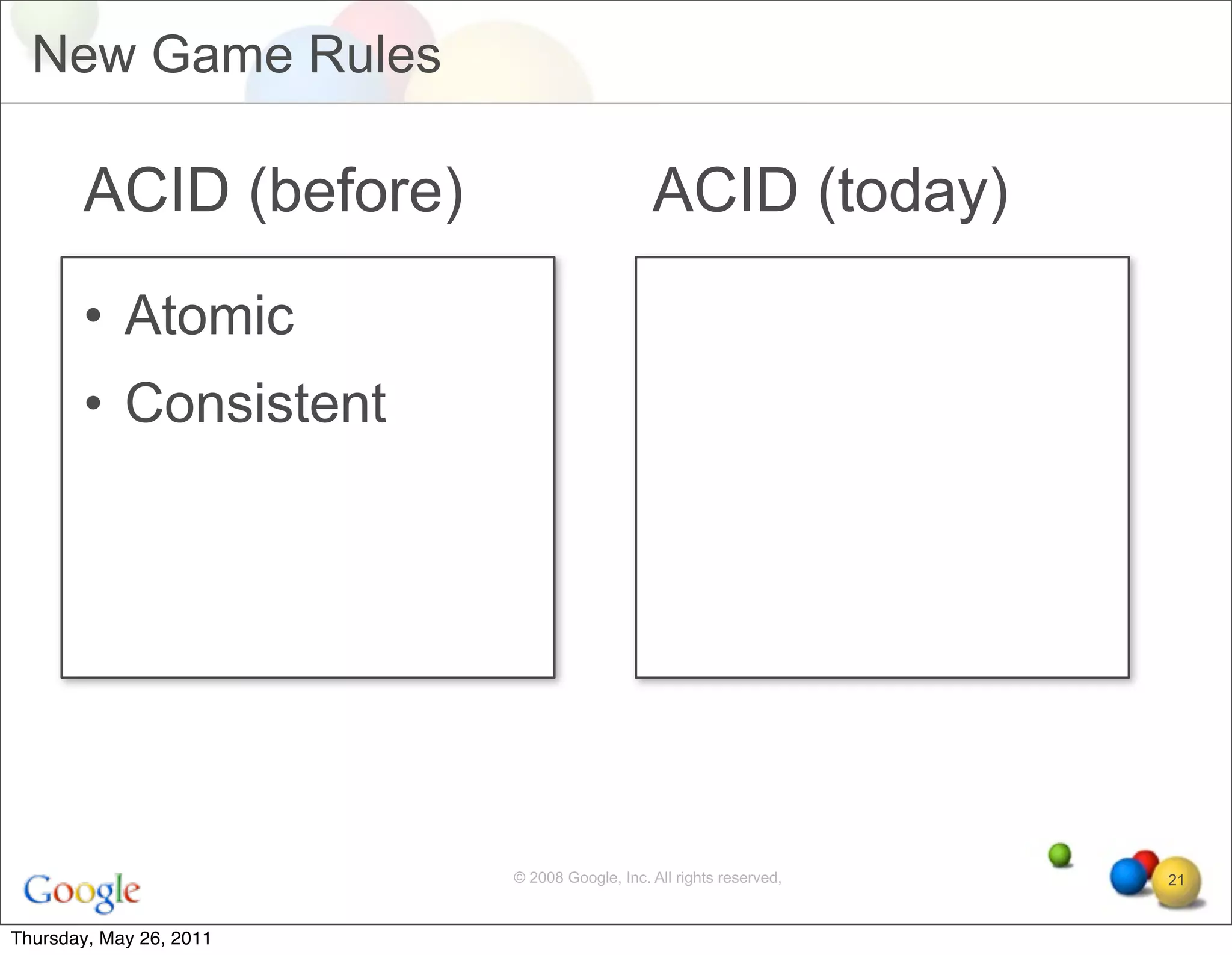
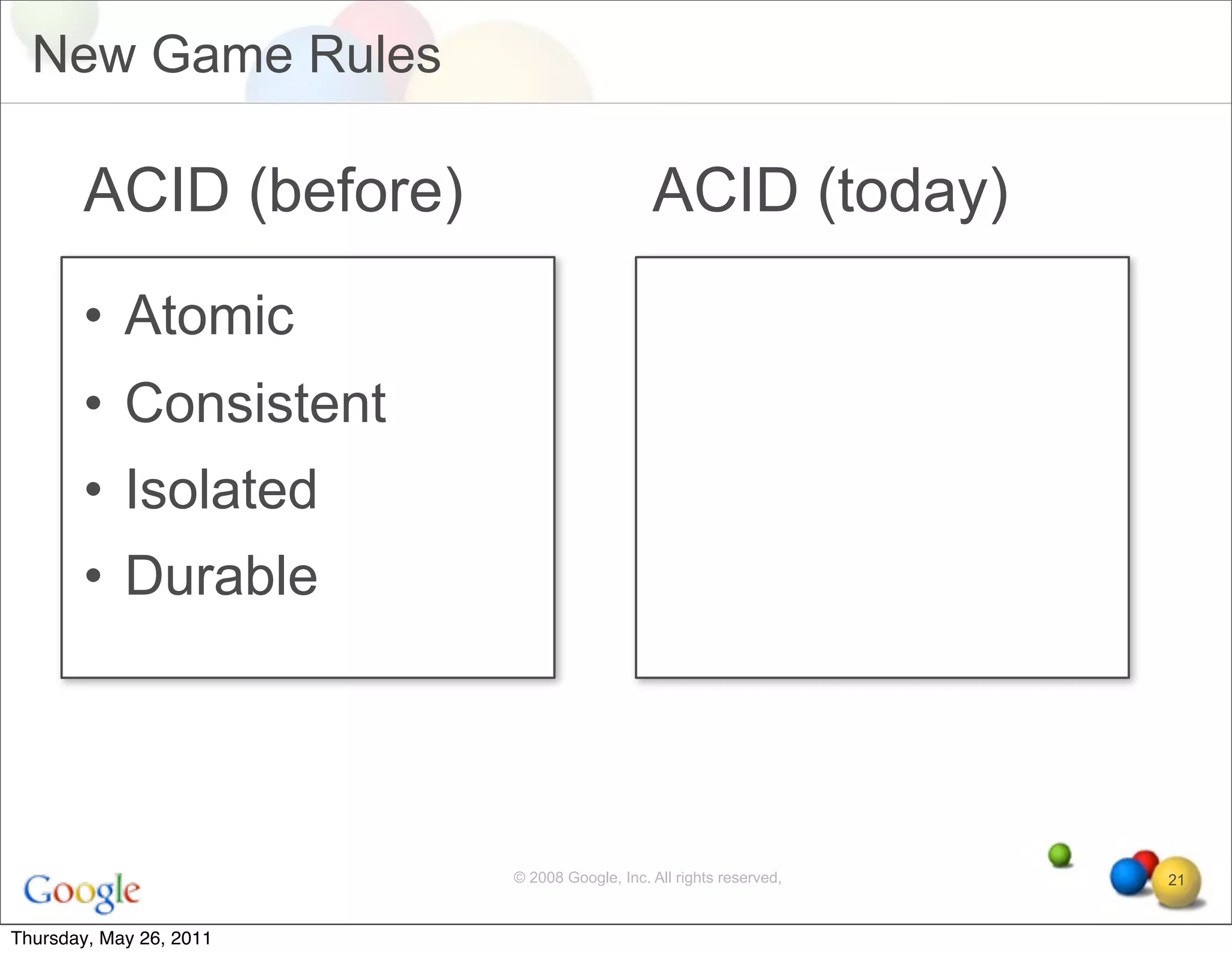
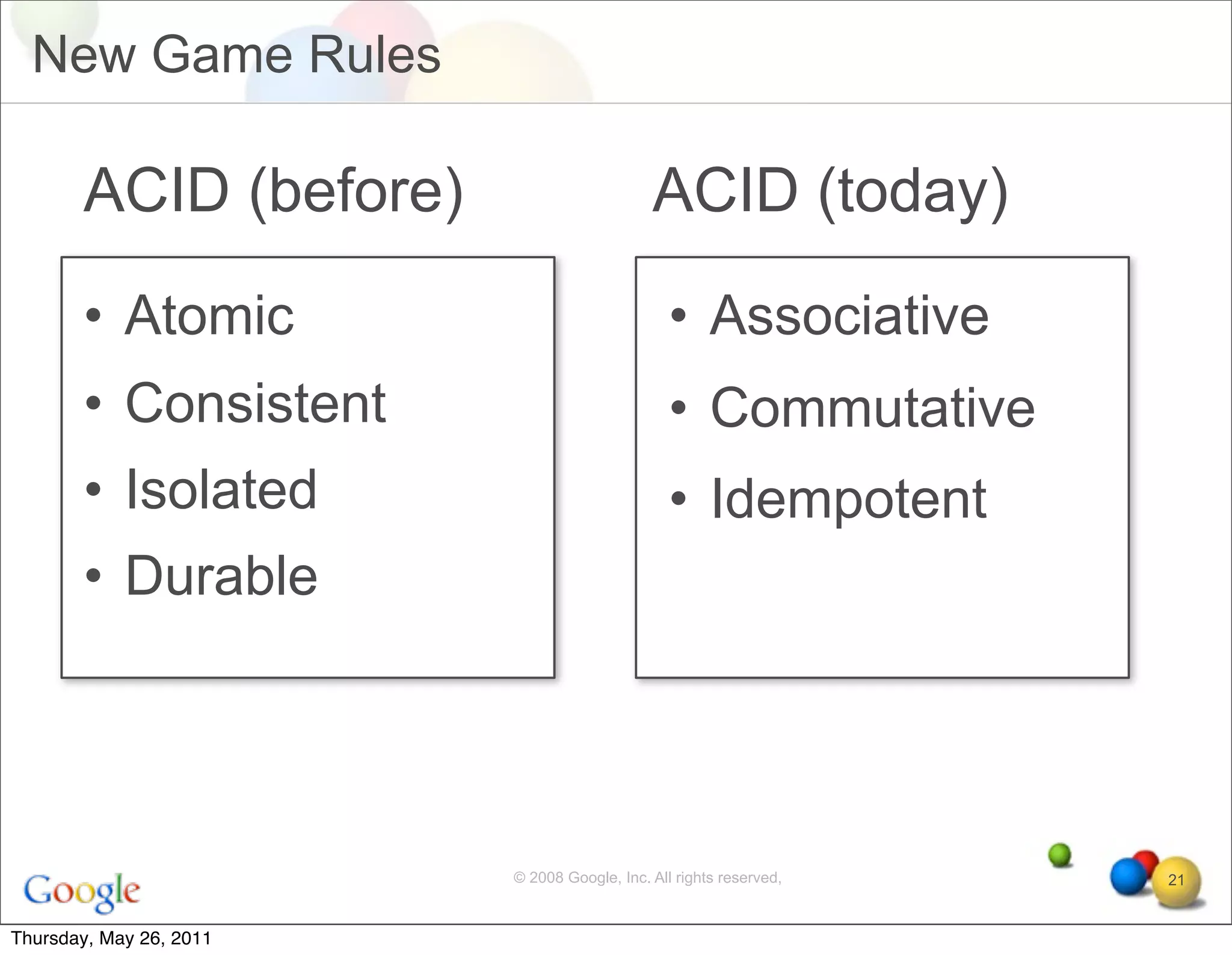
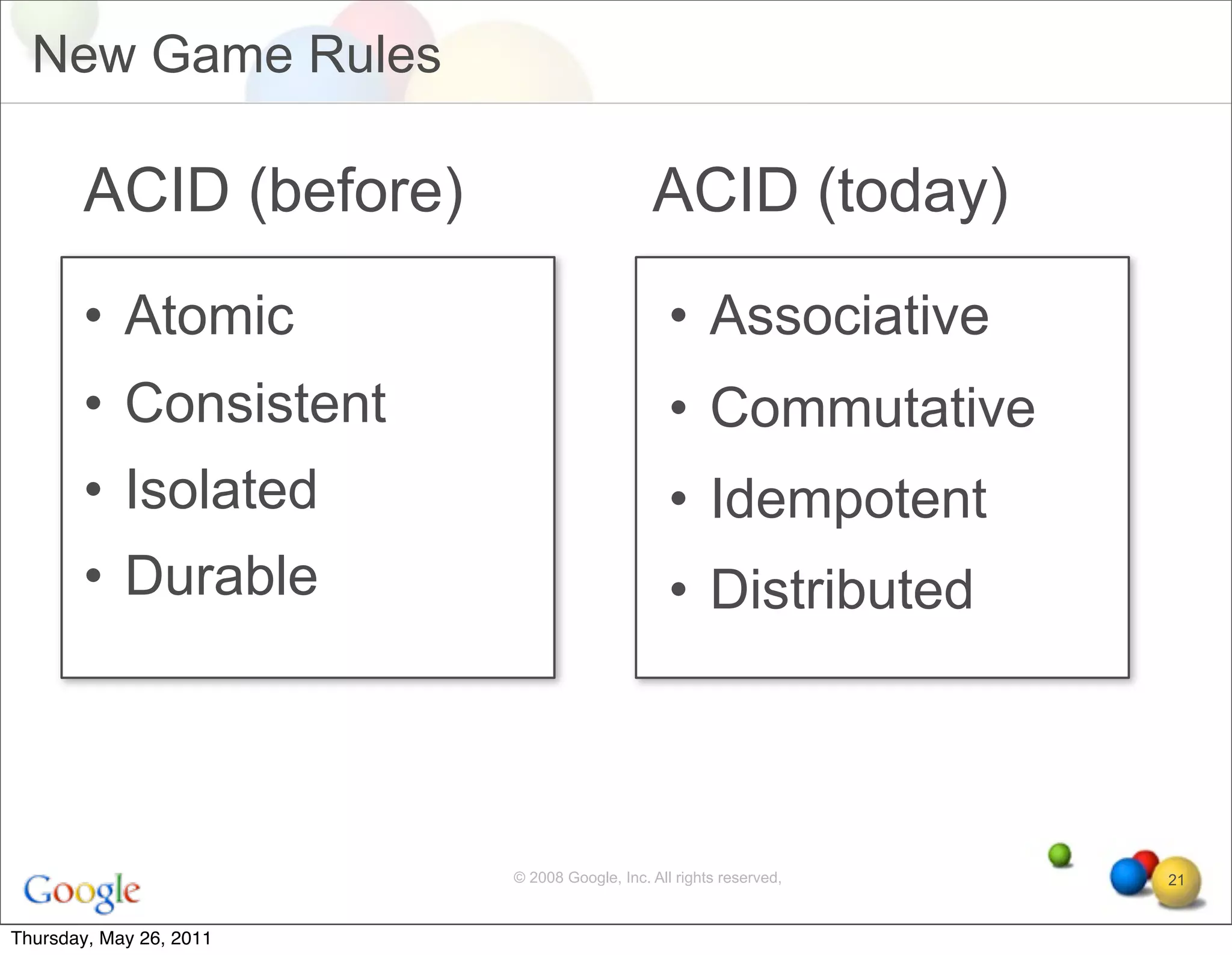
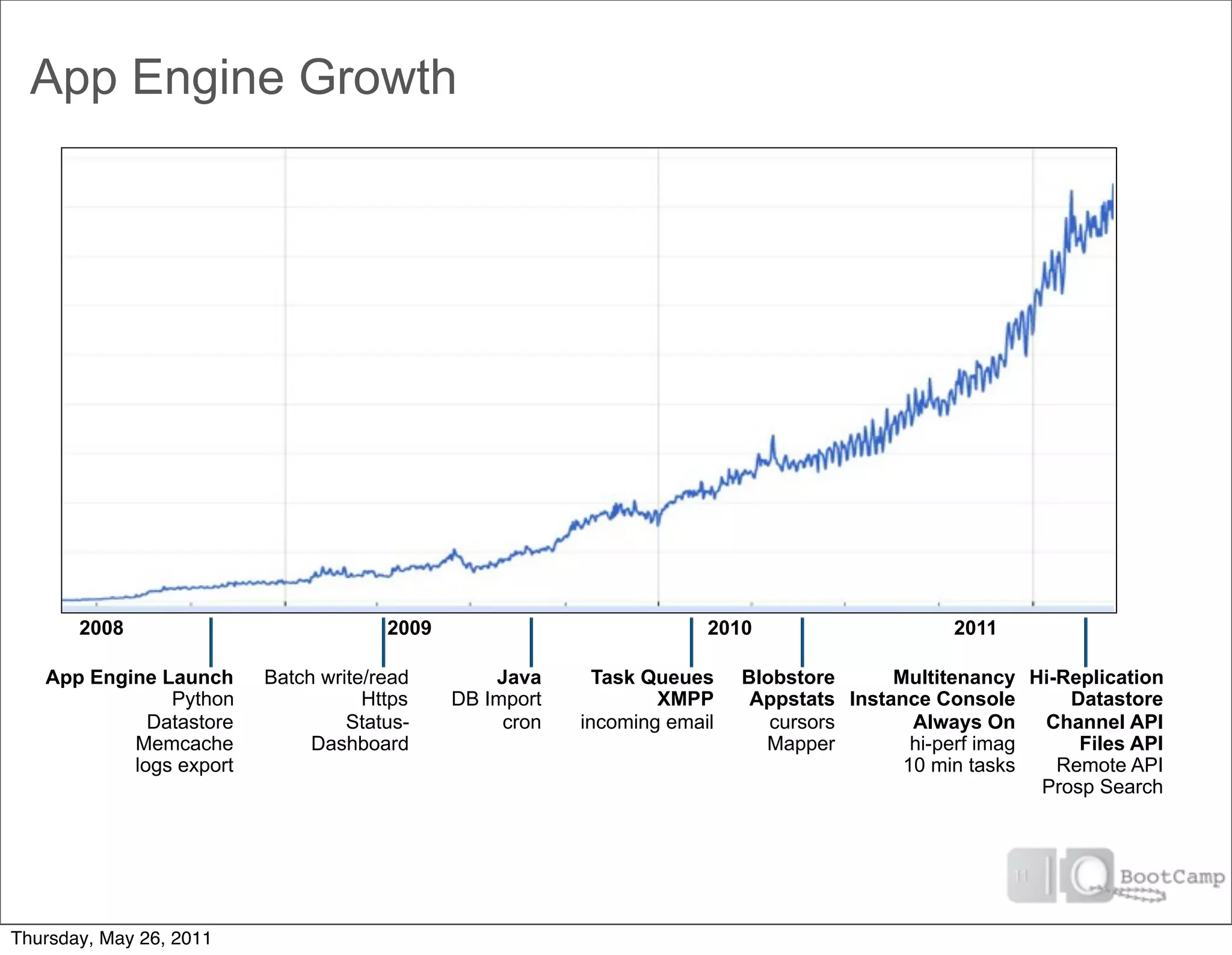
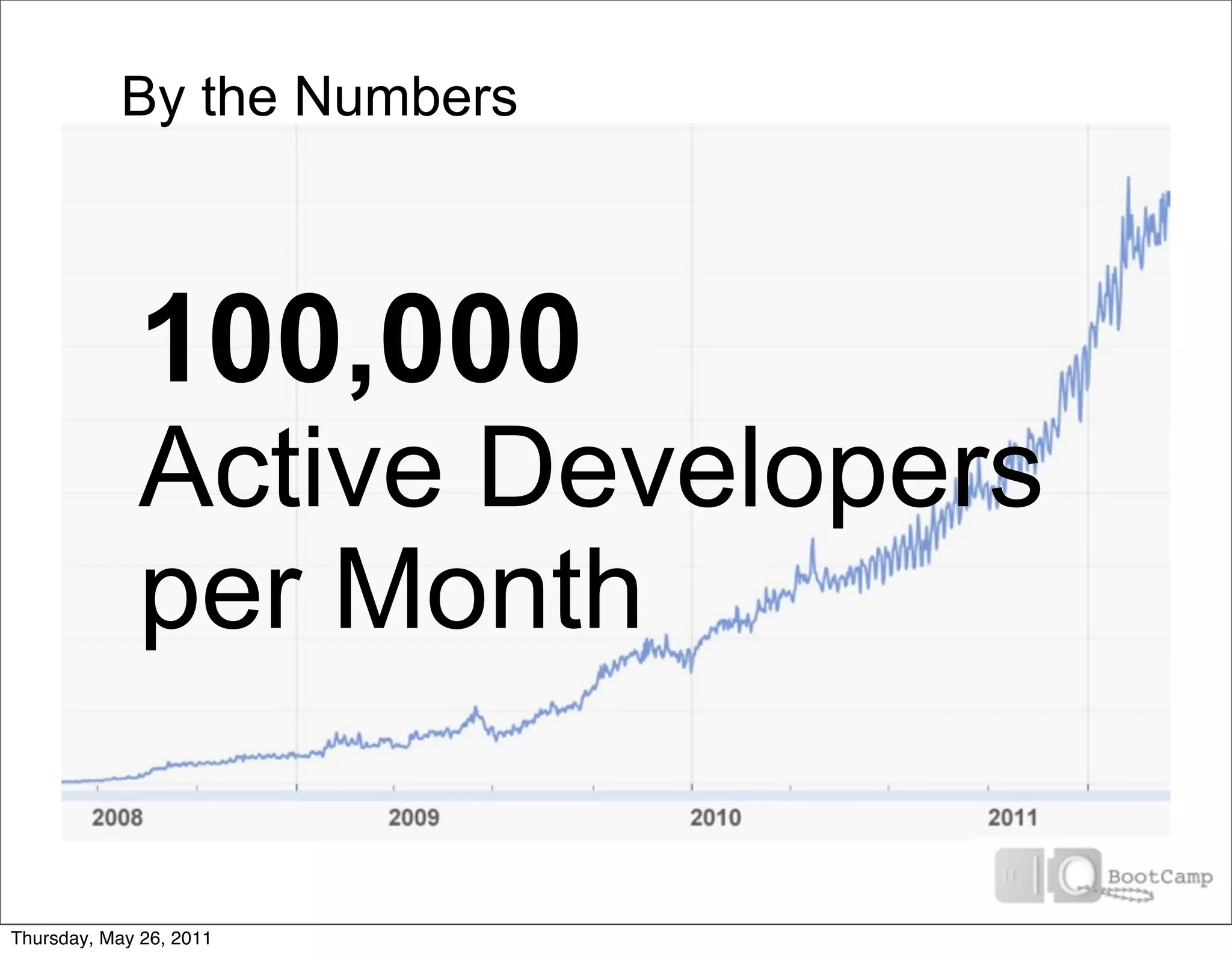
