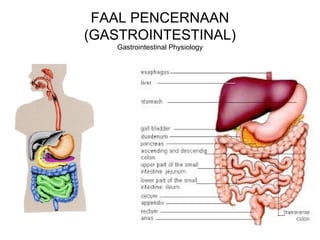
Faal digestif
- 2. Berbagai tantangan fungsi saluran GI The many challenges of the gastrointestinal tract • FUNGSI utama saluran GI adalah mencerna (digesti) dan menyerap (absorpsi) zat gizi. • Secara teknis saluran GI berada di luar tubuh dan mengandung banyak populasi mikroba. • Bagaimana mencegah mikroba itu tidak menginfeksi tubuh? (>2/3 sel imun tubuh ada di saluran GI). • Bagaimana saluran GI mengatur motilitas dan fungsi digesti dan absorpsinya? (banyak pasokan saraf – “otak mini”, hormon dan zat lain) • The major function of the GI tract is to digest and absorb nutrients. • The GI tract is technically outside the body and contains a large population of microorganisms. • How does the GI tract defend against the potential infection of the body by these microorganism? (>2/3 of the immune cells in the body are in the GI tract) • How does the GI tract coordinate it’s motility and digestive and absorptive functions? (The GI tract has a very large nerve supply – “the little brain” - and numerous hormones and signaling peptides.
- 3. Rongga mulut/ Oral cavity Lambung/ Stomach Usus kecil/ Small intestine Kolon/ Colon Motitlias Motility Menelan, mengunyah Swallowing, chewing Peristalsis, mencampur, propulsi Peristalsis, mixing, Propulsion Segmentasi, mencampur, propulsi Segmentation, mixing, propulsion, Mencampur segmental, gerakan massa Segmental mixing, mass movement Sekresi Secretion Amylase, lipase, peptides HCl, pepsinogen, HCO3 Enzim pankreas, empedu, enzim epitel usus. Pancreatic enzymes, bile, brush border enzymes Lendir/ Mucus Digesti Digestion Karbohidrat, lemak (minimal) Carbohydrates fats (minimal) Protein, lemak Proteins, fats Karbohidrat, protein, asam nukleat Carbohydrates, fats, proteins nucleic acids None bacteria only Absorpsi Absorption None Alcohol Monosakarida, asam amino, lipid, vitamin, elektrolit Monosaccharides,amino acids, lipids, vitamins, electrolytes Elektrolit, asam lemak pendek, vitamin Electrolytes, short chain fatty acids, vitamins Rangkuman fungsi saluran GI Summary of the functions of the GI tract
- 4. Kendali fungsi GI: neural dan humoral Control of GI function – neural and humoral
- 5. Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 17 September 2008 10:25 AM) © 2005 Elsevier Aktivitas otot polos saluran cerna disebabkan oleh irama naik-turun aktivitas pompa Na-K sel otot polos. Jika terjadi depolarisasi, timbul potensial aksi berantai, tonus usus naik. Smooth muscle slow wave activity caused by the rhythmic increasing and decreasing of the smooth muscle electrogenic Na,K-pump. When the waves depolarize the membrane to threshold, trains of action potentials occur, increasing tone. Kontraksi ritmis saluran cerna paling cepat di duodenum, paling lambat di kolon. Kontraksi ini dikendalikan oleh aktivitas bergelombang lambat di otot polosnya. Sel Cajal intestinal bertindak sebagai alat pacu gelombang lambat sel otot polos viseral itu. The GI tract has rhythmic waves of contractions, fastest in the duodenum, slowest in the colon. These contractions are controlled by slow wave activity in the muscles. Interstitial cells of Cajal act as pacemakers for the slow wave activity of the visceral smooth muscle cells. Kendali saraf terhadap motilitas/ Neural control of motility
- 6. Sistem saraf enterik memiliki refleks lokal (refleks pendek), tapi dipengaruhi dan dikendalikan oleh otak dan sumsum tulang belakang (refleks panjang). Keduanya menuju ke pleksus saraf di dinding usus (mienterik dan submukosa), mengatur motilitas dan sekresi usus. Refleks panjang mempersiapkan saluran GI terhadap apa yang akan timbul, sedangkan refleks pendek mempersiapkan saluran GI terhadap apa yang sudah timbul. Long reflexes prepare the GI tract for what is coming, e.g. gastrocholic reflex –emptying the colon when the stomach is full. Other similar examples are the duodenocolic, gastroileal and enterogastric reflexes where distension or chemical