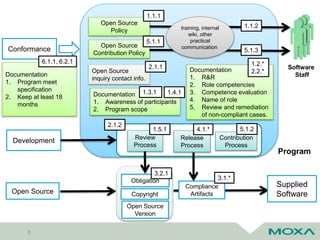
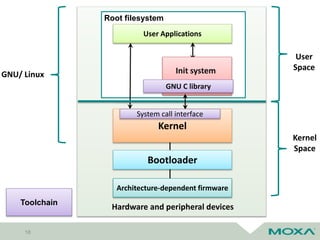
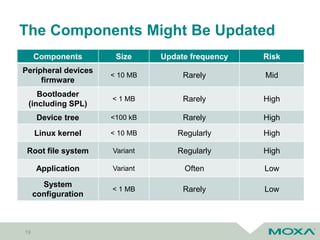
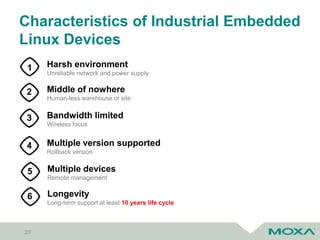
The document discusses software updates for embedded systems using open source software, highlighting the importance of compliance with copyright and patent laws. It outlines key processes, tools, and policies for effective open source management, as well as the challenges associated with firmware updates in industrial applications. Additionally, it compares various update methods and frameworks, emphasizing the significance of fail-safe and rollback features in harsh environments.




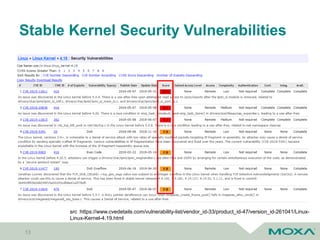

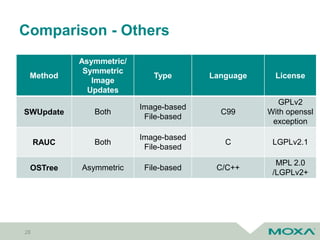
![Asymmetric/ Symmetric Firmware Updates [1]
25
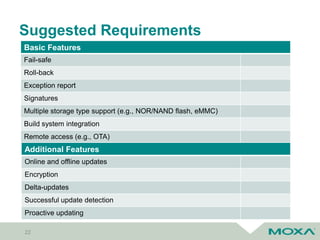
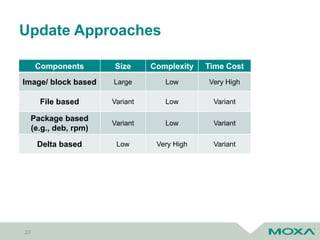
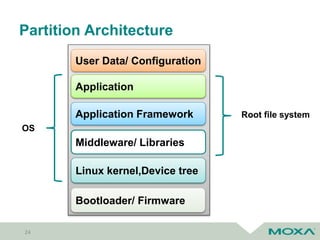
Bootloader/ Firmware
Recovery OS
User Data/ Configuration
Main OS
Bootloader/ Firmware
Main OS – A (Active)
User Data/ Configuration
Main OS – B (Inactive)
Asymmetric Firmware Updates
• Fail-safe
• Downtime
Symmetric Firmware Updates
• Seamless update
• Roll-back
• Fail-safe
• Double copy of OS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coscupsoftwareupdateforembeddedsystems-190822080419/85/Software-update-for-embedded-systems-25-320.jpg)


![References
[1] https://mkrak.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/FOSS-
NORTH_2018_Software_Updates.pdf
[2] https://events.linuxfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/Strategies-
for-Developing-and-Deploying-your-Embedded-Applications-and-Images-
Mirza-Krak-Mender.io_.pdf
[3] System upgrade with SWUpdate
http://events17.linuxfoundation.org/sites/events/files/slides/ELC2017_SWU
pdate.pdf
[4] https://events.linuxfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/ELCE-2018-
Update-Tools-BoF_Jan-Lubbe.pdf
[5] https://events.linuxfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/ELCE-2018-
Update-Tools-BoF_Jan-Lubbe.pdf
[6]
https://elinux.org/images/f/f5/Embedded_Systems_Software_Update_for_I
oT.pdf
[7] https://rauc.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
[8] https://sbabic.github.io/swupdate/swupdate.html
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coscupsoftwareupdateforembeddedsystems-190822080419/85/Software-update-for-embedded-systems-31-320.jpg)
![References
[9] https://wiki.yoctoproject.org/wiki/System_Update
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coscupsoftwareupdateforembeddedsystems-190822080419/85/Software-update-for-embedded-systems-32-320.jpg)