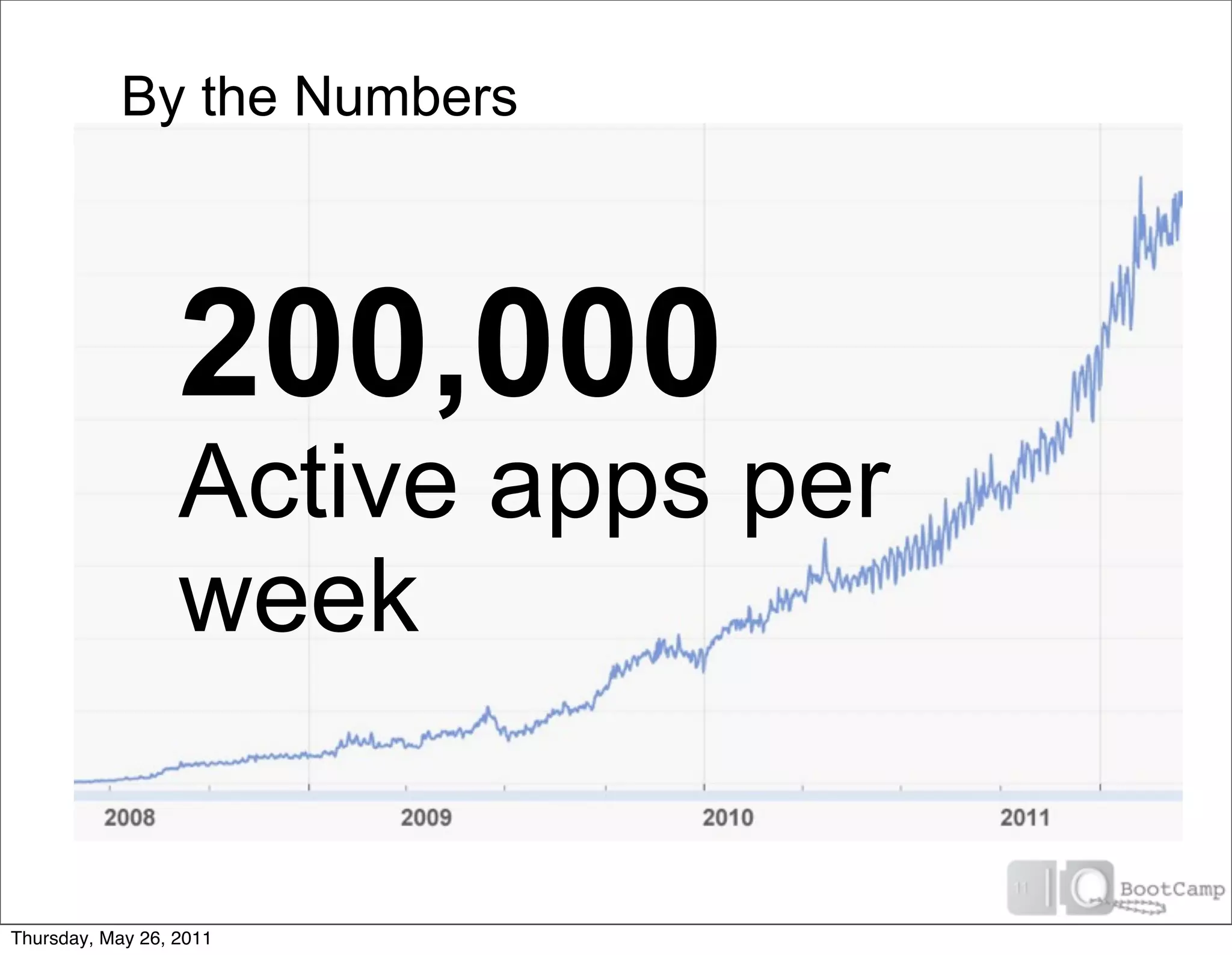
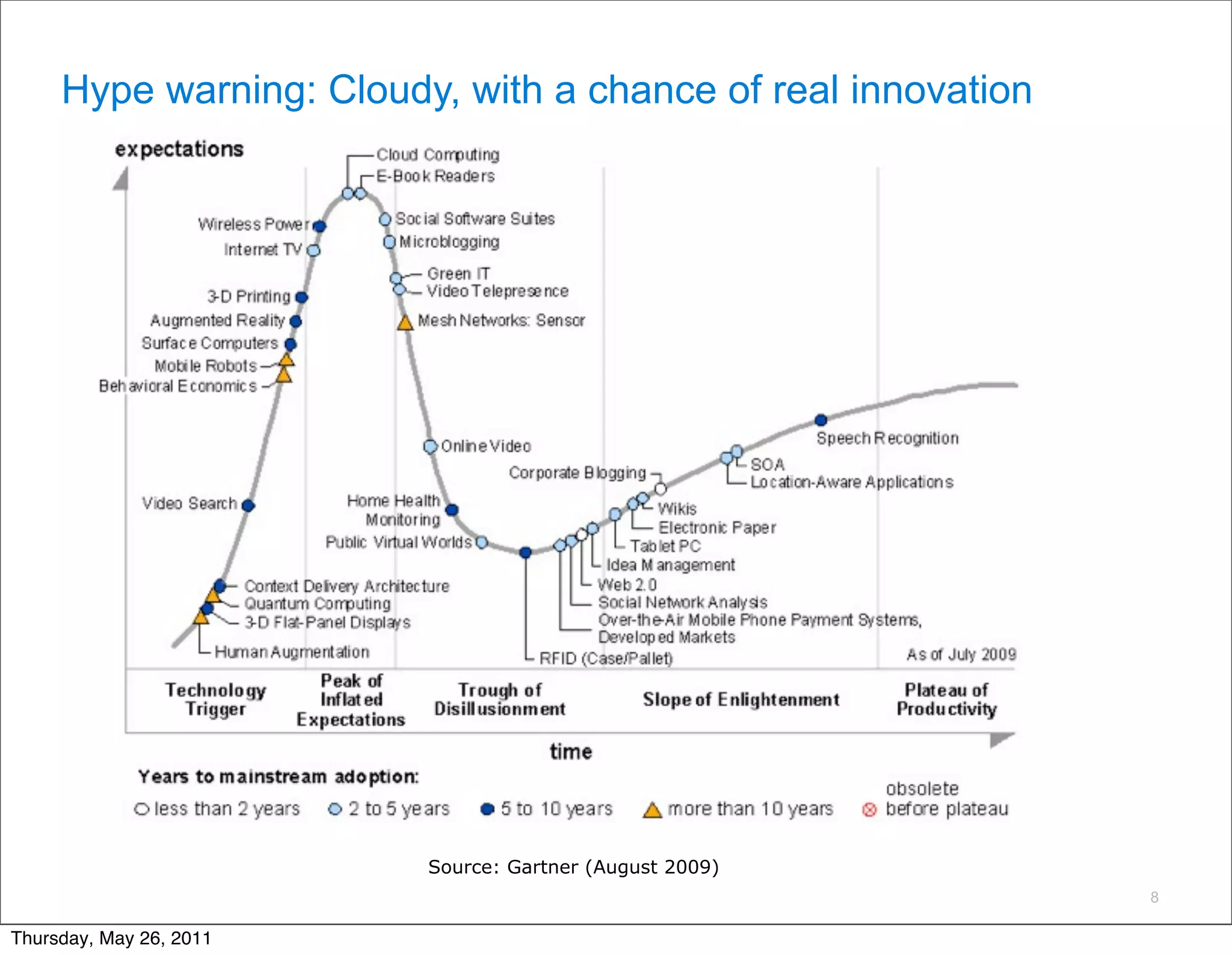
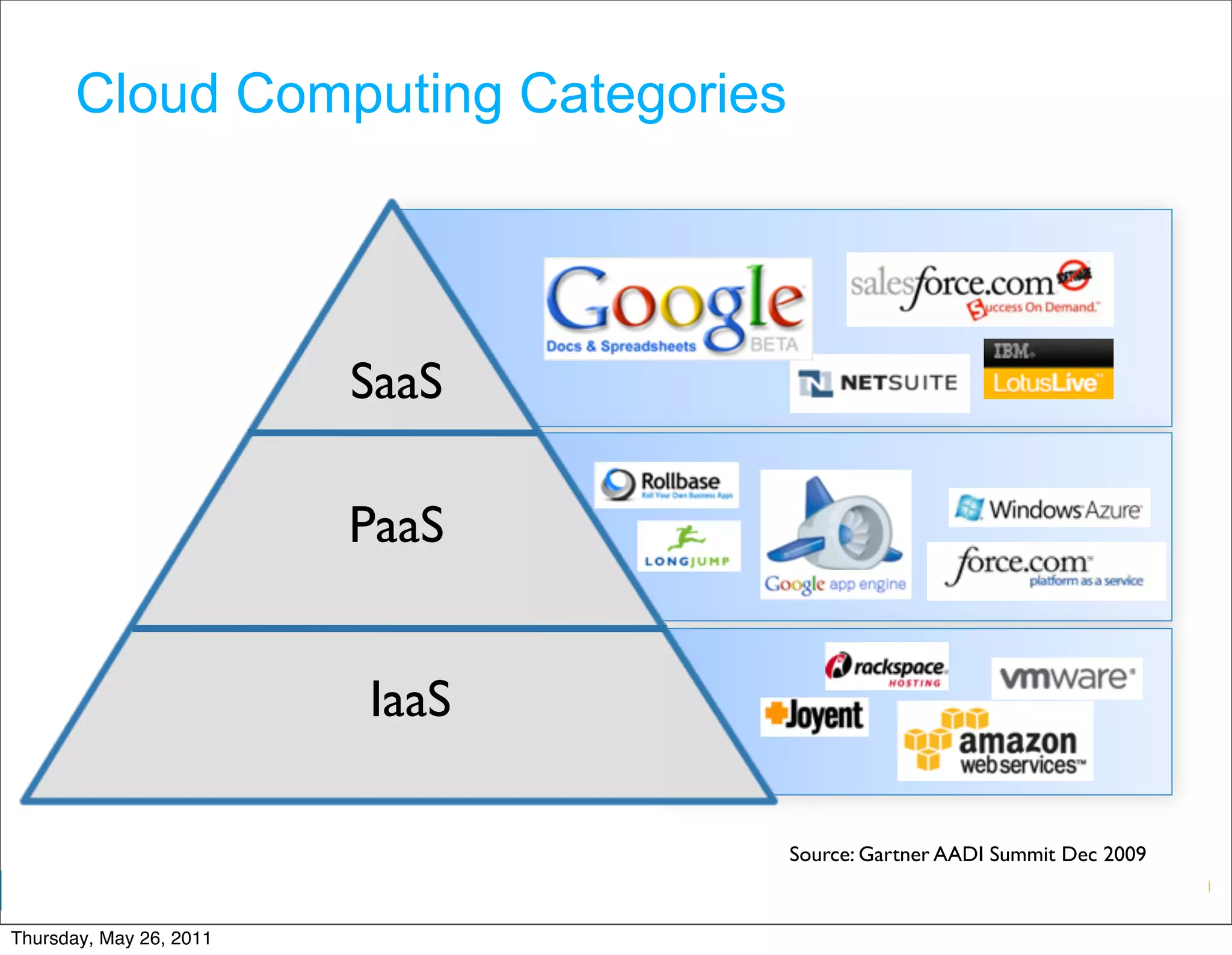
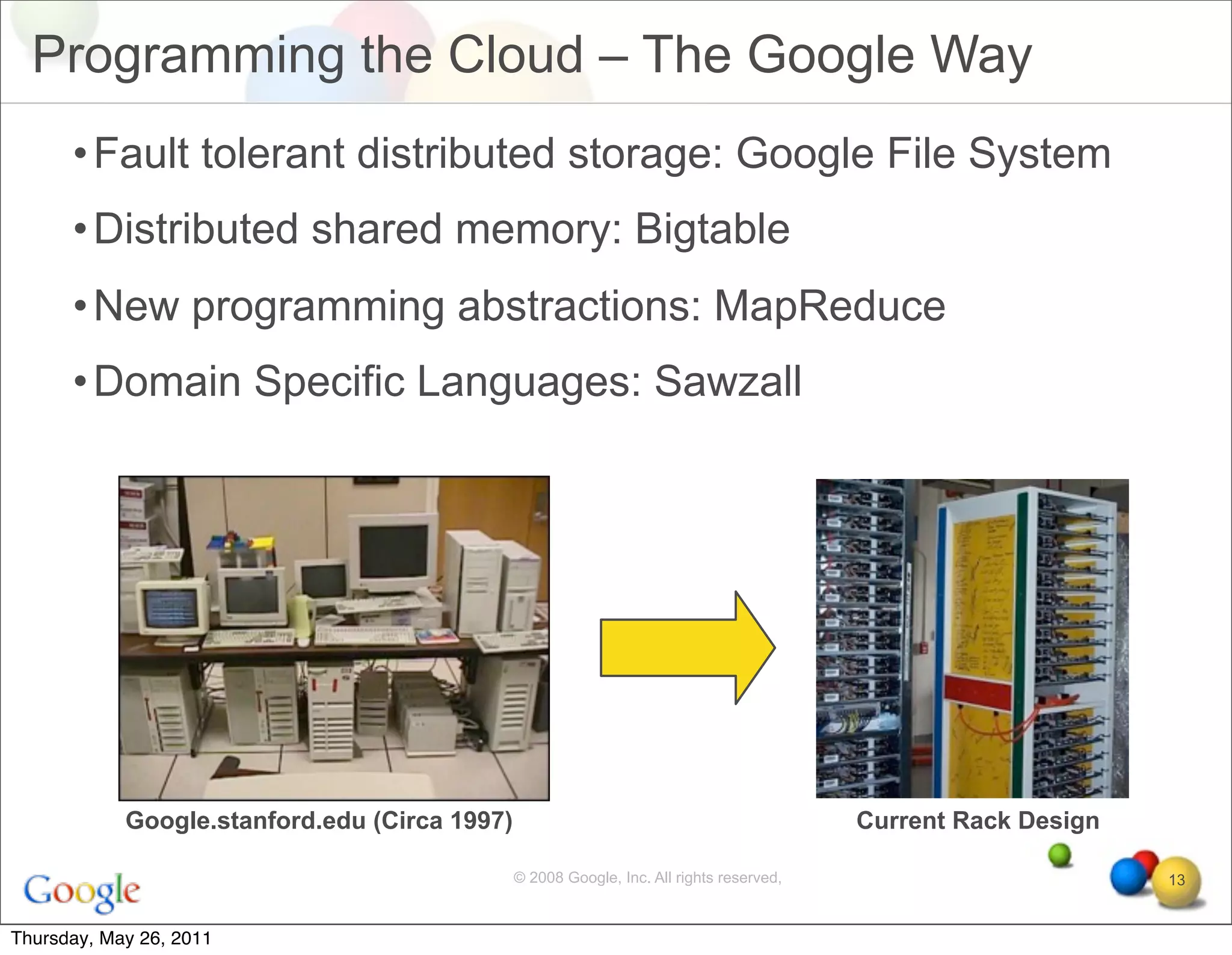
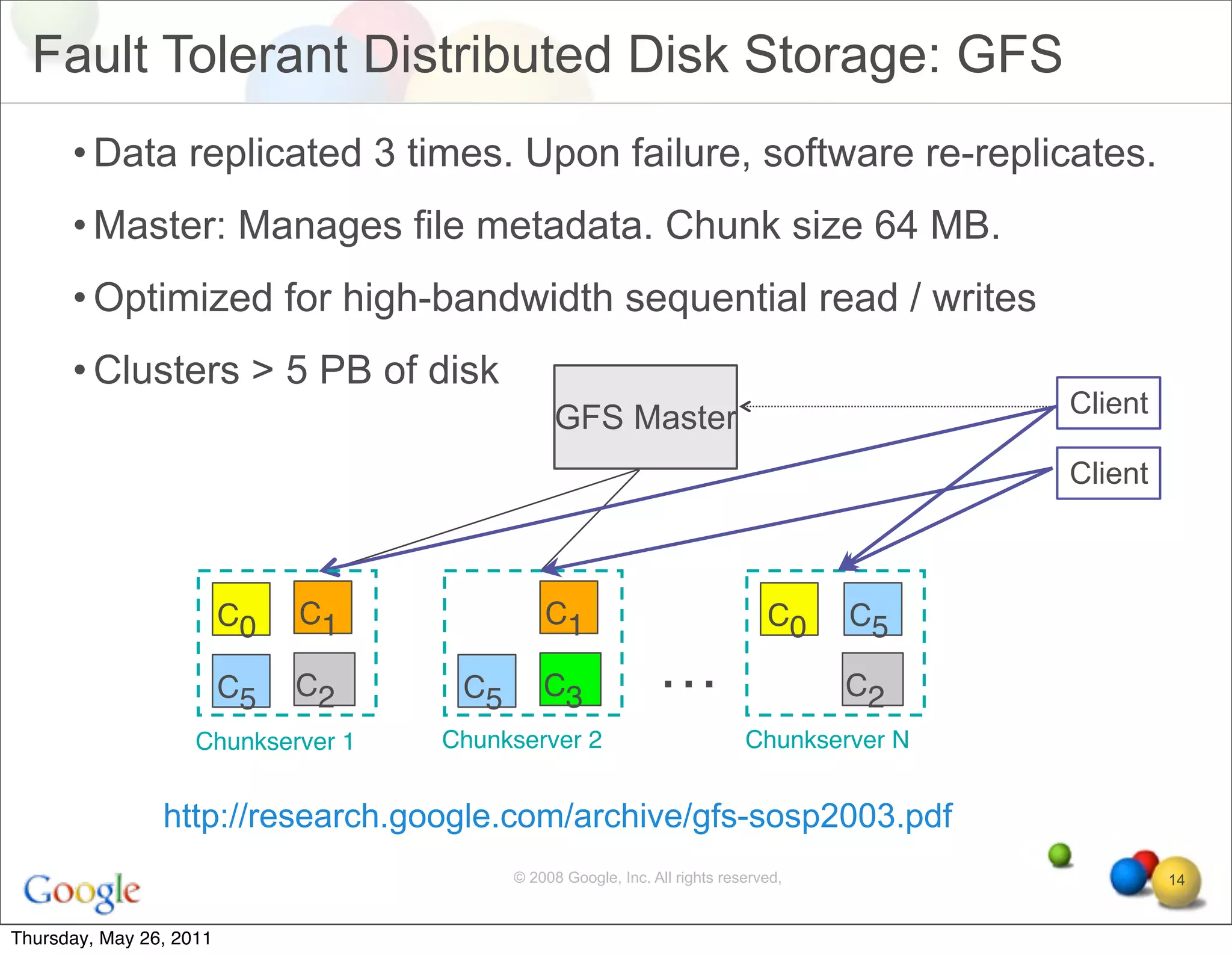