signals upstream increase inhibit peristalsis and secretion upstream. Short reflexes allow the GI tract to respond to what has arrived, e.g. distension or chemical peristalsis and secretion downstream, or where distension or chemical signals downstream signals in one place initiates a reflex that increases secretion or motility at that location. The enteric nervous system can operate local reflexes (short reflexes), but it is influenced and controlled by the brain and spinal cord (long reflexes). The final pathway for neural control is found in the gut wall, primarily in the myenteric plexus (between longitudinal and circular smooth muscle) and the submucosal plexus (between circular smooth muscle and the mucosa). Local and long reflexes acting through these plexi control motility and secretion.The tone of gastrointestinal smooth muscles is constantly being modified by inhibitory (VIP and NO) and excitatory (ACh and substance P) interneurons.
- 8. Selain refleks mengontrol motilitas, digesti, absorpsi, dan sekresi, ada berbagai hormon dan peptida turut dalam regulasi refleks secara kimiawi. In addition to the long and short neural reflexes controlling motility, digestion, absorption and secretion, there are several true hormones and many other peptides making up chemical reflexes. Motilitas saluran cerna: Mengatur isi lumen untuk proses digesti dan absorpsi optimal. Peristalsis adalah gerakan mendorong isi lumen menjauhi mulut (aboral). Otot sirkular di depan relaksasi, di belakang kontraksi. Segmentasi adalah gerakan mencampur isi lumen dan enzim pencernaan di satu lokasi. Katup atau sfinkter ileosekal terletak di antara usus kecil (ileum) dan usus besar (sekum). Sfinkter itu akan relaksasi (terbuka) jika menerima sinyal distensi, pasta makanan (chyme), atau sinyal kimiawi di distal ileum. Jika sekum sudah penuh (terdistensi), sfinkter itu menutup dan peristalsis ileum berkurang, membatasi kima yang masuk ke usus besar. The ileocecal valve (sphincter) is characteristic of a gating mechanism in the GI tract controlling what gets into the next segment. Distension, liquid chyme or chemical signals in the distal ileum relax the ileocecal sphincter, allowing the ileal content into the large intestine. If the cecum is already full (distended) the sphincter is kept closed and ileal peristlasis is decreased, limiting the amount of chyme entering the already-full colon. Peristalsis is the aboral (away from the mouth) movement of chyme. Circular muscle relaxation in front, contraction behind. Segmentation is the mixing of chyme and digestive enzymes in one place. In general, motility is coordinated to move food (chyme) through the GI tract at a rate that allows for optimal digestion and absorption.
- 9. Hormon utama saluran cerna Major hormones of the GI tract • Gastrin: memacu sekresi HCl lambung. • Kolesistokinin: memacu sekresi enzim pankreas dan pengosongan kandung empedu, menghambat pengosongan lambung. • Sekretin: memacu sekresi bikarbonat oleh pankreas dan hati, menghambat pengosongan lambung. • Motilin: memacu motilitas saluran GI superior. • GIP: menghambat sekresi HCl dan motilitas gaster pada konsentrasi tinggi, memacu sekresi insulin. • GLP-1: memacu sekresi insulin, menghambat sekresi glukagon oleh pankreas, memperlambat pengosongan lambung. • Gastrin - stimulates gastric HCl secretion and mucosal growth. • Cholecyctokinin (CCK) - stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion and gallbladder emptying. Inhibits gastric emptying. • Secretin - stimulates HCO3 secretion by the pancreas and liver. Inhibits gastric emptying. • Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) - inhibits HCl secretion and gastric motility at high concentrations and stimulates insulin secretion. • Motilin - Stimulates motility in the upper GI tract. • Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) - stimulates insulin release, inhibits glucagon release by pancreas, slows gastric emptying.
