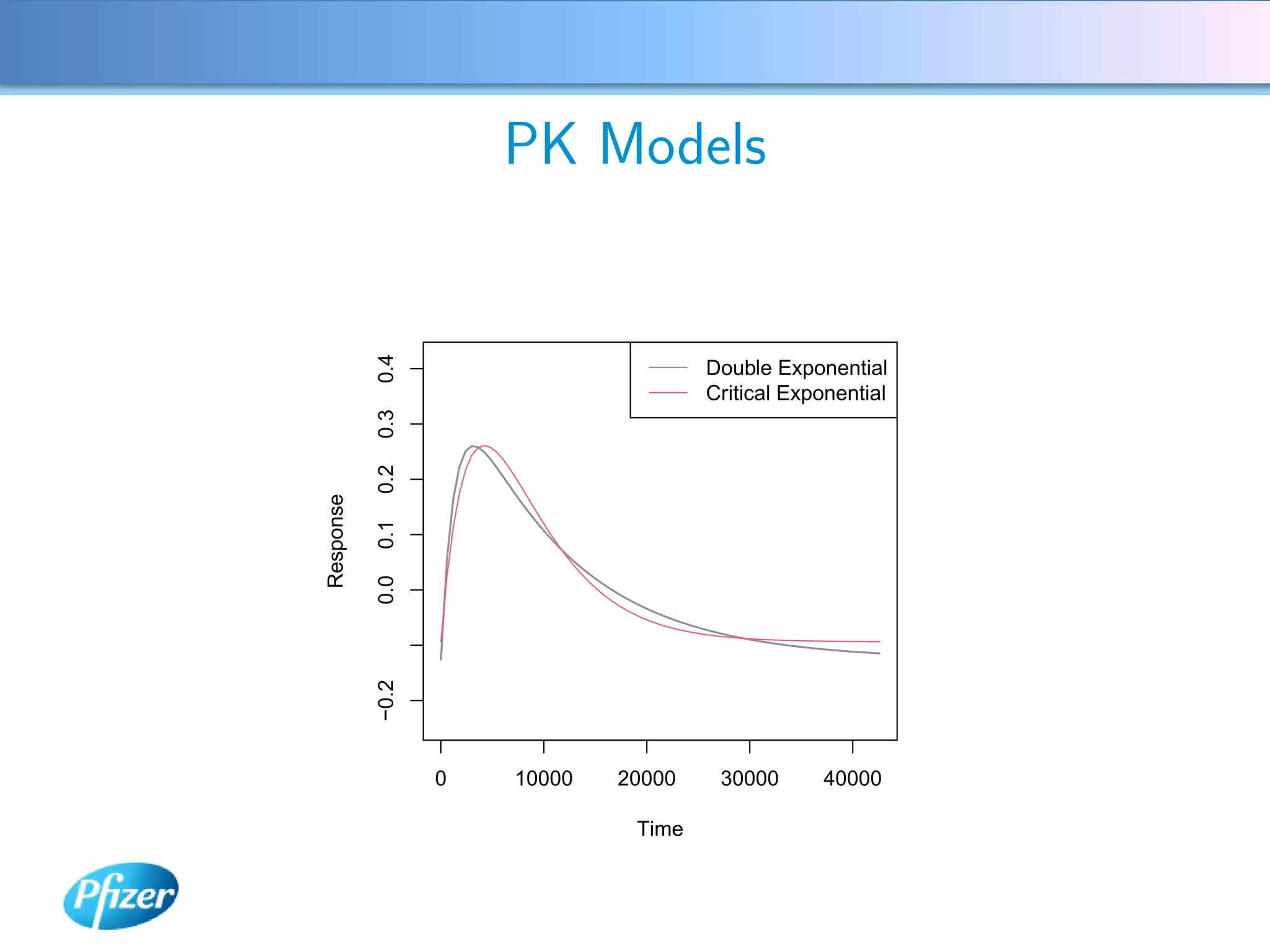
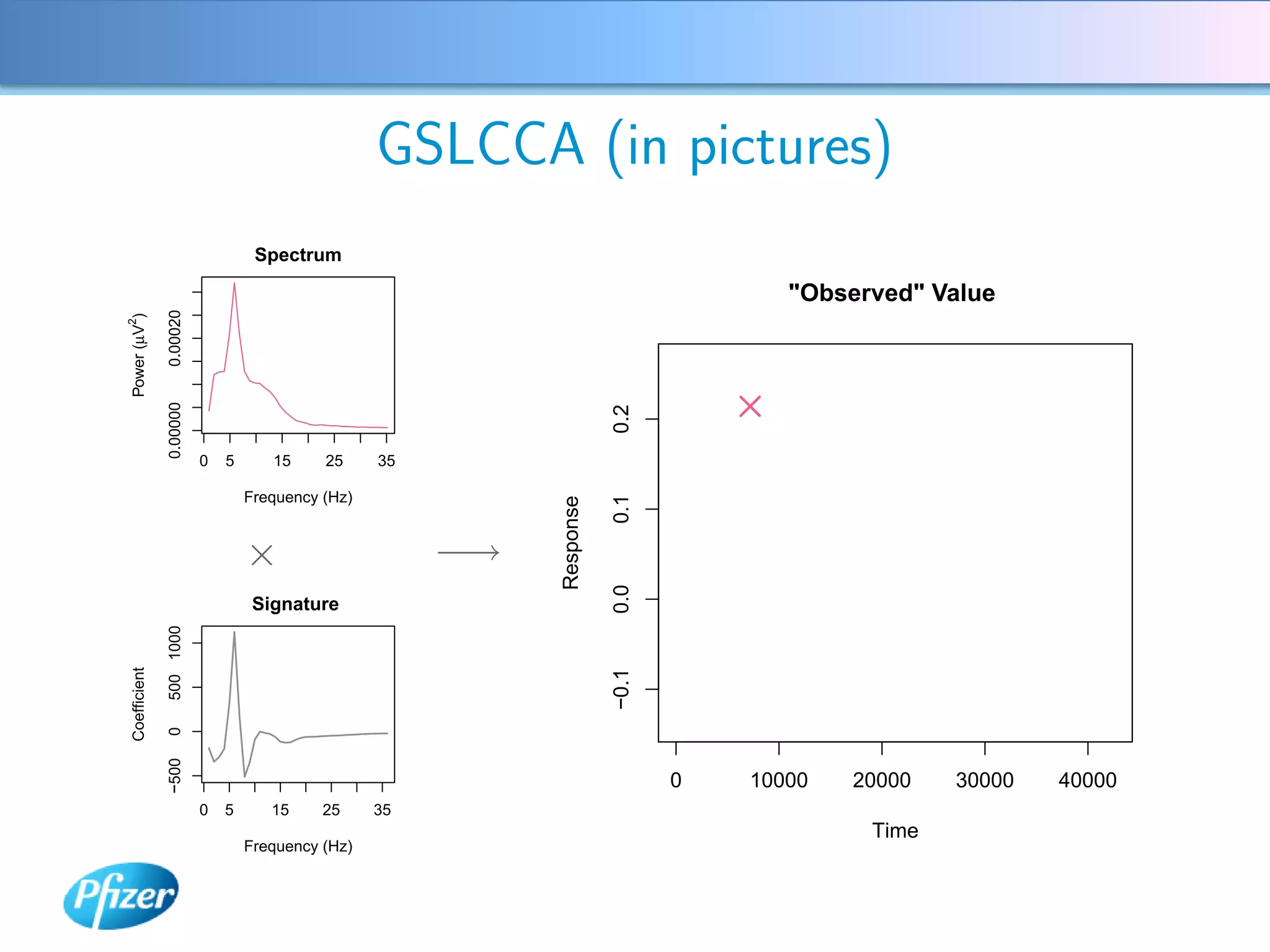
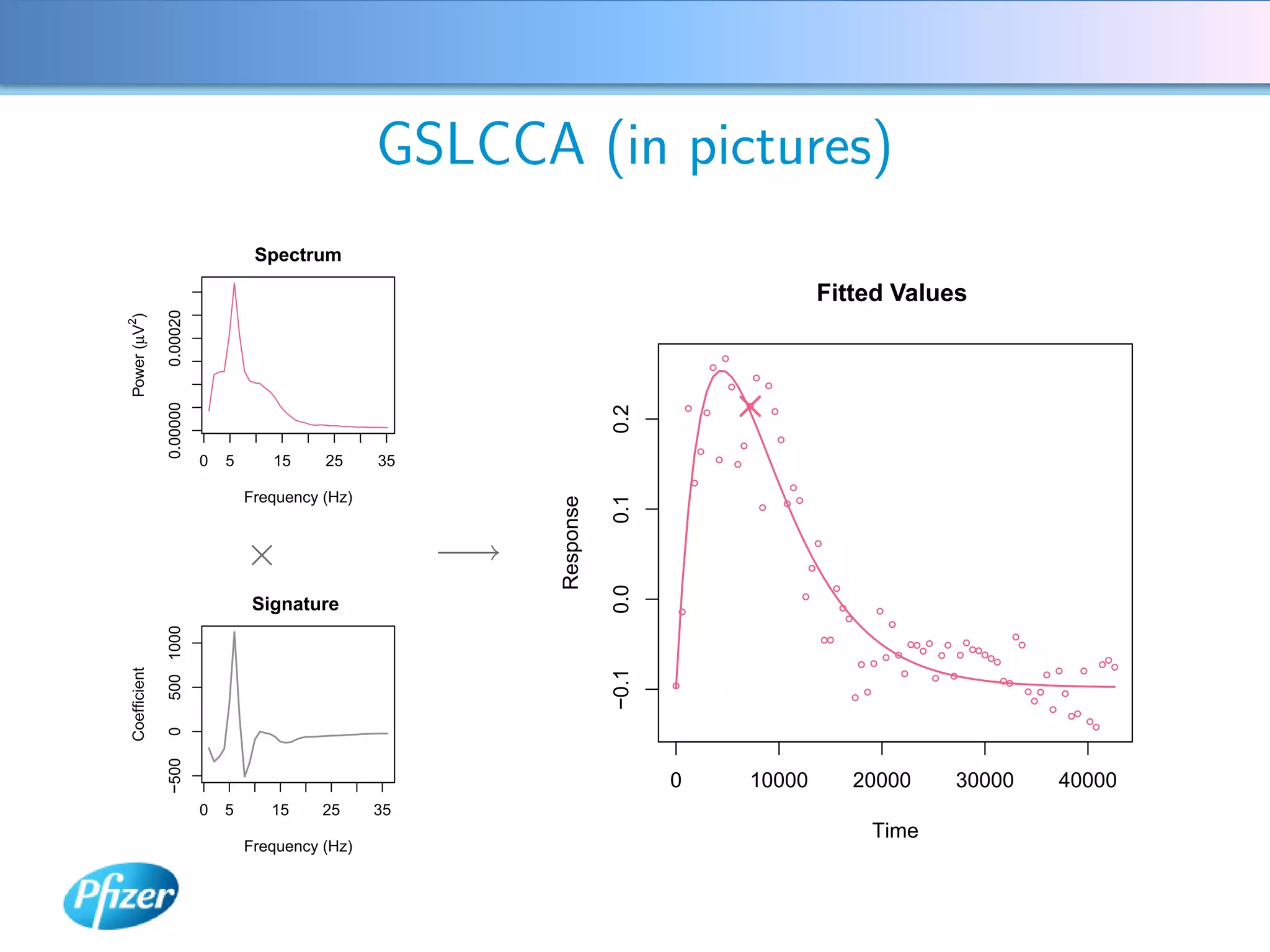
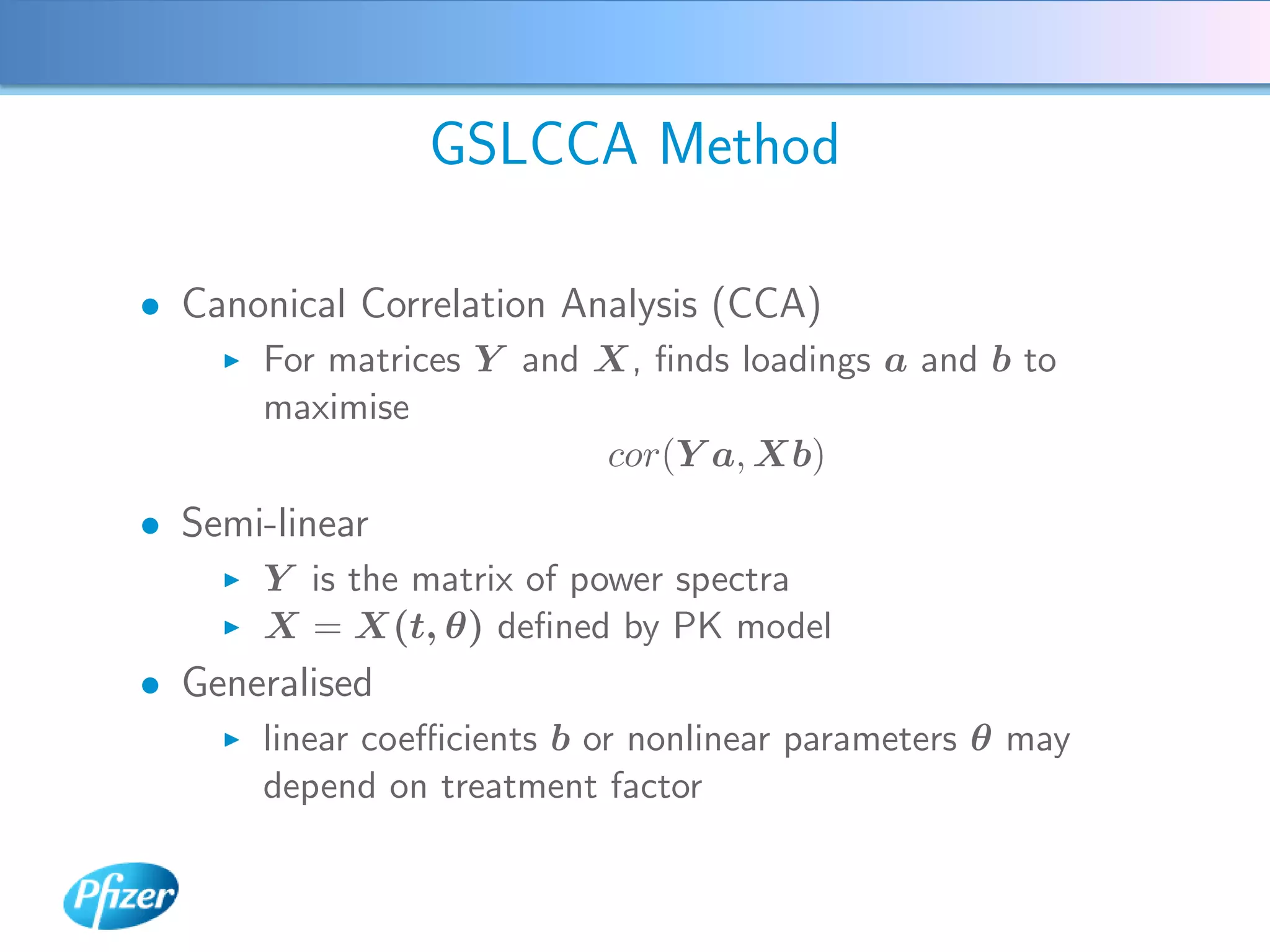
