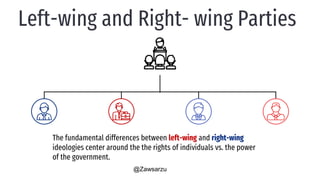
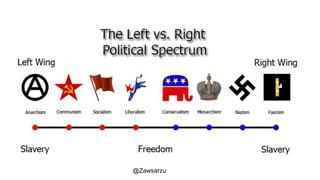
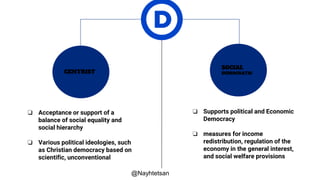
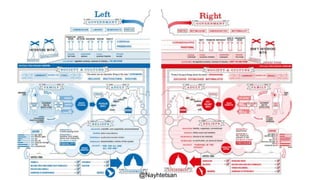
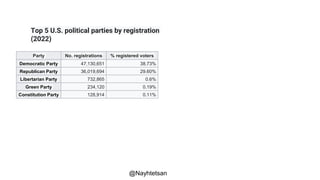
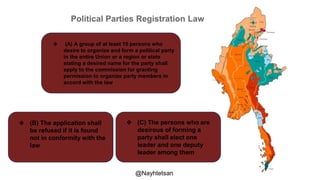
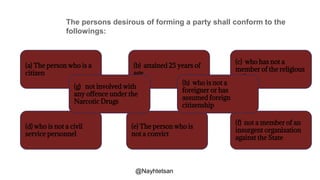
The document provides an overview of political parties, their functions, and systems, detailing their historical evolution from ancient Greece and Rome to modern times. It discusses various party types, including left-wing and right-wing ideologies, as well as contemporary party structures like the two-party system in the U.S. and registration laws for political parties in Myanmar.