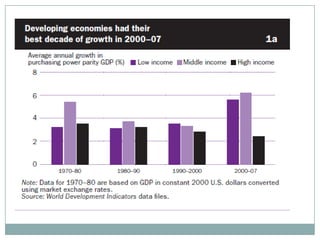
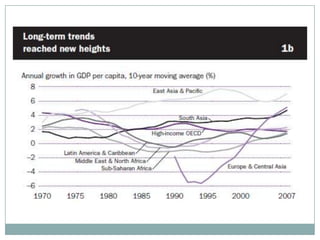
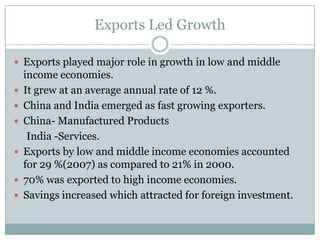
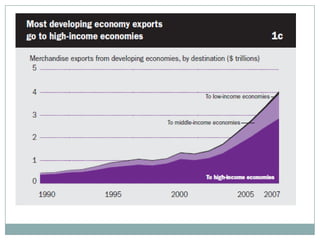
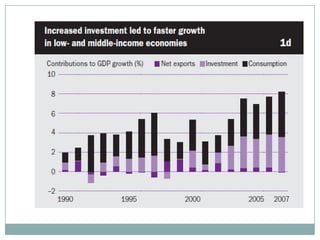
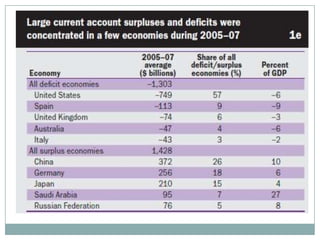
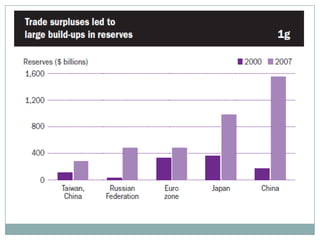
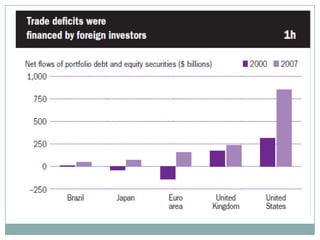
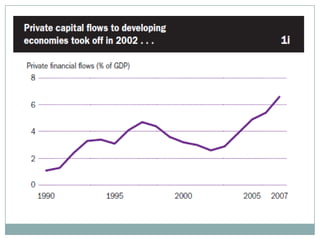
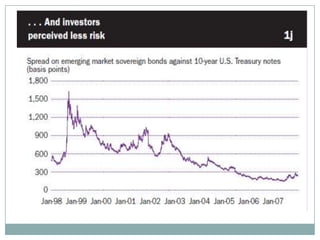
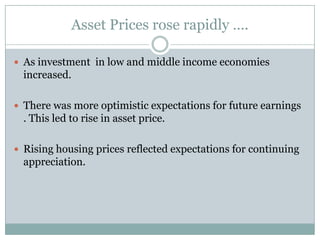
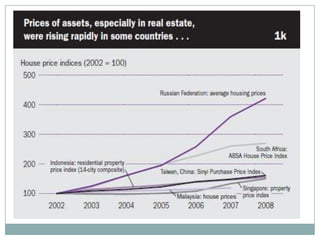
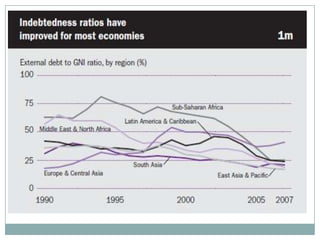
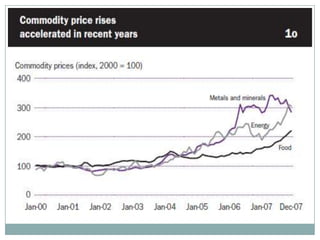
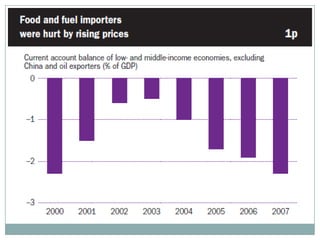
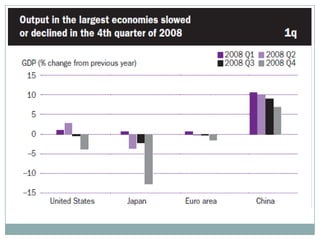
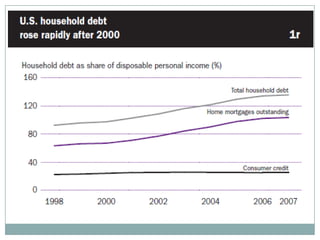
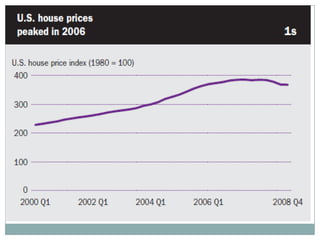
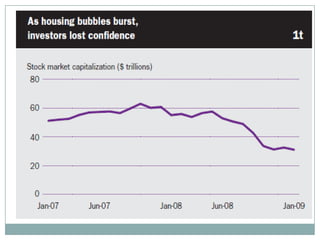
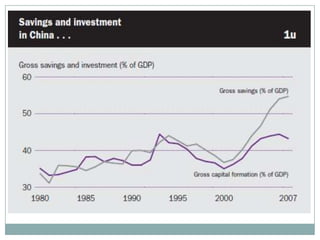
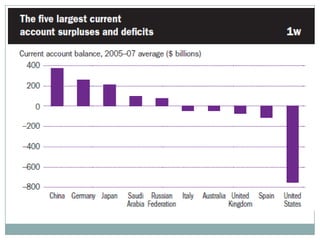