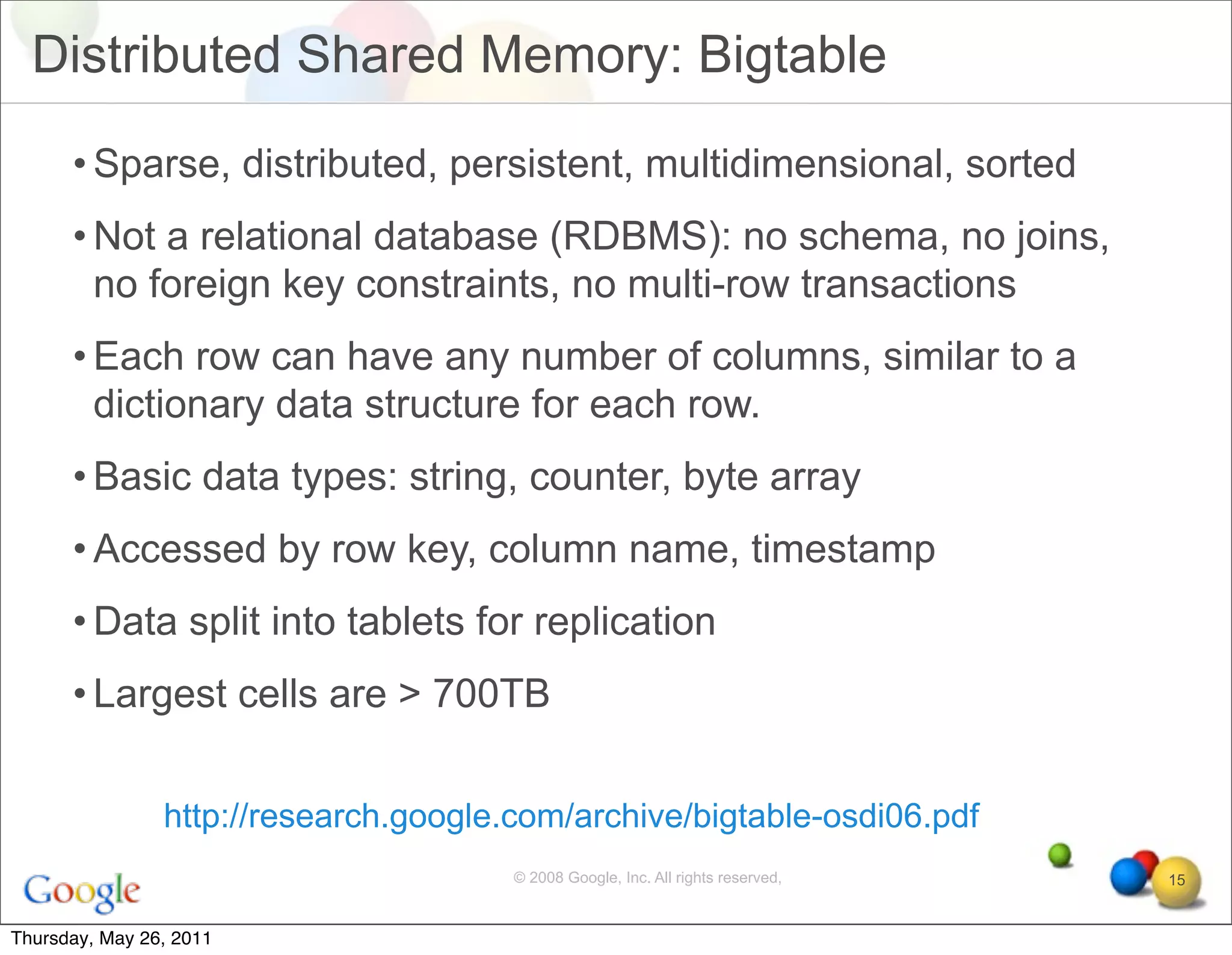
The document discusses several key factors driving adoption of cloud computing:
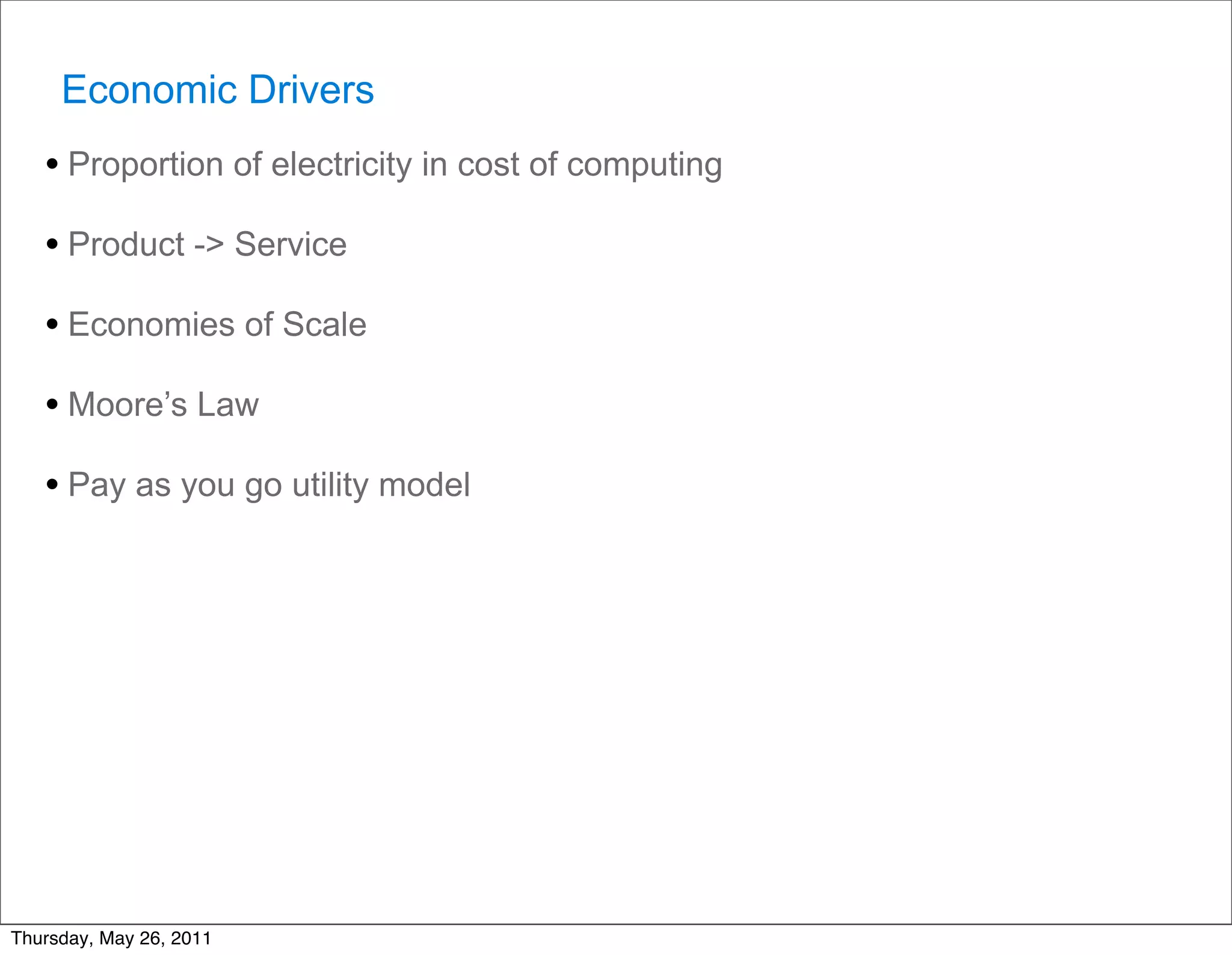
- Economic factors such as the decreasing cost of electricity for computing