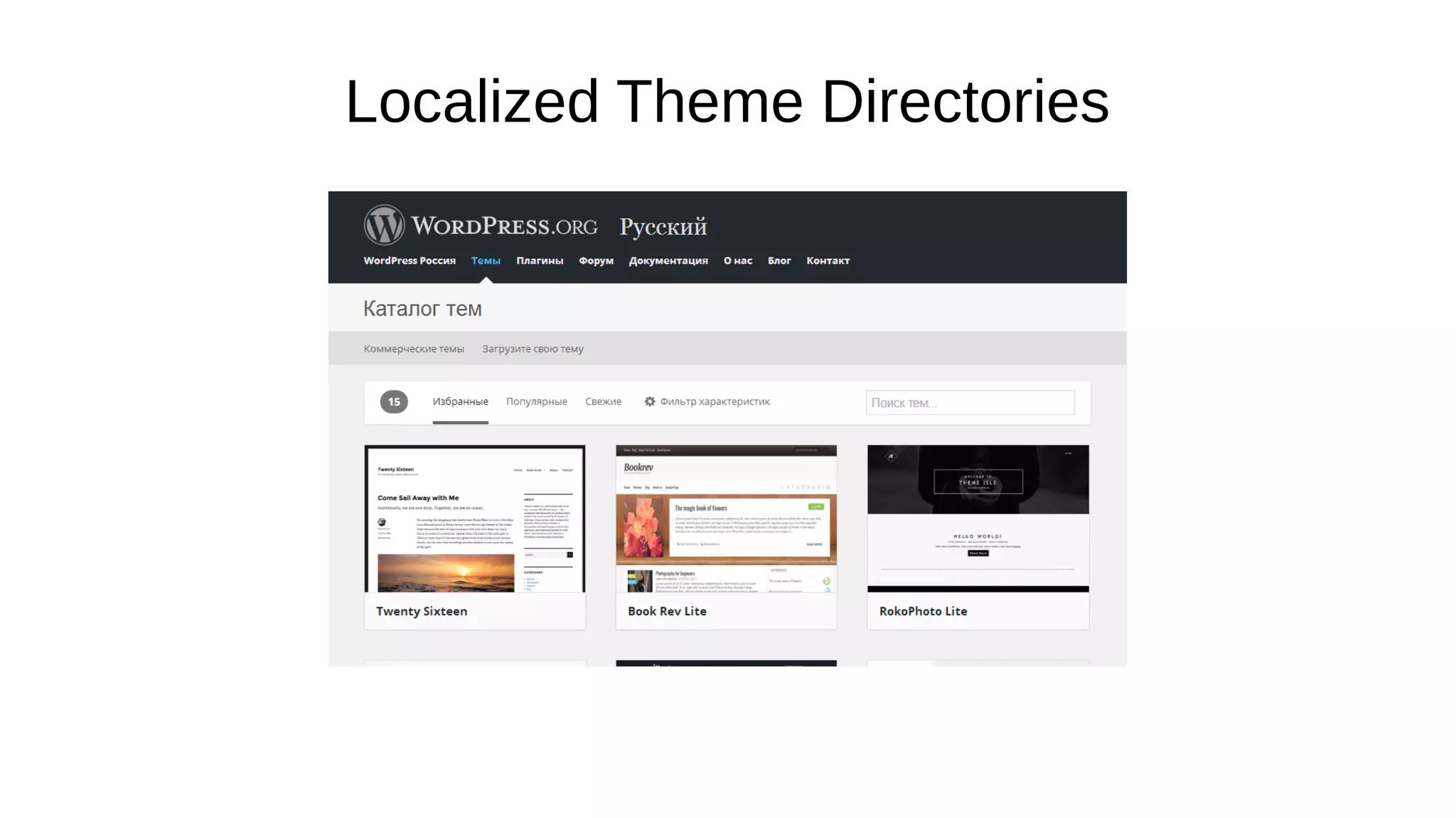
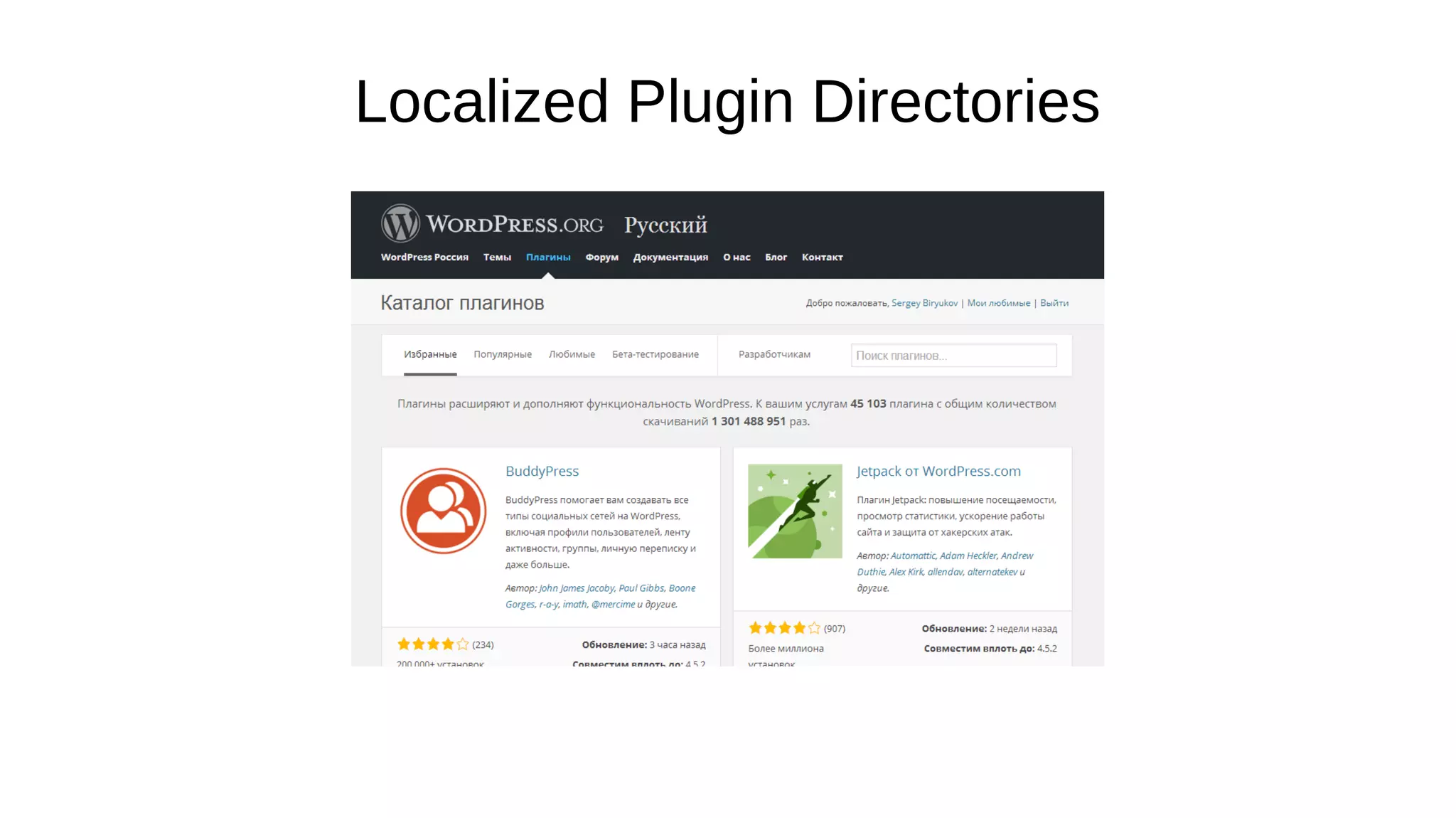
- The document discusses internationalization and localization for WordPress plugin and theme developers. It covers making plugins and themes translatable to other languages through gettext.
