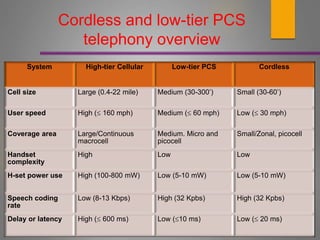
This document discusses personal communication systems (PCS), including high-tier and low-tier digital cellular systems. High-tier systems include AMPS, GSM, IS-136, and IS-95 which use larger cell sizes and support higher user speeds but have higher latency. Low-tier systems like DECT, PHS, and PACS use smaller cell sizes and have lower latency but also lower speeds and throughput. PCS integrates wired and wireless networks to enable communication through small mobile terminals anywhere.













![[Year 2012-13] PCS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mbt-seminar1-180701102033/85/Year-2012-13-PCS-15-320.jpg)