- 10. Air liur/ Saliva • Terutama diproduksi 3 kelenjar liur: kel. parotid (20%), submandibular (70%), dan sublingual (5%). • Bersifat hipotonik, mengandung amilase, faktor pertumbuhan, antibodi sekretorik, peptida antimikroba. • Berfungsi melindungi mulut dan gigi, melumasi pita suara, membantu menelan bolus makanan. • Parasimpatis memacu produksi banyak saliva cair; simpatis menghasilkan produksi saliva sedikit dan kental. • Kendali utama oleh N. fasial (VII), glosofaringeal (IX), parasimpatis. • Mainly produced by three pairs of glands. Parotid – watery, 20%. Submandibular (submaxillary) – moderately viscous, 70%. Sublingual – viscous, 5%. • Hypotonic, salivary amylase, some growth factors, secretory antibodies, antimicrobial peptides. • Protects the mouth and teeth, lubricates the vocal cords. • Lubricates bolus of food for swallowing. • Parasympathetic stimulation results in copious salivary secretion. Sympathetic secretion results in a small volume of a viscous saliva. • The facial and glossopharyngeal cranial, parasympathetic nerves provide the major neural control for the salivary glands. • All exocrine glands (e.g. salivary glands, exocrine pancreas) have a primary secretion produced by acinar cells, which is modified by secretion and absorption in the ducts.
- 11. ADA dua fase utama menelan: fase orofaring dan fase esofagal. Hanya sebagian dari fase orofaring yang bersifat volunter. Saat peristalsis menuruni esofagus, sfinkter inferior esofagus relaksasi sehingga bolus makanan dapat memasuki gaster. Akalasia esofagus: penyakit sfinkter esofagus inferior yang tak dapat relaksasi saat menelan. Problemnya terletak pada saraf pleksus mienterik. There are two major phases of swallowing, the oropharyngeal phase and the esophageal Phase. Only part of the oropharyngeal phase is voluntary. As peristalsis moves down the esophagus the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) relaxes. It is tonically contracted to prevent gastroesophagealreflux. With swallowing, the cardiac portion of the stomach also relaxes so as to accept the bolus of food. There are also secondary waves of peristalsis if food is left in the esophagus. The pharynx acts as an upper esophageal sphincter. ACHALASIA – LES fails to relax on swallowing. Myenteric plexus problem, insufficient NO and VIP-ergic activity. MENELAN/ SWALLOWING
- 12. Profil utama lambung Main features of the stomach • Penting untuk pencernaan protein (pepsin dan pH rendah). • Isinya asam (pH rendah) untuk melindungi saluran GI dari pertumbuhan bakteri. • Menghasilkan faktor intrinsik untuk absorpsi vit. B12. • Tidak berfungsi absorpsi (kecuali alkohol). • Important for digestion of proteins (pepsin and low pH). • Importance of the low pH in protecting the GI tract against bacterial overgrowth. • Produces intrinsic factor necessary for vitamin B12 absorption. • Some storage function (limited). • Not much absorption (except alcohol).
- 13. Sel gaster dan sekretnya Cells of the stomach and what they secrete. • Sel parietal di kelenjar pilorus memproduksi asam klorida (HCl) dan faktor intrinsik. • Sel peptik (chief cell) gaster memproduksi pepsinogen. • Sel G menghasilkan gastrin. • Sel S menghasilkan somatostatin. • Sel ECL menghasilkan histamin. • Parietal (oxyntic) cells in pyloric gland of stomach – secrete HCl and intrinsic factor. • Chief cells – secrete pepsinogen. • G cells, mostly in the antrum, secrete gastrin • S cells –secrete somatostatin. • ECL (enterochromaffin like) cells secrete histamine.