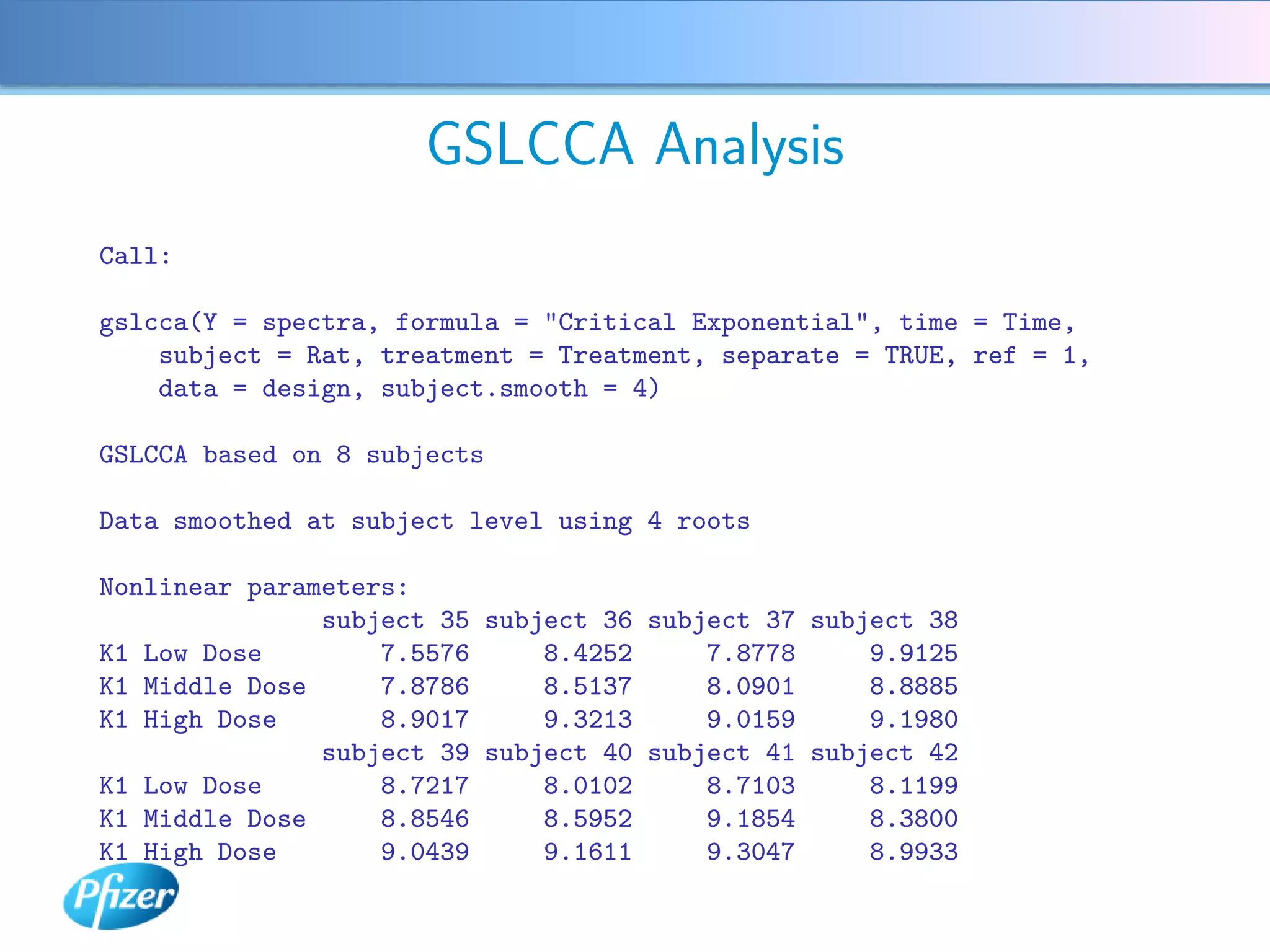
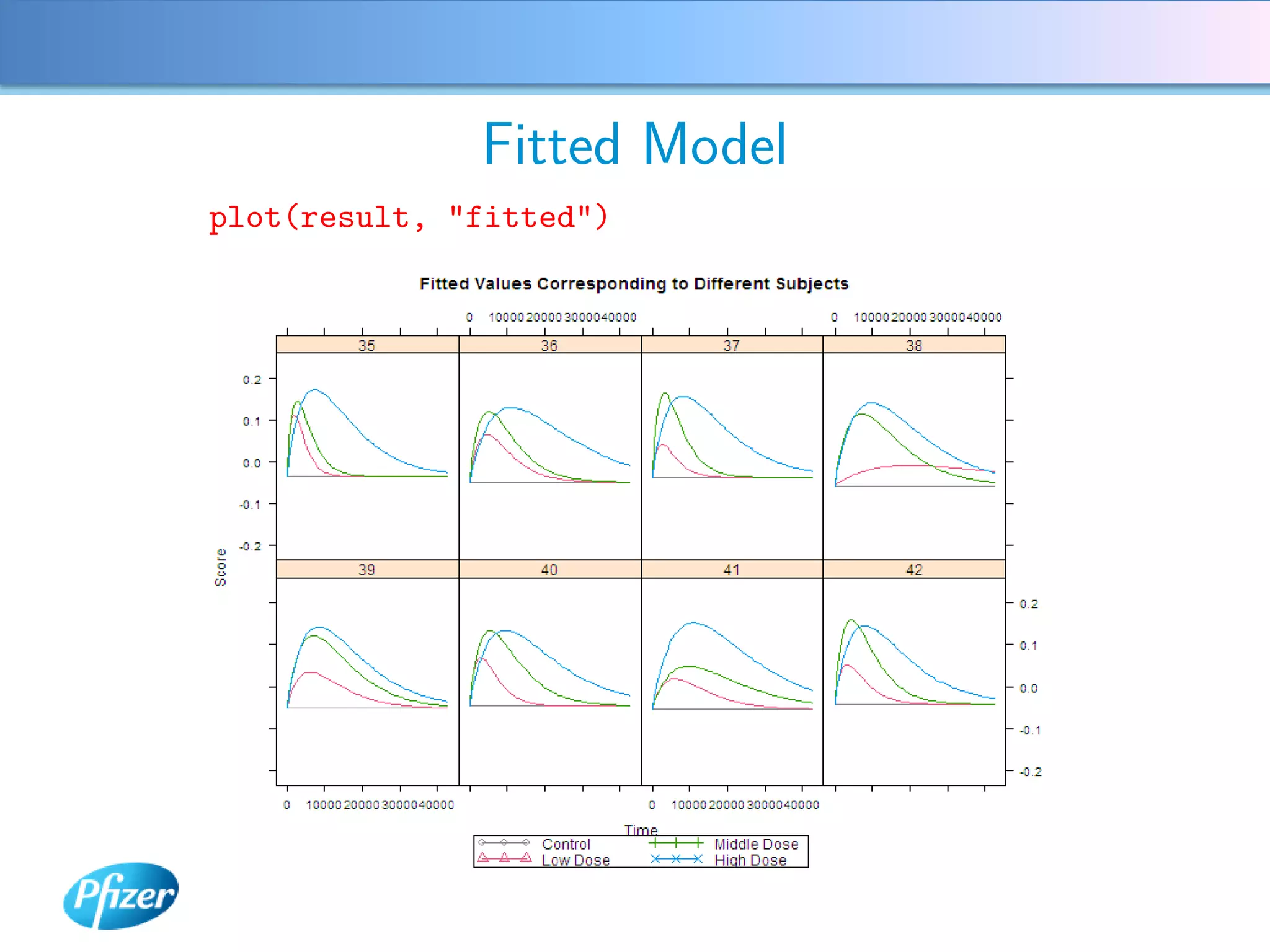
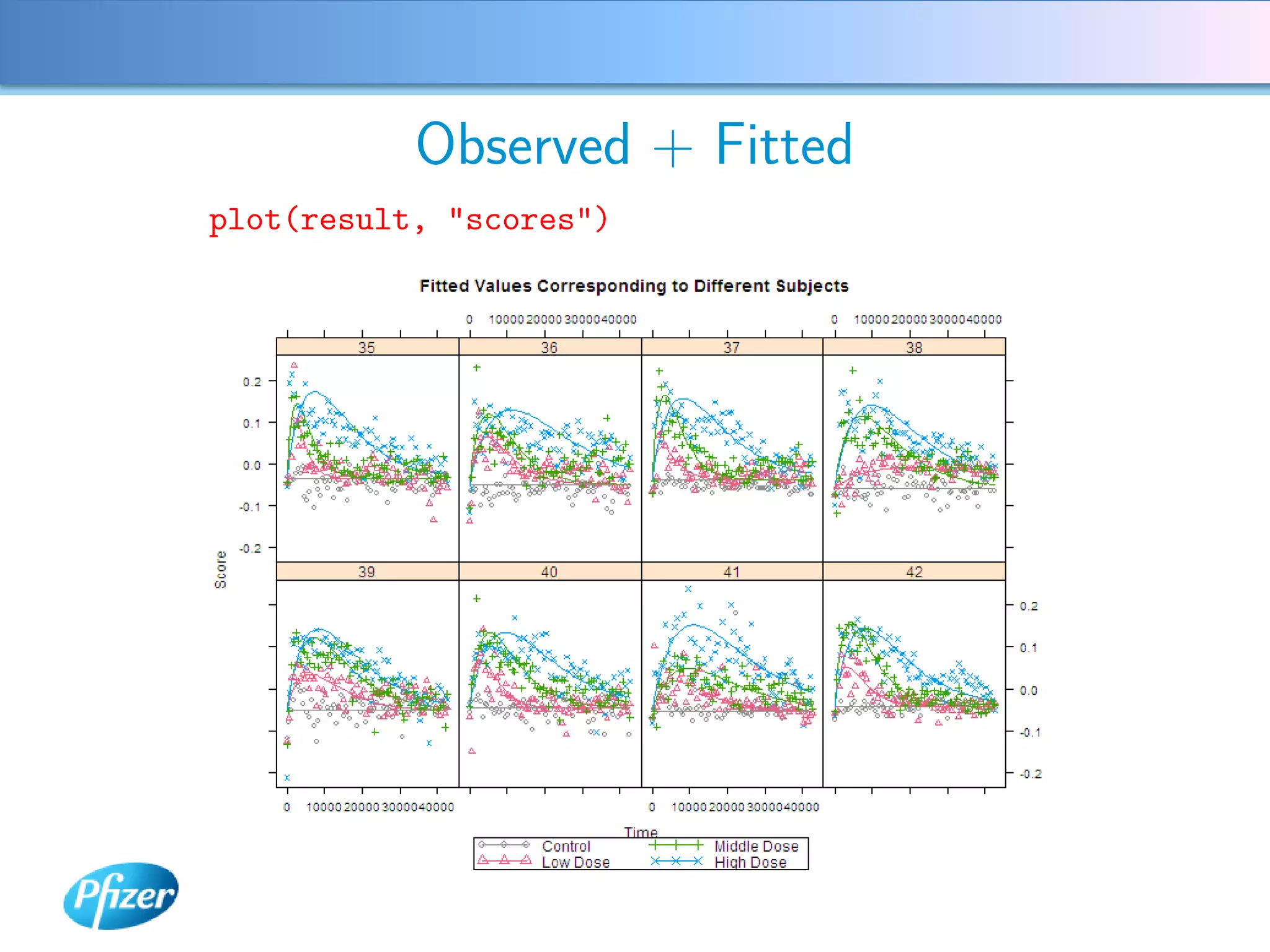