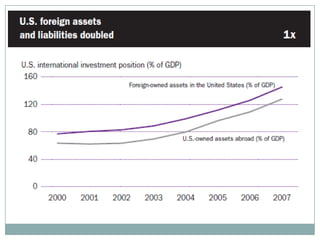
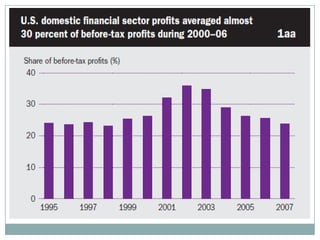
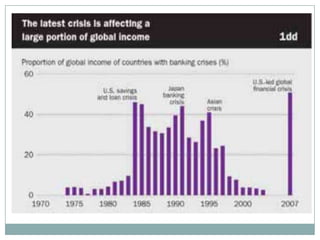
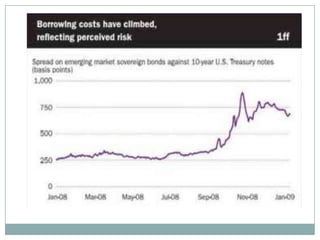
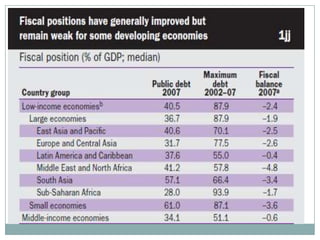
The document summarizes the economic growth in the 2000s, the emergence of macroeconomic imbalances, and the causes and effects of the global financial crisis that began in 2007-2008. It notes that strong economic growth in the 2000s was driven by exports and investment in developing economies. However, imbalances emerged as some countries ran large trade surpluses while others had large deficits, including the US. The crisis had its roots in the US housing bubble and subprime mortgage crisis but spread globally due to interconnected financial markets and a decline in trade. The crisis led to a drop in global output and rise in unemployment worldwide.