and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
- Cultural factors including consumerization of IT and expectations of increased agility, accessibility, and scalability.
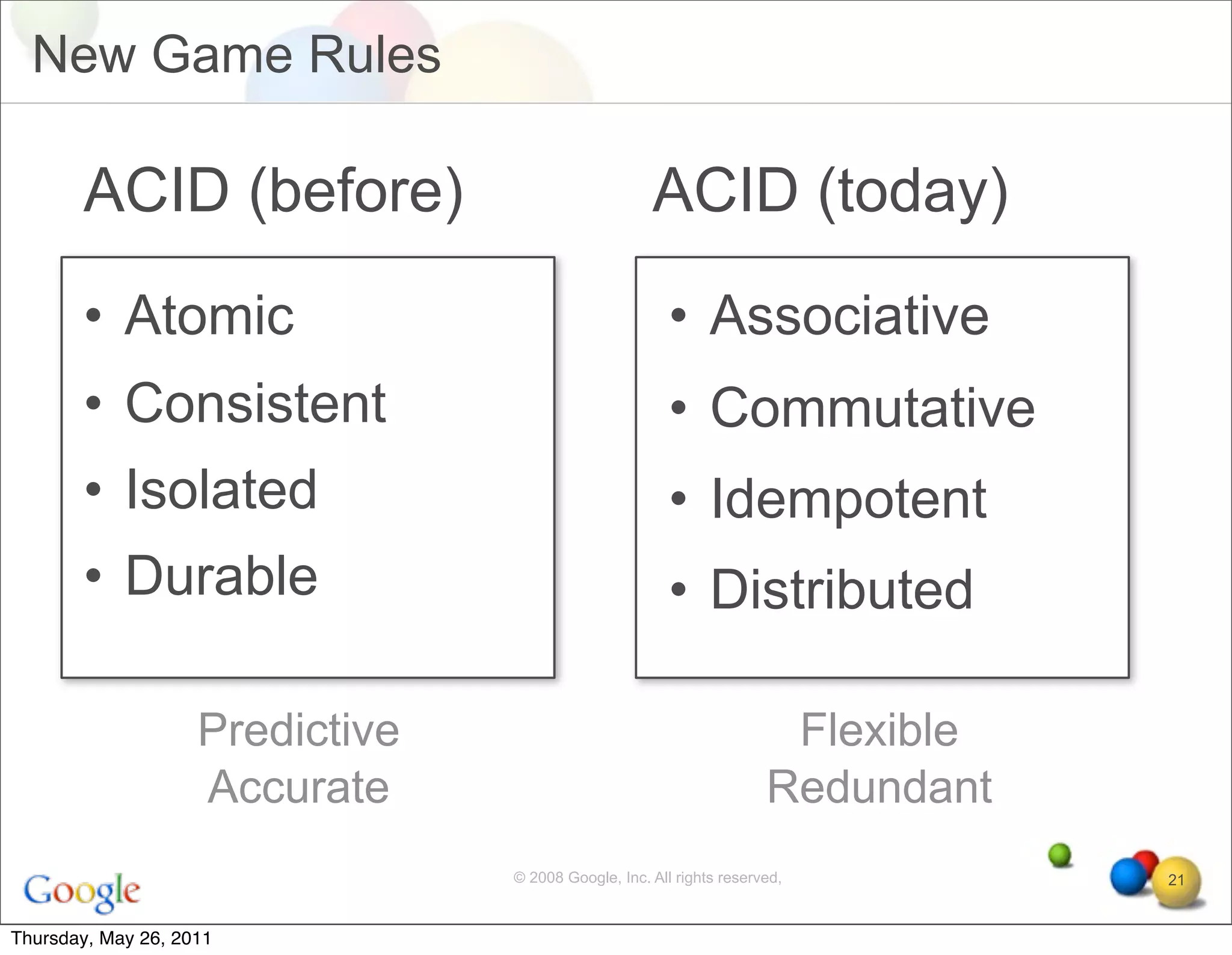