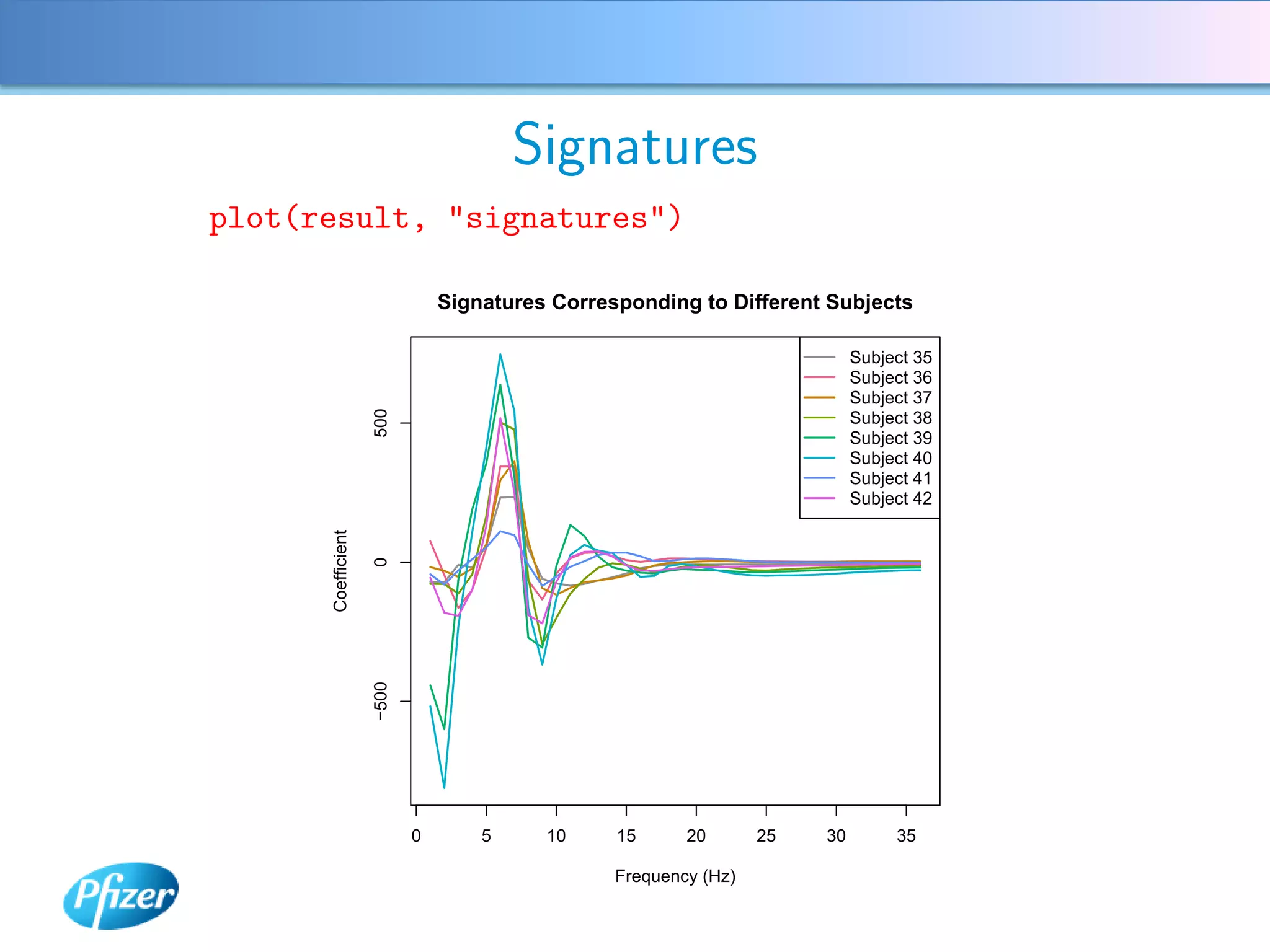
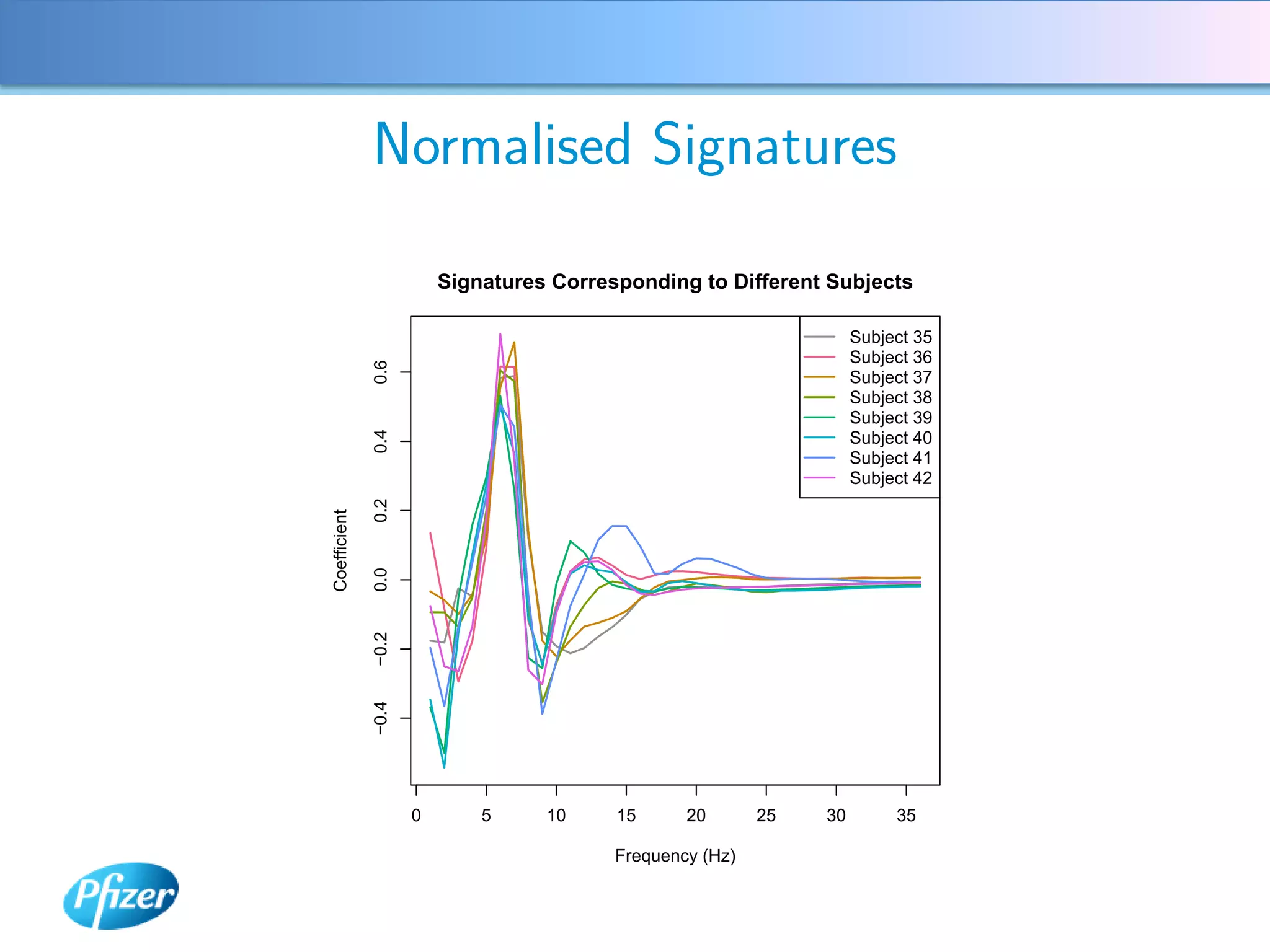
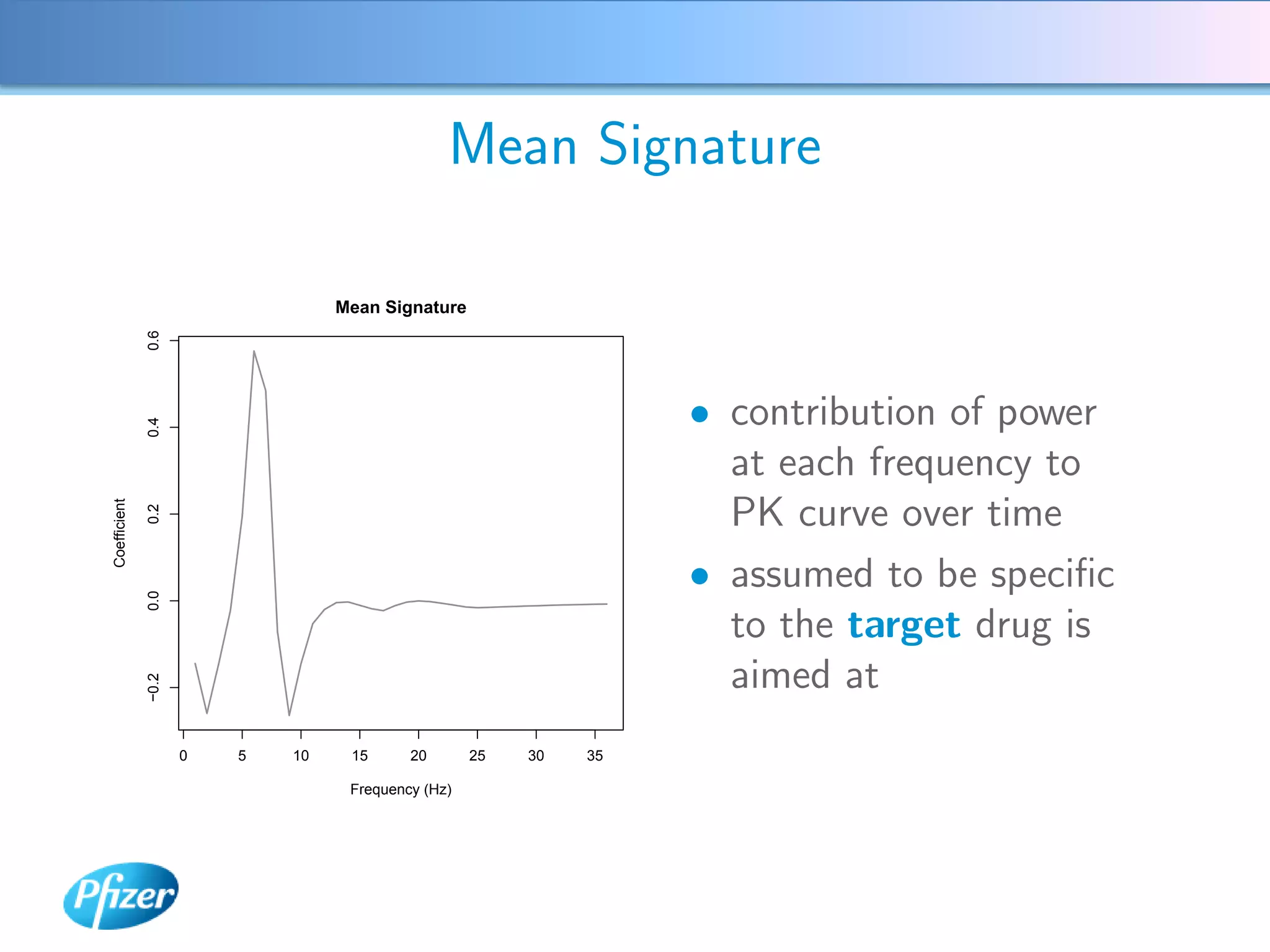
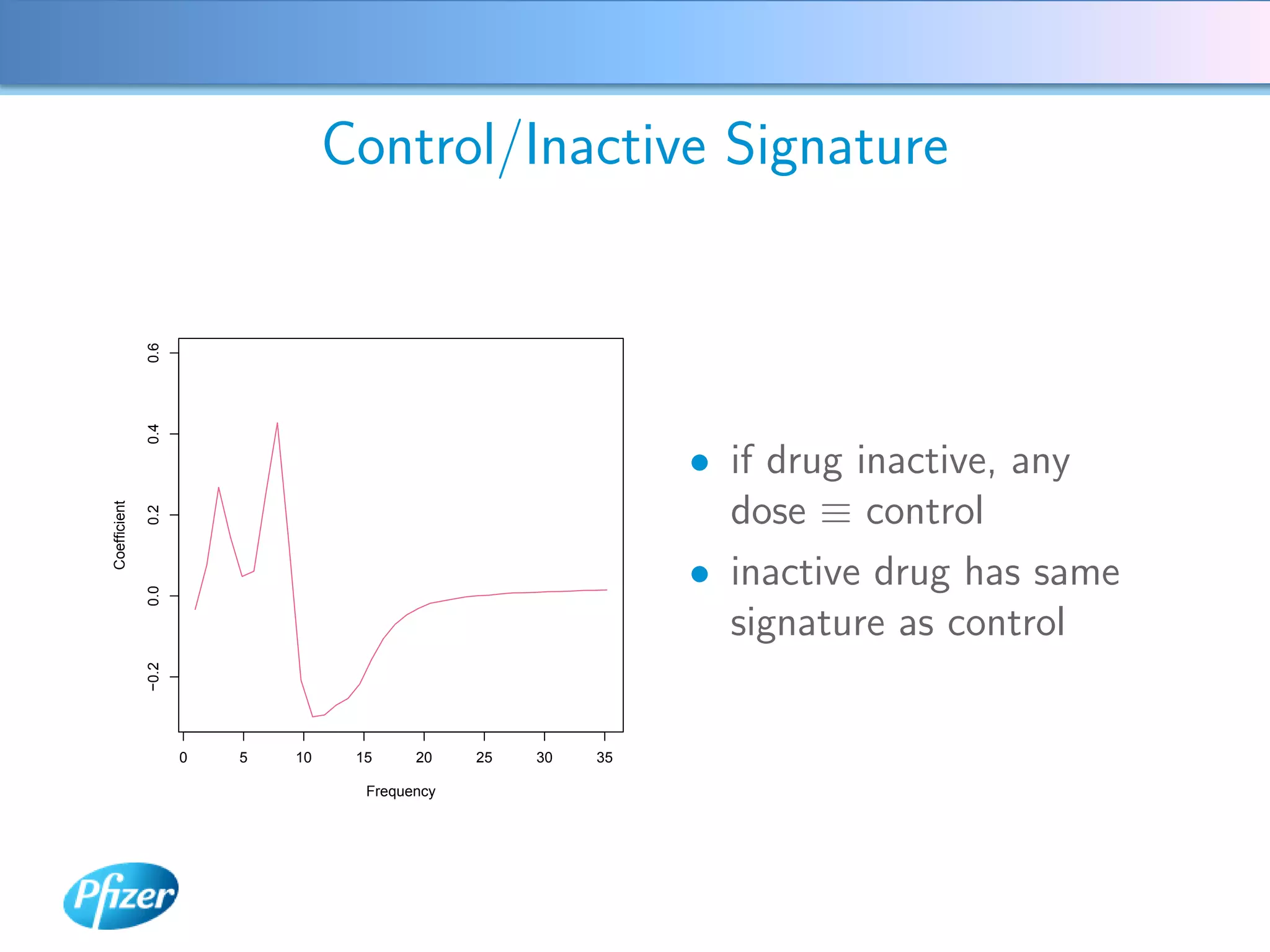
