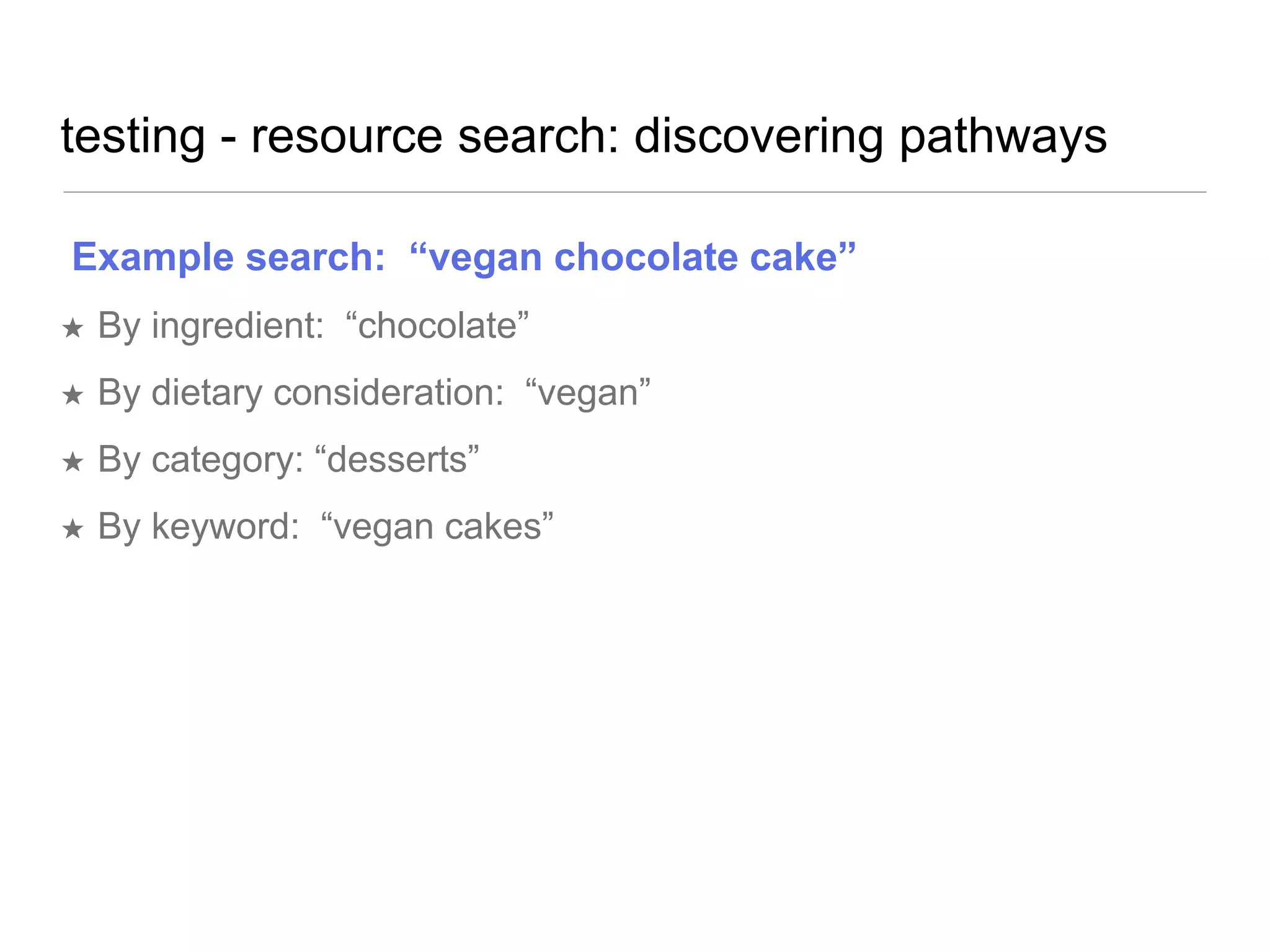
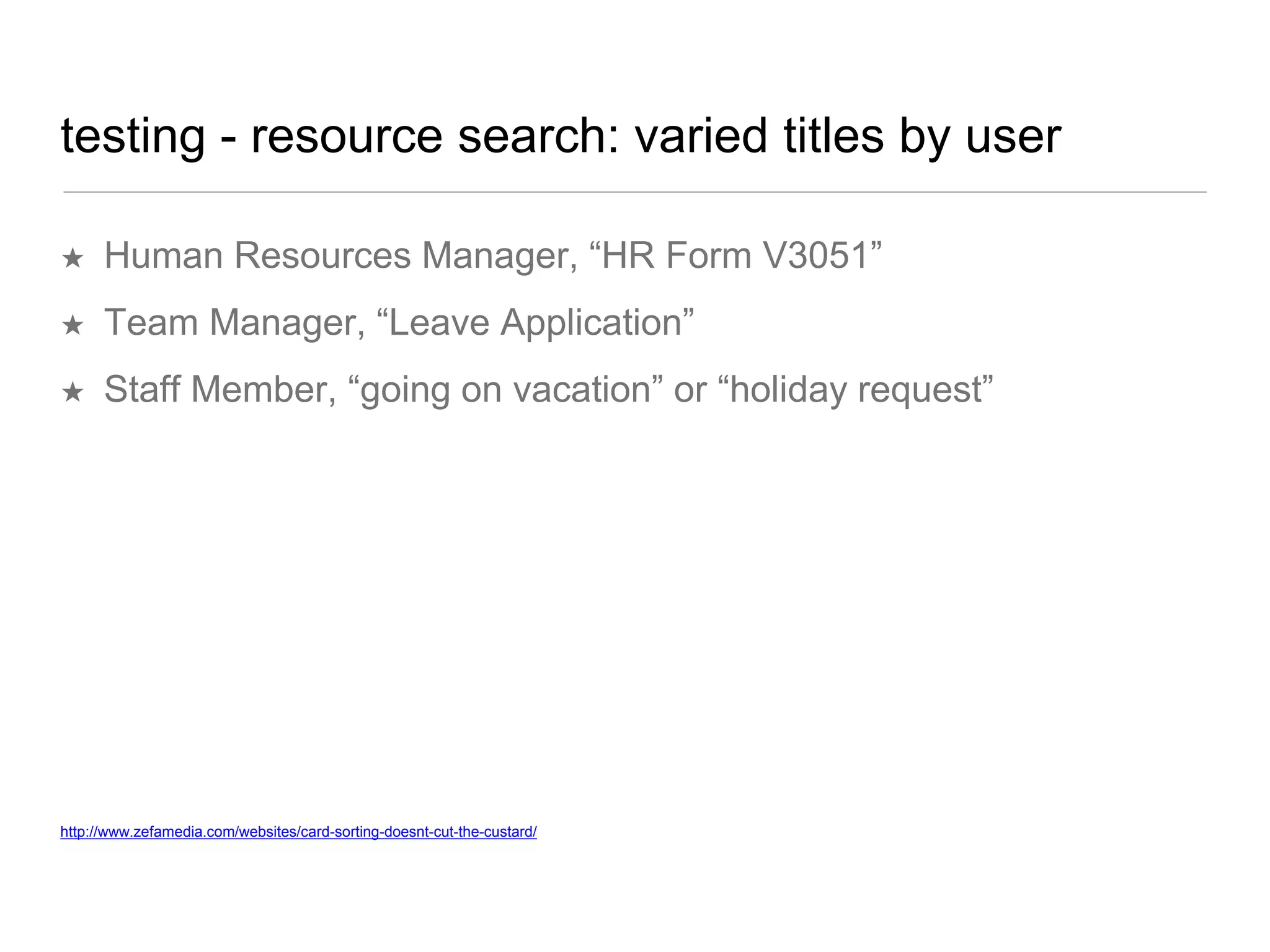
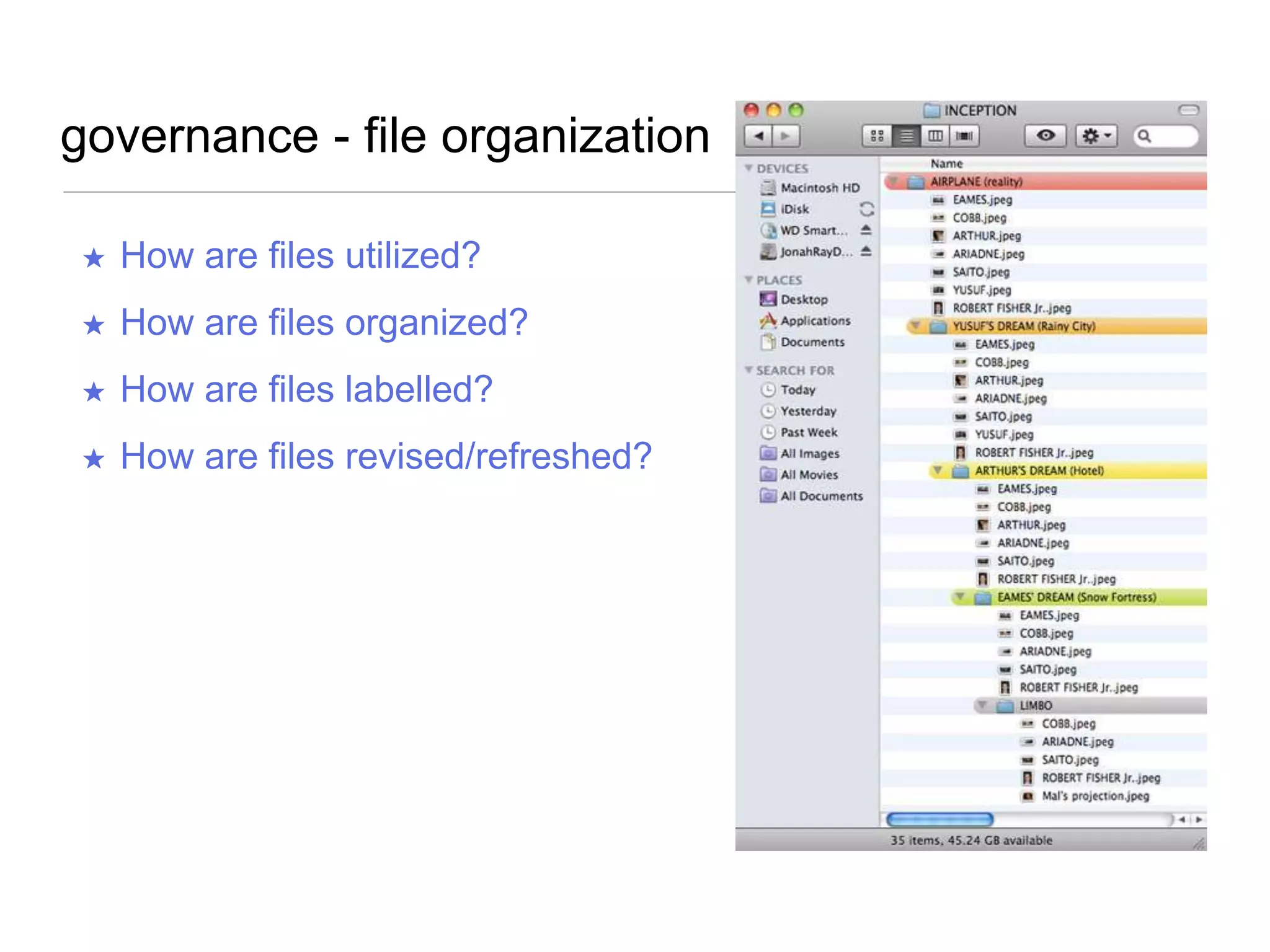
