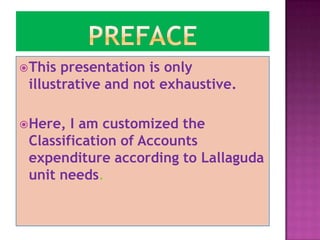
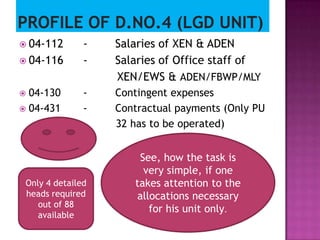
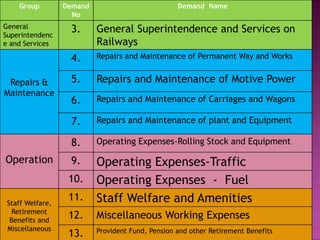
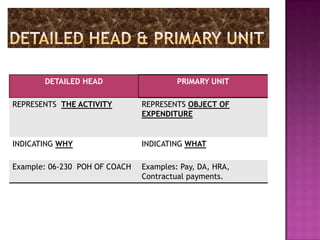
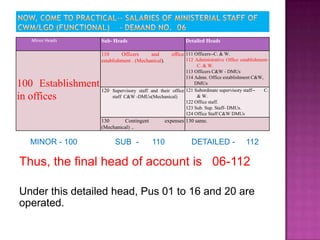
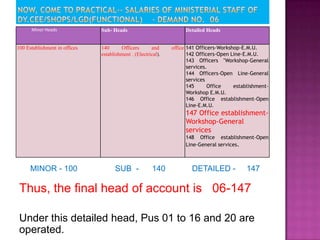
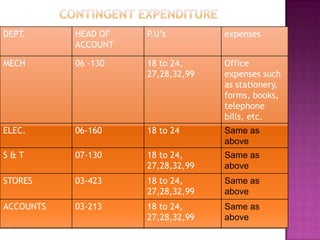
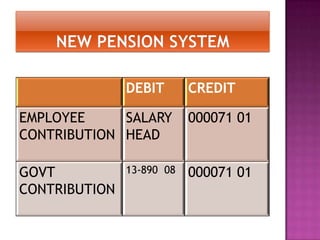
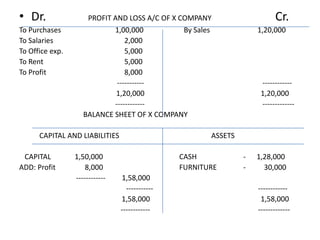
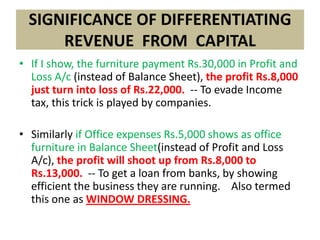
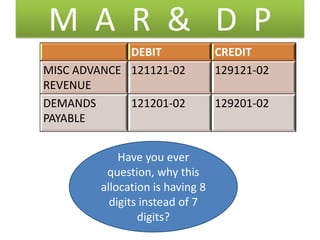
Here are the key points regarding 8 digit vs 7 digit allocation codes in railways accounts:
- Traditionally, railway allocation codes had 7 digits to identify the demand, minor head, sub-head and detailed head.
- However, with the introduction of project accounting and multiple funding sources for projects, it became necessary to capture the project code as well in the allocation.
- To accommodate the project code without changing the existing 7 digit structure, railways moved to an 8 digit allocation code structure.
- In the 8 digit code, the first 7 digits remain the same to identify the demand, minor head, sub-head and detailed head.
- The 8th digit is used to capture the project code,