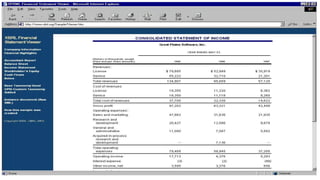
XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language) is a language for electronic communication of business and financial data that provides benefits of cost savings, efficiency and improved accuracy. It applies to listed companies in India with a market capitalization over $5 billion. XBRL was developed in 1998 and its use became mandatory for US public companies in 2011. It can format both financial and non-financial data using unique tags and has benefits like better analysis, cost savings, and avoiding manual data entry. Taxonomies define reporting elements and their relationships, and companies generate valid XBRL documents by mapping their reports to the taxonomy elements.