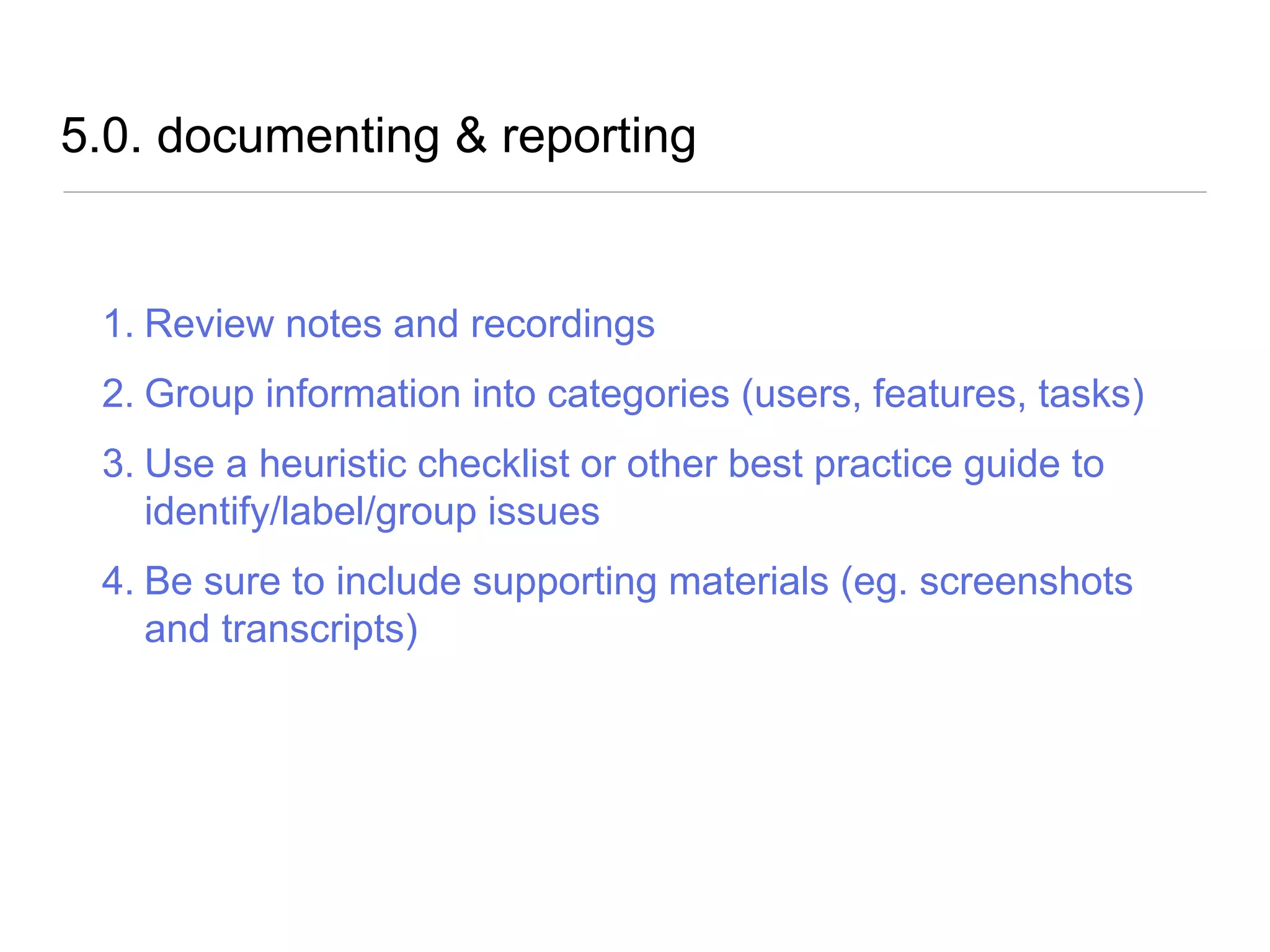
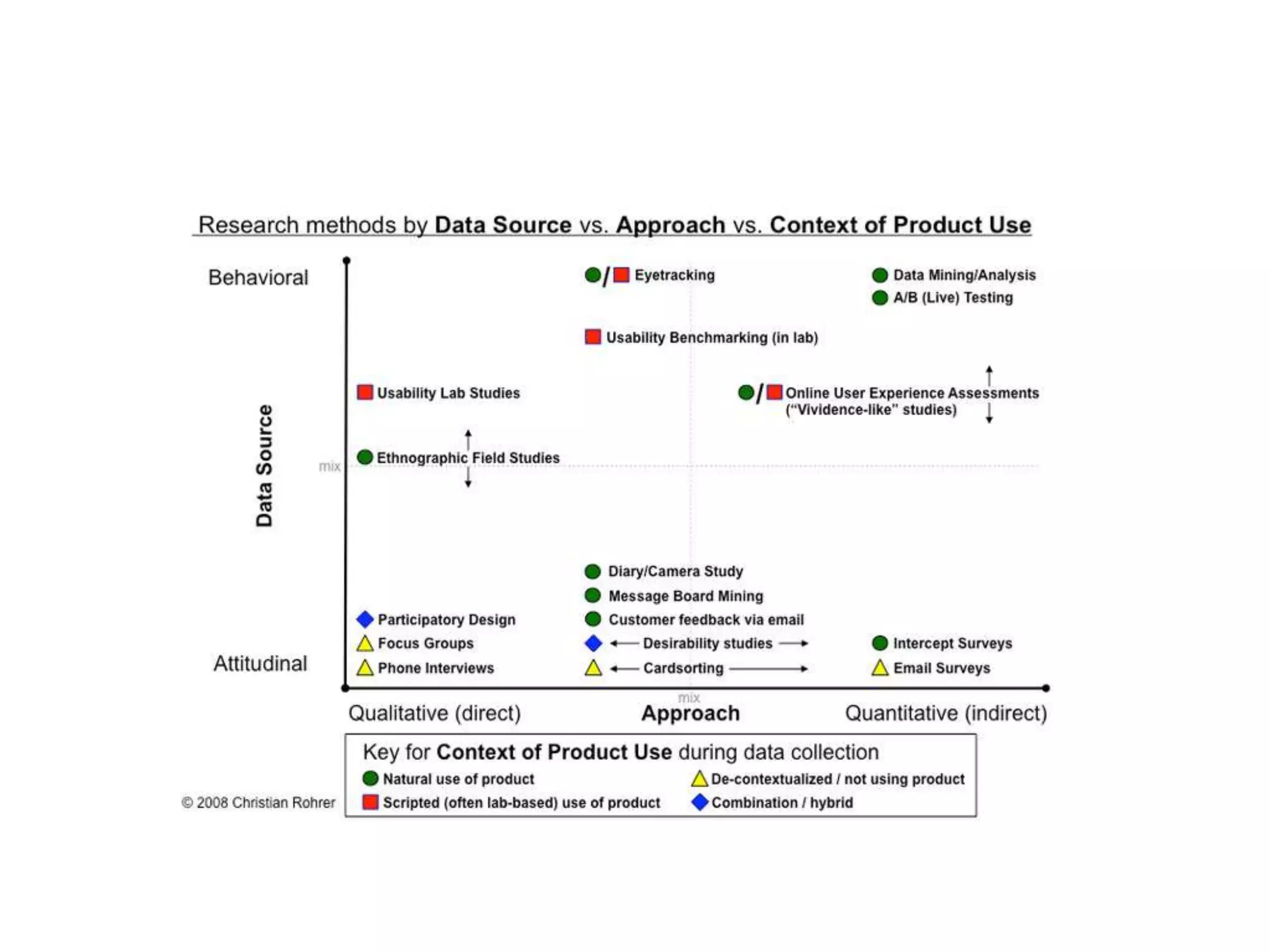
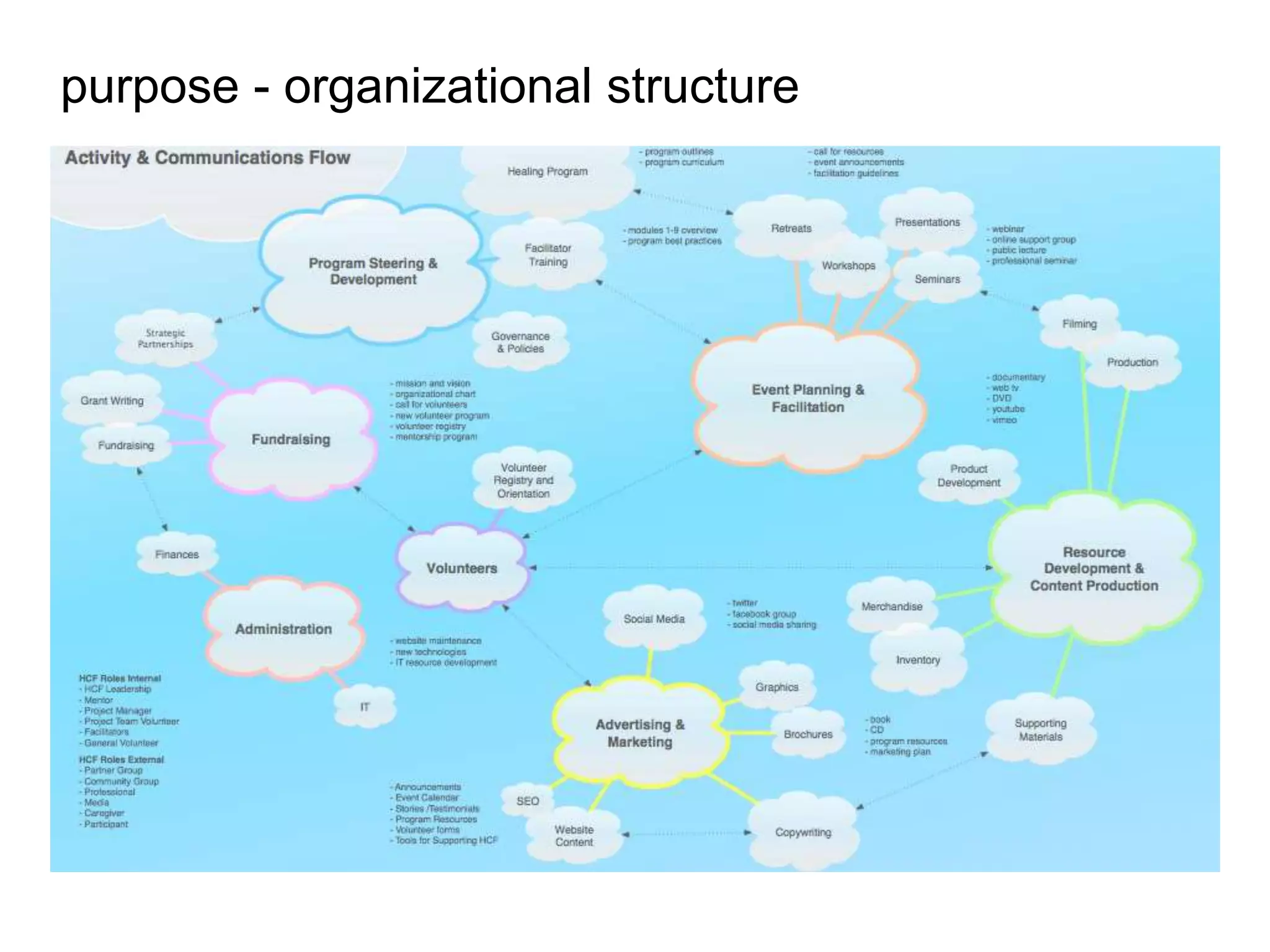