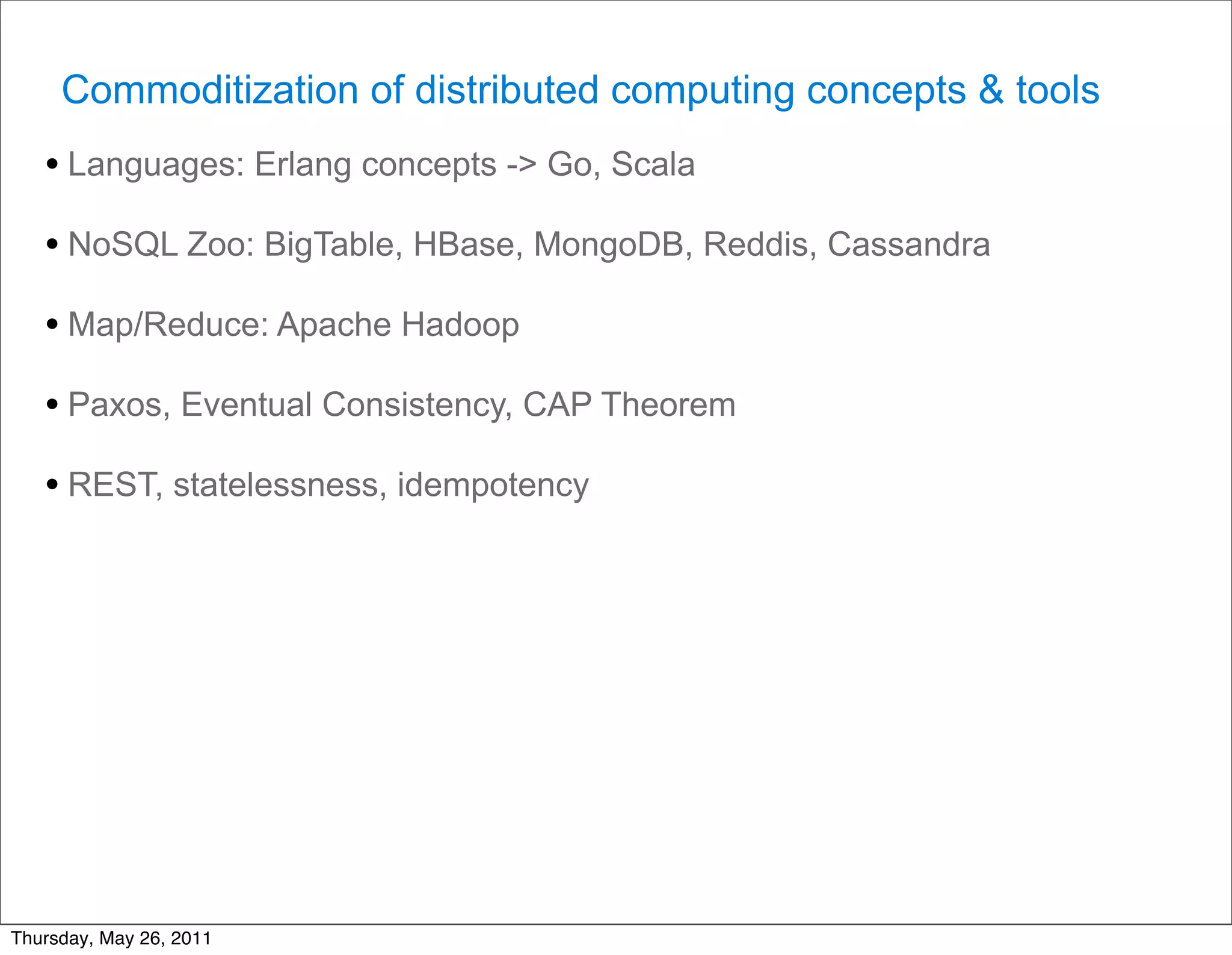
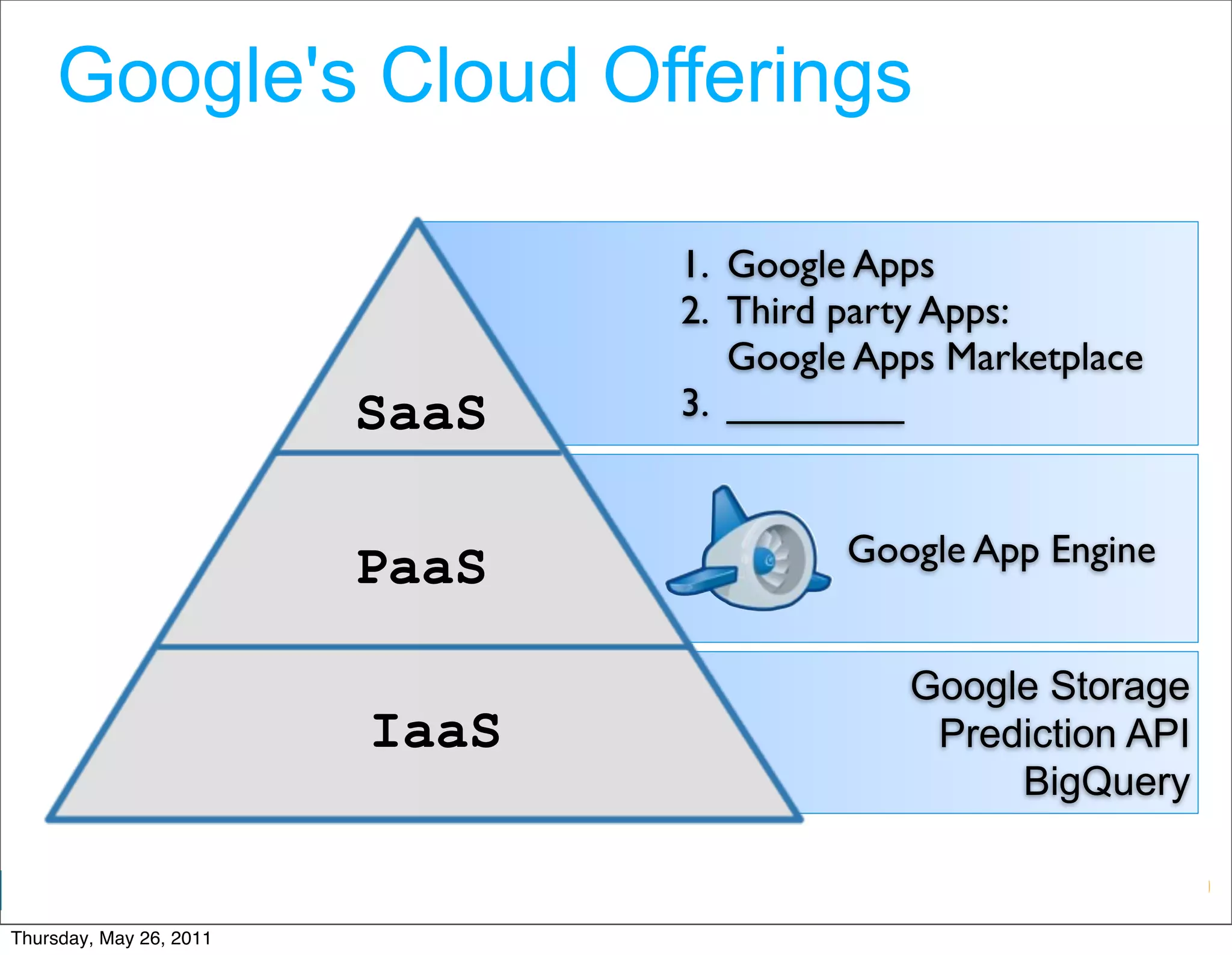
- Technological factors like virtualization, distributed computing tools, and concepts enabling scalable infrastructure.










![Language for Parallel Log Processing: Sawzall
• Commutative and associative operations allow parallel
execution and aggregation
• Language avoids specifying order by replacing loops with
quantifiers (constraints)
count: table sum of int; function(word: string): bool {
total: table sum of float; when(i: some int;
x: float = input; word[i] != word[$-1-i])
return false;
emit count <- 1; return true;
emit total <- x; };
http://labs.google.com/papers/sawzall.html
© 2008 Google, Inc. All rights reserved, 19
Thursday, May 26, 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c4i-cloud-adoption-110526154624-phpapp01/75/AFCEA-C4I-Symposium-The-4th-C-in-C4I-Stands-for-Cloud-Factors-Driving-Adoption-of-Cloud-Computing-22-2048.jpg)