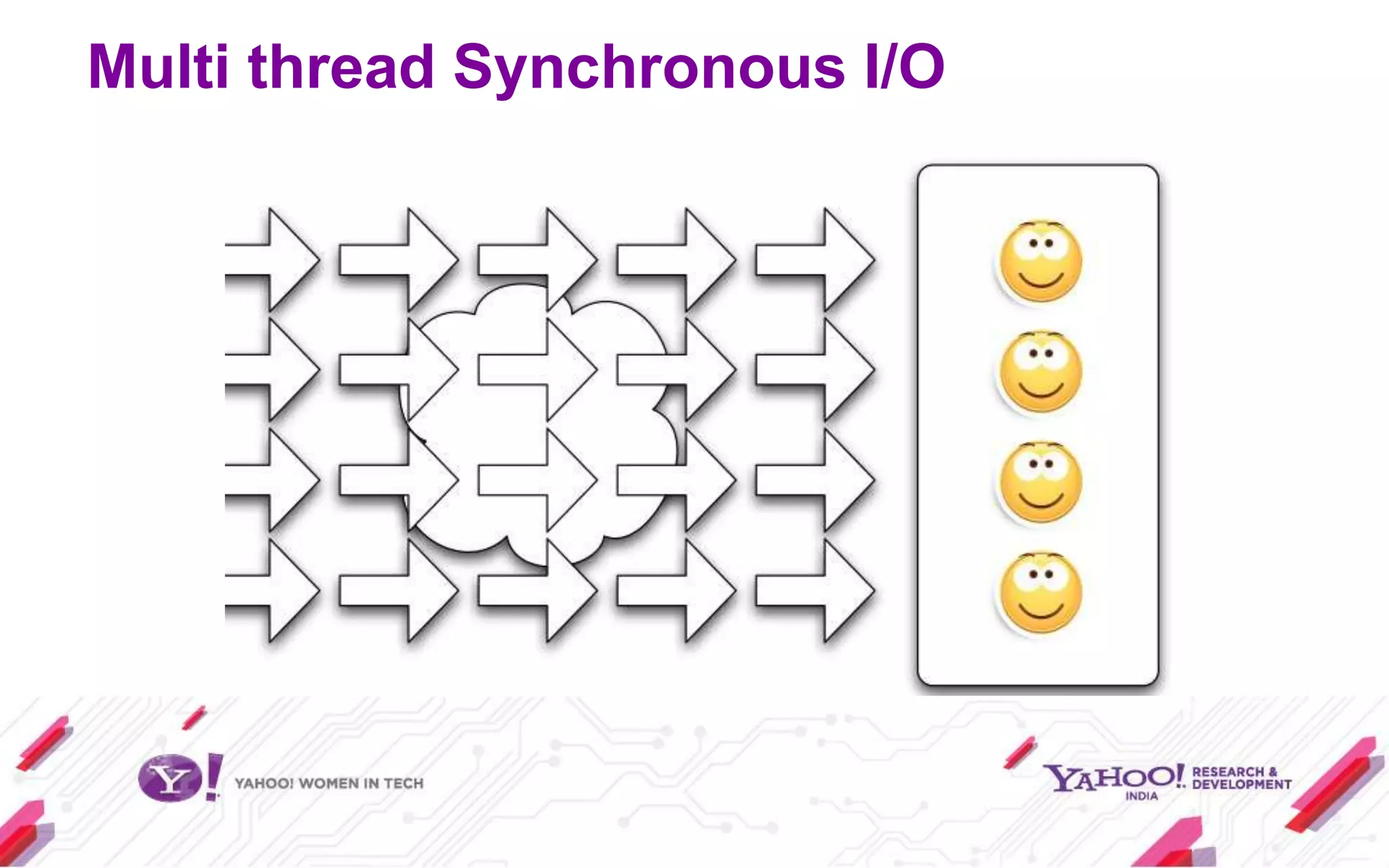
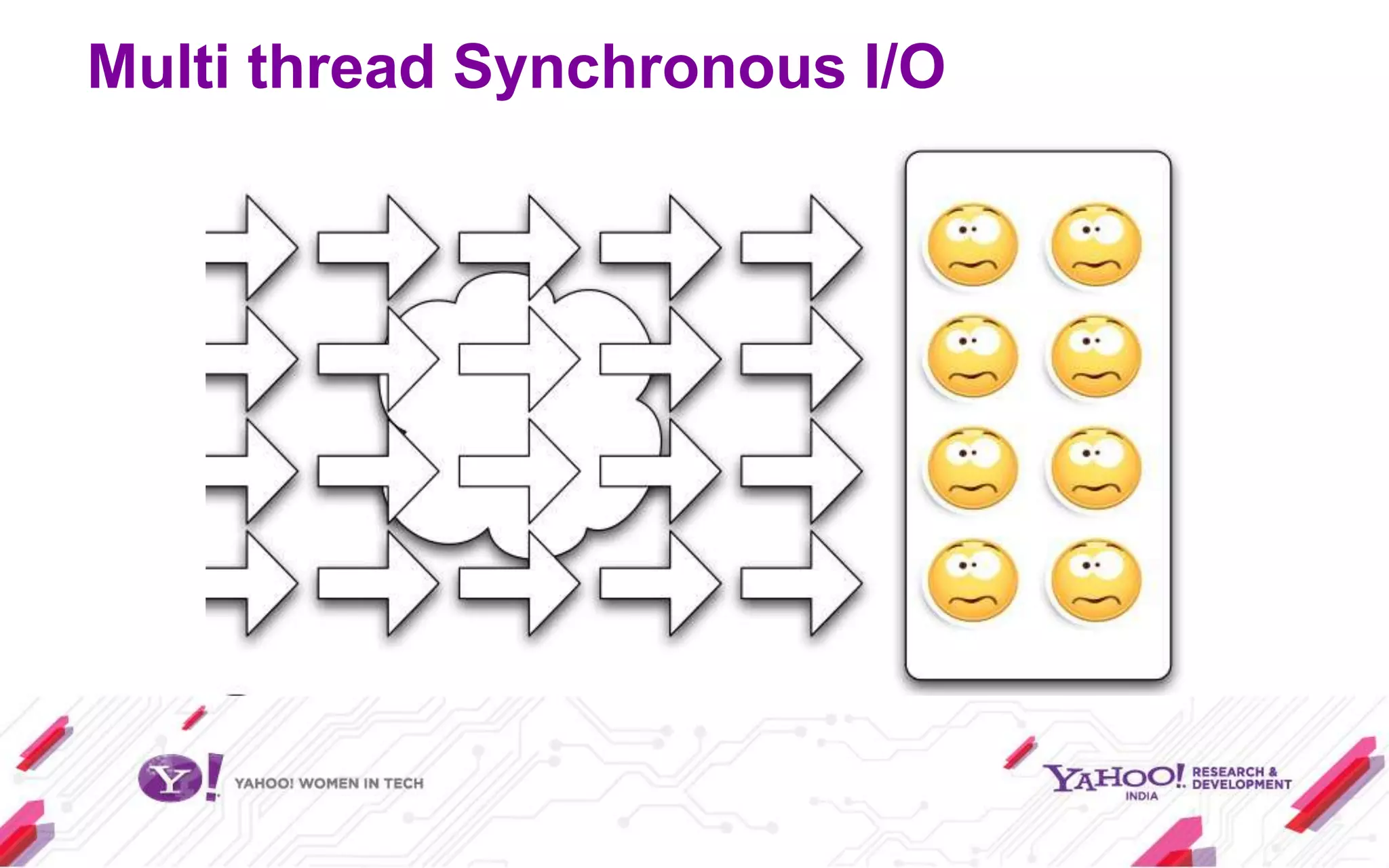