- 14. Fase sekresi gastrik Phases of gastric secretion • Sefalik: dipicu pandangan dan penciuman, refleks panjang via N. vagus. Timbul sekresi gastrin, histamin, HCl, pepsinogen. • Gastrik: dipicu bolus makanan dalam gaster, melibatkan refleks pendek dan hormon, khususnya gastrin (memacu), somatostatin (menghambat). Asam menghambat sekresi HCl tapi memacu sekresi pepsinogen (menjadi pepsin yang aktif dalam pH asam). • Intestinal: dipicu isi gastrik yang memasuki duodenum, dimediasi gastrin duodenal dan mekanisme persarafan. • Cephalic – stimulated by sight and smell – involves long reflexes in vagus nerve: stimulates gastrin release which stimulates the ECL cells to release histamine and stimulate parietal cell HC secretion. Vagal stimulation also stimulates pepsinogen secretion. • Gastric – stimulated by chyme in the stomach – involves short reflexes and hormones, notably gastrin (stimulates), somatostatin (paracrine - inhibits). Acid in the stomach inhibits HCl secretion (somatostatin mediated) but stimulates pepsinogen secretion. The pepsinogen is activated to pepsin by the acidic environment. Controlled by long vaso-vagal reflexes, local enteric reflexes and gastrin-histamine mechanism. • Intestinal – stimulated by gastric content entering the duodenum. Probably mediated by duodenal gastrin and neural mechanisms.
- 15. Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 17 September 2008 10:25 AM) © 2005 Elsevier In the parietal cells H+ secretion by the gastric parietal cells involves an H,K-ATPase that secretes H+ into the canaliculi. H+ is exchanged for K+ which then leaks back out into the canaliculi lumen. Cl- follows the H+ via an active transport mechanism. Carbonic anhydrase is necessary to hydrate CO2 and produce the H+ . The HCO3 - that is left behind diffuses out of the cell via the basolateral membrane into the blood. Three major classes of drugs used in controlling gastric acid. • Antacids. Oldest. Work to neutralize gastric acid. May be a rebound effect. • Histamine receptor blockers. Histamine receptors in the stomach are of the H2 subtype. H2 receptor blockers are currently very popular. • H,K-ATPase inhibitors. Very effective. Particularly for short term use to allow ulcer repair, etc.
- 16. Bagaimana gaster melindungi dirinya tidak tercerna? Mukosa gaster memiliki barier terdiri atas lapisan mukus dan sekresi bikarbonat (HCO3), membentuk barier pH netral yang mantap. Duodenum (usus 12 jari) tidak memiliki proteksi demikian terhadap asam. Tapi getah pankreas dan cairan empedu yang mengalir ke duodenum (melalui sfinkter Oddi) mengandung bikarbonat yang dapat melawan efek asam. How does the stomach avoid digesting itself? The gastric mucosal barrier relies on the mucus blanket and HCO3 secretion. Mucus neck cells secrete mucus to form an unstirred layer over the gastric mucosa. They also secrete HCO3 - into the unstirred layer forming a standing pH gradient, neutral near the mucosa to acidic in the gastric lumen. While the stomach has protection against gastric acid and pepsin, the duodenum does not. That is why it is very important that the stomach does not empty too much acidic content too fast into the small intestine. The major protection for the small intestine against gastric acid is the secretion of HCO3 in the pancreatic juice and, to a lesser extent, bile. In humans both pancreatic juice and bile enter the duodenum through the same sphincter (the sphincter of Oddi).
