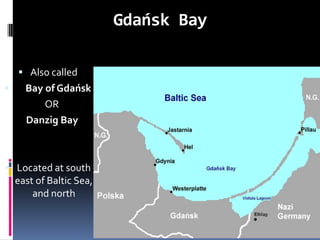
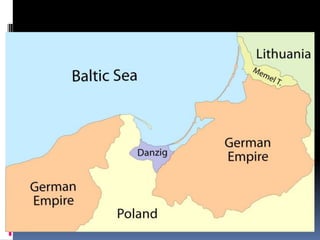
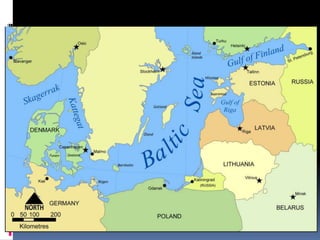
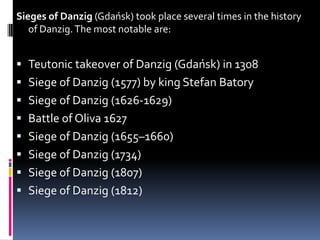
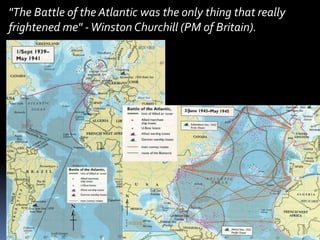
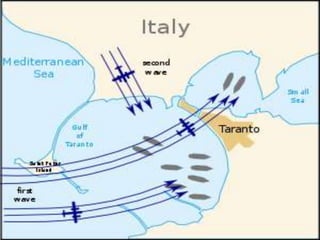
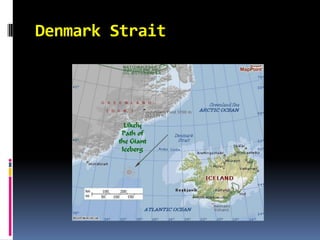
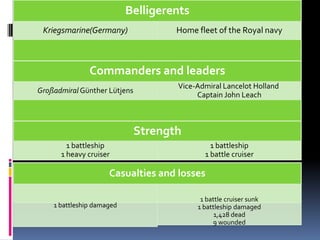
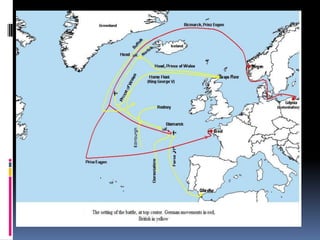
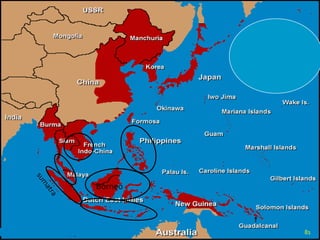
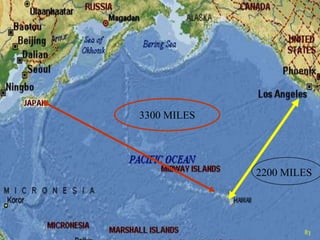
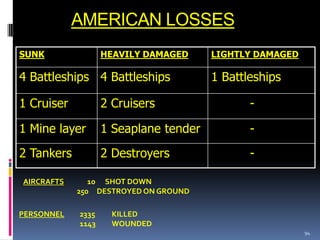
The document discusses naval aspects of World War II, focusing on key battles such as the Battle of Gdańsk Bay, the Battle of the Atlantic, the Battle of the River Plate, and the attack on Pearl Harbor. It details specific operations and strategic importance of naval warfare, underscoring the impact on supply lines and military outcomes. The battles highlighted mark significant moments in naval history during the war, reflecting both military tactics and geopolitical strategies.