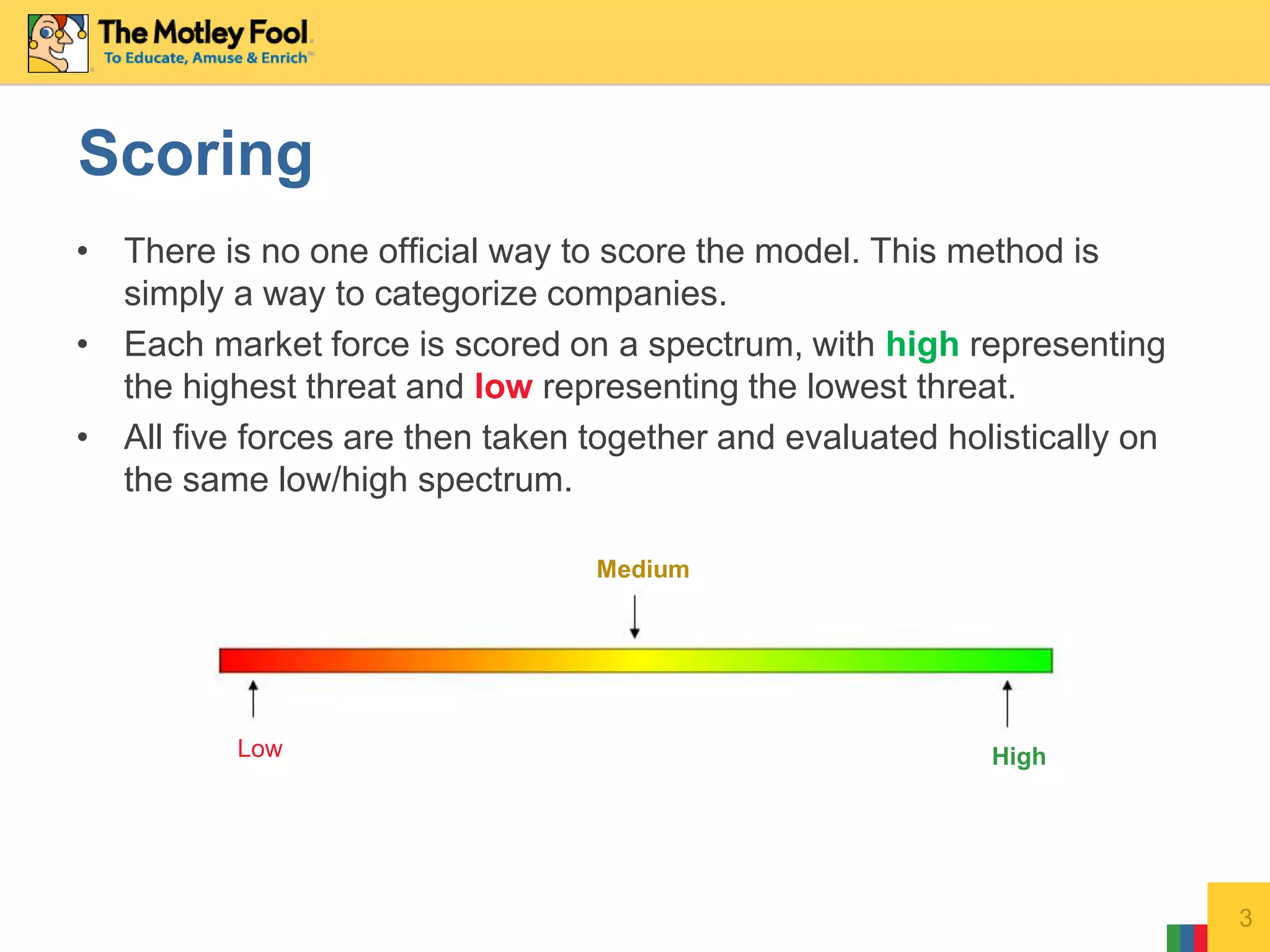
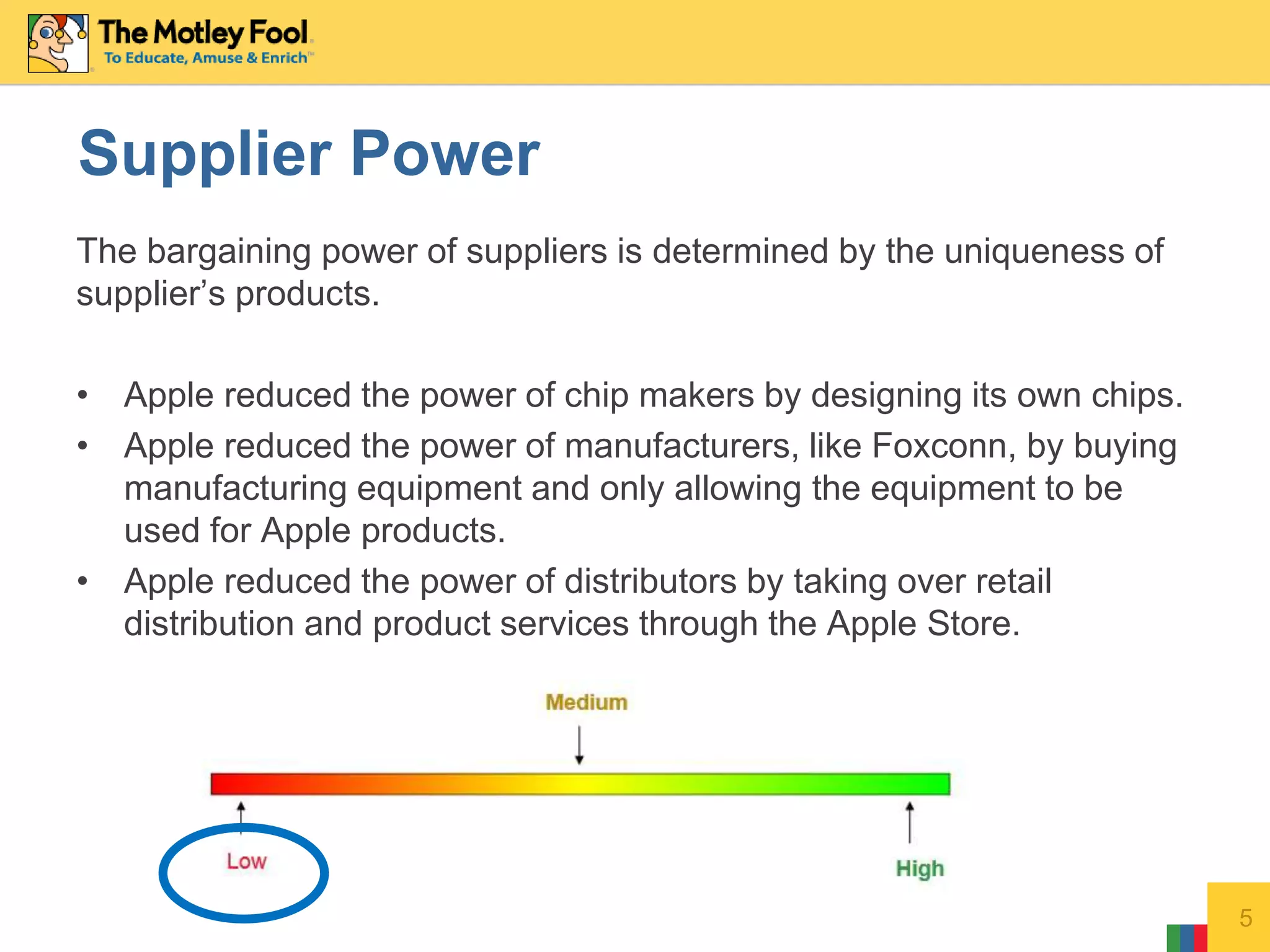
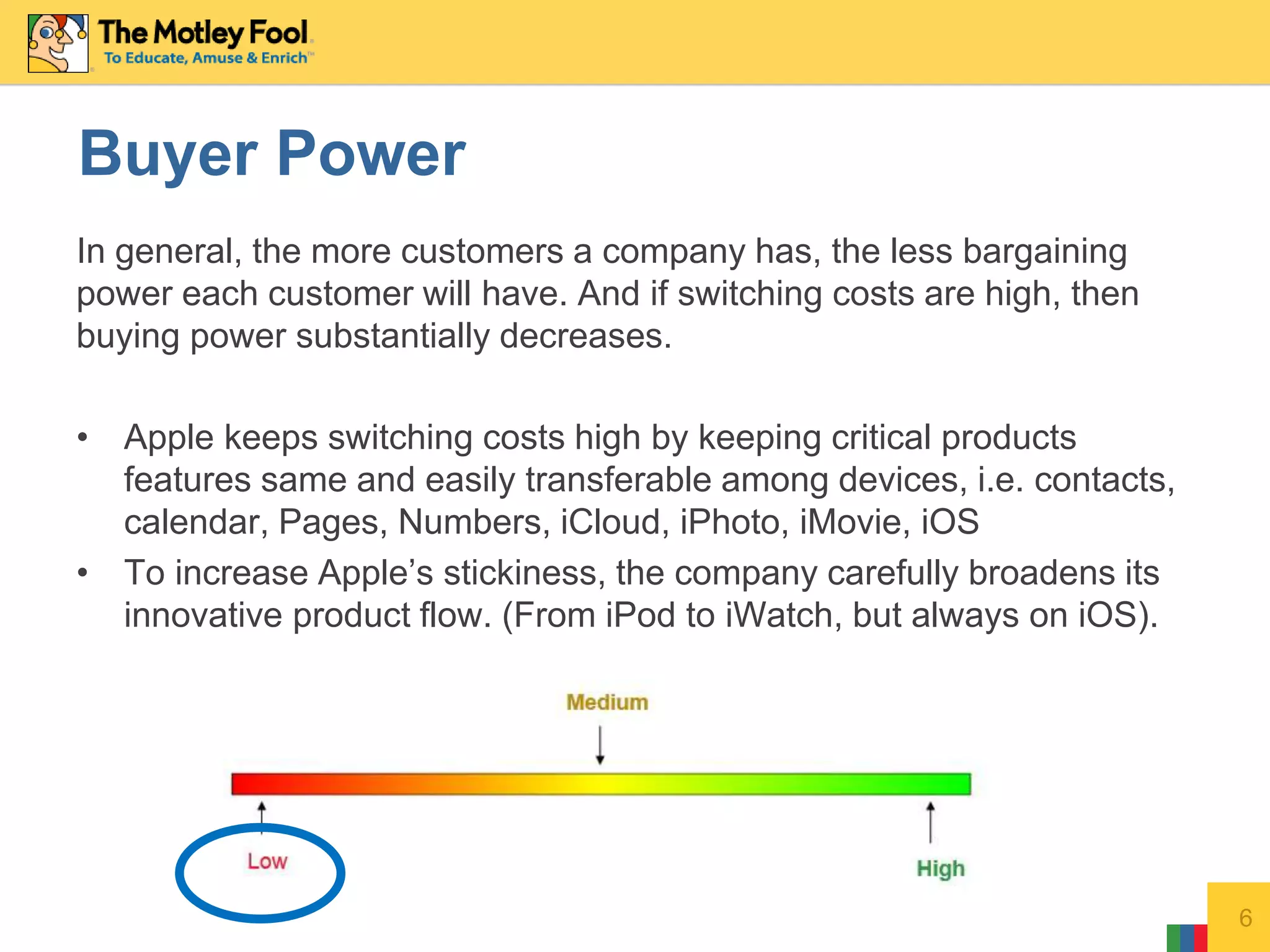
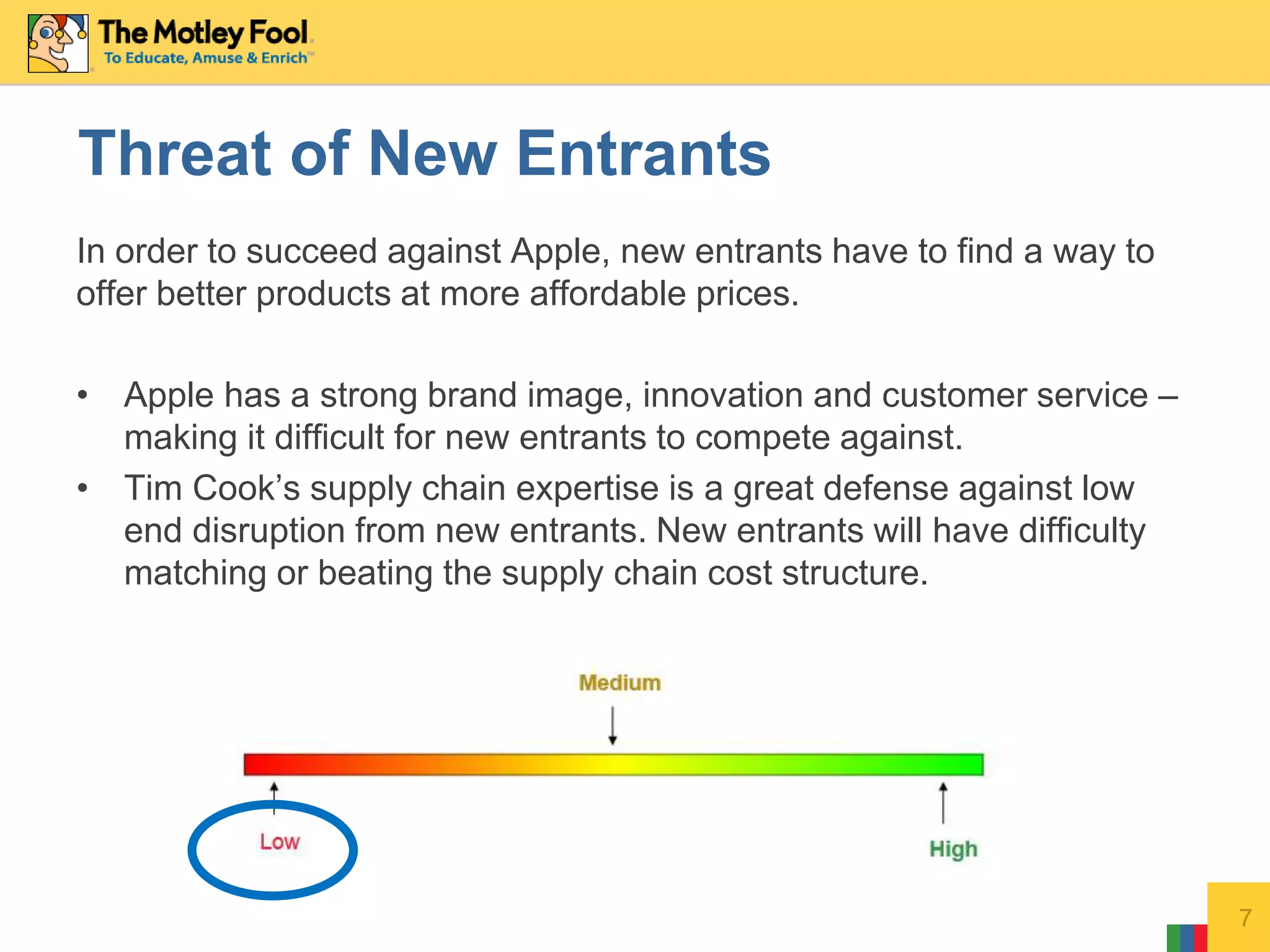
This document discusses Porter's Five Forces model as it applies to Apple Inc. It analyzes Apple across the five forces: competitive rivalry is medium; supplier power is low as Apple designs its own chips; buyer power is low due to high switching costs between Apple products; threat of new entrants is low given Apple's strong brand and innovation; threat of substitutes is medium as Apple makes products that could replace its own.