- 17. When acidic chyme leaves the stomach there is a release of a high [HCO3-], enzyme and bile - rich fluid into the duodenum through the common bile duct. Pengosongan lambung dengan makanan tinggi karbohidrat terjadi dalam sekitar 4 jam. Lebih lambat jika makanan tinggi lemak. Refleks enterogastrik: makanan yang masuk duodenum memberi sinyal umpan balik menghambat pengosongan gastrik, terutama kima yang asam dan kaya asam amino. Gastric emptying depends on the content of the stomach. A high fat meal leaves the stomach very slowly, a high protein meal leaves more quickly and a high carbohydrate meal leaves in about 4 hours. High osmotic pressure chyme entering the duodenum slows gastric emptying – due to duodenal osmoreceptors? Enterogastric reflex – feedback from food entering the duodenum inhibiting gastric emptying, particularly for low pH and amino acid – rich chyme. May have both a neural and humoral component to this reflex. Duodenal distension delays gastric emptying – neural. Several duodenal hormones slow gastric secretion and motility –secretin, CCK, GIP, GLP-1.
- 18. Sekresi pankreas Pancreatic secretion Pankreas memproduksi berbagai enzim pencerna protein, lemak, karbohidrat, dalam bentuk nonaktif. Saluran keluar dari pankreas (duktus pankreatikus) menghasilkan sekret kaya akan bikarbonat (HCO3 - ). Semakin cepat sekresinya, kadar bikarbonat makin tinggi. In the pancreas the acinar cells produce several enzymes, inactive forms of several proteolytic enzymes and phospholipase A2, lipase, colipase, amylase. The inactive forms of these enzymes are activated by trypsin, so if they are activated in the pancreas the pancreas will be severely damaged. Protected by anti-trypsin. The pancreatic ducts produce a HCO3 - -rich secretion. The faster the rate of secretion, the greater the [HCO3 - ].
- 19. Getah pankreas sangat penting mencerna protein, lemak, karbohidrat Pancreatic juice is very important for the digestion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins Protease Amylolytic enzyme Lipase Nuclease Others Trypsinogen Amylase Lipase DNAase Pro- colipase Chymo- trypsinogen Nonspecific esterase RNAase Trypsin Inhibitors Pro- elastase Phospho- lipase A2 Procarboxy- peptidase A Procarboxy- peptidase B
- 20. Enzim-enzim proteolitik pankreas masuk ke duodenum, tripsinogen diaktifkan oleh enteropeptidase (atau enterokinase) di epitel duodenal menjadi tripsin. Tripsin memulai serangkaian reaksi untuk mengaktifkan semua pro-enzim lain. When the inactive proteolytic enzymes enter the duodenum trypsinogen is activated by an enteropeptidase in the duodenal epithelium. The resulting trypsin sets off a chain reaction, activating all the other pro-enzymes. The enteropeptidase is also called enterokinase.
- 21. A general model for a cell that secretes HCO3 - is one that has a HCO3 - - Cl- exchange pump (carrier) on the apical membrane. The Cl- that enters the cell when the HCO3 - leaves has to go back out of the cell. This happens through a CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) channel. This is a major channel in the gut for Cl- secretion. The HCO3 - in the cell is produced by the hydration of CO2 catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase. The remaining H+ leaves the cell at the basolateral border in exchange for Na+ entering. The Cl- for the CFTR channel enters through the basolateral membrane Na,K,2Cl symporter. Bicarbonate secretion
- 22. Apa yang terjadi di duodenum? What happens in the duodenum when the stomach empties? • Beberapa cm awal duodenum terdapat kelenjar Brunner yang memproduksi mukus dan bikarbonat, melindungi duodenum dari asam lambung. Produksinya dipicu saraf vagus dan sekretin. • In the fist few centimeters of the duodenum there are glands – Brunner glands – that secrete heavy mucus and a HCO3 - - rich fluid. Important in protecting the duodenum from gastric contents. Secretion stimulated by vagus and secretin. • Bolus asam dari lambung merangsang mukosa duodenal mensekresi hormon sekretin. Sekretin memicu sekresi pankreas. • Lemak dan asam amino di duodenum memicu sekresi kolesistokinin (memicu sekresi pankreas, relaksasi sfinkter Oddi, kontraksi kandung empedu). • Stimulasi vagal memperkuat sekresi pankreas dan kontraksi kandung empedu. • The acidic chyme stimulates secretin release from the duodenal mucosa, Secretin travels in bloodstream to stimulate pancreatic and bile duct HCO3 - release (pancreas more important). • Fats and amino acids in the duodenum stimulate cholecyctokinin release from the duodenal mucosa, travels in bloodstream and stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion, relaxation of sphincter of Oddi and contraction of gallbladder. • Vagal stimulation backs up the pancreatic enzyme secretion and gallbladder contraction
