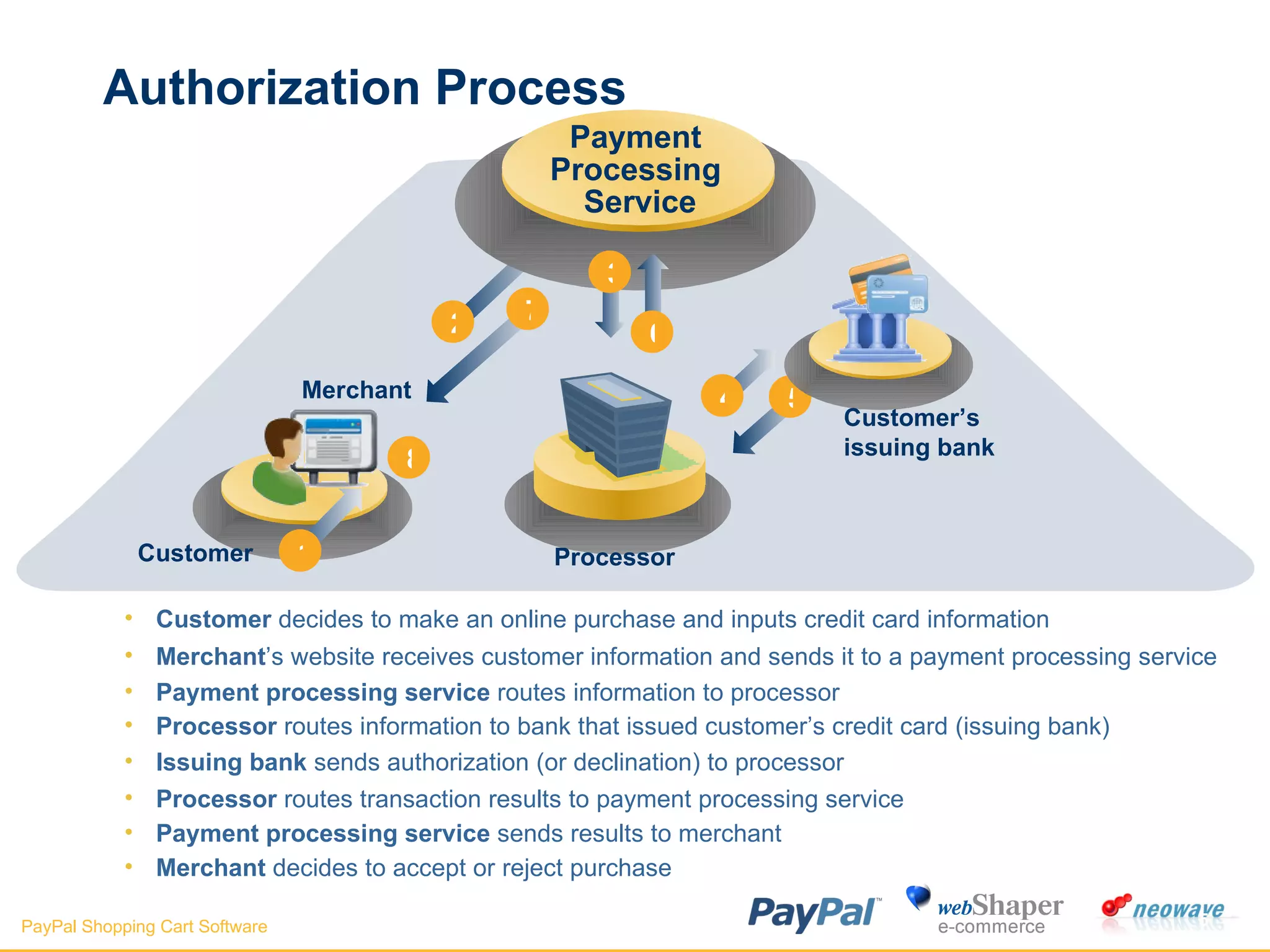
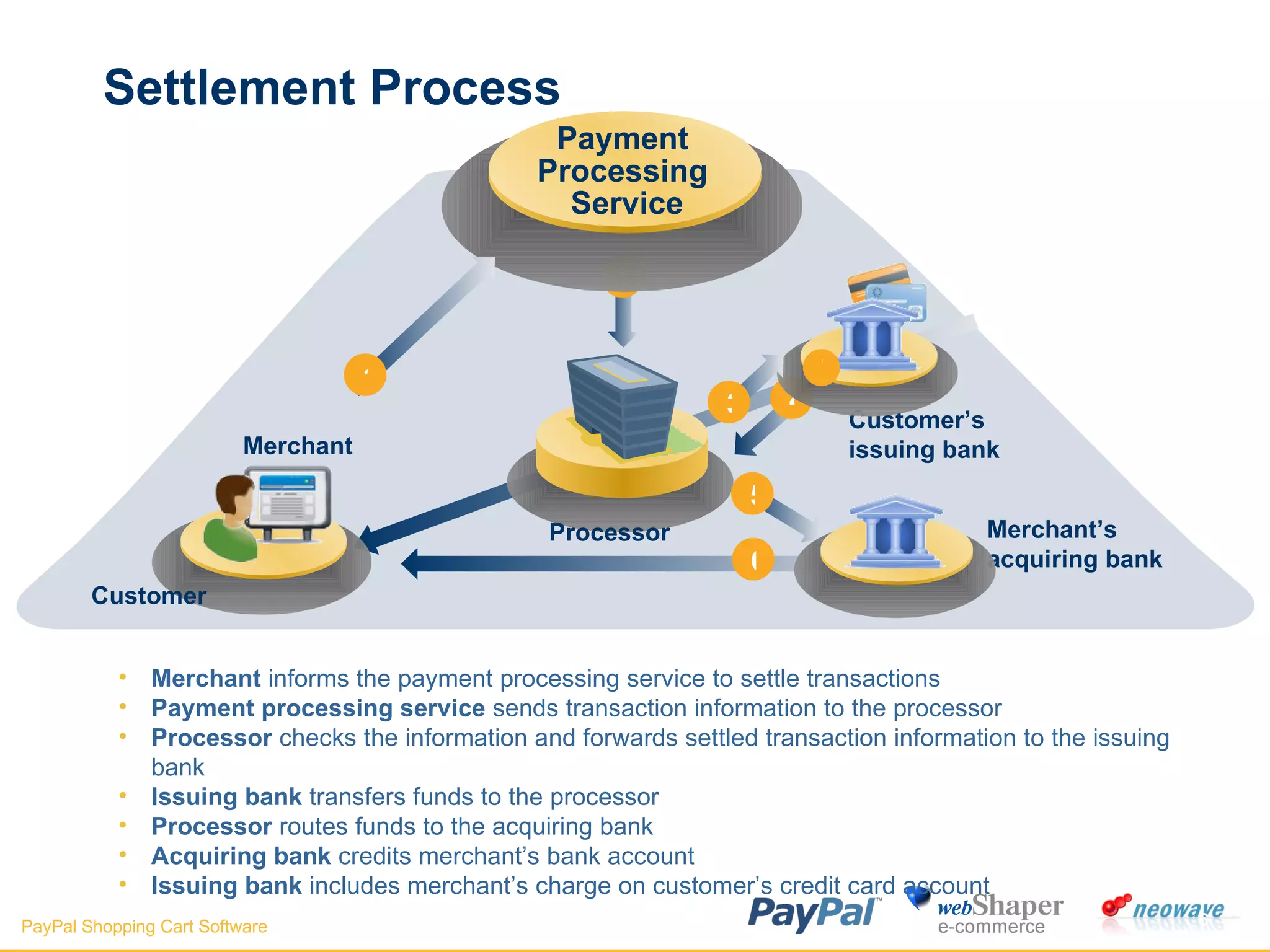
