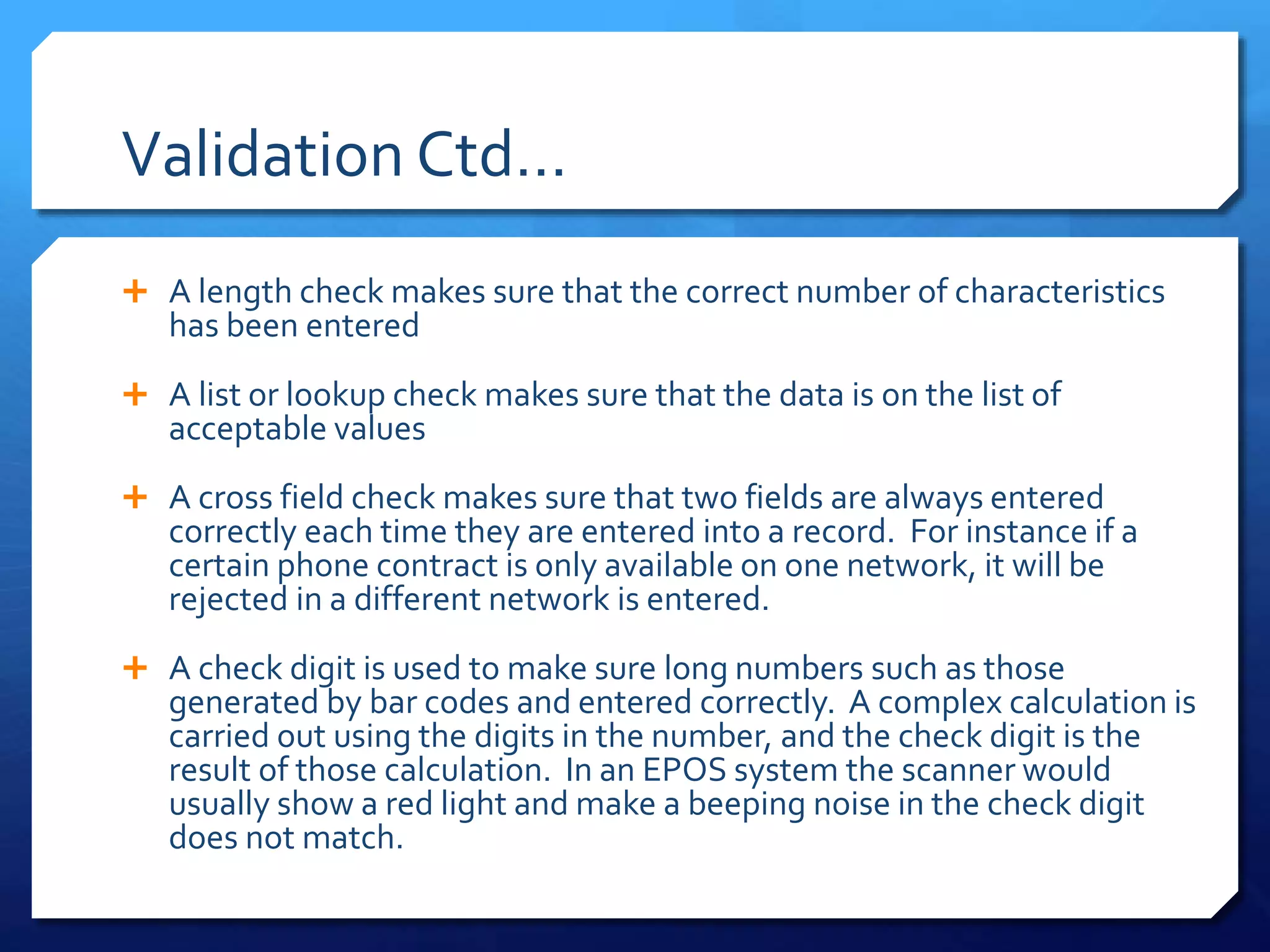
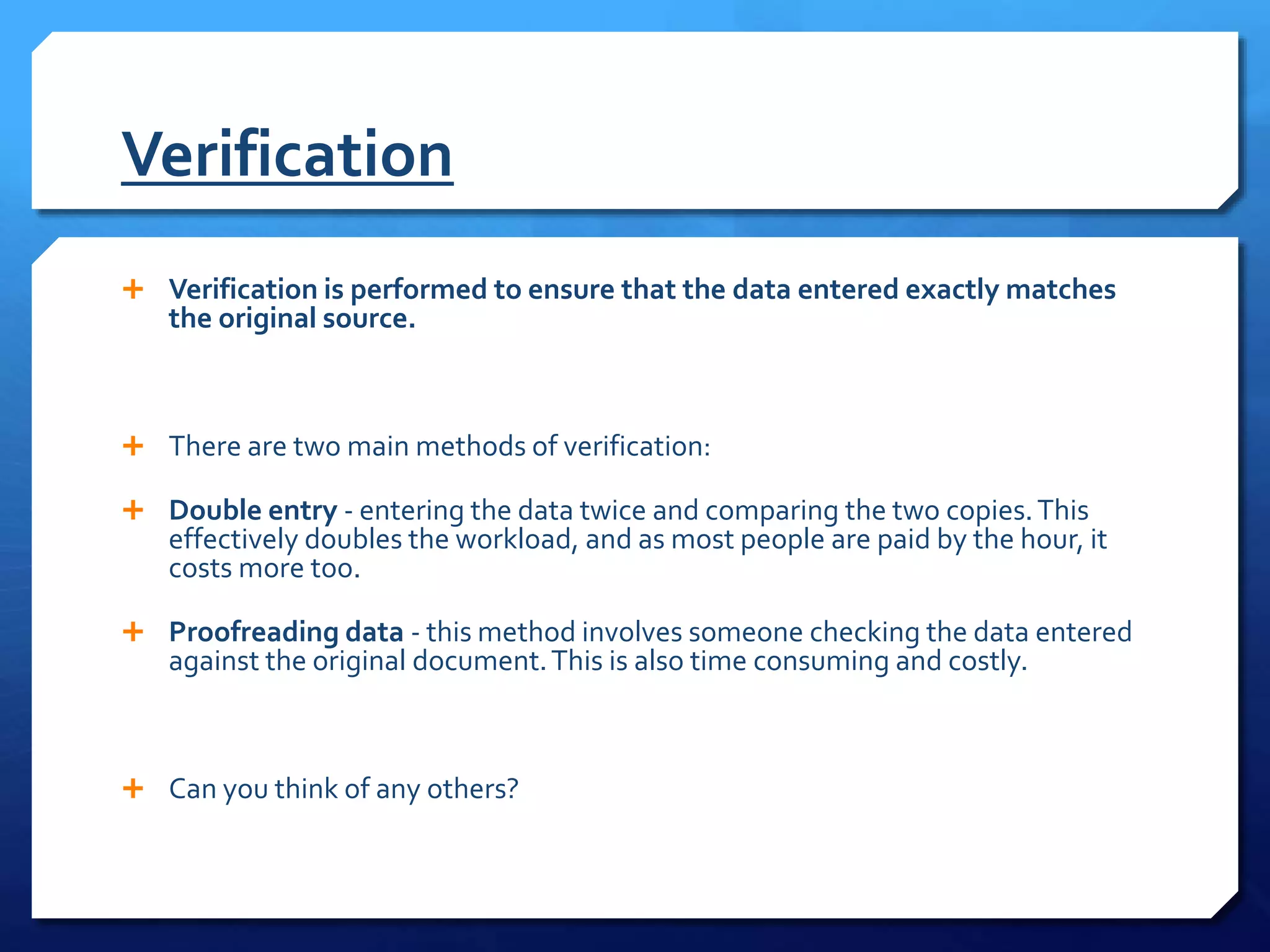
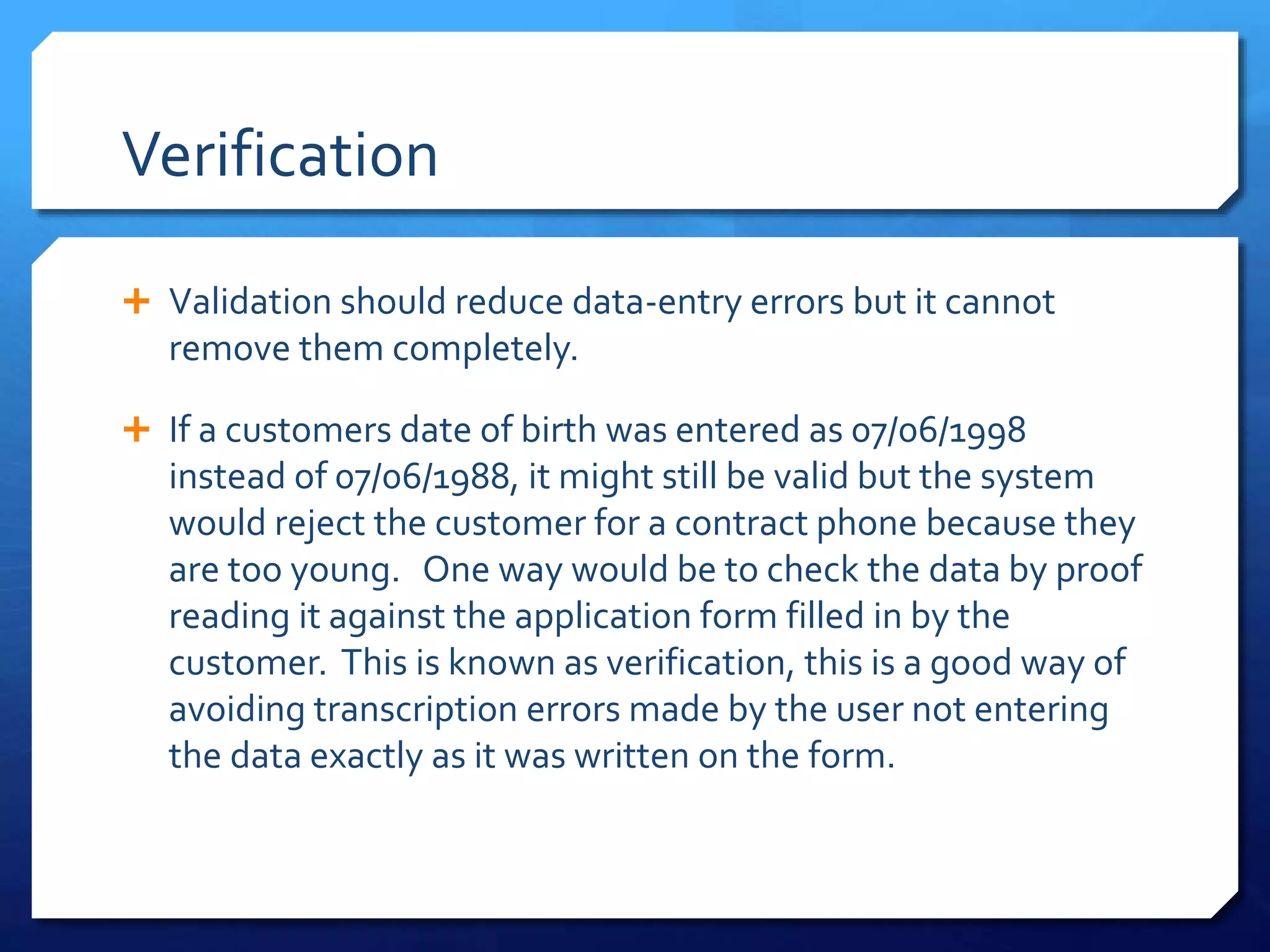
Validation checks that data meets certain criteria like format or value ranges, but does not verify accuracy. There are many types of validation including presence, range, format, and more. Verification ensures data matches the original by methods like double entry or proofreading against source documents. Both help reduce errors, but verification is needed to catch incorrect yet valid entries.