- 23. © 2005 Elsevier * Dinding dalam usus kecil terdiri atas jonjot-jonjot (villi). Morfologi villi dan mikrovilli (brush-border) memaksimalkan permukaan absorpsi nutrisi ke dalam darah menuju hati, dan lipid masuk ke dalam saluran limfe. * Permukaan mikrovilli juga mengandung enzim pencernaan a.l. laktase. Kekurangan enzim laktase intoleransi laktosa/ produk susu (diare osmotik). * Kripta villiaris (ceruk jonjot usus) mengandung sel Paneth penghasil peptida antimikroba untuk melindungi sel punca epitel usus. Juga terdapat sel globlet penghasil mukus untuk proteksi dan pelumas. * Sel epitel usus diganti setiap 3-5 hari. The crypts contain Paneth cells at their base that secrete antimicrobial peptides to protect the stem cells. These stem cell produce the epithelial cells that migrate up the villi, differentiating as they go to become better able to absorb nutrients. The crypts also produce goblet cells that provide the mucus that protects the crypts themselves and protects and lubricates the mucosal epithelium of the villi. The morphology of the villus maximizes absorptive surface area and removal of nutrients, carbohydrates and amino acids directly to the liver, and lipids mostly into the circulation via the lymph. Epithelial cells turn over every 3 – 5 days. Brush border maximizes surface area for absorption and also contains some digestive enzymes, a few exopeptidases, lactase, sucrase, maltase and isomaltase. There is also a minor amount of lipase on the brush border. Lactase deficiency leads to dairy products intolerance – osmotic diarrhea.
- 24. Hati adalah organ multifungsi, esensial untuk metabolisme dan pengolahan senyawa esensial. Produknya garam empedu esensial bagi pencernaan lemak di usus kecil. Ia juga organ utama untuk detoksifikasi. Jika sebagian dibedah, dengan cepat akan tumbuh kembali. Pada saat empedu tak terpakai, ia disimpan di kandung empedu, mengalami pemekatan sampai 20 kali. Kandung empedu berkontraksi lemah dengan stimulasi vagal dan sfinkter Oddi relaksasi. Kolesistokinin adalah hormon pemicu terkuat kontraksi kandung empedu. The liver is a multifunctional organ, essential for metabolic functions and processing essential compounds. The bile salts it produces are essential for lipid digestion in the intestine. It is the major organ for detoxification. If sections are surgically removed it can grow back rapidly. Bile is made up two parts, the first coming from the hepatocytes contains bile salts and bile pigments. The ducts this bile passes through (terminal bile ducts and hepatic duct) adds a HCO3 - - rich fluid which is stimulated by secretin, just as in the pancreas. In the interdigestive period the sphincter of Oddi is closed and bile is diverted into the gallbladder where it is concentrated up to 20 fold. The gallbladder contracts weakly with vagal stimulation (ACh) and the sphincter of Oddi relaxes (VIP, NO) CCK is the strongest stimulant for galbladder contraction. Hati dan kandung empedu The liver and gallbladder
- 25. Drainasi vena saluran cerna langsung ke hati melalui vena porta, membawa nutrisi untuk disimpan dan diolah di hati. Pada gagal jantung kanan, darah terbendung di vena hepatika dan hati, membuat hati membengkak. With right heart failure blood backs up in the hepatic vein and liver, causing the very distensible liver to swell. Distension of the liver below the border of the ribs is a sign of heart failure. The venous drainage of the GI tract goes directly to the liver via the hepatic portal vein, carrying absorbed nutrients for storage and processing. Hati diperdarahai oleh arteri hepatika dan vena porta hepatika. The liver has two incoming blood supplies, one the heptic artery carrying arterial blood and the other in the larger hepatic vein carrying splanchnic venous drainage.
