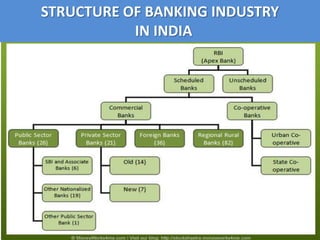
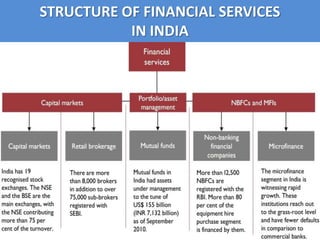
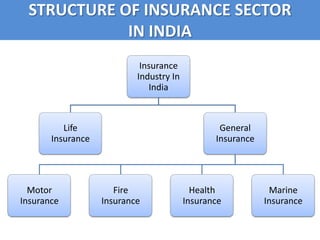
The document summarizes the banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) sector in India. It discusses the history and growth of banking, financial services, and insurance in India. It also describes the structure and future prospects of the BFSI sector, which is an important industry in India and expected to experience continued growth.