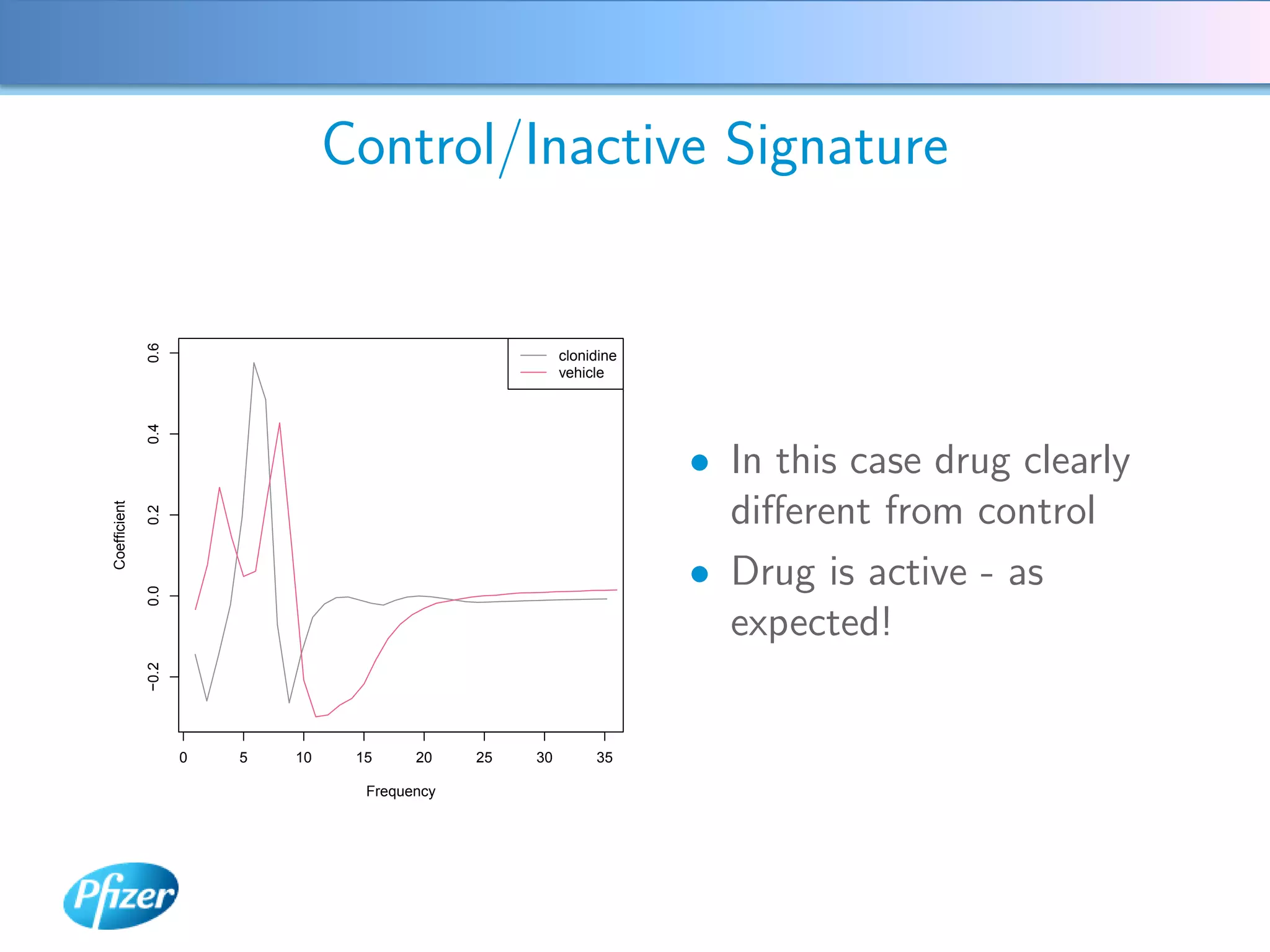
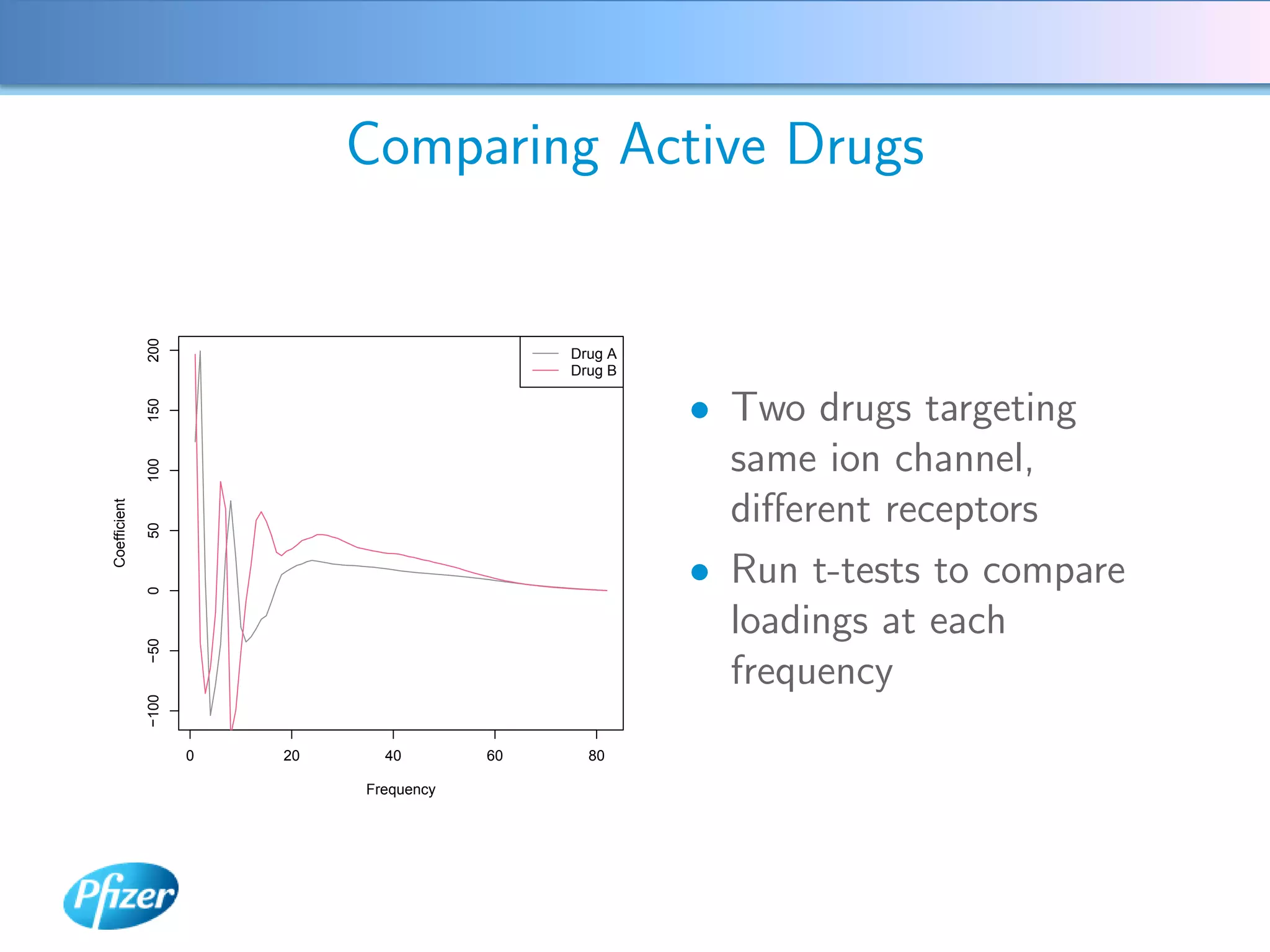
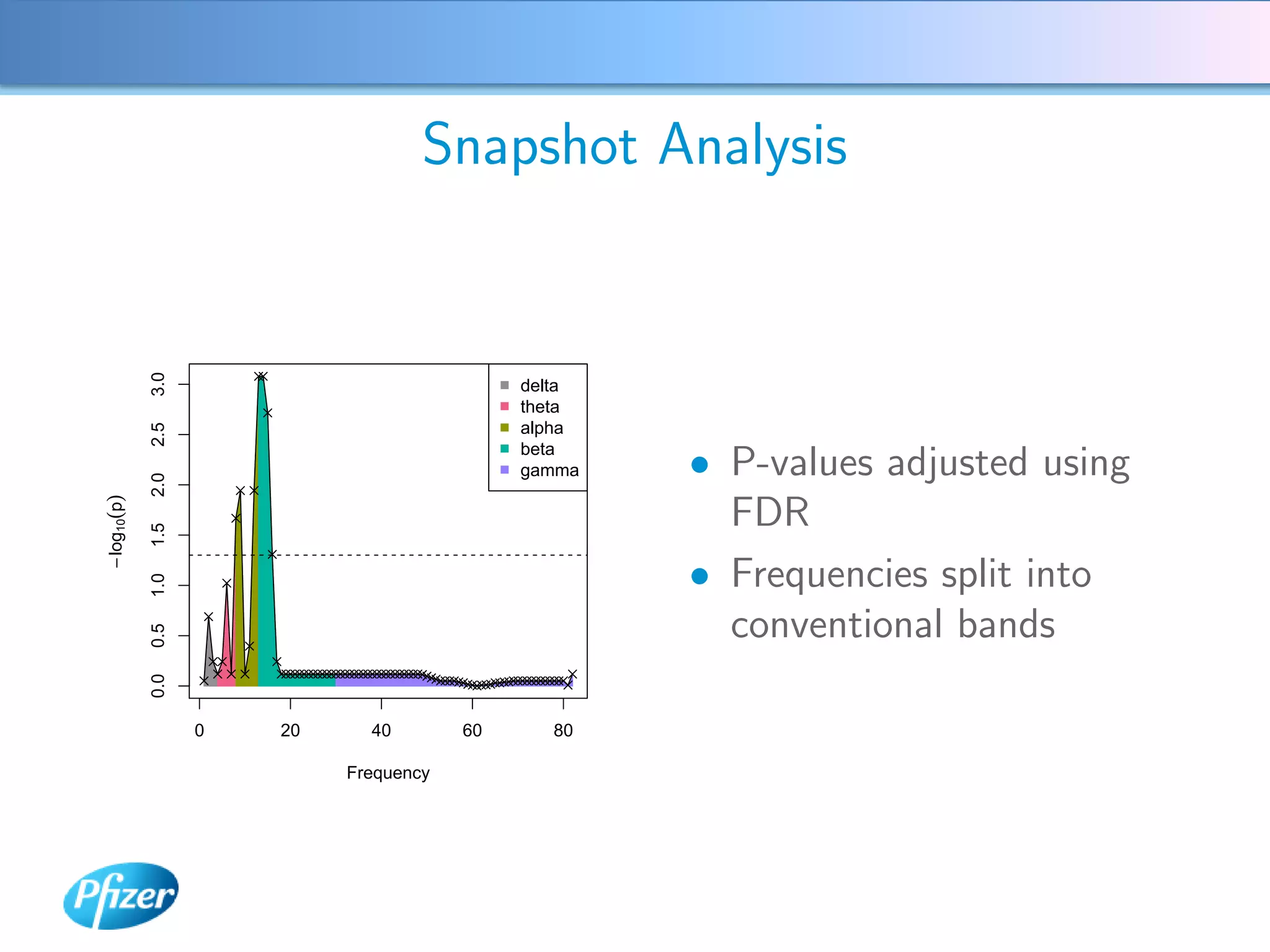
The document describes using Generalised Semi-linear Canonical Correlation Analysis (GSLCCA) to analyze EEG data from a drug experiment and identify the effect of different doses of clonidine on brain activity over time. GSLCCA fits a pharmacokinetic model to the EEG power spectra data and extracts "signatures" representing the contribution of different brain frequencies to the drug's time-dependent response. The analysis revealed dose-dependent changes in the signatures compared to vehicle control, indicating clonidine had an active effect on brain activity as expected.