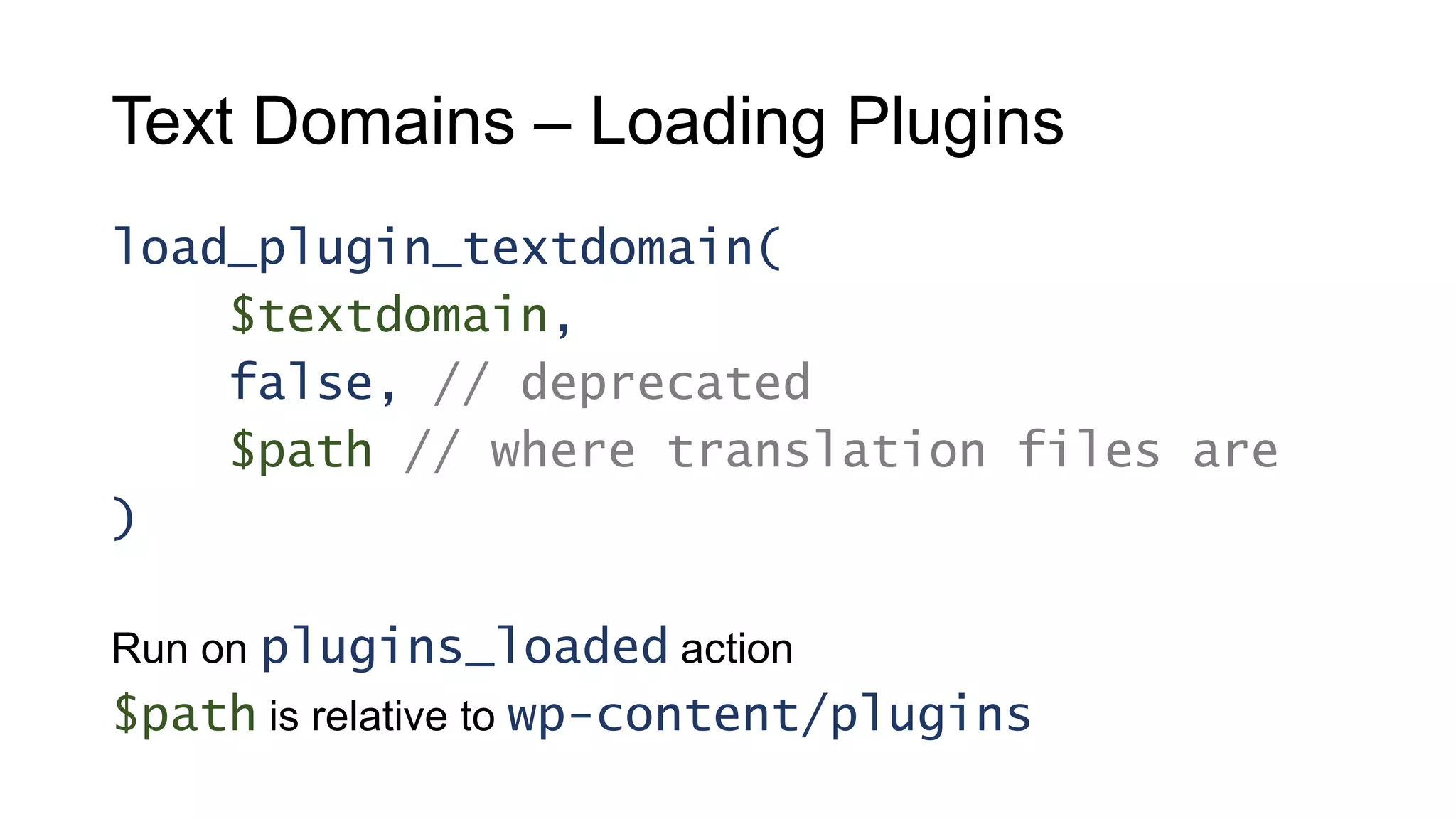
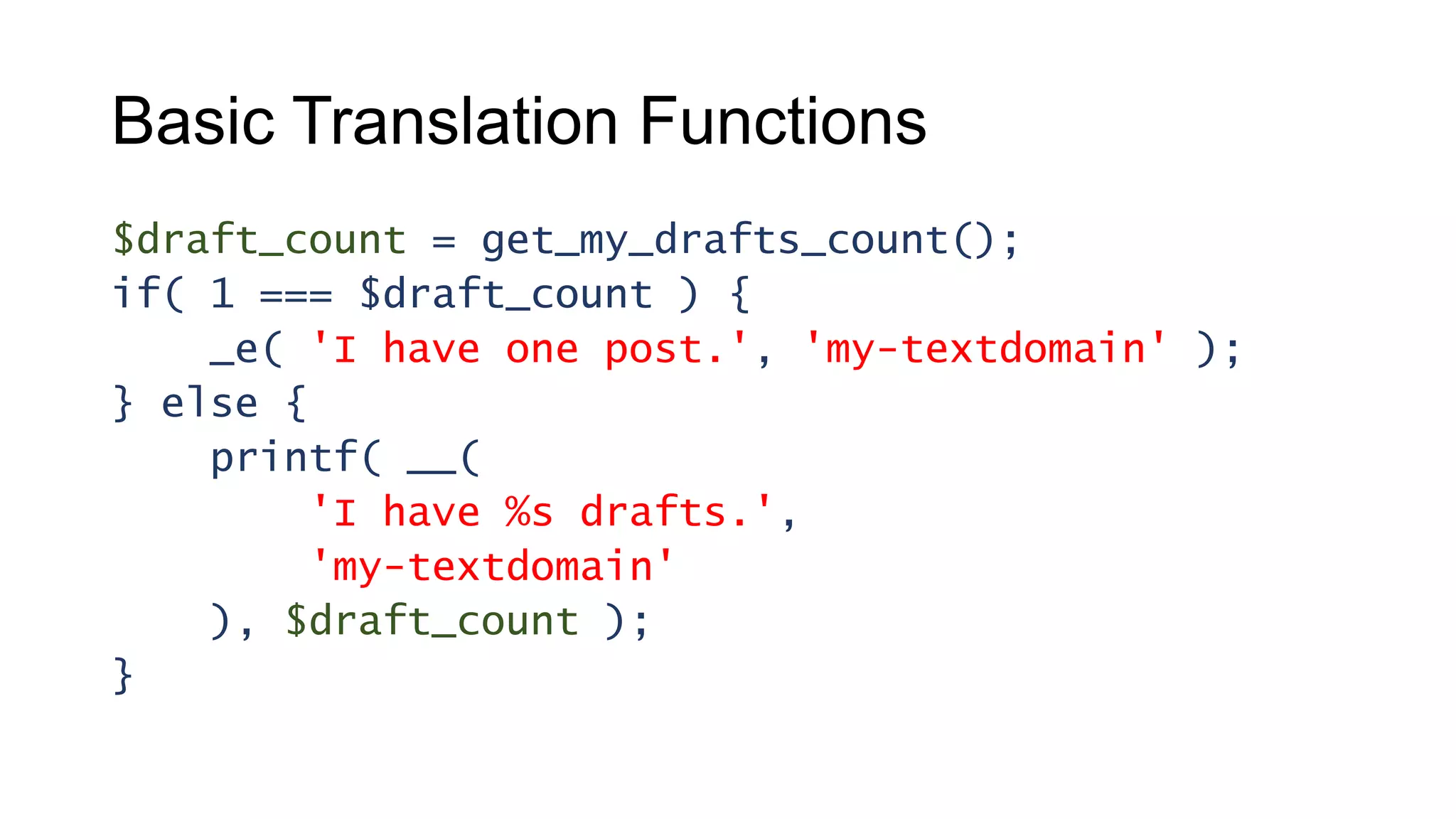
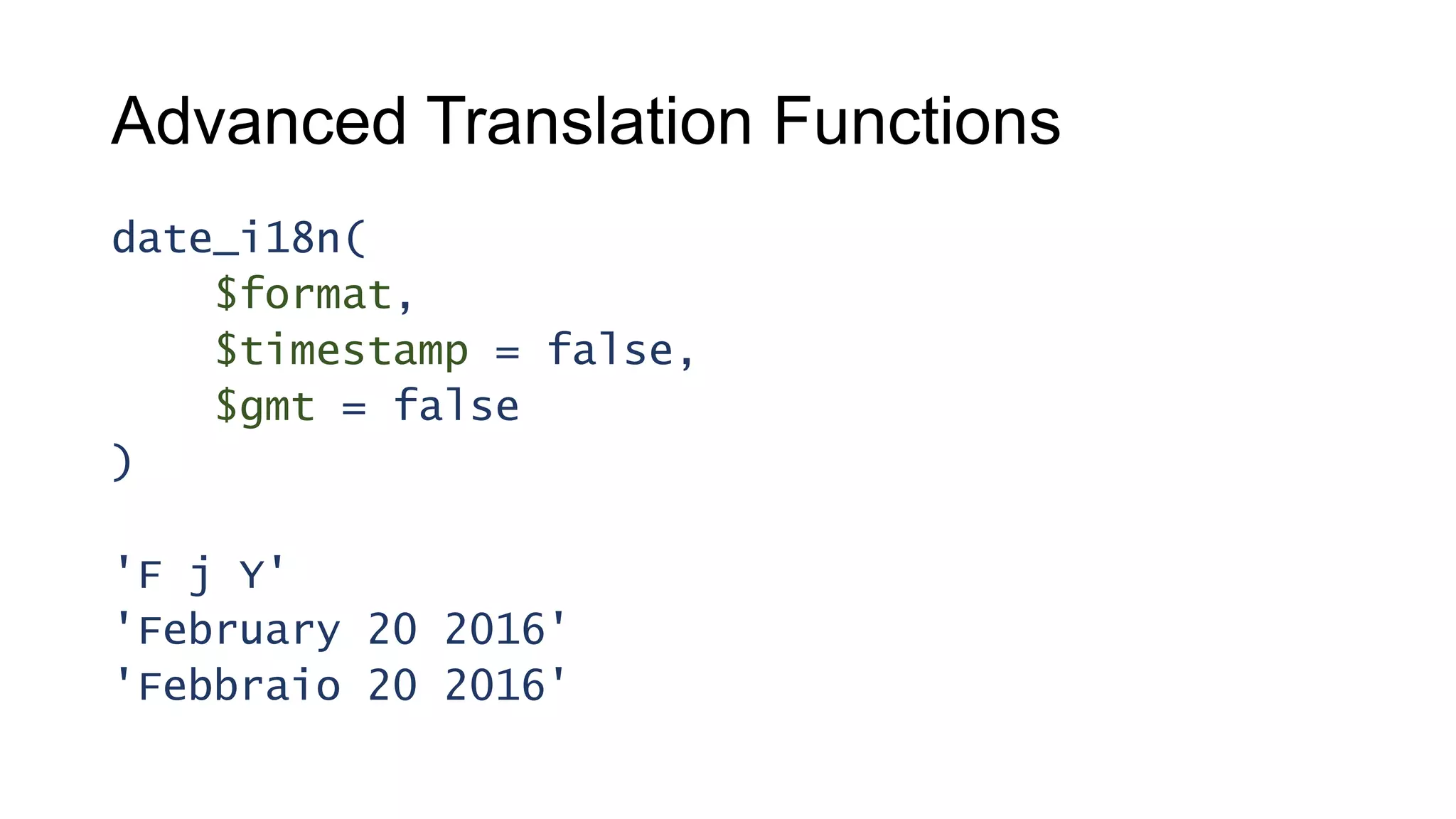
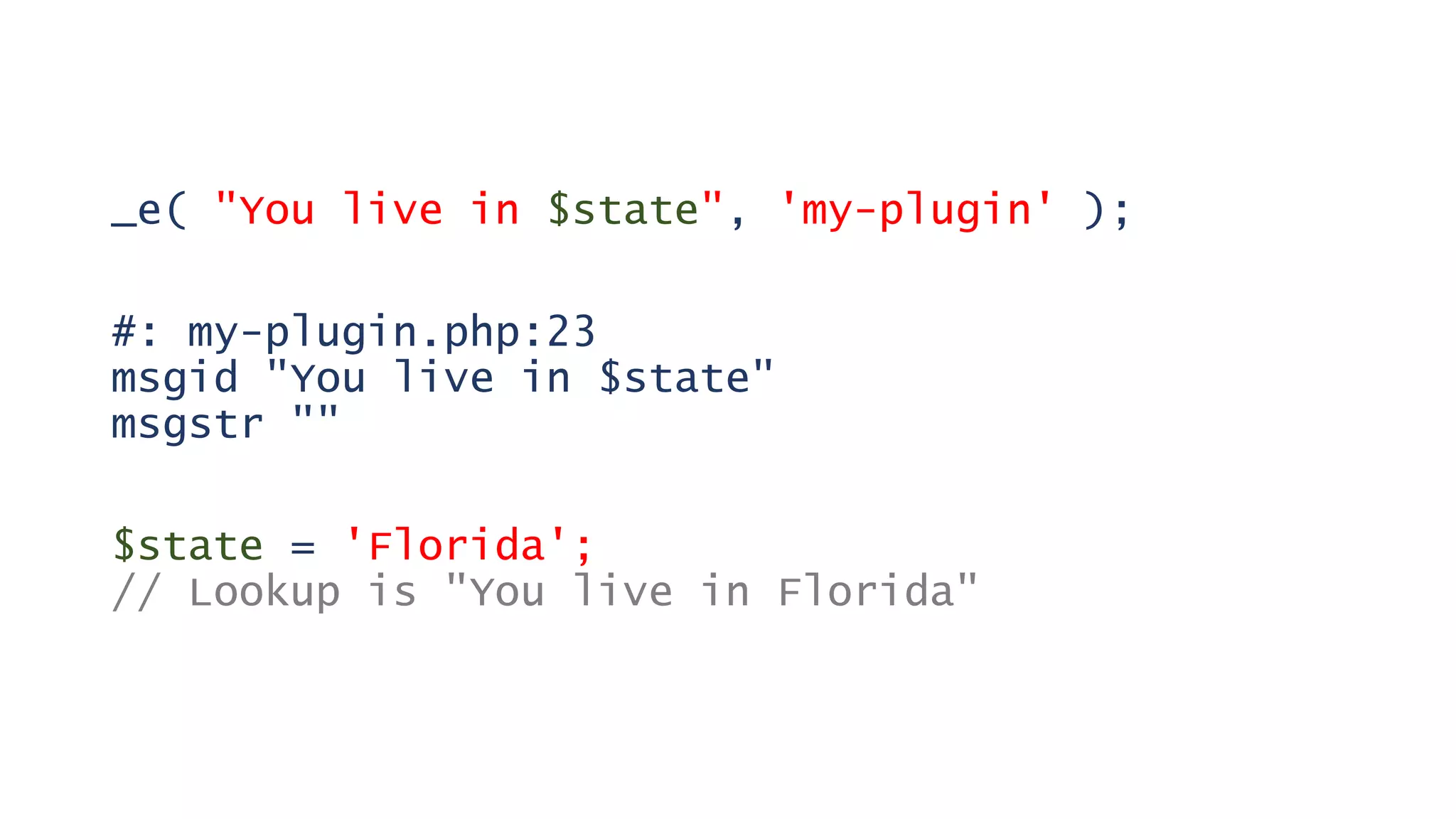
This document provides guidance on creating multilingual WordPress plugins and themes, emphasizing the importance of internationalization (i18n) and localization (l10n). It outlines necessary steps for making code translatable, such as using unique text domains and employing various translation functions, alongside best practices and potential challenges. The document also highlights tools available for translation and encourages developers to enhance their reach by accommodating non-English speaking users.