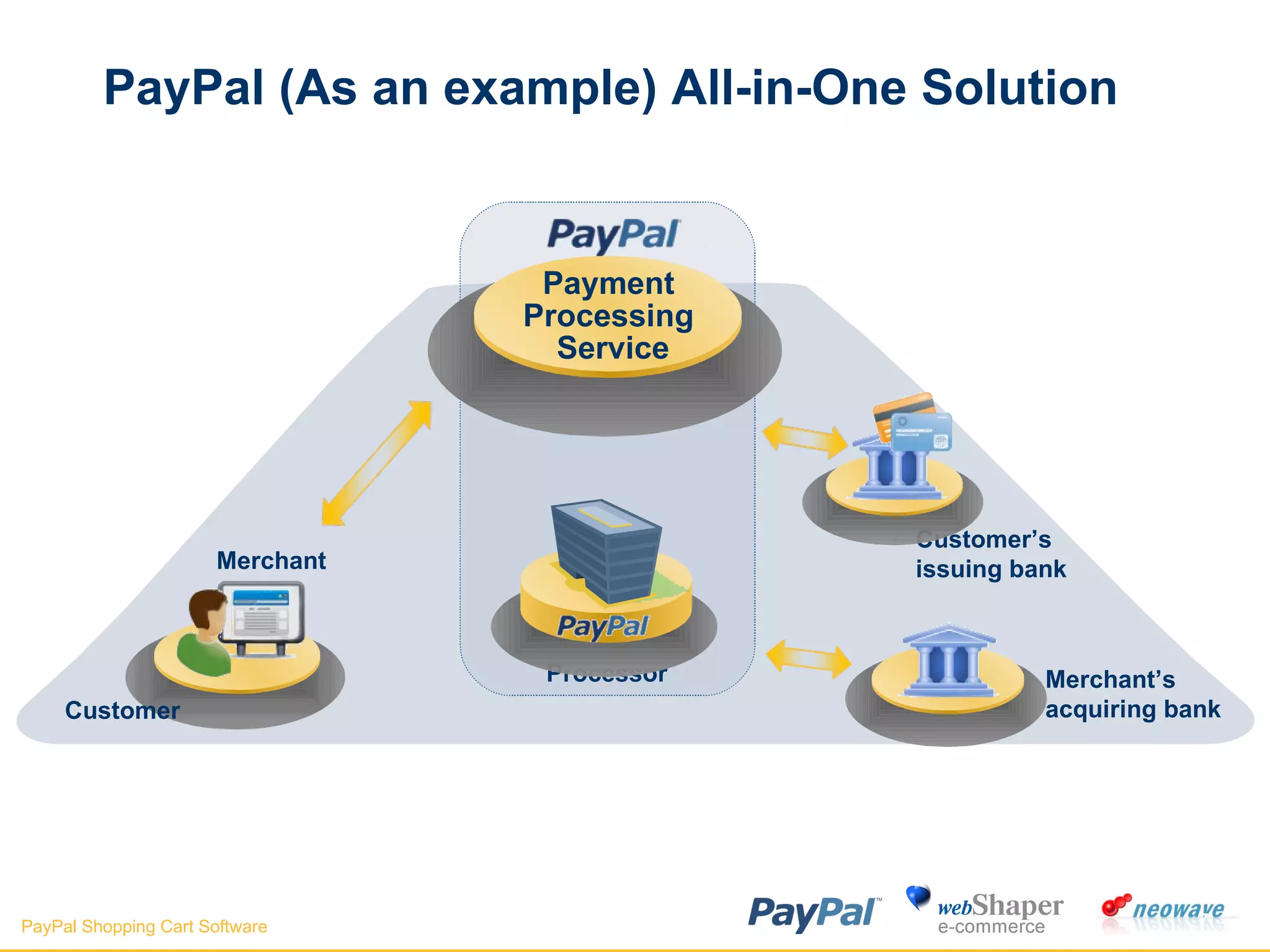
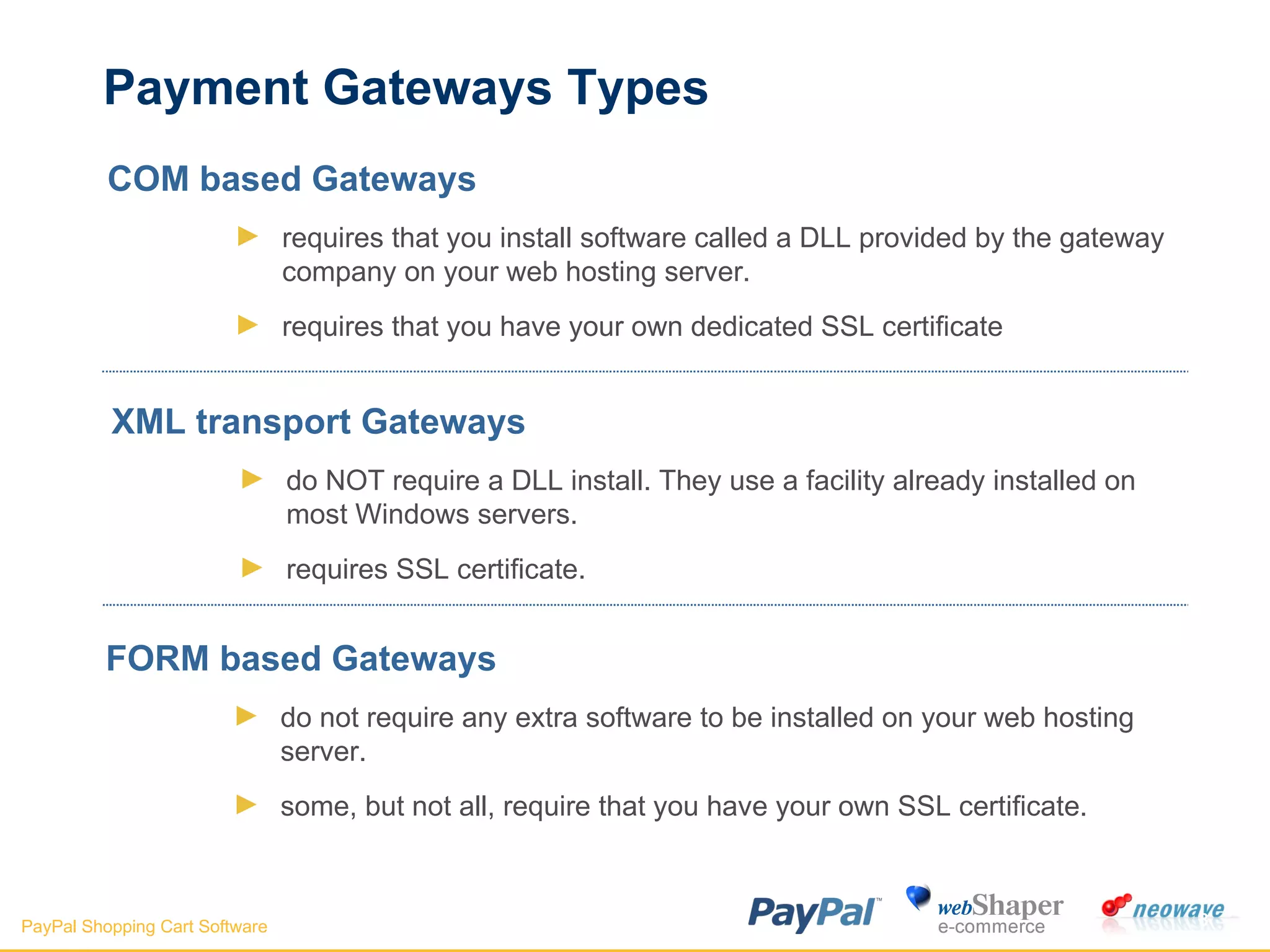
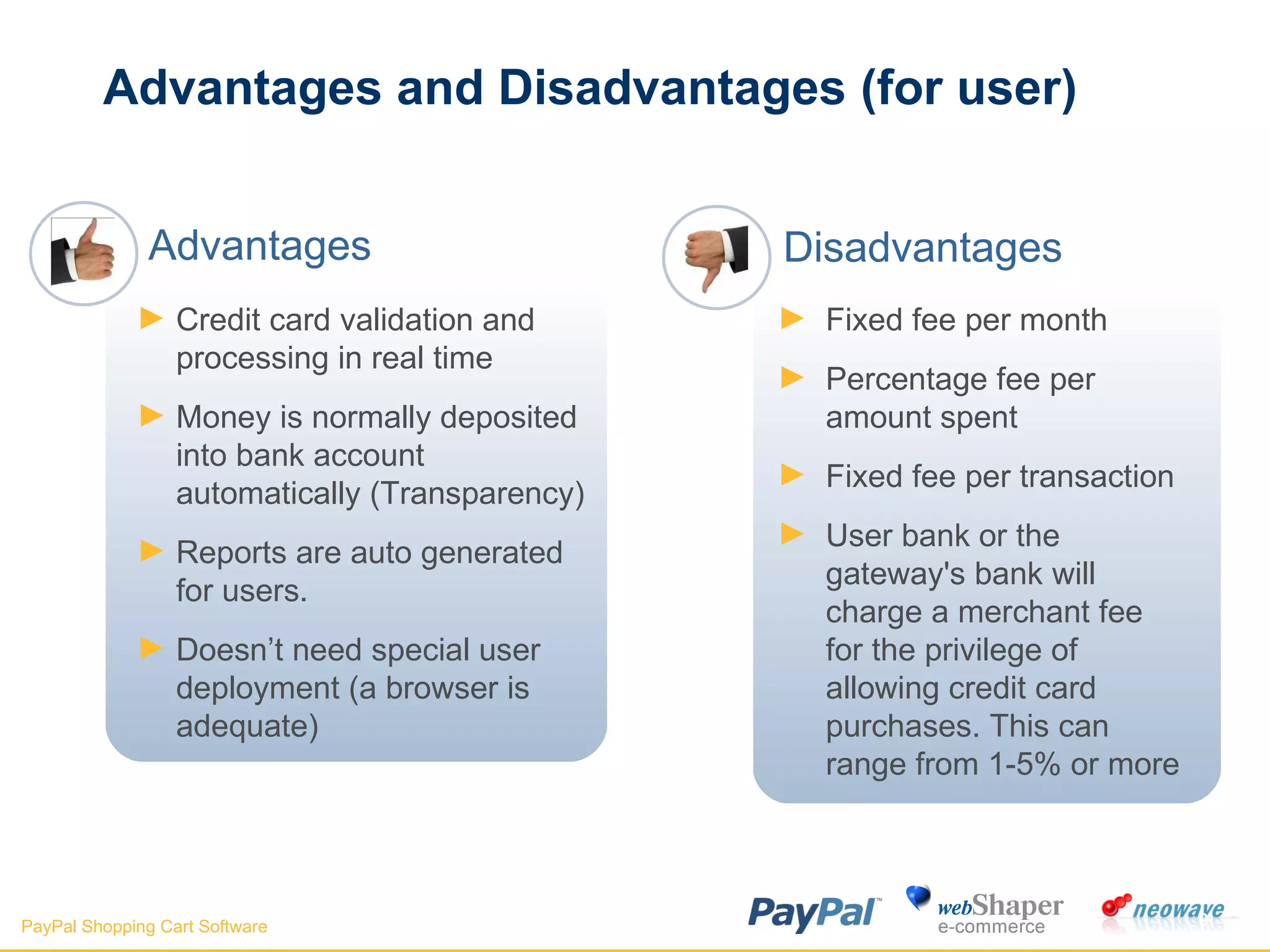