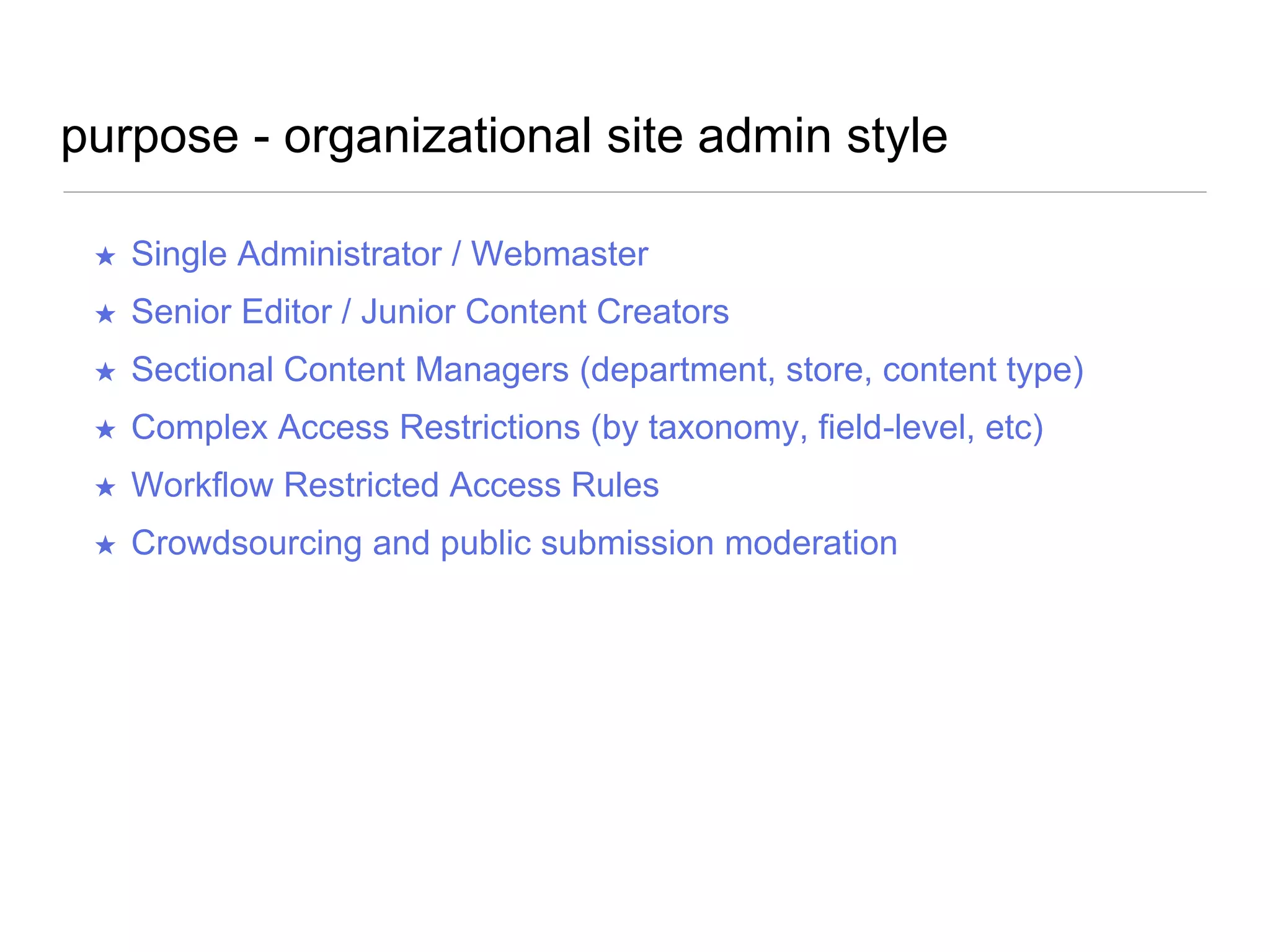
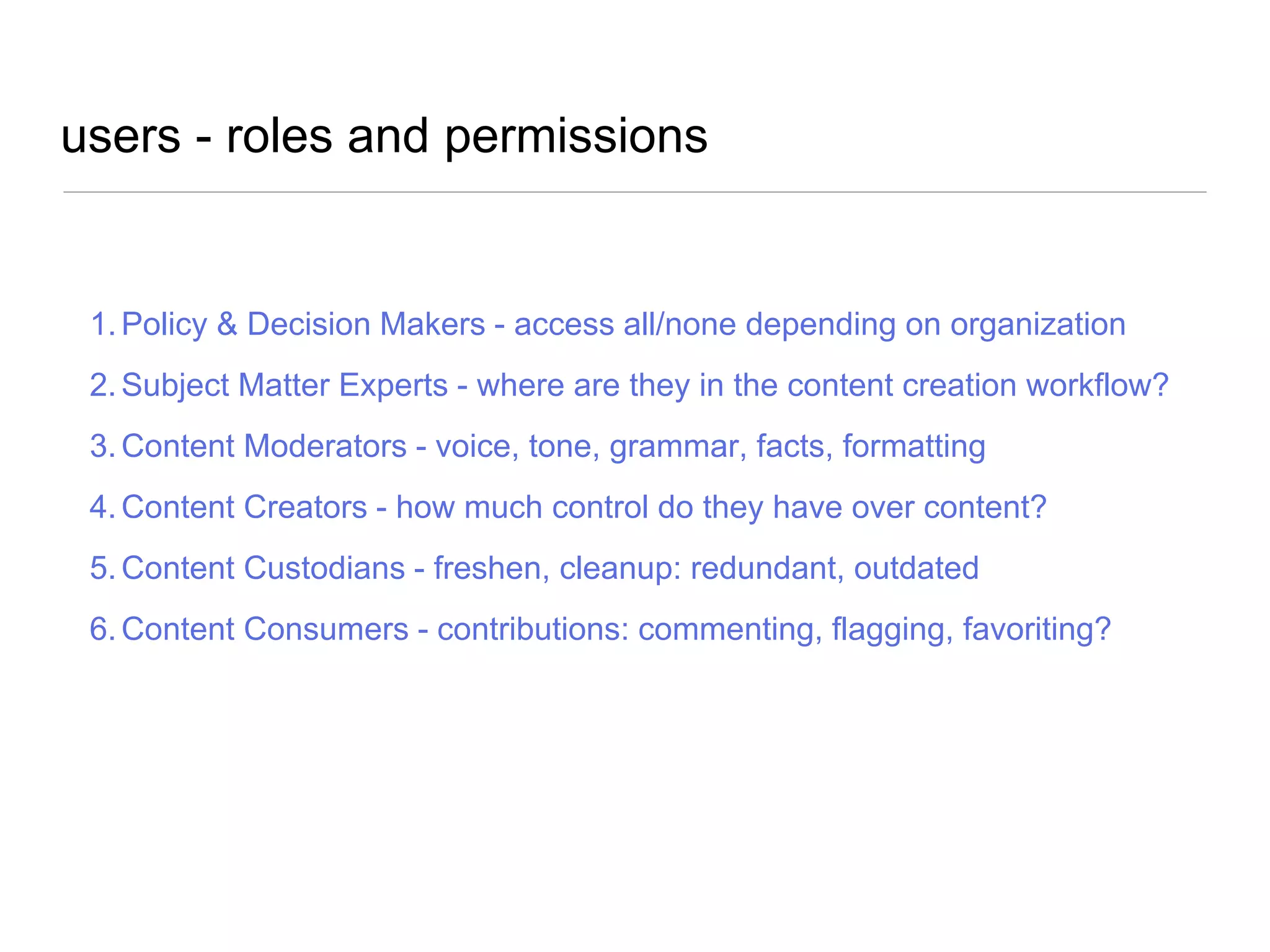
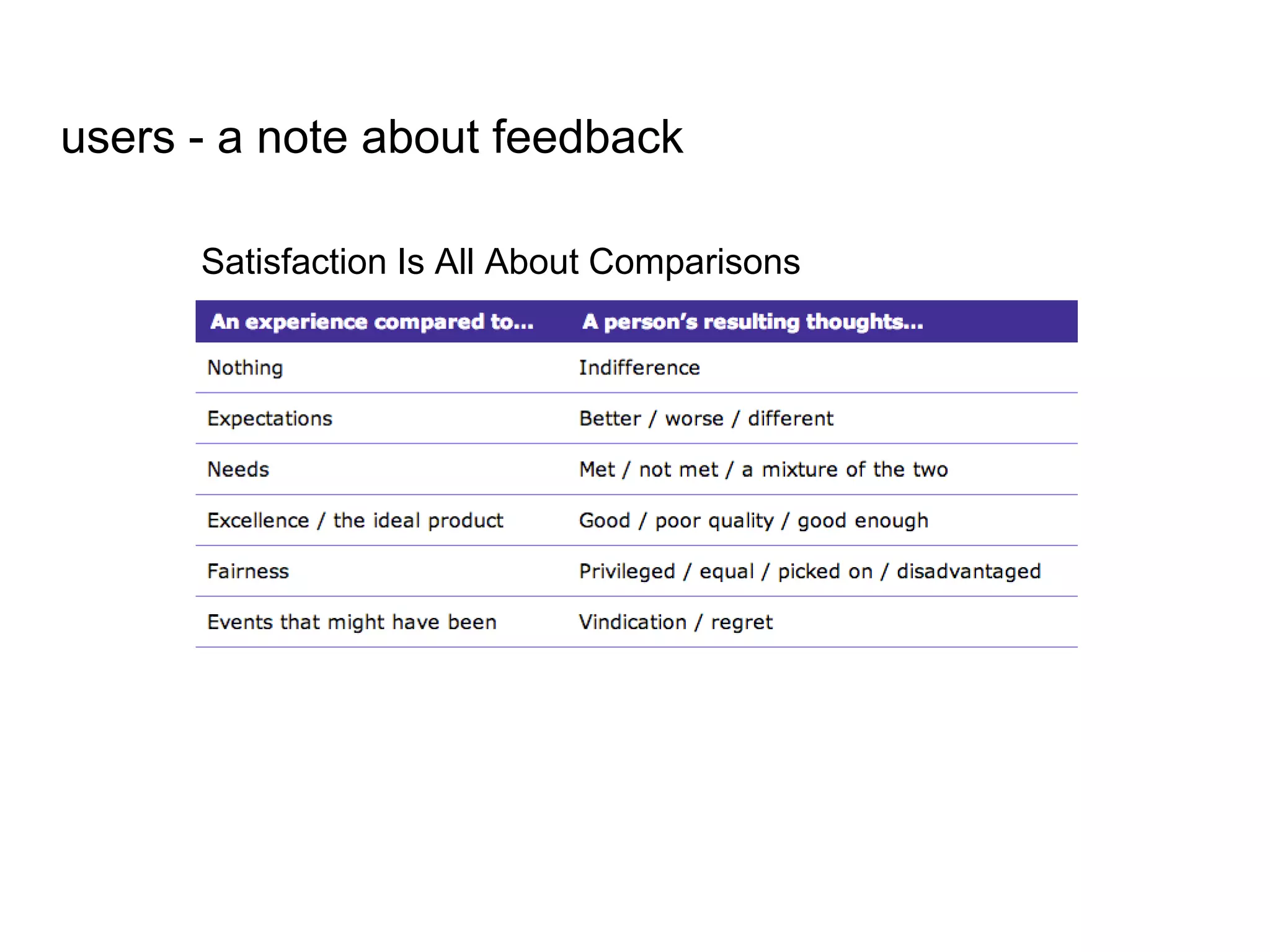
The document outlines a user experience design track focused on usability testing for Drupal administration, covering the purpose of usability studies, user roles, planning, testing methodologies, documentation, and development planning. It provides frameworks and checklists for organizing a usability study, identifying user needs, and addressing common obstacles. The emphasis is on improving user interactions and processes while collecting and documenting feedback for effective implementation of changes.