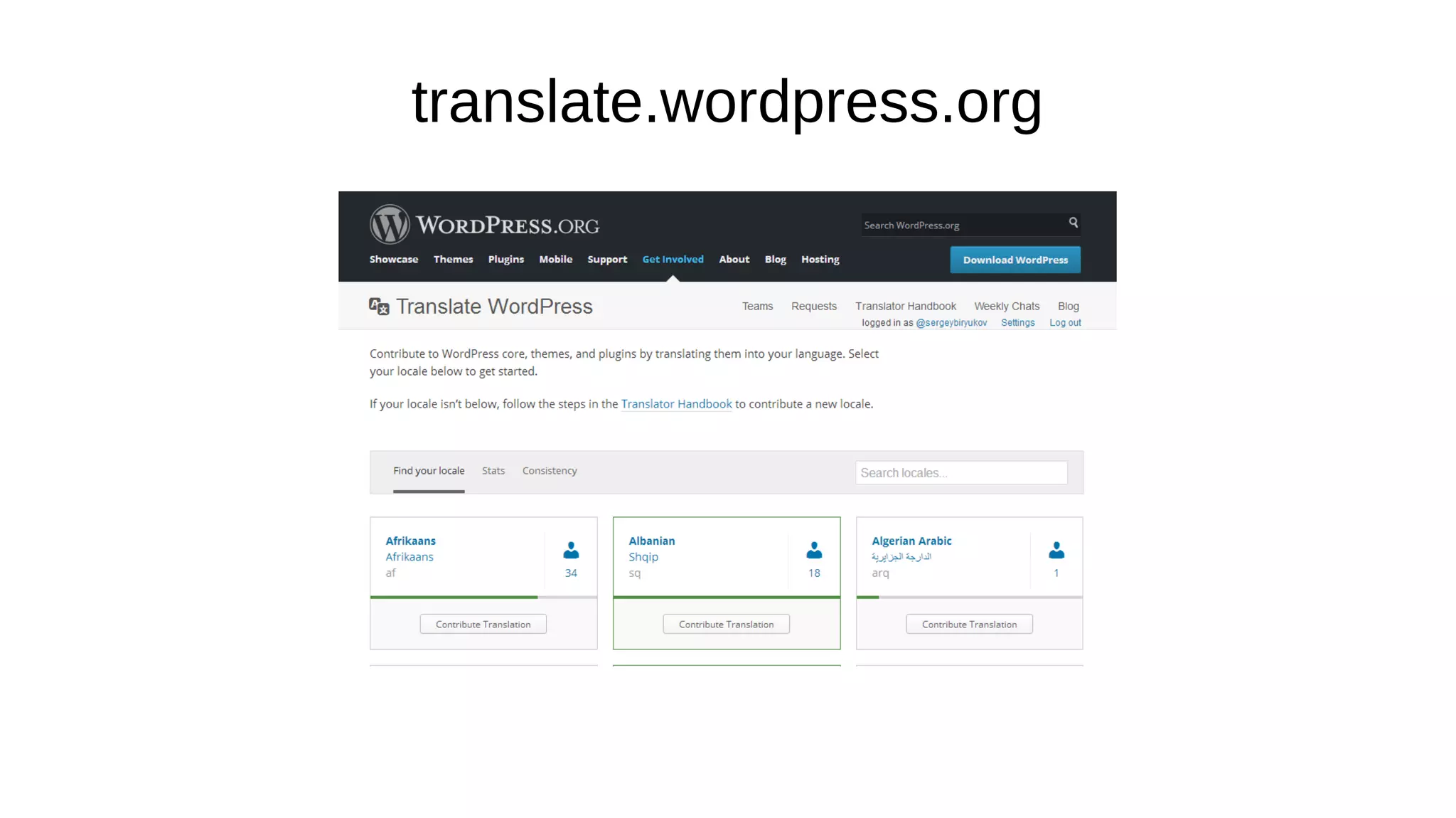
- Key aspects covered include using text domains, preparing translatable strings, plural forms, language files like POT, PO and MO, and utilizing the translate.wordpress.org platform for translations.
- The document provides guidance on proper internationalization practices and working with translators.