- 26. Pencernaan karbohidrat dimulai di rongga mulut oleh amilase air liur, tapi yang lebih penting adalah amilase getah pankreas. Selain itu terdapat enzim disakaridase di jonjot usus kecil. Carbohydrate digestion starts with salivary amylase, but pancreatic amylase is more important. The disaccharidases, maltase, sucrase, isomaltase and lactase are located on the epithelial cell brush border. Thus there is some digestion in the mouth, much more in the duodenal lumen, and finally some at the brush border, next to the hexase carriers. Glukosa (sekitar 80% karbohidrat makanan) dan galaktosa masuk sel lewat transportasi aktif, sedangkan fruktosa masuk sel lewat difusi difasilitasi. Sebagian besar fruktosa diubah menjadi glukosa dalam sel epitel usus. Glucose (about 80% of dietary carbohydrate) and galactose use the same secondary active transport system at the apical membrane (SGLT1) and pass out the basolateral membrane by facilitated diffusion (GLUT2), while fructose transport at the apical membrane is not Na+ dependent, using a facilitated diffusion carrier. Most fructose is converted to glucose in the epithelial cell Digesti dan absorpsi karbohidrat Carbohydrate digestion and absorption
- 27. Pencernaan protein terutama oleh enzim proteolitik getah pankreas. Sebagian eksopeptidase terdapat di “brush border” (mikrovilli). Penyerapan protein (asam amino dan peptida) terjadi secara transportasi aktif dan difusi difasilitasi. Sebagian kecil absorpsi protein melalui transitosis, ini masalah bagi timbulnya alergi. Pepsin and pancreatic proteolytic enzymes are the major factors in protein digestion, but some exopeptidases are also attached to the brush border. There are at least 5 transport proteins for amino acids on the brush border membrane. Most transport across the apical membrane is of single amino acids and is secondary active transport. There is also facilitated diffusion and H+ coupled cotransporters for di and even tripeptides. Some very small amount of protein is absorbed by transcytosis – a problem for allergies. Digesti dan absorpsi protein Protein digestion and absorption
- 28. Digesti dan absorpsi lemak Digestion and absorption of fats Sangat rumit, membutuhkan: Memerlukan enzim lipase dan kolipase pankreas untuk digesti. Memerlukan garam empedu untuk emulsifikasi (lemak “melarut” dalam air) agar mudah dicerna dan diserap. Malabsorpsi atau maldigesti lemak steatore (feses berlemak, pucat, dan mengambang). Very complex. Requires: • Pancreatic lipase and colipase for digestion. • Bile salts to emulsify fats for digestion. • Adequate surface area and slow enough transit time for absorption. • Malabsorption or maldigestion results in steatorrhea (fatty stool – light colored and floating). Lemak makanan umumnya berupa senyawa trigliserida. Trigliserida dipecah oleh enzim lipase menjadi monogliserida dan asam lemak yang siap diserap dalam bentuk misel (micelles), Much of our dietary fat is in the form of triglyceride, which must be broken down to free fatty acids and monoglycerides for absorption. But lipase and colipase cannot function in a solid lipid phase. They need an emulsion with a large lipid-water interface. Bile salts act as detergents and produce the emulsion so that lipase can digest fatty acids. Emulsion eventually decreases in size to micelles. Lipids are absorbed as micelles.
