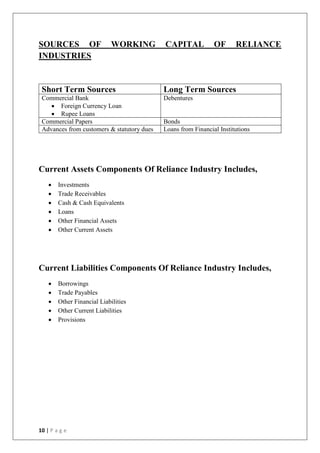
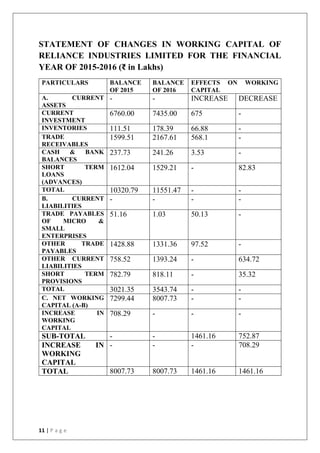
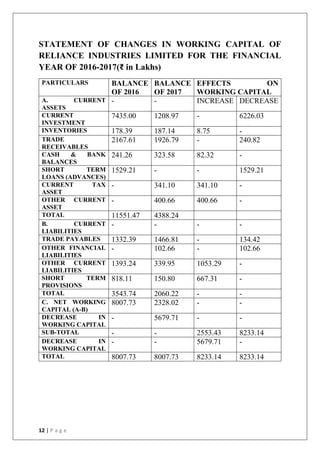
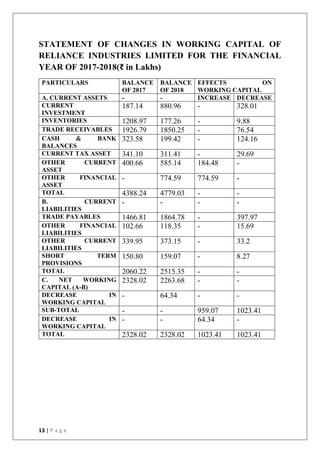
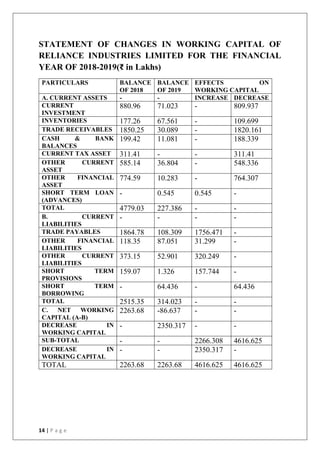
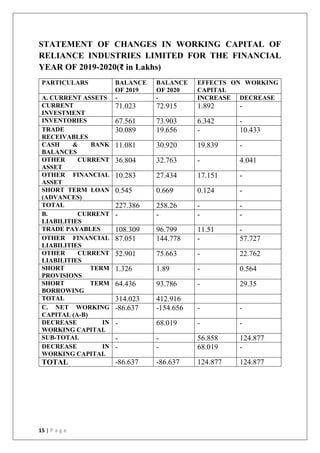
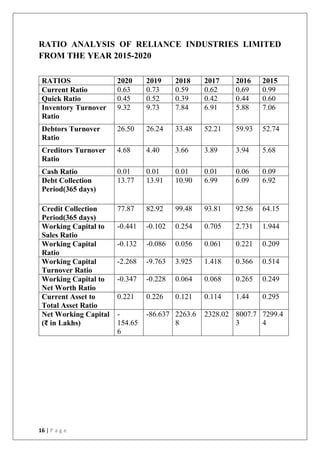
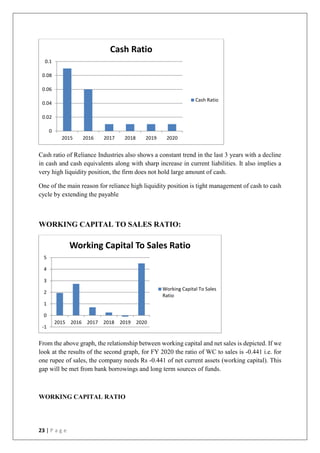
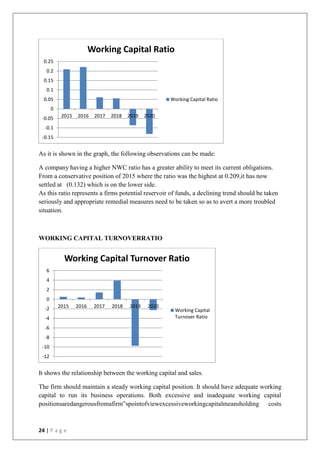
This document discusses the importance of working capital management, focusing on its role in managing daily operations, short-term liabilities, and resource allocation for Reliance Industries Ltd. It includes objectives of studying working capital trends from 2015-2020, methodology using secondary data, and detailed financial analysis through various ratios and sources of working capital. The report highlights significant findings in the company's liquidity and activity ratios, providing insights for operational efficiency.