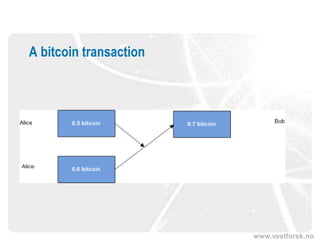
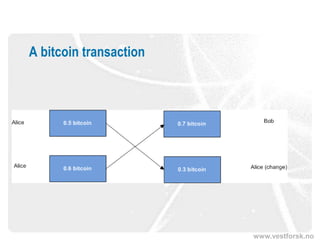
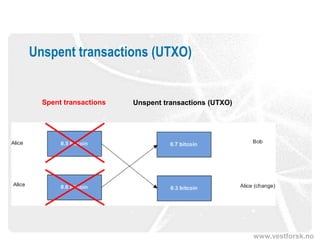
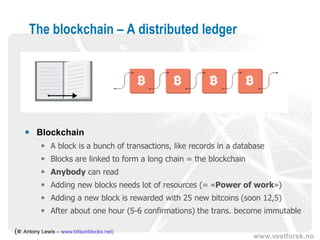
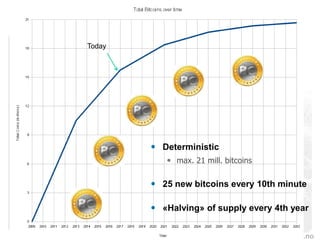
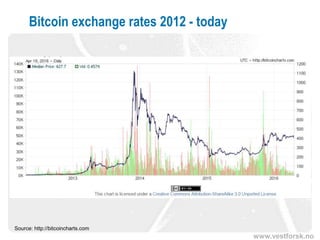
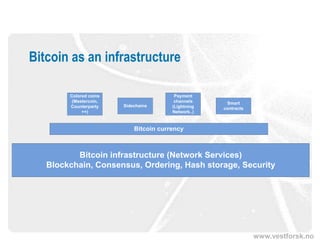
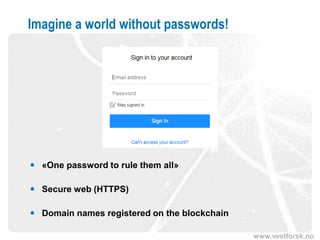
This document provides an introduction to Bitcoin and blockchain technology. It describes Vestlandsforsking, a Norwegian research institute where the author works and his background in Bitcoin. The core concepts of Bitcoin as a digital currency and blockchain as its underlying infrastructure are explained. Key aspects like how transactions work and how the blockchain ledger is distributed across nodes are summarized. Examples of potential applications beyond currency like smart contracts and digital certificates are also briefly mentioned.










![www.vestforsk.no
Centralized, decentralized og distributed
Paul Baran: «On Distributed Communications Network»
[Baran invented packet switching, together with Donald Davies, UK]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bitcoin-jonbingsminneseminar19-160418164535/85/Jon-Bing-Memorial-Seminar-12-320.jpg)