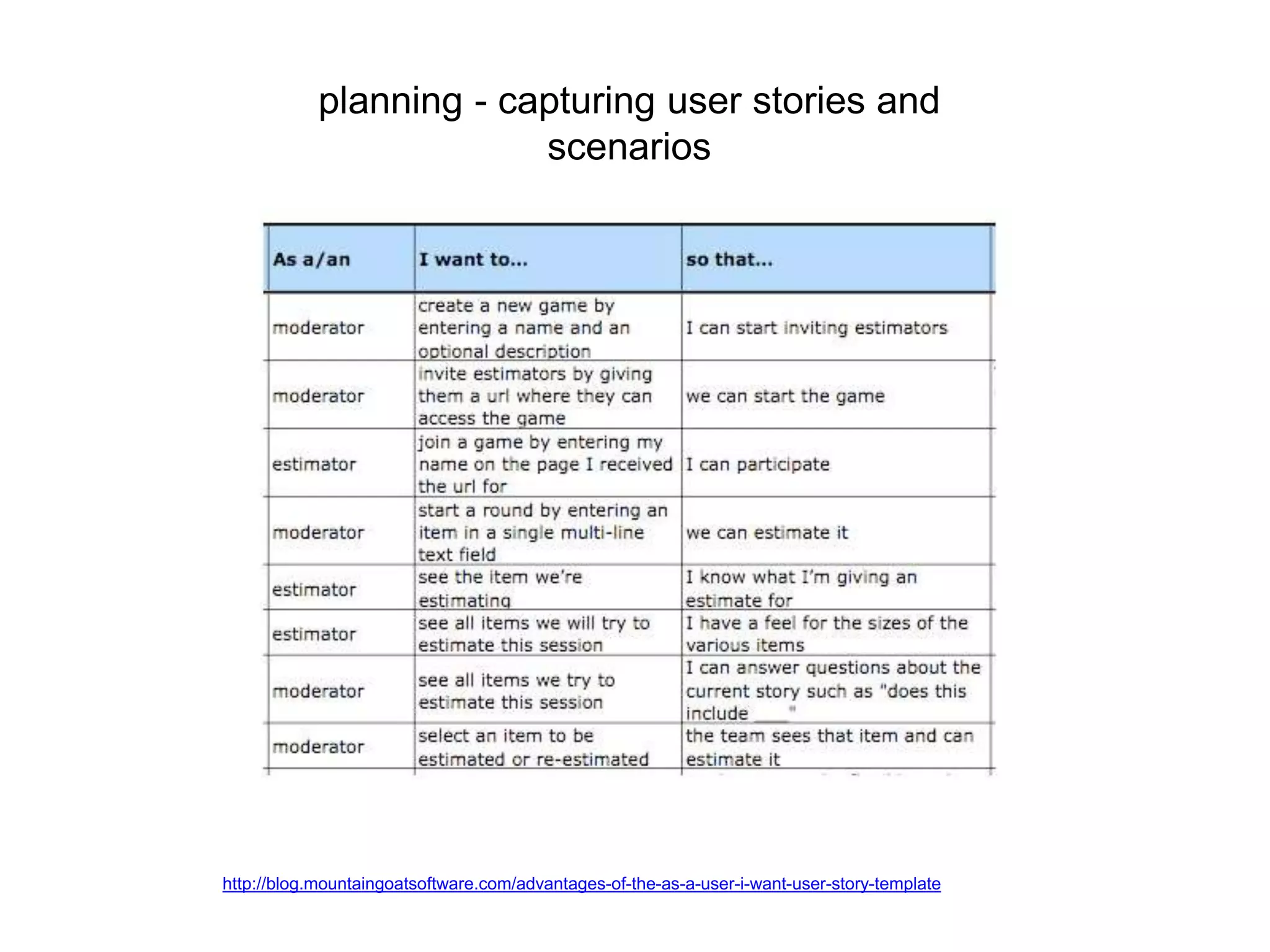
![as a [type of user] I want to [goal]
so that I can [reason].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/user-testing-drupal-admin-140627160657-phpapp02/75/User-Testing-your-Drupal-Administration-Process-17-2048.jpg)