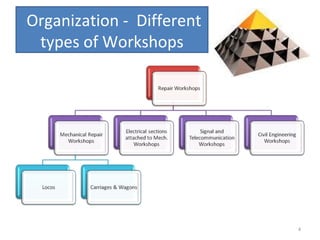
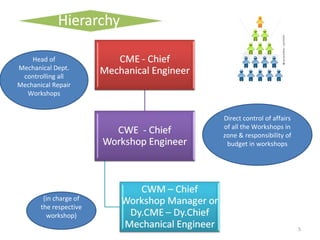
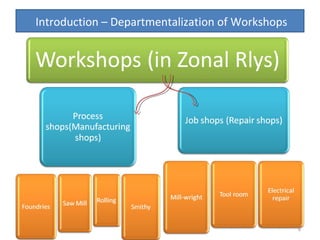
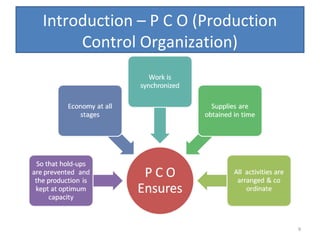
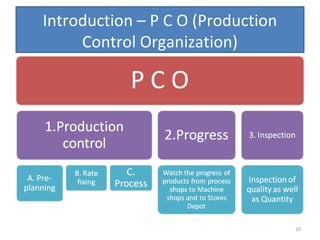
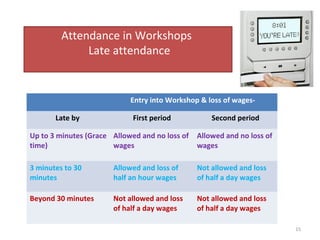
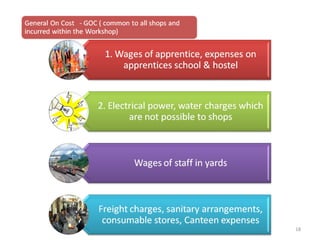
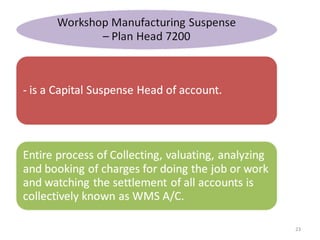
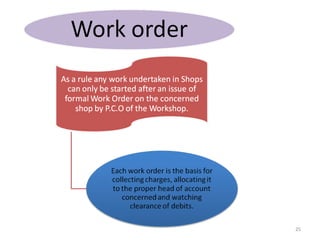
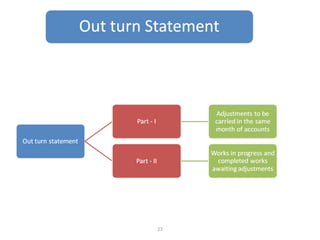
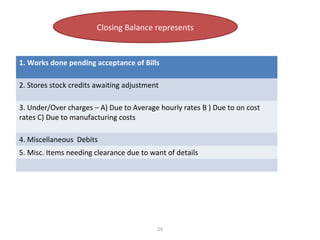
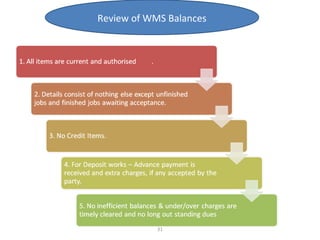
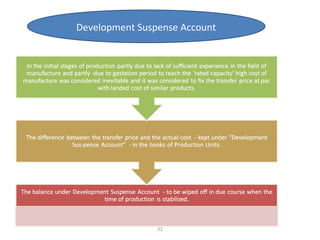
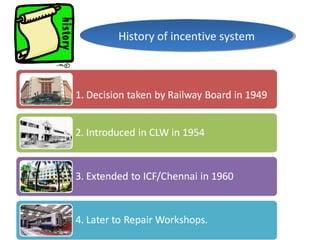
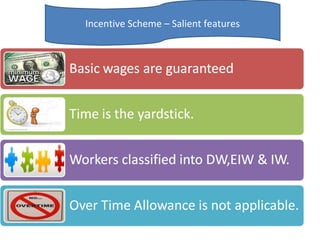
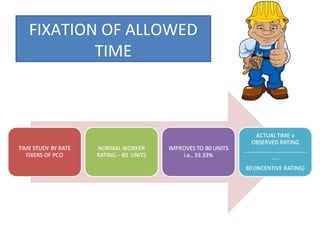
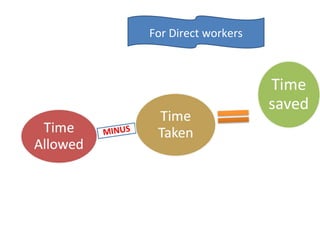
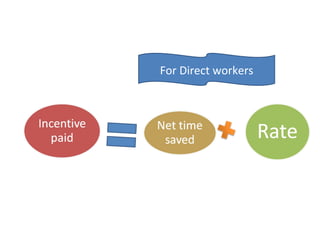
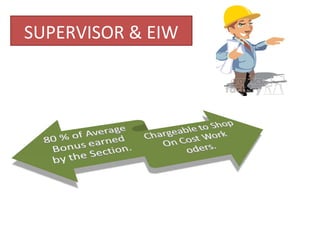
The document outlines the operation and organization of railway workshops for maintaining rolling stock, highlighting the importance of spare parts and efficient repair processes. It emphasizes the need for cost control in workshops to prevent excess expenditures that could impact the overall profitability of the railways. Additionally, it discusses attendance regulations under the Factories Act and details related to workshop financial accounts and the incentive system for workers.