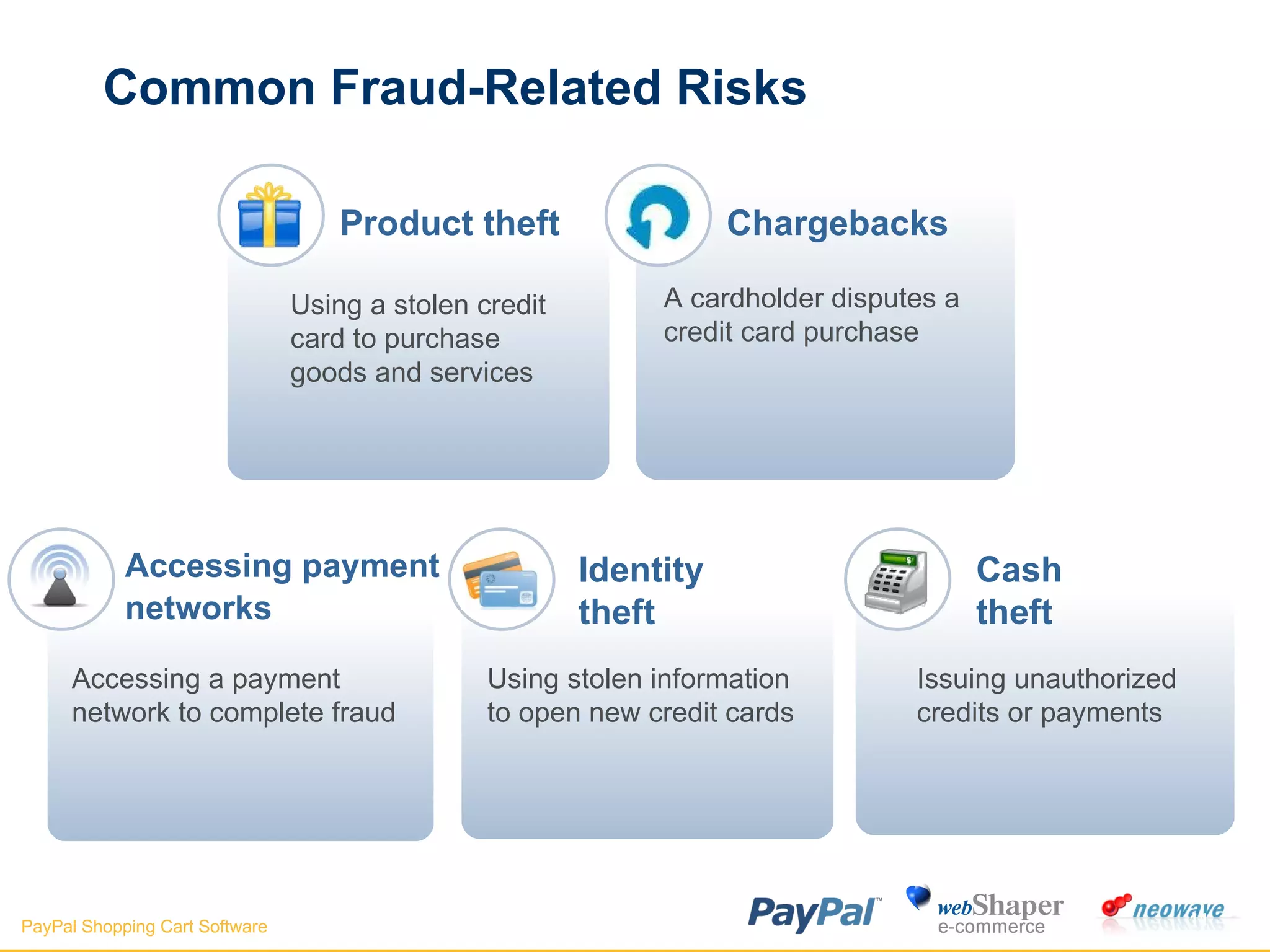
The document discusses payment gateways, including their terminology, life cycle, types, advantages and disadvantages, security issues and vulnerabilities. It provides details on authorization and settlement processes, common payment gateways like PayPal, security best practices for payment gateways, and questions to ask third party payment gateway providers.