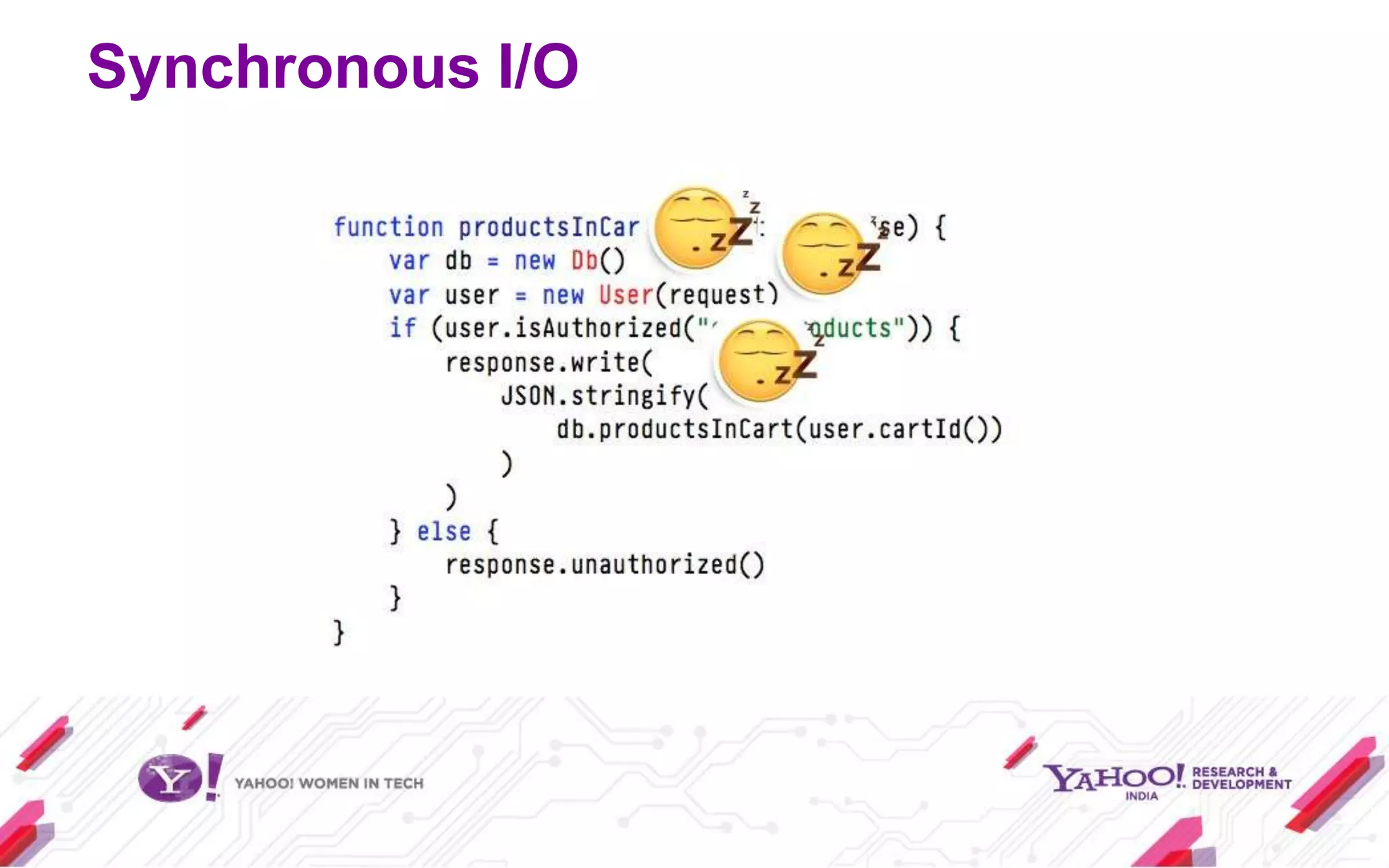
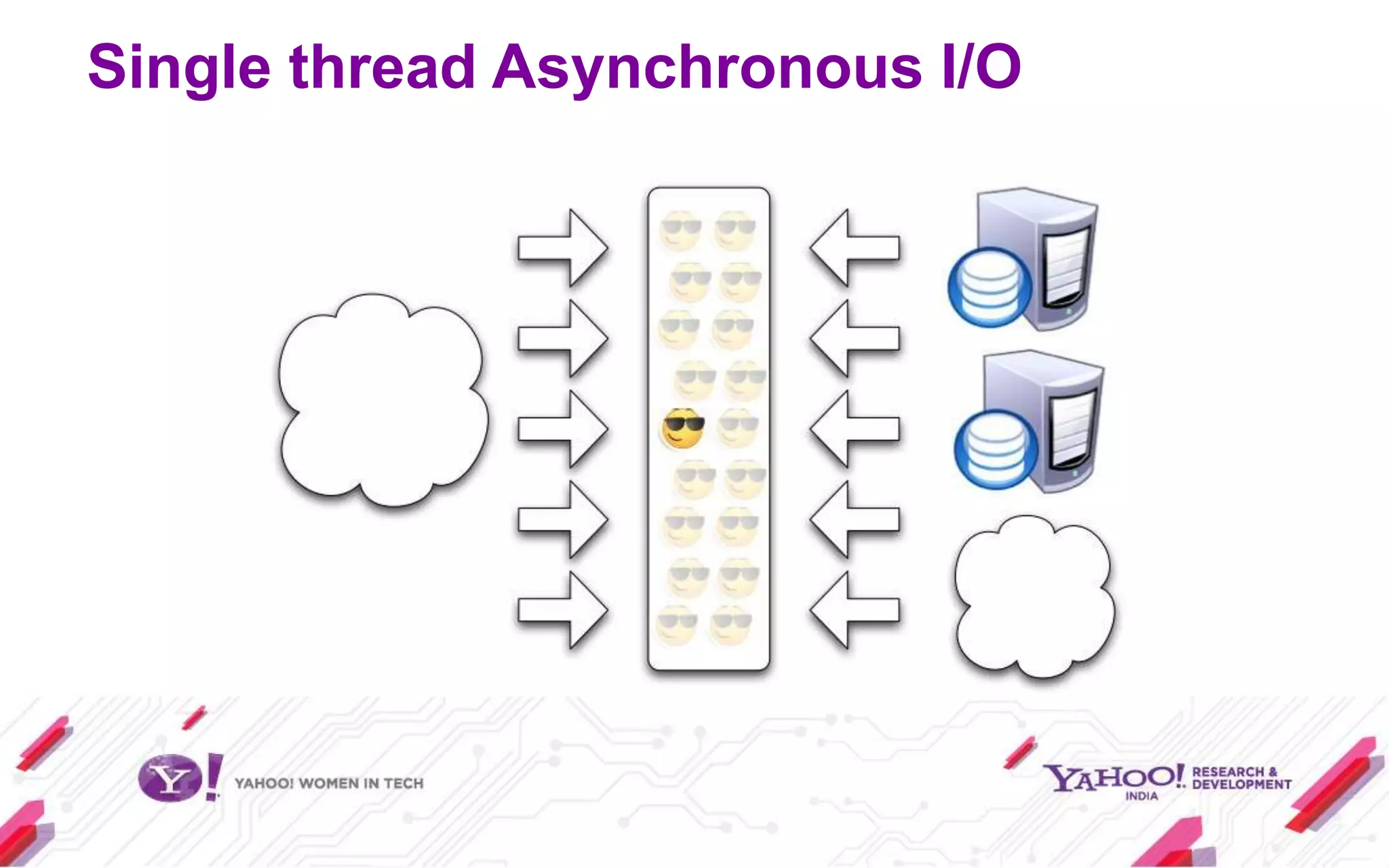
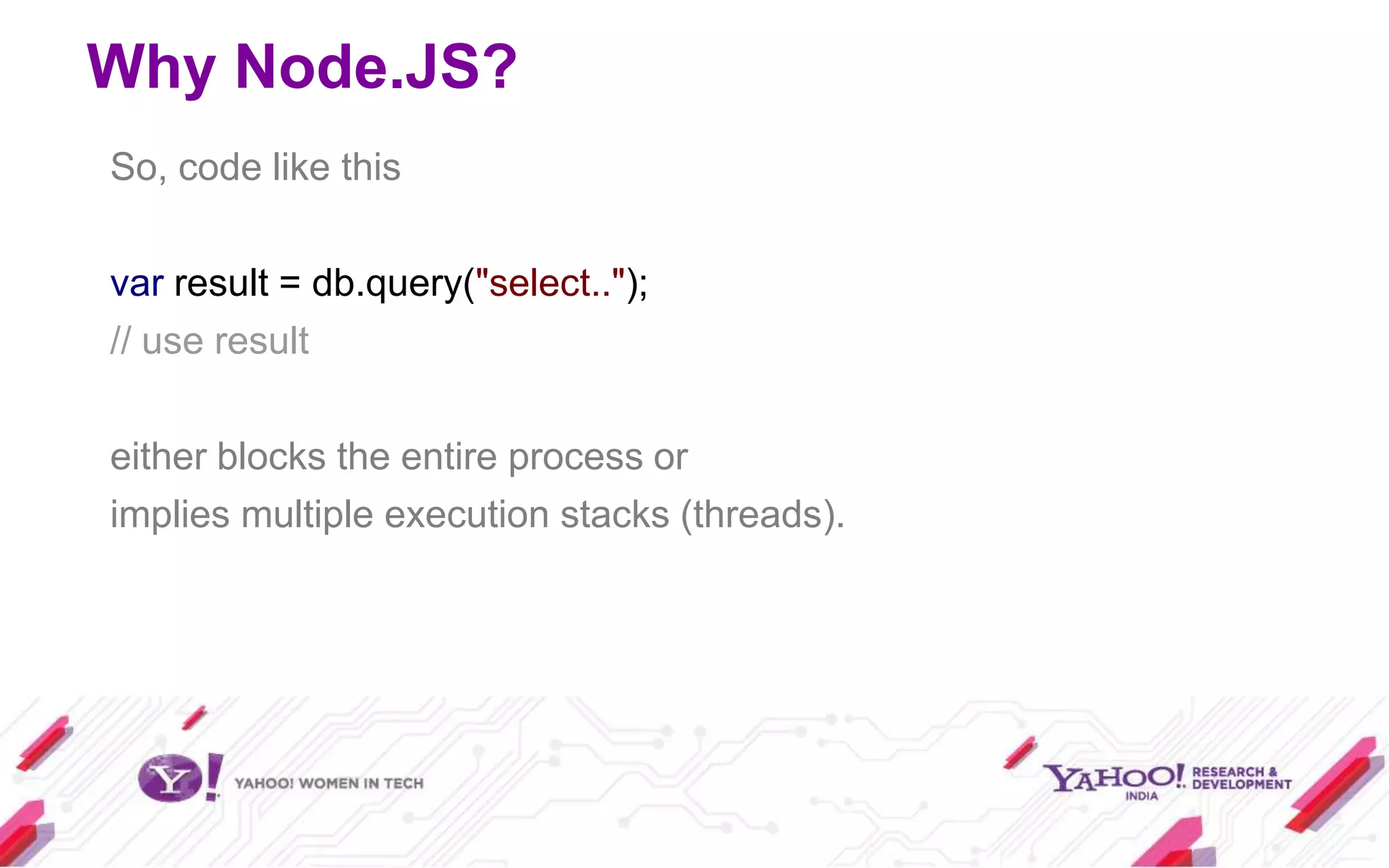