- 29. Monogliserida dan asam lemak setelah diserap lalu dibentuk lagi menjadi trigliserida dalam sel epitel usus. Lipid itu lalu dibungkus selapis protein dan disalurkan ke saluran limfe dalam bentuk kilomikron. Asam lemak berantai pendek dapat langsung masuk ke kapiler darah dan menuju ke hati. Monoglycerides and fatty acids are absorbed in micelles.Triglycerides are reassembled in the epithelial cell. The lipids are then covered with a layer of protein and exported into the lymph as chylomicrons. Short chain fatty acids can go into the capillaries and directly to the liver. Garam empedu di ileum diserap kembali (95%) ke darah, menuju ke hati (lewat vena porta) untuk kembali dikeluarkan dalam empedu untuk emulsifikasi lemak. Siklus ini disebut sirkulasi enterohepatik. Bile salts are taken back up in the ileum and recycled through the liver into the bile – ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION. Bile salts in the blood are taken up by the liver and stimulate more bile production.
- 30. Keseimbangan cairan di saluran cerna Fluid balance in the gastrointestinal tract is the result of absorption and secretion • Sekresi/ masukan • Secretion/intake Konsumsi/ Consumption, 2.0L Air liur/ Saliva, 1.5L Getah lambung/ Gastric juice, 2.0L Getah pankreas/ Pancreatic juice, 1.5L Empedu/ Bile, 0.5L Sekresi usus/ Intestinal secretion, 1.5L Total, 9.0L • Absorpsi/ absorption Dari usus kecil/ From the small intestine, 7.5L Dari usus besar/ From the large intestine, 1.4L Total , 8.9L Ekskresi dalam feses/ Excreted in stool, 0.1L
- 31. Absorpsi dan sekresi di usus kecil Absorption and secretion in the small intestine • Absorpsi terbesar air dan elektrolit terjadi di sel epitel dekat puncak villi. Air mengikut elektrolit dan non-elektrolit yang ditransportasi aktif. • Sekresi air dan elektrolit terjadi di kripti. Saluran CFTR dapat ditambah atau dikurangi untuk menambah atau mengurangi sekresi. • Differentiated epithelial cells near the villus tips do most of the absorption of water and electrolytes. Water follows electrolytes and non-electrolytes transported by secondary active transport. • Standing osmotic pressure established between cells by the Na+ pump. • Secretion of water and electrolytes occurs in the crypts. A CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator) channel in the apical surface can be increased or decreased to increase or decrease secretion.
- 32. Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 17 September 2008 10:25 AM) © 2005 Elsevier Usus besar (kolon) The large intestine • Mengandung banyak bakteri. • Tiap hari dapat menyerap 5-8 L air dan elektrolit, jika beban melebihi itu, akan timbul diare. • Isinya semakin padat dari kolon asenden hingga ke rektum. • Huge bacterial load. • Can absorb up to 5 to 8 L of water and electrolyte per day. If load exceeds this the individual will have diarrhea. • Content gets less fluid going from ascending colon to rectum.
- 33. Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 18 September 2008 03:43 AM) © 2005 Elsevier Refleks defekasi Defecation reflex Distensi rektum mencetuskan peristalsis lokal di kolon desenden dan sigmoid dan rektum, serta merelaksasi sfinkter anal internal. Untuk defekasi volunter masih perlu merelaksasi sfinkter anal eksternal, menahan napas, mengedan untuk menaikkan tekanan intraabdominal. Distension of the rectum causes local peristalsis of descending and sigmoid colon and rectum and relaxes internal anal sphincter (weak, myenteric plexus). Periodically get defecation reflex, mediated In the sacral cord, to increase movement (pelvic n. efferents). For voluntary defecation need to also relax external anal sphincter, hold breath, strain to increase intraabdominal pressure.
- 34. Terapi diare sekretorik dengan Oralit Treatment of secretory diarrhea using ORT – the rationale Pada kolera, dan diare sekretorik lain, transporter aktif Na-glukosa dan Na-asam amino masih intak. Cairan pengganti oral (Oralit) berisi glukosa dan asam amino, elektrolit dan basa telah menolong jutaan jiwa di seluruh dunia. In cholera, and other the secretory diarrheas, sodium-glucose and sodium-amino acid co-transporters are preserved. Oral replacement fluids containing glucose and amino acids, electrolytes and a base have saved millions of lives worldwide.