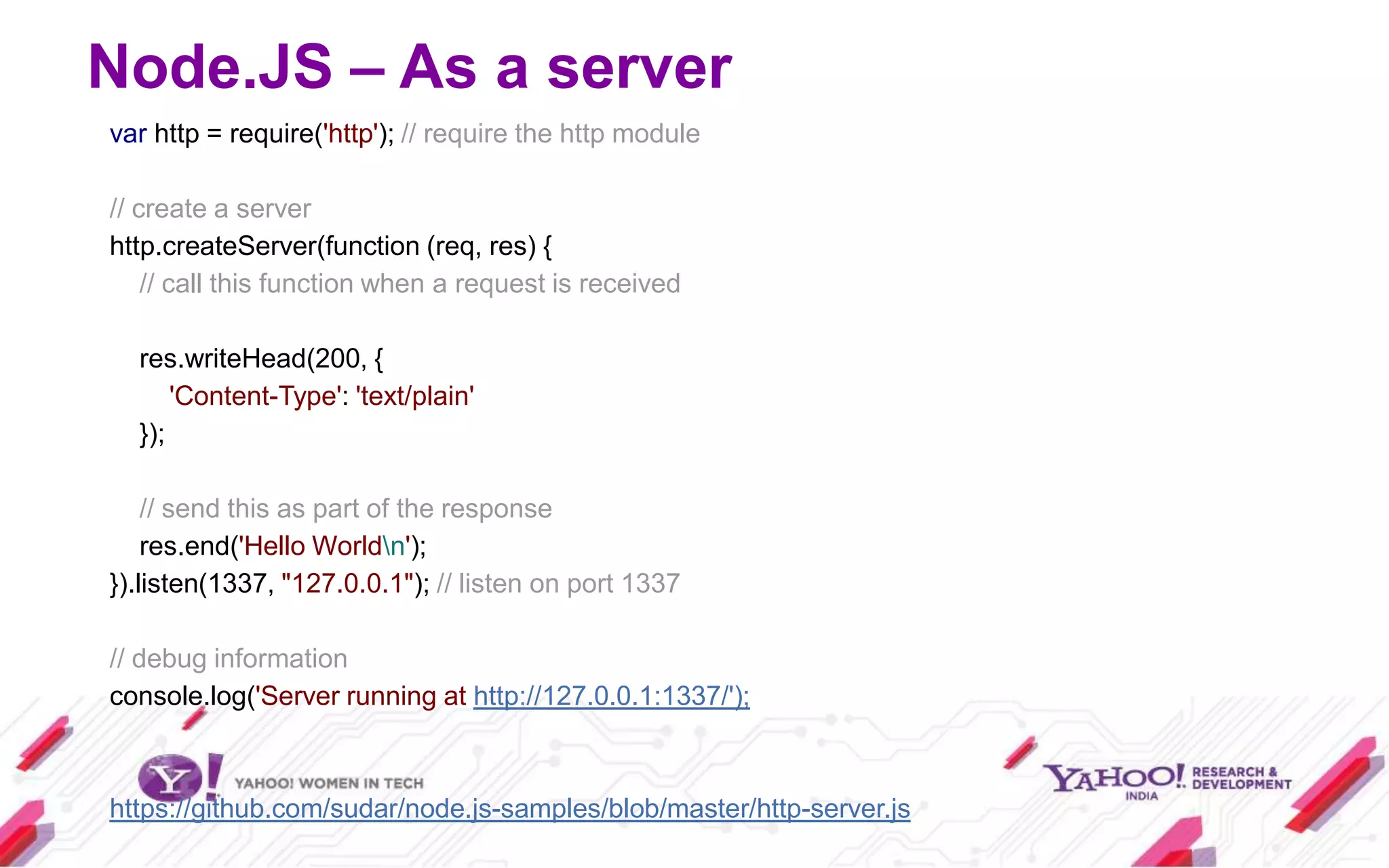
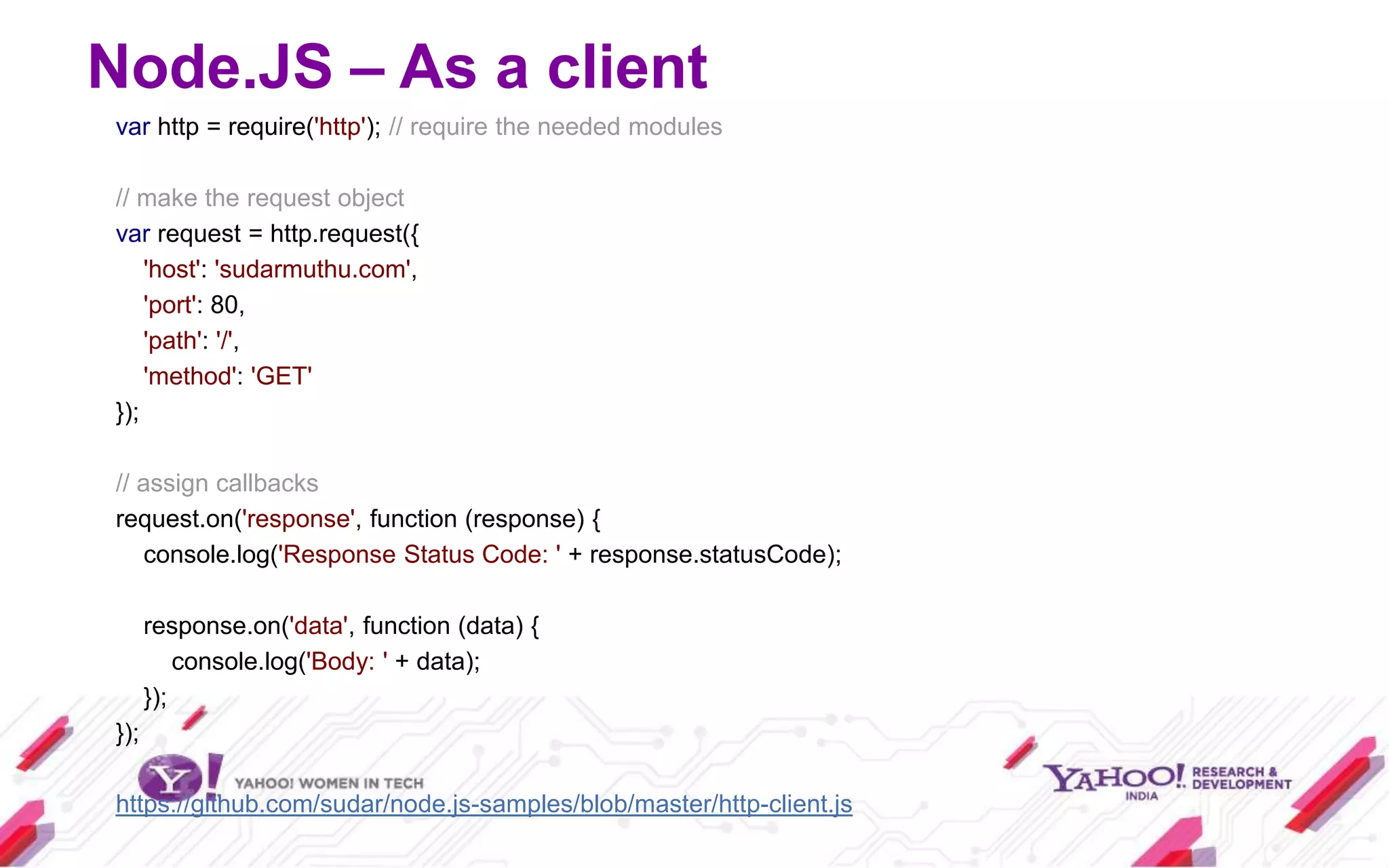
Node.js is a JavaScript environment for building scalable network applications, utilizing an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. It distinguishes itself from frameworks like Ruby on Rails by being minimal and allowing community-driven enhancements such as Express. The document covers installation, usage as a server and client, core modules, and provides examples and resources for further learning.